# Objective
- Prep for https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/10164
- Make deferred_lighting_pass_id a ColorAttachment
- Correctly extract shadow view frusta so that the view uniforms get
populated
- Make some needed things public
- Misc formatting
# Objective
Make it easier to create bounding boxes in user code by providing a
constructor that computes a box surrounding an arbitrary number of
points.
## Solution
Add `Aabb::enclosing`, which accepts iterators, slices, or arrays.
---------
Co-authored-by: Tristan Guichaoua <33934311+tguichaoua@users.noreply.github.com>
# Objective
This PR's first aim is to fix a mistake in `HalfSpace`'s documentation.
When defining a `Frustum` myself in bevy_basic_portals, I realised that
the "distance" of the `HalfSpace` is not, as the current doc defines,
the "distance from the origin along the normal", but actually the
opposite of that.
See the example I gave in this PR.
This means one of two things:
1. The documentation about `HalfSpace` is wrong (it is either way
because of the `n.p + d > 0` formula given later anyway, which is how it
behaves, but in that formula `d` is indeed the opposite of the "distance
from the origin along the normal", otherwise it should be `n.p > d`)
2. The distance is supposed to be the "distance from the origin along
the normal" but when used in a Frustum it's used as the opposite, and it
is a mistake
3. Same as 2, but it is somehow intended
Since I think `HalfSpace` is only used for `Frustum`, and it's easier to
fix documentation than code, I assumed for this PR we're in case number
1. If we're in case number 3, the documentation of `Frustum` needs to
change, and in case number 2, the code needs to be fixed.
While I was at it, I also :
- Tried to improve the documentation for `Frustum`, `Aabb`, and
`VisibilitySystems`, among others, since they're all related to
`Frustum`.
- Fixed documentation about frustum culling not applying to 2d objects,
which is not true since https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/7885
## Remarks and questions
- What about a `HalfSpace` with an infinite distance, is it allowed and
does it represents the whole space? If so it should probably be
mentioned.
- I referenced the `update_frusta` system in
`bevy_render::view::visibility` directly instead of referencing its
system set, should I reference the system set instead? It's a bit
annoying since it's in 3 sets.
- `visibility_propagate` is not public for some reason, I think it
probably should be, but for now I only documented its system set, should
I make it public? I don't think that would count as a breaking change?
- Why is `Aabb` inserted by a system, with `NoFrustumCulling` as an
opt-out, instead of having it inserted by default in `PbrBundle` for
example and then the system calculating it when it's added? Is it
because there is still no way to have an optional component inside a
bundle?
---------
Co-authored-by: SpecificProtagonist <vincentjunge@posteo.net>
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
# Objective
- Significantly reduce the size of MeshUniform by only including
necessary data.
## Solution
Local to world, model transforms are affine. This means they only need a
4x3 matrix to represent them.
`MeshUniform` stores the current, and previous model transforms, and the
inverse transpose of the current model transform, all as 4x4 matrices.
Instead we can store the current, and previous model transforms as 4x3
matrices, and we only need the upper-left 3x3 part of the inverse
transpose of the current model transform. This change allows us to
reduce the serialized MeshUniform size from 208 bytes to 144 bytes,
which is over a 30% saving in data to serialize, and VRAM bandwidth and
space.
## Benchmarks
On an M1 Max, running `many_cubes -- sphere`, main is in yellow, this PR
is in red:
<img width="1484" alt="Screenshot 2023-08-11 at 02 36 43"
src="https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/assets/302146/7d99c7b3-f2bb-4004-a8d0-4c00f755cb0d">
A reduction in frame time of ~14%.
---
## Changelog
- Changed: Redefined `MeshUniform` to improve performance by using 4x3
affine transforms and reconstructing 4x4 matrices in the shader. Helper
functions were added to `bevy_pbr::mesh_functions` to unpack the data.
`affine_to_square` converts the packed 4x3 in 3x4 matrix data to a 4x4
matrix. `mat2x4_f32_to_mat3x3` converts the 3x3 in mat2x4 + f32 matrix
data back into a 3x3.
## Migration Guide
Shader code before:
```
var model = mesh[instance_index].model;
```
Shader code after:
```
#import bevy_pbr::mesh_functions affine_to_square
var model = affine_to_square(mesh[instance_index].model);
```
# Objective
**This implementation is based on
https://github.com/bevyengine/rfcs/pull/59.**
---
Resolves#4597
Full details and motivation can be found in the RFC, but here's a brief
summary.
`FromReflect` is a very powerful and important trait within the
reflection API. It allows Dynamic types (e.g., `DynamicList`, etc.) to
be formed into Real ones (e.g., `Vec<i32>`, etc.).
This mainly comes into play concerning deserialization, where the
reflection deserializers both return a `Box<dyn Reflect>` that almost
always contain one of these Dynamic representations of a Real type. To
convert this to our Real type, we need to use `FromReflect`.
It also sneaks up in other ways. For example, it's a required bound for
`T` in `Vec<T>` so that `Vec<T>` as a whole can be made `FromReflect`.
It's also required by all fields of an enum as it's used as part of the
`Reflect::apply` implementation.
So in other words, much like `GetTypeRegistration` and `Typed`, it is
very much a core reflection trait.
The problem is that it is not currently treated like a core trait and is
not automatically derived alongside `Reflect`. This makes using it a bit
cumbersome and easy to forget.
## Solution
Automatically derive `FromReflect` when deriving `Reflect`.
Users can then choose to opt-out if needed using the
`#[reflect(from_reflect = false)]` attribute.
```rust
#[derive(Reflect)]
struct Foo;
#[derive(Reflect)]
#[reflect(from_reflect = false)]
struct Bar;
fn test<T: FromReflect>(value: T) {}
test(Foo); // <-- OK
test(Bar); // <-- Panic! Bar does not implement trait `FromReflect`
```
#### `ReflectFromReflect`
This PR also automatically adds the `ReflectFromReflect` (introduced in
#6245) registration to the derived `GetTypeRegistration` impl— if the
type hasn't opted out of `FromReflect` of course.
<details>
<summary><h4>Improved Deserialization</h4></summary>
> **Warning**
> This section includes changes that have since been descoped from this
PR. They will likely be implemented again in a followup PR. I am mainly
leaving these details in for archival purposes, as well as for reference
when implementing this logic again.
And since we can do all the above, we might as well improve
deserialization. We can now choose to deserialize into a Dynamic type or
automatically convert it using `FromReflect` under the hood.
`[Un]TypedReflectDeserializer::new` will now perform the conversion and
return the `Box`'d Real type.
`[Un]TypedReflectDeserializer::new_dynamic` will work like what we have
now and simply return the `Box`'d Dynamic type.
```rust
// Returns the Real type
let reflect_deserializer = UntypedReflectDeserializer::new(®istry);
let mut deserializer = ron:🇩🇪:Deserializer::from_str(input)?;
let output: SomeStruct = reflect_deserializer.deserialize(&mut deserializer)?.take()?;
// Returns the Dynamic type
let reflect_deserializer = UntypedReflectDeserializer::new_dynamic(®istry);
let mut deserializer = ron:🇩🇪:Deserializer::from_str(input)?;
let output: DynamicStruct = reflect_deserializer.deserialize(&mut deserializer)?.take()?;
```
</details>
---
## Changelog
* `FromReflect` is now automatically derived within the `Reflect` derive
macro
* This includes auto-registering `ReflectFromReflect` in the derived
`GetTypeRegistration` impl
* ~~Renamed `TypedReflectDeserializer::new` and
`UntypedReflectDeserializer::new` to
`TypedReflectDeserializer::new_dynamic` and
`UntypedReflectDeserializer::new_dynamic`, respectively~~ **Descoped**
* ~~Changed `TypedReflectDeserializer::new` and
`UntypedReflectDeserializer::new` to automatically convert the
deserialized output using `FromReflect`~~ **Descoped**
## Migration Guide
* `FromReflect` is now automatically derived within the `Reflect` derive
macro. Items with both derives will need to remove the `FromReflect`
one.
```rust
// OLD
#[derive(Reflect, FromReflect)]
struct Foo;
// NEW
#[derive(Reflect)]
struct Foo;
```
If using a manual implementation of `FromReflect` and the `Reflect`
derive, users will need to opt-out of the automatic implementation.
```rust
// OLD
#[derive(Reflect)]
struct Foo;
impl FromReflect for Foo {/* ... */}
// NEW
#[derive(Reflect)]
#[reflect(from_reflect = false)]
struct Foo;
impl FromReflect for Foo {/* ... */}
```
<details>
<summary><h4>Removed Migrations</h4></summary>
> **Warning**
> This section includes changes that have since been descoped from this
PR. They will likely be implemented again in a followup PR. I am mainly
leaving these details in for archival purposes, as well as for reference
when implementing this logic again.
* The reflect deserializers now perform a `FromReflect` conversion
internally. The expected output of `TypedReflectDeserializer::new` and
`UntypedReflectDeserializer::new` is no longer a Dynamic (e.g.,
`DynamicList`), but its Real counterpart (e.g., `Vec<i32>`).
```rust
let reflect_deserializer =
UntypedReflectDeserializer::new_dynamic(®istry);
let mut deserializer = ron:🇩🇪:Deserializer::from_str(input)?;
// OLD
let output: DynamicStruct = reflect_deserializer.deserialize(&mut
deserializer)?.take()?;
// NEW
let output: SomeStruct = reflect_deserializer.deserialize(&mut
deserializer)?.take()?;
```
Alternatively, if this behavior isn't desired, use the
`TypedReflectDeserializer::new_dynamic` and
`UntypedReflectDeserializer::new_dynamic` methods instead:
```rust
// OLD
let reflect_deserializer = UntypedReflectDeserializer::new(®istry);
// NEW
let reflect_deserializer =
UntypedReflectDeserializer::new_dynamic(®istry);
```
</details>
---------
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
# Objective
Discovered that PointLight did not implement FromReflect. Adding
FromReflect where Reflect is used. I overreached and applied this rule
everywhere there was a Reflect without a FromReflect, except from where
the compiler wouldn't allow me.
Based from question: https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/discussions/8774
## Solution
- Adding FromReflect where Reflect was already derived
## Notes
First PR I do in this ecosystem, so not sure if this is the usual
approach, that is, to touch many files at once.
---------
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
# Objective
- Rename the `render::primitives::Plane` struct as to not confuse it
with `bevy_render::mesh::shape::Plane`
- Fixes https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/8730
## Solution
- Refactor the `render::primitives::Plane` struct to
`render::primitives::HalfSpace`
- Modify documentation to reflect this change
## Changelog
- Renamed `Plane` to `HalfSpace` to more accurately represent it's use
- Renamed `planes` member in `Frustum` to `half_spaces` to reflect
changes
## Migration Guide
- `Plane` has been renamed to `HalfSpace`
- `planes` member in `Frustum` has been renamed to `half_spaces`
---------
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Nicola Papale <nicopap@users.noreply.github.com>
# Objective
Add a `FromReflect` derive to the `Aabb` type, like all other math types, so we can reflect `Vec<Aabb>`.
## Solution
Just add it :)
---
## Changelog
### Added
- Implemented `FromReflect` for `Aabb`.
Co-authored-by: Robert Swain <robert.swain@gmail.com>
# Objective
Implements cascaded shadow maps for directional lights, which produces better quality shadows without needing excessively large shadow maps.
Fixes#3629
Before
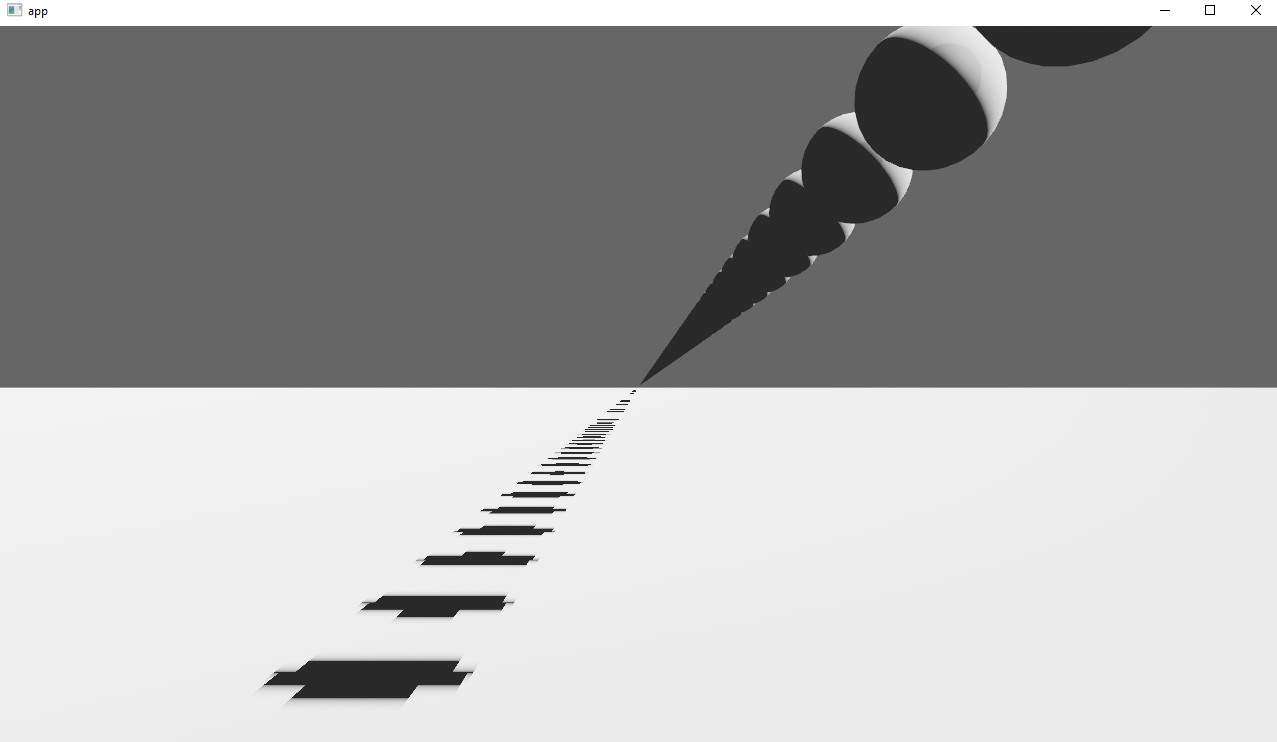
After
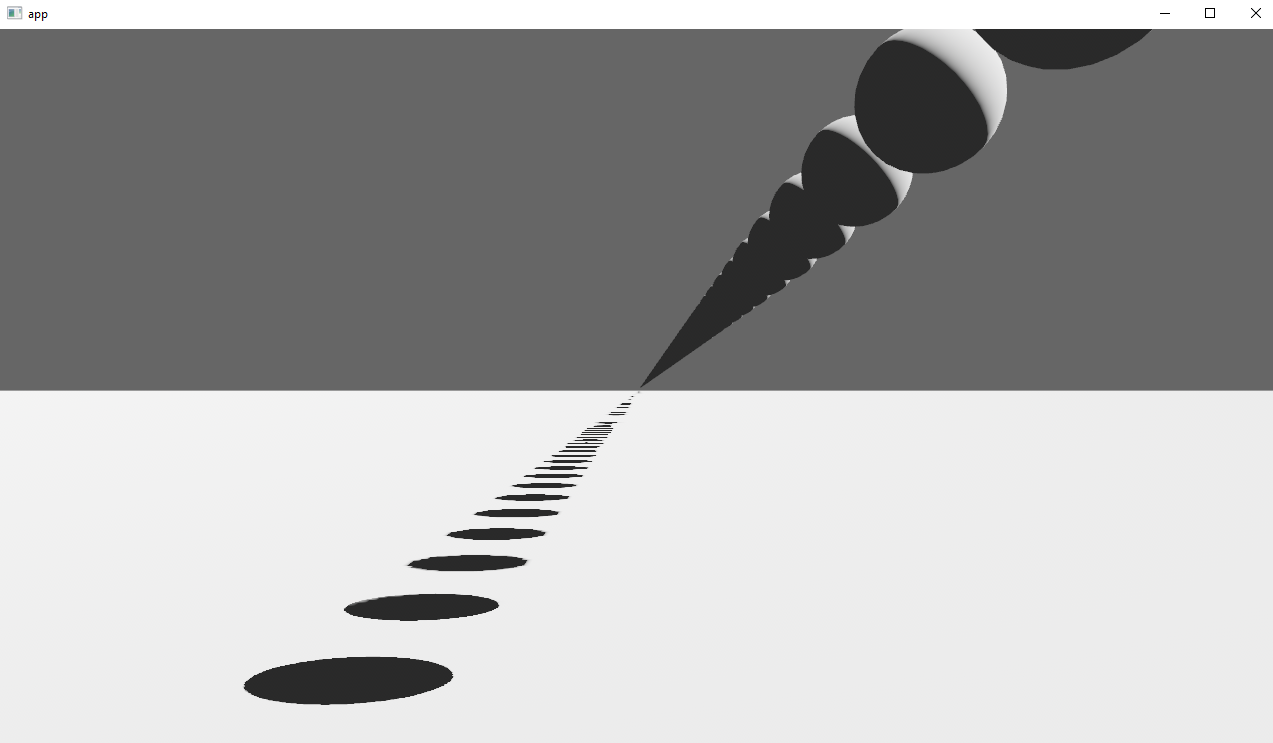
## Solution
Rather than rendering a single shadow map for directional light, the view frustum is divided into a series of cascades, each of which gets its own shadow map. The correct cascade is then sampled for shadow determination.
---
## Changelog
Directional lights now use cascaded shadow maps for improved shadow quality.
## Migration Guide
You no longer have to manually specify a `shadow_projection` for a directional light, and these settings should be removed. If customization of how cascaded shadow maps work is desired, modify the `CascadeShadowConfig` component instead.
# Objective
- Added a bunch of backticks to things that should have them, like equations, abstract variable names,
- Changed all small x, y, and z to capitals X, Y, Z.
This might be more annoying than helpful; Feel free to refuse this PR.
# Objective
add spotlight support
## Solution / Changelog
- add spotlight angles (inner, outer) to ``PointLight`` struct. emitted light is linearly attenuated from 100% to 0% as angle tends from inner to outer. Direction is taken from the existing transform rotation.
- add spotlight direction (vec3) and angles (f32,f32) to ``GpuPointLight`` struct (60 bytes -> 80 bytes) in ``pbr/render/lights.rs`` and ``mesh_view_bind_group.wgsl``
- reduce no-buffer-support max point light count to 204 due to above
- use spotlight data to attenuate light in ``pbr.wgsl``
- do additional cluster culling on spotlights to minimise cost in ``assign_lights_to_clusters``
- changed one of the lights in the lighting demo to a spotlight
- also added a ``spotlight`` demo - probably not justified but so reviewers can see it more easily
## notes
increasing the size of the GpuPointLight struct on my machine reduces the FPS of ``many_lights -- sphere`` from ~150fps to 140fps.
i thought this was a reasonable tradeoff, and felt better than handling spotlights separately which is possible but would mean introducing a new bind group, refactoring light-assignment code and adding new spotlight-specific code in pbr.wgsl. the FPS impact for smaller numbers of lights should be very small.
the cluster culling strategy reintroduces the cluster aabb code which was recently removed... sorry. the aabb is used to get a cluster bounding sphere, which can then be tested fairly efficiently using the strategy described at the end of https://bartwronski.com/2017/04/13/cull-that-cone/. this works well with roughly cubic clusters (where the cluster z size is close to the same as x/y size), less well for other cases like single Z slice / tiled forward rendering. In the worst case we will end up just keeping the culling of the equivalent point light.
Co-authored-by: François <mockersf@gmail.com>
# Objective
- Fixes#4234
- Fixes#4473
- Built on top of #3989
- Improve performance of `assign_lights_to_clusters`
## Solution
- Remove the OBB-based cluster light assignment algorithm and calculation of view space AABBs
- Implement the 'iterative sphere refinement' algorithm used in Just Cause 3 by Emil Persson as documented in the Siggraph 2015 Practical Clustered Shading talk by Persson, on pages 42-44 http://newq.net/dl/pub/s2015_practical.pdf
- Adapt to also support orthographic projections
- Add `many_lights -- orthographic` for testing many lights using an orthographic projection
## Results
- `assign_lights_to_clusters` in `many_lights` before this PR on an M1 Max over 1500 frames had a median execution time of 1.71ms. With this PR it is 1.51ms, a reduction of 0.2ms or 11.7% for this system.
---
## Changelog
- Changed: Improved cluster light assignment performance
Co-authored-by: robtfm <50659922+robtfm@users.noreply.github.com>
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
# Objective
- Reduce time spent in the `check_visibility` system
## Solution
- Use `Vec3A` for all bounding volume types to leverage SIMD optimisations and to avoid repeated runtime conversions from `Vec3` to `Vec3A`
- Inline all bounding volume intersection methods
- Add on-the-fly calculated `Aabb` -> `Sphere` and do `Sphere`-`Frustum` intersection tests before `Aabb`-`Frustum` tests. This is faster for `many_cubes` but could be slower in other cases where the sphere test gives a false-positive that the `Aabb` test discards. Also, I tested precalculating the `Sphere`s and inserting them alongside the `Aabb` but this was slower.
- Do not test meshes against the far plane. Apparently games don't do this anymore with infinite projections, and it's one fewer plane to test against. I made it optional and still do the test for culling lights but that is up for discussion.
- These collectively reduce `check_visibility` execution time in `many_cubes -- sphere` from 2.76ms to 1.48ms and increase frame rate from ~42fps to ~44fps
# Objective
Fixes#3744
## Solution
The old code used the formula `normal . center + d + radius <= 0` to determine if the sphere with center `center` and radius `radius` is outside the plane with normal `normal` and distance from origin `d`. This only works if `normal` is normalized, which is not necessarily the case. Instead, `normal` and `d` are both multiplied by some factor that `radius` isn't multiplied by. So the additional code multiplied `radius` by that factor.
# Objective
- Add support for loading lights from glTF 2.0 files
## Solution
- This adds support for the KHR_punctual_lights extension which supports point, directional, and spot lights, though we don't yet support spot lights.
- Inserting light bundles when creating scenes required registering some more light bundle component types.
This makes the [New Bevy Renderer](#2535) the default (and only) renderer. The new renderer isn't _quite_ ready for the final release yet, but I want as many people as possible to start testing it so we can identify bugs and address feedback prior to release.
The examples are all ported over and operational with a few exceptions:
* I removed a good portion of the examples in the `shader` folder. We still have some work to do in order to make these examples possible / ergonomic / worthwhile: #3120 and "high level shader material plugins" are the big ones. This is a temporary measure.
* Temporarily removed the multiple_windows example: doing this properly in the new renderer will require the upcoming "render targets" changes. Same goes for the render_to_texture example.
* Removed z_sort_debug: entity visibility sort info is no longer available in app logic. we could do this on the "render app" side, but i dont consider it a priority.