3a8355f1ad
29 Commits
| Author | SHA1 | Message | Date | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
d0550f58ae
|
Remove 's lifetime from WorldQuery::Fetch (#19720)
# Objective Unblock #18162. #15396 added the `'s` lifetime to `QueryData::Item` to make it possible for query items to borrow from the state. The state isn't passed directly to `QueryData::fetch()`, so it also added the `'s` lifetime to `WorldQuery::Fetch` so that we can pass the borrows through there. Unfortunately, having `WorldQuery::Fetch` borrow from the state makes it impossible to have owned state, because we store the state and the `Fetch` in the same `struct` during iteration. ## Solution Undo the change to add the `'s` lifetime to `WorldQuery::Fetch`. Instead, add a `&'s Self::State` parameter to `QueryData::fetch()` and `QueryFilter::filter_fetch()` so that borrows from the state can be passed directly to query items. --------- Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com> Co-authored-by: Emerson Coskey <emerson@coskey.dev> |
||
|
|
f7e112a3c9
|
Let query items borrow from query state to avoid needing to clone (#15396)
# Objective Improve the performance of `FilteredEntity(Ref|Mut)` and `Entity(Ref|Mut)Except`. `FilteredEntityRef` needs an `Access<ComponentId>` to determine what components it can access. There is one stored in the query state, but query items cannot borrow from the state, so it has to `clone()` the access for each row. Cloning the access involves memory allocations and can be expensive. ## Solution Let query items borrow from their query state. Add an `'s` lifetime to `WorldQuery::Item` and `WorldQuery::Fetch`, similar to the one in `SystemParam`, and provide `&'s Self::State` to the fetch so that it can borrow from the state. Unfortunately, there are a few cases where we currently return query items from temporary query states: the sorted iteration methods create a temporary state to query the sort keys, and the `EntityRef::components<Q>()` methods create a temporary state for their query. To allow these to continue to work with most `QueryData` implementations, introduce a new subtrait `ReleaseStateQueryData` that converts a `QueryItem<'w, 's>` to `QueryItem<'w, 'static>`, and is implemented for everything except `FilteredEntity(Ref|Mut)` and `Entity(Ref|Mut)Except`. `#[derive(QueryData)]` will generate `ReleaseStateQueryData` implementations that apply when all of the subqueries implement `ReleaseStateQueryData`. This PR does not actually change the implementation of `FilteredEntity(Ref|Mut)` or `Entity(Ref|Mut)Except`! That will be done as a follow-up PR so that the changes are easier to review. I have pushed the changes as chescock/bevy#5. ## Testing I ran performance traces of many_foxes, both against main and against chescock/bevy#5, both including #15282. These changes do appear to make generalized animation a bit faster: (Red is main, yellow is chescock/bevy#5)  ## Migration Guide The `WorldQuery::Item` and `WorldQuery::Fetch` associated types and the `QueryItem` and `ROQueryItem` type aliases now have an additional lifetime parameter corresponding to the `'s` lifetime in `Query`. Manual implementations of `WorldQuery` will need to update the method signatures to include the new lifetimes. Other uses of the types will need to be updated to include a lifetime parameter, although it can usually be passed as `'_`. In particular, `ROQueryItem` is used when implementing `RenderCommand`. Before: ```rust fn render<'w>( item: &P, view: ROQueryItem<'w, Self::ViewQuery>, entity: Option<ROQueryItem<'w, Self::ItemQuery>>, param: SystemParamItem<'w, '_, Self::Param>, pass: &mut TrackedRenderPass<'w>, ) -> RenderCommandResult; ``` After: ```rust fn render<'w>( item: &P, view: ROQueryItem<'w, '_, Self::ViewQuery>, entity: Option<ROQueryItem<'w, '_, Self::ItemQuery>>, param: SystemParamItem<'w, '_, Self::Param>, pass: &mut TrackedRenderPass<'w>, ) -> RenderCommandResult; ``` --- Methods on `QueryState` that take `&mut self` may now result in conflicting borrows if the query items capture the lifetime of the mutable reference. This affects `get()`, `iter()`, and others. To fix the errors, first call `QueryState::update_archetypes()`, and then replace a call `state.foo(world, param)` with `state.query_manual(world).foo_inner(param)`. Alternately, you may be able to restructure the code to call `state.query(world)` once and then make multiple calls using the `Query`. Before: ```rust let mut state: QueryState<_, _> = ...; let d1 = state.get(world, e1); let d2 = state.get(world, e2); // Error: cannot borrow `state` as mutable more than once at a time println!("{d1:?}"); println!("{d2:?}"); ``` After: ```rust let mut state: QueryState<_, _> = ...; state.update_archetypes(world); let d1 = state.get_manual(world, e1); let d2 = state.get_manual(world, e2); // OR state.update_archetypes(world); let d1 = state.query(world).get_inner(e1); let d2 = state.query(world).get_inner(e2); // OR let query = state.query(world); let d1 = query.get_inner(e1); let d1 = query.get_inner(e2); println!("{d1:?}"); println!("{d2:?}"); ``` |
||
|
|
38c3423693
|
Event Split: Event, EntityEvent, and BufferedEvent (#19647)
# Objective Closes #19564. The current `Event` trait looks like this: ```rust pub trait Event: Send + Sync + 'static { type Traversal: Traversal<Self>; const AUTO_PROPAGATE: bool = false; fn register_component_id(world: &mut World) -> ComponentId { ... } fn component_id(world: &World) -> Option<ComponentId> { ... } } ``` The `Event` trait is used by both buffered events (`EventReader`/`EventWriter`) and observer events. If they are observer events, they can optionally be targeted at specific `Entity`s or `ComponentId`s, and can even be propagated to other entities. However, there has long been a desire to split the trait semantically for a variety of reasons, see #14843, #14272, and #16031 for discussion. Some reasons include: - It's very uncommon to use a single event type as both a buffered event and targeted observer event. They are used differently and tend to have distinct semantics. - A common footgun is using buffered events with observers or event readers with observer events, as there is no type-level error that prevents this kind of misuse. - #19440 made `Trigger::target` return an `Option<Entity>`. This *seriously* hurts ergonomics for the general case of entity observers, as you need to `.unwrap()` each time. If we could statically determine whether the event is expected to have an entity target, this would be unnecessary. There's really two main ways that we can categorize events: push vs. pull (i.e. "observer event" vs. "buffered event") and global vs. targeted: | | Push | Pull | | ------------ | --------------- | --------------------------- | | **Global** | Global observer | `EventReader`/`EventWriter` | | **Targeted** | Entity observer | - | There are many ways to approach this, each with their tradeoffs. Ultimately, we kind of want to split events both ways: - A type-level distinction between observer events and buffered events, to prevent people from using the wrong kind of event in APIs - A statically designated entity target for observer events to avoid accidentally using untargeted events for targeted APIs This PR achieves these goals by splitting event traits into `Event`, `EntityEvent`, and `BufferedEvent`, with `Event` being the shared trait implemented by all events. ## `Event`, `EntityEvent`, and `BufferedEvent` `Event` is now a very simple trait shared by all events. ```rust pub trait Event: Send + Sync + 'static { // Required for observer APIs fn register_component_id(world: &mut World) -> ComponentId { ... } fn component_id(world: &World) -> Option<ComponentId> { ... } } ``` You can call `trigger` for *any* event, and use a global observer for listening to the event. ```rust #[derive(Event)] struct Speak { message: String, } // ... app.add_observer(|trigger: On<Speak>| { println!("{}", trigger.message); }); // ... commands.trigger(Speak { message: "Y'all like these reworked events?".to_string(), }); ``` To allow an event to be targeted at entities and even propagated further, you can additionally implement the `EntityEvent` trait: ```rust pub trait EntityEvent: Event { type Traversal: Traversal<Self>; const AUTO_PROPAGATE: bool = false; } ``` This lets you call `trigger_targets`, and to use targeted observer APIs like `EntityCommands::observe`: ```rust #[derive(Event, EntityEvent)] #[entity_event(traversal = &'static ChildOf, auto_propagate)] struct Damage { amount: f32, } // ... let enemy = commands.spawn((Enemy, Health(100.0))).id(); // Spawn some armor as a child of the enemy entity. // When the armor takes damage, it will bubble the event up to the enemy. let armor_piece = commands .spawn((ArmorPiece, Health(25.0), ChildOf(enemy))) .observe(|trigger: On<Damage>, mut query: Query<&mut Health>| { // Note: `On::target` only exists because this is an `EntityEvent`. let mut health = query.get(trigger.target()).unwrap(); health.0 -= trigger.amount(); }); commands.trigger_targets(Damage { amount: 10.0 }, armor_piece); ``` > [!NOTE] > You *can* still also trigger an `EntityEvent` without targets using `trigger`. We probably *could* make this an either-or thing, but I'm not sure that's actually desirable. To allow an event to be used with the buffered API, you can implement `BufferedEvent`: ```rust pub trait BufferedEvent: Event {} ``` The event can then be used with `EventReader`/`EventWriter`: ```rust #[derive(Event, BufferedEvent)] struct Message(String); fn write_hello(mut writer: EventWriter<Message>) { writer.write(Message("I hope these examples are alright".to_string())); } fn read_messages(mut reader: EventReader<Message>) { // Process all buffered events of type `Message`. for Message(message) in reader.read() { println!("{message}"); } } ``` In summary: - Need a basic event you can trigger and observe? Derive `Event`! - Need the event to be targeted at an entity? Derive `EntityEvent`! - Need the event to be buffered and support the `EventReader`/`EventWriter` API? Derive `BufferedEvent`! ## Alternatives I'll now cover some of the alternative approaches I have considered and briefly explored. I made this section collapsible since it ended up being quite long :P <details> <summary>Expand this to see alternatives</summary> ### 1. Unified `Event` Trait One option is not to have *three* separate traits (`Event`, `EntityEvent`, `BufferedEvent`), and to instead just use associated constants on `Event` to determine whether an event supports targeting and buffering or not: ```rust pub trait Event: Send + Sync + 'static { type Traversal: Traversal<Self>; const AUTO_PROPAGATE: bool = false; const TARGETED: bool = false; const BUFFERED: bool = false; fn register_component_id(world: &mut World) -> ComponentId { ... } fn component_id(world: &World) -> Option<ComponentId> { ... } } ``` Methods can then use bounds like `where E: Event<TARGETED = true>` or `where E: Event<BUFFERED = true>` to limit APIs to specific kinds of events. This would keep everything under one `Event` trait, but I don't think it's necessarily a good idea. It makes APIs harder to read, and docs can't easily refer to specific types of events. You can also create weird invariants: what if you specify `TARGETED = false`, but have `Traversal` and/or `AUTO_PROPAGATE` enabled? ### 2. `Event` and `Trigger` Another option is to only split the traits between buffered events and observer events, since that is the main thing people have been asking for, and they have the largest API difference. If we did this, I think we would need to make the terms *clearly* separate. We can't really use `Event` and `BufferedEvent` as the names, since it would be strange that `BufferedEvent` doesn't implement `Event`. Something like `ObserverEvent` and `BufferedEvent` could work, but it'd be more verbose. For this approach, I would instead keep `Event` for the current `EventReader`/`EventWriter` API, and call the observer event a `Trigger`, since the "trigger" terminology is already used in the observer context within Bevy (both as a noun and a verb). This is also what a long [bikeshed on Discord](https://discord.com/channels/691052431525675048/749335865876021248/1298057661878898791) seemed to land on at the end of last year. ```rust // For `EventReader`/`EventWriter` pub trait Event: Send + Sync + 'static {} // For observers pub trait Trigger: Send + Sync + 'static { type Traversal: Traversal<Self>; const AUTO_PROPAGATE: bool = false; const TARGETED: bool = false; fn register_component_id(world: &mut World) -> ComponentId { ... } fn component_id(world: &World) -> Option<ComponentId> { ... } } ``` The problem is that "event" is just a really good term for something that "happens". Observers are rapidly becoming the more prominent API, so it'd be weird to give them the `Trigger` name and leave the good `Event` name for the less common API. So, even though a split like this seems neat on the surface, I think it ultimately wouldn't really work. We want to keep the `Event` name for observer events, and there is no good alternative for the buffered variant. (`Message` was suggested, but saying stuff like "sends a collision message" is weird.) ### 3. `GlobalEvent` + `TargetedEvent` What if instead of focusing on the buffered vs. observed split, we *only* make a distinction between global and targeted events? ```rust // A shared event trait to allow global observers to work pub trait Event: Send + Sync + 'static { fn register_component_id(world: &mut World) -> ComponentId { ... } fn component_id(world: &World) -> Option<ComponentId> { ... } } // For buffered events and non-targeted observer events pub trait GlobalEvent: Event {} // For targeted observer events pub trait TargetedEvent: Event { type Traversal: Traversal<Self>; const AUTO_PROPAGATE: bool = false; } ``` This is actually the first approach I implemented, and it has the neat characteristic that you can only use non-targeted APIs like `trigger` with a `GlobalEvent` and targeted APIs like `trigger_targets` with a `TargetedEvent`. You have full control over whether the entity should or should not have a target, as they are fully distinct at the type-level. However, there's a few problems: - There is no type-level indication of whether a `GlobalEvent` supports buffered events or just non-targeted observer events - An `Event` on its own does literally nothing, it's just a shared trait required to make global observers accept both non-targeted and targeted events - If an event is both a `GlobalEvent` and `TargetedEvent`, global observers again have ambiguity on whether an event has a target or not, undermining some of the benefits - The names are not ideal ### 4. `Event` and `EntityEvent` We can fix some of the problems of Alternative 3 by accepting that targeted events can also be used in non-targeted contexts, and simply having the `Event` and `EntityEvent` traits: ```rust // For buffered events and non-targeted observer events pub trait Event: Send + Sync + 'static { fn register_component_id(world: &mut World) -> ComponentId { ... } fn component_id(world: &World) -> Option<ComponentId> { ... } } // For targeted observer events pub trait EntityEvent: Event { type Traversal: Traversal<Self>; const AUTO_PROPAGATE: bool = false; } ``` This is essentially identical to this PR, just without a dedicated `BufferedEvent`. The remaining major "problem" is that there is still zero type-level indication of whether an `Event` event *actually* supports the buffered API. This leads us to the solution proposed in this PR, using `Event`, `EntityEvent`, and `BufferedEvent`. </details> ## Conclusion The `Event` + `EntityEvent` + `BufferedEvent` split proposed in this PR aims to solve all the common problems with Bevy's current event model while keeping the "weirdness" factor minimal. It splits in terms of both the push vs. pull *and* global vs. targeted aspects, while maintaining a shared concept for an "event". ### Why I Like This - The term "event" remains as a single concept for all the different kinds of events in Bevy. - Despite all event types being "events", they use fundamentally different APIs. Instead of assuming that you can use an event type with any pattern (when only one is typically supported), you explicitly opt in to each one with dedicated traits. - Using separate traits for each type of event helps with documentation and clearer function signatures. - I can safely make assumptions on expected usage. - If I see that an event is an `EntityEvent`, I can assume that I can use `observe` on it and get targeted events. - If I see that an event is a `BufferedEvent`, I can assume that I can use `EventReader` to read events. - If I see both `EntityEvent` and `BufferedEvent`, I can assume that both APIs are supported. In summary: This allows for a unified concept for events, while limiting the different ways to use them with opt-in traits. No more guess-work involved when using APIs. ### Problems? - Because `BufferedEvent` implements `Event` (for more consistent semantics etc.), you can still use all buffered events for non-targeted observers. I think this is fine/good. The important part is that if you see that an event implements `BufferedEvent`, you know that the `EventReader`/`EventWriter` API should be supported. Whether it *also* supports other APIs is secondary. - I currently only support `trigger_targets` for an `EntityEvent`. However, you can technically target components too, without targeting any entities. I consider that such a niche and advanced use case that it's not a huge problem to only support it for `EntityEvent`s, but we could also split `trigger_targets` into `trigger_entities` and `trigger_components` if we wanted to (or implement components as entities :P). - You can still trigger an `EntityEvent` *without* targets. I consider this correct, since `Event` implements the non-targeted behavior, and it'd be weird if implementing another trait *removed* behavior. However, it does mean that global observers for entity events can technically return `Entity::PLACEHOLDER` again (since I got rid of the `Option<Entity>` added in #19440 for ergonomics). I think that's enough of an edge case that it's not a huge problem, but it is worth keeping in mind. - ~~Deriving both `EntityEvent` and `BufferedEvent` for the same type currently duplicates the `Event` implementation, so you instead need to manually implement one of them.~~ Changed to always requiring `Event` to be derived. ## Related Work There are plans to implement multi-event support for observers, especially for UI contexts. [Cart's example](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/14649#issuecomment-2960402508) API looked like this: ```rust // Truncated for brevity trigger: Trigger<( OnAdd<Pressed>, OnRemove<Pressed>, OnAdd<InteractionDisabled>, OnRemove<InteractionDisabled>, OnInsert<Hovered>, )>, ``` I believe this shouldn't be in conflict with this PR. If anything, this PR might *help* achieve the multi-event pattern for entity observers with fewer footguns: by statically enforcing that all of these events are `EntityEvent`s in the context of `EntityCommands::observe`, we can avoid misuse or weird cases where *some* events inside the trigger are targeted while others are not. |
||
|
|
e5dc177b4b
|
Rename Trigger to On (#19596)
# Objective
Currently, the observer API looks like this:
```rust
app.add_observer(|trigger: Trigger<Explode>| {
info!("Entity {} exploded!", trigger.target());
});
```
Future plans for observers also include "multi-event observers" with a
trigger that looks like this (see [Cart's
example](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/14649#issuecomment-2960402508)):
```rust
trigger: Trigger<(
OnAdd<Pressed>,
OnRemove<Pressed>,
OnAdd<InteractionDisabled>,
OnRemove<InteractionDisabled>,
OnInsert<Hovered>,
)>,
```
In scenarios like this, there is a lot of repetition of `On`. These are
expected to be very high-traffic APIs especially in UI contexts, so
ergonomics and readability are critical.
By renaming `Trigger` to `On`, we can make these APIs read more cleanly
and get rid of the repetition:
```rust
app.add_observer(|trigger: On<Explode>| {
info!("Entity {} exploded!", trigger.target());
});
```
```rust
trigger: On<(
Add<Pressed>,
Remove<Pressed>,
Add<InteractionDisabled>,
Remove<InteractionDisabled>,
Insert<Hovered>,
)>,
```
Names like `On<Add<Pressed>>` emphasize the actual event listener nature
more than `Trigger<OnAdd<Pressed>>`, and look cleaner. This *also* frees
up the `Trigger` name if we want to use it for the observer event type,
splitting them out from buffered events (bikeshedding this is out of
scope for this PR though).
For prior art:
[`bevy_eventlistener`](https://github.com/aevyrie/bevy_eventlistener)
used
[`On`](https://docs.rs/bevy_eventlistener/latest/bevy_eventlistener/event_listener/struct.On.html)
for its event listener type. Though in our case, the observer is the
event listener, and `On` is just a type containing information about the
triggered event.
## Solution
Steal from `bevy_event_listener` by @aevyrie and use `On`.
- Rename `Trigger` to `On`
- Rename `OnAdd` to `Add`
- Rename `OnInsert` to `Insert`
- Rename `OnReplace` to `Replace`
- Rename `OnRemove` to `Remove`
- Rename `OnDespawn` to `Despawn`
## Discussion
### Naming Conflicts??
Using a name like `Add` might initially feel like a very bad idea, since
it risks conflict with `core::ops::Add`. However, I don't expect this to
be a big problem in practice.
- You rarely need to actually implement the `Add` trait, especially in
modules that would use the Bevy ECS.
- In the rare cases where you *do* get a conflict, it is very easy to
fix by just disambiguating, for example using `ops::Add`.
- The `Add` event is a struct while the `Add` trait is a trait (duh), so
the compiler error should be very obvious.
For the record, renaming `OnAdd` to `Add`, I got exactly *zero* errors
or conflicts within Bevy itself. But this is of course not entirely
representative of actual projects *using* Bevy.
You might then wonder, why not use `Added`? This would conflict with the
`Added` query filter, so it wouldn't work. Additionally, the current
naming convention for observer events does not use past tense.
### Documentation
This does make documentation slightly more awkward when referring to
`On` or its methods. Previous docs often referred to `Trigger::target`
or "sends a `Trigger`" (which is... a bit strange anyway), which would
now be `On::target` and "sends an observer `Event`".
You can see the diff in this PR to see some of the effects. I think it
should be fine though, we may just need to reword more documentation to
read better.
|
||
|
|
030edbf3fe
|
Rename bevy_ecs::world::Entry to ComponentEntry (#19517)
# Objective As discussed in #19285, some of our names conflict. `Entry` in bevy_ecs is one of those overly general names. ## Solution Rename this type (and the related types) to `ComponentEntry`. --------- Co-authored-by: urben1680 <55257931+urben1680@users.noreply.github.com> |
||
|
|
6ddd0f16a8
|
Component lifecycle reorganization and documentation (#19543)
# Objective I set out with one simple goal: clearly document the differences between each of the component lifecycle events via module docs. Unfortunately, no such module existed: the various lifecycle code was scattered to the wind. Without a unified module, it's very hard to discover the related types, and there's nowhere good to put my shiny new documentation. ## Solution 1. Unify the assorted types into a single `bevy_ecs::component_lifecycle` module. 2. Write docs. 3. Write a migration guide. ## Testing Thanks CI! ## Follow-up 1. The lifecycle event names are pretty confusing, especially `OnReplace`. We should consider renaming those. No bikeshedding in my PR though! 2. Observers need real module docs too :( 3. Any additional functional changes should be done elsewhere; this is a simple docs and re-org PR. --------- Co-authored-by: theotherphil <phil.j.ellison@gmail.com> |
||
|
|
064e5e48b4
|
Remove entity placeholder from observers (#19440)
# Objective `Entity::PLACEHOLDER` acts as a magic number that will *probably* never really exist, but it certainly could. And, `Entity` has a niche, so the only reason to use `PLACEHOLDER` is as an alternative to `MaybeUninit` that trades safety risks for logic risks. As a result, bevy has generally advised against using `PLACEHOLDER`, but we still use if for a lot internally. This pr starts removing internal uses of it, starting from observers. ## Solution Change all trigger target related types from `Entity` to `Option<Entity>` Small migration guide to come. ## Testing CI ## Future Work This turned a lot of code from ```rust trigger.target() ``` to ```rust trigger.target().unwrap() ``` The extra panic is no worse than before; it's just earlier than panicking after passing the placeholder to something else. But this is kinda annoying. I would like to add a `TriggerMode` or something to `Event` that would restrict what kinds of targets can be used for that event. Many events like `Removed` etc, are always triggered with a target. We can make those have a way to assume Some, etc. But I wanted to save that for a future pr. |
||
|
|
3d9fc5ca10
|
Register some types (#19361)
# Objective Fill in some `Reflect` and `app.register_type` gaps. I only really wanted `GlobalZIndex` but figured I'd fill in a few others as well. |
||
|
|
60cdefd128
|
Derive clone_behavior for Components (#18811)
Allow Derive(Component) to specify a clone_behavior ```rust #[derive(Component)] #[component(clone_behavior = Ignore)] MyComponent; ``` |
||
|
|
e9a0ef49f9
|
Rename bevy_platform_support to bevy_platform (#18813)
# Objective The goal of `bevy_platform_support` is to provide a set of platform agnostic APIs, alongside platform-specific functionality. This is a high traffic crate (providing things like HashMap and Instant). Especially in light of https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/discussions/18799, it deserves a friendlier / shorter name. Given that it hasn't had a full release yet, getting this change in before Bevy 0.16 makes sense. ## Solution - Rename `bevy_platform_support` to `bevy_platform`. |
||
|
|
2944f5e79d
|
Ignore RenderEntity during entity clones (#18798)
# Objective Fixes #18795 ## Solution Ignore RenderEntity during entity clones |
||
|
|
35cfef7cf2
|
Rename EntityBorrow/TrustedEntityBorrow to ContainsEntity/EntityEquivalent (#18470)
# Objective Fixes #9367. Yet another follow-up to #16547. These traits were initially based on `Borrow<Entity>` because that trait was what they were replacing, and it felt close enough in meaning. However, they ultimately don't quite match: `borrow` always returns references, whereas `EntityBorrow` always returns a plain `Entity`. Additionally, `EntityBorrow` can imply that we are borrowing an `Entity` from the ECS, which is not what it does. Due to its safety contract, `TrustedEntityBorrow` is important an important and widely used trait for `EntitySet` functionality. In contrast, the safe `EntityBorrow` does not see much use, because even outside of `EntitySet`-related functionality, it is a better idea to accept `TrustedEntityBorrow` over `EntityBorrow`. Furthermore, as #9367 points out, abstracting over returning `Entity` from pointers/structs that contain it can skip some ergonomic friction. On top of that, there are aspects of #18319 and #18408 that are relevant to naming: We've run into the issue that relying on a type default can switch generic order. This is livable in some contexts, but unacceptable in others. To remedy that, we'd need to switch to a type alias approach: The "defaulted" `Entity` case becomes a `UniqueEntity*`/`Entity*Map`/`Entity*Set` alias, and the base type receives a more general name. `TrustedEntityBorrow` does not mesh clearly with sensible base type names. ## Solution Replace any `EntityBorrow` bounds with `TrustedEntityBorrow`. + Rename them as such: `EntityBorrow` -> `ContainsEntity` `TrustedEntityBorrow` -> `EntityEquivalent` For `EntityBorrow` we produce a change in meaning; We designate it for types that aren't necessarily strict wrappers around `Entity` or some pointer to `Entity`, but rather any of the myriad of types that contain a single associated `Entity`. This pattern can already be seen in the common `entity`/`id` methods across the engine. We do not mean for `ContainsEntity` to be a trait that abstracts input API (like how `AsRef<T>` is often used, f.e.), because eliding `entity()` would be too implicit in the general case. We prefix "Contains" to match the intuition of a struct with an `Entity` field, like some contain a `length` or `capacity`. It gives the impression of structure, which avoids the implication of a relationship to the `ECS`. `HasEntity` f.e. could be interpreted as "a currently live entity", As an input trait for APIs like #9367 envisioned, `TrustedEntityBorrow` is a better fit, because it *does* restrict itself to strict wrappers and pointers. Which is why we replace any `EntityBorrow`/`ContainsEntity` bounds with `TrustedEntityBorrow`/`EntityEquivalent`. Here, the name `EntityEquivalent` is a lot closer to its actual meaning, which is "A type that is both equivalent to an `Entity`, and forms the same total order when compared". Prior art for this is the [`Equivalent`](https://docs.rs/hashbrown/latest/hashbrown/trait.Equivalent.html) trait in `hashbrown`, which utilizes both `Borrow` and `Eq` for its one blanket impl! Given that we lose the `Borrow` moniker, and `Equivalent` can carry various meanings, we expand on the safety comment of `EntityEquivalent` somewhat. That should help prevent the confusion we saw in [#18408](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/18408#issuecomment-2742094176). The new name meshes a lot better with the type aliasing approach in #18408, by aligning with the base name `EntityEquivalentHashMap`. For a consistent scheme among all set types, we can use this scheme for the `UniqueEntity*` wrapper types as well! This allows us to undo the switched generic order that was introduced to `UniqueEntityArray` by its `Entity` default. Even without the type aliases, I think these renames are worth doing! ## Migration Guide Any use of `EntityBorrow` becomes `ContainsEntity`. Any use of `TrustedEntityBorrow` becomes `EntityEquivalent`. |
||
|
|
9b32e09551
|
bevy_reflect: Add clone registrations project-wide (#18307)
# Objective Now that #13432 has been merged, it's important we update our reflected types to properly opt into this feature. If we do not, then this could cause issues for users downstream who want to make use of reflection-based cloning. ## Solution This PR is broken into 4 commits: 1. Add `#[reflect(Clone)]` on all types marked `#[reflect(opaque)]` that are also `Clone`. This is mandatory as these types would otherwise cause the cloning operation to fail for any type that contains it at any depth. 2. Update the reflection example to suggest adding `#[reflect(Clone)]` on opaque types. 3. Add `#[reflect(clone)]` attributes on all fields marked `#[reflect(ignore)]` that are also `Clone`. This prevents the ignored field from causing the cloning operation to fail. Note that some of the types that contain these fields are also `Clone`, and thus can be marked `#[reflect(Clone)]`. This makes the `#[reflect(clone)]` attribute redundant. However, I think it's safer to keep it marked in the case that the `Clone` impl/derive is ever removed. I'm open to removing them, though, if people disagree. 4. Finally, I added `#[reflect(Clone)]` on all types that are also `Clone`. While not strictly necessary, it enables us to reduce the generated output since we can just call `Clone::clone` directly instead of calling `PartialReflect::reflect_clone` on each variant/field. It also means we benefit from any optimizations or customizations made in the `Clone` impl, including directly dereferencing `Copy` values and increasing reference counters. Along with that change I also took the liberty of adding any missing registrations that I saw could be applied to the type as well, such as `Default`, `PartialEq`, and `Hash`. There were hundreds of these to edit, though, so it's possible I missed quite a few. That last commit is **_massive_**. There were nearly 700 types to update. So it's recommended to review the first three before moving onto that last one. Additionally, I can break the last commit off into its own PR or into smaller PRs, but I figured this would be the easiest way of doing it (and in a timely manner since I unfortunately don't have as much time as I used to for code contributions). ## Testing You can test locally with a `cargo check`: ``` cargo check --workspace --all-features ``` |
||
|
|
1f6642df4c
|
Fix unsound query transmutes on queries obtained from Query::as_readonly() (#17973)
# Objective
Fix unsound query transmutes on queries obtained from
`Query::as_readonly()`.
The following compiles, and the call to `transmute_lens()` should panic,
but does not:
```rust
fn bad_system(query: Query<&mut A>) {
let mut readonly = query.as_readonly();
let mut lens: QueryLens<&mut A> = readonly.transmute_lens();
let other_readonly: Query<&A> = query.as_readonly();
// `lens` and `other_readonly` alias, and are both alive here!
}
```
To make `Query::as_readonly()` zero-cost, we pointer-cast
`&QueryState<D, F>` to `&QueryState<D::ReadOnly, F>`. This means that
the `component_access` for a read-only query's state may include
accesses for the original mutable version, but the `Query` does not have
exclusive access to those components! `transmute` and `join` use that
access to ensure that a join is valid, and will incorrectly allow a
transmute that includes mutable access.
As a bonus, allow `Query::join`s that output `FilteredEntityRef` or
`FilteredEntityMut` to receive access from the `other` query. Currently
they only receive access from `self`.
## Solution
When transmuting or joining from a read-only query, remove any writes
before performing checking that the transmute is valid. For joins, be
sure to handle the case where one input query was the result of
`as_readonly()` but the other has valid mutable access.
This requires identifying read-only queries, so add a
`QueryData::IS_READ_ONLY` associated constant. Note that we only call
`QueryState::as_transmuted_state()` with `NewD: ReadOnlyQueryData`, so
checking for read-only queries is sufficient to check for
`as_transmuted_state()`.
Removing writes requires allocating a new `FilteredAccess`, so only do
so if the query is read-only and the state has writes. Otherwise, the
existing access is correct and we can continue using a reference to it.
Use the new read-only state to call `NewD::set_access`, so that
transmuting to a `FilteredAccessMut` results in a read-only
`FilteredAccessMut`. Otherwise, it would take the original write access,
and then the transmute would panic because it had too much access.
Note that `join` was previously passing `self.component_access` to
`NewD::set_access`. Switching it to `joined_component_access` also
allows a join that outputs `FilteredEntity(Ref|Mut)` to receive access
from `other`. The fact that it didn't do that before seems like an
oversight, so I didn't try to prevent that change.
## Testing
Added unit tests with the unsound transmute and join.
|
||
|
|
2ad5908e58
|
Make Query::single (and friends) return a Result (#18082)
# Objective As discussed in #14275, Bevy is currently too prone to panic, and makes the easy / beginner-friendly way to do a large number of operations just to panic on failure. This is seriously frustrating in library code, but also slows down development, as many of the `Query::single` panics can actually safely be an early return (these panics are often due to a small ordering issue or a change in game state. More critically, in most "finished" products, panics are unacceptable: any unexpected failures should be handled elsewhere. That's where the new With the advent of good system error handling, we can now remove this. Note: I was instrumental in a) introducing this idea in the first place and b) pushing to make the panicking variant the default. The introduction of both `let else` statements in Rust and the fancy system error handling work in 0.16 have changed my mind on the right balance here. ## Solution 1. Make `Query::single` and `Query::single_mut` (and other random related methods) return a `Result`. 2. Handle all of Bevy's internal usage of these APIs. 3. Deprecate `Query::get_single` and friends, since we've moved their functionality to the nice names. 4. Add detailed advice on how to best handle these errors. Generally I like the diff here, although `get_single().unwrap()` in tests is a bit of a downgrade. ## Testing I've done a global search for `.single` to track down any missed deprecated usages. As to whether or not all the migrations were successful, that's what CI is for :) ## Future work ~~Rename `Query::get_single` and friends to `Query::single`!~~ ~~I've opted not to do this in this PR, and smear it across two releases in order to ease the migration. Successive deprecations are much easier to manage than the semantics and types shifting under your feet.~~ Cart has convinced me to change my mind on this; see https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/18082#discussion_r1974536085. ## Migration guide `Query::single`, `Query::single_mut` and their `QueryState` equivalents now return a `Result`. Generally, you'll want to: 1. Use Bevy 0.16's system error handling to return a `Result` using the `?` operator. 2. Use a `let else Ok(data)` block to early return if it's an expected failure. 3. Use `unwrap()` or `Ok` destructuring inside of tests. The old `Query::get_single` (etc) methods which did this have been deprecated. |
||
|
|
7fc122ad16
|
Retain bins from frame to frame. (#17698)
This PR makes Bevy keep entities in bins from frame to frame if they haven't changed. This reduces the time spent in `queue_material_meshes` and related functions to near zero for static geometry. This patch uses the same change tick technique that #17567 uses to detect when meshes have changed in such a way as to require re-binning. In order to quickly find the relevant bin for an entity when that entity has changed, we introduce a new type of cache, the *bin key cache*. This cache stores a mapping from main world entity ID to cached bin key, as well as the tick of the most recent change to the entity. As we iterate through the visible entities in `queue_material_meshes`, we check the cache to see whether the entity needs to be re-binned. If it doesn't, then we mark it as clean in the `valid_cached_entity_bin_keys` bit set. If it does, then we insert it into the correct bin, and then mark the entity as clean. At the end, all entities not marked as clean are removed from the bins. This patch has a dramatic effect on the rendering performance of most benchmarks, as it effectively eliminates `queue_material_meshes` from the profile. Note, however, that it generally simultaneously regresses `batch_and_prepare_binned_render_phase` by a bit (not by enough to outweigh the win, however). I believe that's because, before this patch, `queue_material_meshes` put the bins in the CPU cache for `batch_and_prepare_binned_render_phase` to use, while with this patch, `batch_and_prepare_binned_render_phase` must load the bins into the CPU cache itself. On Caldera, this reduces the time spent in `queue_material_meshes` from 5+ ms to 0.2ms-0.3ms. Note that benchmarking on that scene is very noisy right now because of https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/17535. 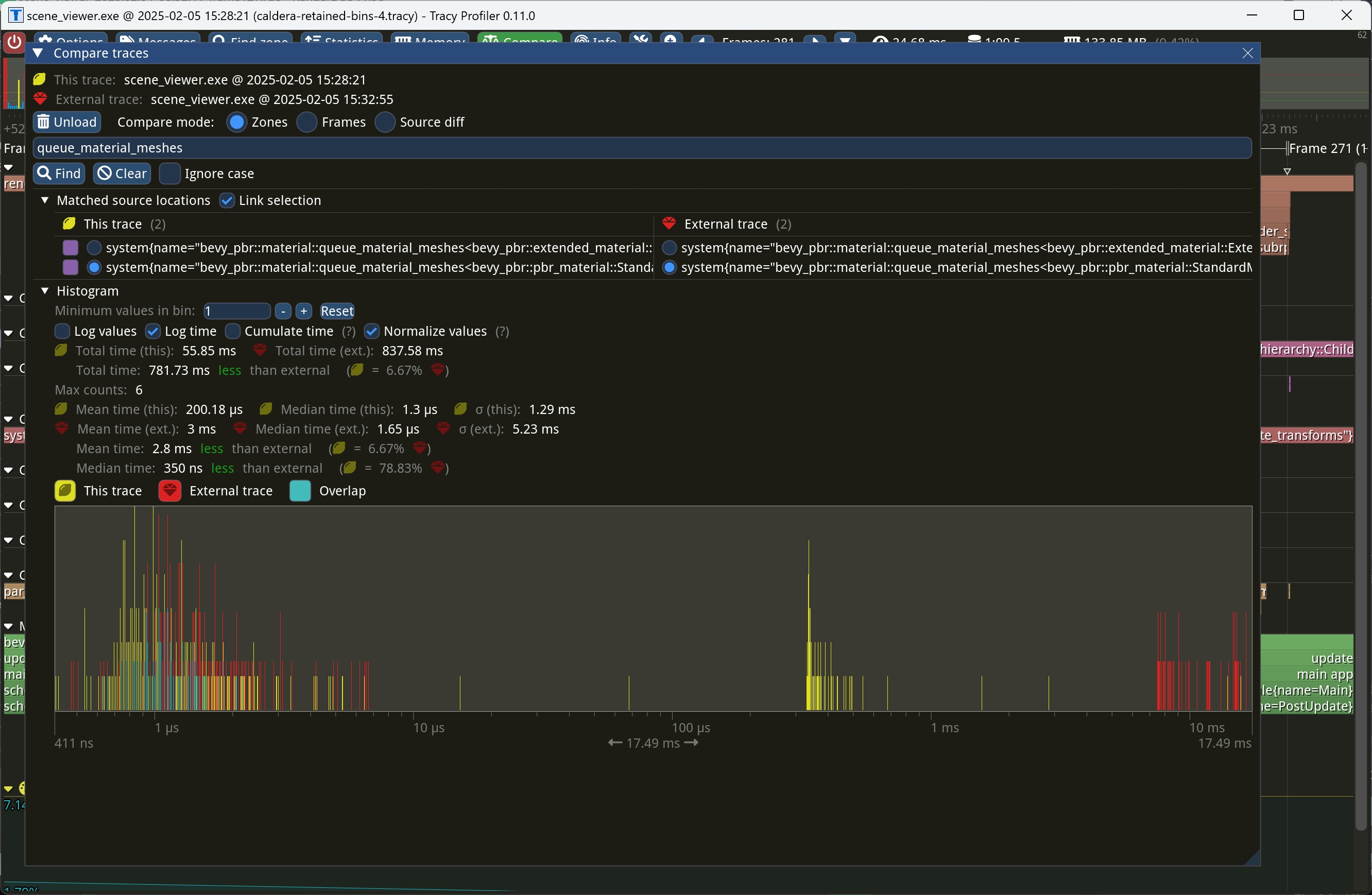 |
||
|
|
03af547c28
|
Move Item and fetch to QueryData from WorldQuery (#17679)
# Objective Fixes #17662 ## Solution Moved `Item` and `fetch` from `WorldQuery` to `QueryData`, and adjusted their implementations accordingly. Currently, documentation related to `fetch` is written under `WorldQuery`. It would be more appropriate to move it to the `QueryData` documentation for clarity. I am not very experienced with making contributions. If there are any mistakes or areas for improvement, I would appreciate any suggestions you may have. ## Migration Guide The `WorldQuery::Item` type and `WorldQuery::fetch` method have been moved to `QueryData`, as they were not useful for `QueryFilter` types. --------- Co-authored-by: Chris Russell <8494645+chescock@users.noreply.github.com> |
||
|
|
9bc0ae33c3
|
Move hashbrown and foldhash out of bevy_utils (#17460)
# Objective - Contributes to #16877 ## Solution - Moved `hashbrown`, `foldhash`, and related types out of `bevy_utils` and into `bevy_platform_support` - Refactored the above to match the layout of these types in `std`. - Updated crates as required. ## Testing - CI --- ## Migration Guide - The following items were moved out of `bevy_utils` and into `bevy_platform_support::hash`: - `FixedState` - `DefaultHasher` - `RandomState` - `FixedHasher` - `Hashed` - `PassHash` - `PassHasher` - `NoOpHash` - The following items were moved out of `bevy_utils` and into `bevy_platform_support::collections`: - `HashMap` - `HashSet` - `bevy_utils::hashbrown` has been removed. Instead, import from `bevy_platform_support::collections` _or_ take a dependency on `hashbrown` directly. - `bevy_utils::Entry` has been removed. Instead, import from `bevy_platform_support::collections::hash_map` or `bevy_platform_support::collections::hash_set` as appropriate. - All of the above equally apply to `bevy::utils` and `bevy::platform_support`. ## Notes - I left `PreHashMap`, `PreHashMapExt`, and `TypeIdMap` in `bevy_utils` as they might be candidates for micro-crating. They can always be moved into `bevy_platform_support` at a later date if desired. |
||
|
|
44ad3bf62b
|
Move Resource trait to its own file (#17469)
# Objective `bevy_ecs`'s `system` module is something of a grab bag, and *very* large. This is particularly true for the `system_param` module, which is more than 2k lines long! While it could be defensible to put `Res` and `ResMut` there (lol no they're in change_detection.rs, obviously), it doesn't make any sense to put the `Resource` trait there. This is confusing to navigate (and painful to work on and review). ## Solution - Create a root level `bevy_ecs/resource.rs` module to mirror `bevy_ecs/component.rs` - move the `Resource` trait to that module - move the `Resource` derive macro to that module as well (Rust really likes when you pun on the names of the derive macro and trait and put them in the same path) - fix all of the imports ## Notes to reviewers - We could probably move more stuff into here, but I wanted to keep this PR as small as possible given the absurd level of import changes. - This PR is ground work for my upcoming attempts to store resource data on components (resources-as-entities). Splitting this code out will make the work and review a bit easier, and is the sort of overdue refactor that's good to do as part of more meaningful work. ## Testing cargo build works! ## Migration Guide `bevy_ecs::system::Resource` has been moved to `bevy_ecs::resource::Resource`. |
||
|
|
5b899dcc3a
|
impl EntityBorrow for more types (#16917)
# Objective Some types like `RenderEntity` and `MainEntity` are just wrappers around `Entity`, so they should be able to implement `EntityBorrow`/`TrustedEntityBorrow`. This allows using them with `EntitySet` functionality. The `EntityRef` family are more than direct wrappers around `Entity`, but can still benefit from being unique in a collection. ## Solution Implement `EntityBorrow` and `TrustedEntityBorrow` for simple `Entity` newtypes and `EntityRef` types. These impls are an explicit decision to have the `EntityRef` types compare like just `Entity`. `EntityWorldMut` is omitted from this impl, because it explicitly contains a `&mut World` as well, and we do not ever use more than one at a time. Add `EntityBorrow` to the `bevy_ecs` prelude. ## Migration Guide `NormalizedWindowRef::entity` has been replaced with an `EntityBorrow::entity` impl. |
||
|
|
56688b387c
|
Fix registering all reflection types that are components as reflection components (#16800)
# Objective Fixes #16659 ## Solution - I just added all the `#[reflect(Component)]` attributes where necessary. ## Testing I wrote a small program that scans the bevy code for all structs and enums that derive `Component` and `Reflect`, but don't have the attribute `#[reflect(Component)]`. I don't know if this testing program should be part of the testing suite of bevy. It takes a bit of time to scan the whole codebase. In any case, I've published it [here](https://github.com/anlumo/bevy-reflect-check). --------- Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com> |
||
|
|
61b98ec80f
|
Rename trigger.entity() to trigger.target() (#16716)
# Objective - A `Trigger` has multiple associated `Entity`s - the entity observing the event, and the entity that was targeted by the event. - The field `entity: Entity` encodes no semantic information about what the entity is used for, you can already tell that it's an `Entity` by the type signature! ## Solution - Rename `trigger.entity()` to `trigger.target()` --- ## Changelog - `Trigger`s are associated with multiple entities. `Trigger::entity()` has been renamed to `Trigger::target()` to reflect the semantics of the entity being returned. ## Migration Guide - Rename `Trigger::entity()` to `Trigger::target()`. - Rename `ObserverTrigger::entity` to `ObserverTrigger::target` |
||
|
|
35de45277c
|
Use default storage for TemporaryRenderEntity (#16462)
# Objective `TemporaryRenderEntity` currently uses `SparseSet` storage, but doesn't seem to fit the criteria for a component that would benefit from this. Typical usage of `TemporaryRenderEntity` (and all current usages of it in engine as far as I can tell) would be to spawn an entity with it once and then iterate over it once to despawn that entity. `SparseSet` is said to be useful for insert/removal perf at the cost of iteration perf. ## Solution Use the default table storage ## Testing Possibly this could show up in stress tests like `many_buttons`. I didn't do any benchmarking. |
||
|
|
984ff9ba88
|
Make render world sync marker components Copy (#16461)
# Objective Original motivation was a bundle I am migrating that is `Copy` which needs to be synced to the render world. It probably doesn't actually *need* to be `Copy`, so this isn't critical or anything. I am continuing to use this bundle while bundles still exist to give users an easier migration path. ## Solution These ZSTs might as well be `Copy`. Add `Copy` derives. |
||
|
|
88d1692105
|
Derive same attributes as MainEntity for RenderEntity (#16191)
Spotted while working on updating bevy_egui. Discord context: https://discordapp.com/channels/691052431525675048/1301212128115687454/1301469954465464320 |
||
|
|
a7e9330af9
|
Implement WorldQuery for MainWorld and RenderWorld components (#15745)
# Objective #15320 is a particularly painful breaking change, and the new `RenderEntity` in particular is very noisy, with a lot of `let entity = entity.id()` spam. ## Solution Implement `WorldQuery`, `QueryData` and `ReadOnlyQueryData` for `RenderEntity` and `WorldEntity`. These work the same as the `Entity` impls from a user-facing perspective: they simply return an owned (copied) `Entity` identifier. This dramatically reduces noise and eases migration. Under the hood, these impls defer to the implementations for `&T` for everything other than the "call .id() for the user" bit, as they involve read-only access to component data. Doing it this way (as opposed to implementing a custom fetch, as tried in the first commit) dramatically reduces the maintenance risk of complex unsafe code outside of `bevy_ecs`. To make this easier (and encourage users to do this themselves!), I've made `ReadFetch` and `WriteFetch` slightly more public: they're no longer `doc(hidden)`. This is a good change, since trying to vendor the logic is much worse than just deferring to the existing tested impls. ## Testing I've run a handful of rendering examples (breakout, alien_cake_addict, auto_exposure, fog_volumes, box_shadow) and nothing broke. ## Follow-up We should lint for the uses of `&RenderEntity` and `&MainEntity` in queries: this is just less nice for no reason. --------- Co-authored-by: Trashtalk217 <trashtalk217@gmail.com> |
||
|
|
dd812b3e49
|
Type safe retained render world (#15756)
# Objective In the Render World, there are a number of collections that are derived from Main World entities and are used to drive rendering. The most notable are: - `VisibleEntities`, which is generated in the `check_visibility` system and contains visible entities for a view. - `ExtractedInstances`, which maps entity ids to asset ids. In the old model, these collections were trivially kept in sync -- any extracted phase item could look itself up because the render entity id was guaranteed to always match the corresponding main world id. After #15320, this became much more complicated, and was leading to a number of subtle bugs in the Render World. The main rendering systems, i.e. `queue_material_meshes` and `queue_material2d_meshes`, follow a similar pattern: ```rust for visible_entity in visible_entities.iter::<With<Mesh2d>>() { let Some(mesh_instance) = render_mesh_instances.get_mut(visible_entity) else { continue; }; // Look some more stuff up and specialize the pipeline... let bin_key = Opaque2dBinKey { pipeline: pipeline_id, draw_function: draw_opaque_2d, asset_id: mesh_instance.mesh_asset_id.into(), material_bind_group_id: material_2d.get_bind_group_id().0, }; opaque_phase.add( bin_key, *visible_entity, BinnedRenderPhaseType::mesh(mesh_instance.automatic_batching), ); } ``` In this case, `visible_entities` and `render_mesh_instances` are both collections that are created and keyed by Main World entity ids, and so this lookup happens to work by coincidence. However, there is a major unintentional bug here: namely, because `visible_entities` is a collection of Main World ids, the phase item being queued is created with a Main World id rather than its correct Render World id. This happens to not break mesh rendering because the render commands used for drawing meshes do not access the `ItemQuery` parameter, but demonstrates the confusion that is now possible: our UI phase items are correctly being queued with Render World ids while our meshes aren't. Additionally, this makes it very easy and error prone to use the wrong entity id to look up things like assets. For example, if instead we ignored visibility checks and queued our meshes via a query, we'd have to be extra careful to use `&MainEntity` instead of the natural `Entity`. ## Solution Make all collections that are derived from Main World data use `MainEntity` as their key, to ensure type safety and avoid accidentally looking up data with the wrong entity id: ```rust pub type MainEntityHashMap<V> = hashbrown::HashMap<MainEntity, V, EntityHash>; ``` Additionally, we make all `PhaseItem` be able to provide both their Main and Render World ids, to allow render phase implementors maximum flexibility as to what id should be used to look up data. You can think of this like tracking at the type level whether something in the Render World should use it's "primary key", i.e. entity id, or needs to use a foreign key, i.e. `MainEntity`. ## Testing ##### TODO: This will require extensive testing to make sure things didn't break! Additionally, some extraction logic has become more complicated and needs to be checked for regressions. ## Migration Guide With the advent of the retained render world, collections that contain references to `Entity` that are extracted into the render world have been changed to contain `MainEntity` in order to prevent errors where a render world entity id is used to look up an item by accident. Custom rendering code may need to be changed to query for `&MainEntity` in order to look up the correct item from such a collection. Additionally, users who implement their own extraction logic for collections of main world entity should strongly consider extracting into a different collection that uses `MainEntity` as a key. Additionally, render phases now require specifying both the `Entity` and `MainEntity` for a given `PhaseItem`. Custom render phases should ensure `MainEntity` is available when queuing a phase item. |
||
|
|
219b5930f1
|
Rename App/World::observe to add_observer, EntityWorldMut::observe_entity to observe. (#15754)
# Objective - Closes #15752 Calling the functions `App::observe` and `World::observe` doesn't make sense because you're not "observing" the `App` or `World`, you're adding an observer that listens for an event that occurs *within* the `World`. We should rename them to better fit this. ## Solution Renames: - `App::observe` -> `App::add_observer` - `World::observe` -> `World::add_observer` - `Commands::observe` -> `Commands::add_observer` - `EntityWorldMut::observe_entity` -> `EntityWorldMut::observe` (Note this isn't a breaking change as the original rename was introduced earlier this cycle.) ## Testing Reusing current tests. |
||
|
|
2d1b4939d2
|
Synchronize removed components with the render world (#15582)
# Objective Fixes #15560 Fixes (most of) #15570 Currently a lot of examples (and presumably some user code) depend on toggling certain render features by adding/removing a single component to an entity, e.g. `SpotLight` to toggle a light. Because of the retained render world this no longer works: Extract will add any new components, but when it is removed the entity persists unchanged in the render world. ## Solution Add `SyncComponentPlugin<C: Component>` that registers `SyncToRenderWorld` as a required component for `C`, and adds a component hook that will clear all components from the render world entity when `C` is removed. We add this plugin to `ExtractComponentPlugin` which fixes most instances of the problem. For custom extraction logic we can manually add `SyncComponentPlugin` for that component. We also rename `WorldSyncPlugin` to `SyncWorldPlugin` so we start a naming convention like all the `Extract` plugins. In this PR I also fixed a bunch of breakage related to the retained render world, stemming from old code that assumed that `Entity` would be the same in both worlds. I found that using the `RenderEntity` wrapper instead of `Entity` in data structures when referring to render world entities makes intent much clearer, so I propose we make this an official pattern. ## Testing Run examples like ``` cargo run --features pbr_multi_layer_material_textures --example clearcoat cargo run --example volumetric_fog ``` and see that they work, and that toggles work correctly. But really we should test every single example, as we might not even have caught all the breakage yet. --- ## Migration Guide The retained render world notes should be updated to explain this edge case and `SyncComponentPlugin` --------- Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com> Co-authored-by: Trashtalk217 <trashtalk217@gmail.com> |