6edb78a8c3
225 Commits
| Author | SHA1 | Message | Date | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
70a592f31a
|
Update to wgpu 0.18 (#10266)
# Objective Keep up to date with wgpu. ## Solution Update the wgpu version. Currently blocked on naga_oil updating to naga 0.14 and releasing a new version. 3d scenes (or maybe any scene with lighting?) currently don't render anything due to ``` error: naga_oil bug, please file a report: composer failed to build a valid header: Type [2] '' is invalid = Capability Capabilities(CUBE_ARRAY_TEXTURES) is required ``` I'm not sure what should be passed in for `wgpu::InstanceFlags`, or if we want to make the gles3minorversion configurable (might be useful for debugging?) Currently blocked on https://github.com/bevyengine/naga_oil/pull/63, and https://github.com/gfx-rs/wgpu/issues/4569 to be fixed upstream in wgpu first. ## Known issues Amd+windows+vulkan has issues with texture_binding_arrays (see the image [here](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/10266#issuecomment-1819946278)), but that'll be fixed in the next wgpu/naga version, and you can just use dx12 as a workaround for now (Amd+linux mesa+vulkan texture_binding_arrays are fixed though). --- ## Changelog Updated wgpu to 0.18, naga to 0.14.2, and naga_oil to 0.11. - Windows desktop GL should now be less painful as it no longer requires Angle. - You can now toggle shader validation and debug information for debug and release builds using `WgpuSettings.instance_flags` and [InstanceFlags](https://docs.rs/wgpu/0.18.0/wgpu/struct.InstanceFlags.html) ## Migration Guide - `RenderPassDescriptor` `color_attachments` (as well as `RenderPassColorAttachment`, and `RenderPassDepthStencilAttachment`) now use `StoreOp::Store` or `StoreOp::Discard` instead of a `boolean` to declare whether or not they should be stored. - `RenderPassDescriptor` now have `timestamp_writes` and `occlusion_query_set` fields. These can safely be set to `None`. - `ComputePassDescriptor` now have a `timestamp_writes` field. This can be set to `None` for now. - See the [wgpu changelog](https://github.com/gfx-rs/wgpu/blob/trunk/CHANGELOG.md#v0180-2023-10-25) for additional details |
||
|
|
fd308571c4
|
Remove unnecessary path prefixes (#10749)
# Objective - Shorten paths by removing unnecessary prefixes ## Solution - Remove the prefixes from many paths which do not need them. Finding the paths was done automatically using built-in refactoring tools in Jetbrains RustRover. |
||
|
|
e67cfdf82b
|
Enable clippy::undocumented_unsafe_blocks warning across the workspace (#10646)
# Objective Enables warning on `clippy::undocumented_unsafe_blocks` across the workspace rather than only in `bevy_ecs`, `bevy_transform` and `bevy_utils`. This adds a little awkwardness in a few areas of code that have trivial safety or explain safety for multiple unsafe blocks with one comment however automatically prevents these comments from being missed. ## Solution This adds `undocumented_unsafe_blocks = "warn"` to the workspace `Cargo.toml` and fixes / adds a few missed safety comments. I also added `#[allow(clippy::undocumented_unsafe_blocks)]` where the safety is explained somewhere above. There are a couple of safety comments I added I'm not 100% sure about in `bevy_animation` and `bevy_render/src/view` and I'm not sure about the use of `#[allow(clippy::undocumented_unsafe_blocks)]` compared to adding comments like `// SAFETY: See above`. |
||
|
|
951c9bb1a2
|
Add [lints] table, fix adding #![allow(clippy::type_complexity)] everywhere (#10011)
# Objective - Fix adding `#![allow(clippy::type_complexity)]` everywhere. like #9796 ## Solution - Use the new [lints] table that will land in 1.74 (https://doc.rust-lang.org/nightly/cargo/reference/unstable.html#lints) - inherit lint to the workspace, crates and examples. ``` [lints] workspace = true ``` ## Changelog - Bump rust version to 1.74 - Enable lints table for the workspace ```toml [workspace.lints.clippy] type_complexity = "allow" ``` - Allow type complexity for all crates and examples ```toml [lints] workspace = true ``` --------- Co-authored-by: Martín Maita <47983254+mnmaita@users.noreply.github.com> |
||
|
|
a830530be4
|
Replace all labels with interned labels (#7762)
# Objective First of all, this PR took heavy inspiration from #7760 and #5715. It intends to also fix #5569, but with a slightly different approach. This also fixes #9335 by reexporting `DynEq`. ## Solution The advantage of this API is that we can intern a value without allocating for zero-sized-types and for enum variants that have no fields. This PR does this automatically in the `SystemSet` and `ScheduleLabel` derive macros for unit structs and fieldless enum variants. So this should cover many internal and external use cases of `SystemSet` and `ScheduleLabel`. In these optimal use cases, no memory will be allocated. - The interning returns a `Interned<dyn SystemSet>`, which is just a wrapper around a `&'static dyn SystemSet`. - `Hash` and `Eq` are implemented in terms of the pointer value of the reference, similar to my first approach of anonymous system sets in #7676. - Therefore, `Interned<T>` does not implement `Borrow<T>`, only `Deref`. - The debug output of `Interned<T>` is the same as the interned value. Edit: - `AppLabel` is now also interned and the old `derive_label`/`define_label` macros were replaced with the new interning implementation. - Anonymous set ids are reused for different `Schedule`s, reducing the amount of leaked memory. ### Pros - `InternedSystemSet` and `InternedScheduleLabel` behave very similar to the current `BoxedSystemSet` and `BoxedScheduleLabel`, but can be copied without an allocation. - Many use cases don't allocate at all. - Very fast lookups and comparisons when using `InternedSystemSet` and `InternedScheduleLabel`. - The `intern` module might be usable in other areas. - `Interned{ScheduleLabel, SystemSet, AppLabel}` does implement `{ScheduleLabel, SystemSet, AppLabel}`, increasing ergonomics. ### Cons - Implementors of `SystemSet` and `ScheduleLabel` still need to implement `Hash` and `Eq` (and `Clone`) for it to work. ## Changelog ### Added - Added `intern` module to `bevy_utils`. - Added reexports of `DynEq` to `bevy_ecs` and `bevy_app`. ### Changed - Replaced `BoxedSystemSet` and `BoxedScheduleLabel` with `InternedSystemSet` and `InternedScheduleLabel`. - Replaced `impl AsRef<dyn ScheduleLabel>` with `impl ScheduleLabel`. - Replaced `AppLabelId` with `InternedAppLabel`. - Changed `AppLabel` to use `Debug` for error messages. - Changed `AppLabel` to use interning. - Changed `define_label`/`derive_label` to use interning. - Replaced `define_boxed_label`/`derive_boxed_label` with `define_label`/`derive_label`. - Changed anonymous set ids to be only unique inside a schedule, not globally. - Made interned label types implement their label trait. ### Removed - Removed `define_boxed_label` and `derive_boxed_label`. ## Migration guide - Replace `BoxedScheduleLabel` and `Box<dyn ScheduleLabel>` with `InternedScheduleLabel` or `Interned<dyn ScheduleLabel>`. - Replace `BoxedSystemSet` and `Box<dyn SystemSet>` with `InternedSystemSet` or `Interned<dyn SystemSet>`. - Replace `AppLabelId` with `InternedAppLabel` or `Interned<dyn AppLabel>`. - Types manually implementing `ScheduleLabel`, `AppLabel` or `SystemSet` need to implement: - `dyn_hash` directly instead of implementing `DynHash` - `as_dyn_eq` - Pass labels to `World::try_schedule_scope`, `World::schedule_scope`, `World::try_run_schedule`. `World::run_schedule`, `Schedules::remove`, `Schedules::remove_entry`, `Schedules::contains`, `Schedules::get` and `Schedules::get_mut` by value instead of by reference. --------- Co-authored-by: Joseph <21144246+JoJoJet@users.noreply.github.com> Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com> |
||
|
|
6bd3cca0ca
|
Improve linking within RenderSet docs. (#10143)
# Objective - Improve formatting and linking within `RenderSet` docs. ## Solution - Used backticks and intradoc links. |
||
|
|
4a61f894b7
|
chore: Renamed RenderInstance trait to ExtractInstance (#10065)
# Objective Fixes [#10061] ## Solution Renamed `RenderInstance` to `ExtractInstance`, `RenderInstances` to `ExtractedInstances` and `RenderInstancePlugin` to `ExtractInstancesPlugin` |
||
|
|
e67d63aa79
|
Refactor the render instance logic in #9903 so that it's easier for other components to adopt. (#10002)
# Objective Currently, the only way for custom components that participate in rendering to opt into the higher-performance extraction method in #9903 is to implement the `RenderInstances` data structure and the extraction logic manually. This is inconvenient compared to the `ExtractComponent` API. ## Solution This commit creates a new `RenderInstance` trait that mirrors the existing `ExtractComponent` method but uses the higher-performance approach that #9903 uses. Additionally, `RenderInstance` is more flexible than `ExtractComponent`, because it can extract multiple components at once. This makes high-performance rendering components essentially as easy to write as the existing ones based on component extraction. --- ## Changelog ### Added A new `RenderInstance` trait is available mirroring `ExtractComponent`, but using a higher-performance method to extract one or more components to the render world. If you have custom components that rendering takes into account, you may consider migration from `ExtractComponent` to `RenderInstance` for higher performance. |
||
|
|
687e379800
|
Updates for rust 1.73 (#10035)
# Objective - Updates for rust 1.73 ## Solution - new doc check for `redundant_explicit_links` - updated to text for compile fail tests --- ## Changelog - updates for rust 1.73 |
||
|
|
bc88f33e48
|
Allow other plugins to create renderer resources (#9925)
This is a duplicate of #9632, it was created since I forgot to make a new branch when I first made this PR, so I was having trouble resolving merge conflicts, meaning I had to rebuild my PR. # Objective - Allow other plugins to create the renderer resources. An example of where this would be required is my [OpenXR plugin](https://github.com/awtterpip/bevy_openxr) ## Solution - Changed the bevy RenderPlugin to optionally take precreated render resources instead of a configuration. ## Migration Guide The `RenderPlugin` now takes a `RenderCreation` enum instead of `WgpuSettings`. `RenderSettings::default()` returns `RenderSettings::Automatic(WgpuSettings::default())`. `RenderSettings` also implements `From<WgpuSettings>`. ```rust // before RenderPlugin { wgpu_settings: WgpuSettings { ... }, } // now RenderPlugin { render_creation: RenderCreation::Automatic(WgpuSettings { ... }), } // or RenderPlugin { render_creation: WgpuSettings { ... }.into(), } ``` --------- Co-authored-by: Malek <pocmalek@gmail.com> Co-authored-by: Robert Swain <robert.swain@gmail.com> |
||
|
|
5c884c5a15
|
Automatic batching/instancing of draw commands (#9685)
# Objective - Implement the foundations of automatic batching/instancing of draw commands as the next step from #89 - NOTE: More performance improvements will come when more data is managed and bound in ways that do not require rebinding such as mesh, material, and texture data. ## Solution - The core idea for batching of draw commands is to check whether any of the information that has to be passed when encoding a draw command changes between two things that are being drawn according to the sorted render phase order. These should be things like the pipeline, bind groups and their dynamic offsets, index/vertex buffers, and so on. - The following assumptions have been made: - Only entities with prepared assets (pipelines, materials, meshes) are queued to phases - View bindings are constant across a phase for a given draw function as phases are per-view - `batch_and_prepare_render_phase` is the only system that performs this batching and has sole responsibility for preparing the per-object data. As such the mesh binding and dynamic offsets are assumed to only vary as a result of the `batch_and_prepare_render_phase` system, e.g. due to having to split data across separate uniform bindings within the same buffer due to the maximum uniform buffer binding size. - Implement `GpuArrayBuffer` for `Mesh2dUniform` to store Mesh2dUniform in arrays in GPU buffers rather than each one being at a dynamic offset in a uniform buffer. This is the same optimisation that was made for 3D not long ago. - Change batch size for a range in `PhaseItem`, adding API for getting or mutating the range. This is more flexible than a size as the length of the range can be used in place of the size, but the start and end can be otherwise whatever is needed. - Add an optional mesh bind group dynamic offset to `PhaseItem`. This avoids having to do a massive table move just to insert `GpuArrayBufferIndex` components. ## Benchmarks All tests have been run on an M1 Max on AC power. `bevymark` and `many_cubes` were modified to use 1920x1080 with a scale factor of 1. I run a script that runs a separate Tracy capture process, and then runs the bevy example with `--features bevy_ci_testing,trace_tracy` and `CI_TESTING_CONFIG=../benchmark.ron` with the contents of `../benchmark.ron`: ```rust ( exit_after: Some(1500) ) ``` ...in order to run each test for 1500 frames. The recent changes to `many_cubes` and `bevymark` added reproducible random number generation so that with the same settings, the same rng will occur. They also added benchmark modes that use a fixed delta time for animations. Combined this means that the same frames should be rendered both on main and on the branch. The graphs compare main (yellow) to this PR (red). ### 3D Mesh `many_cubes --benchmark` <img width="1411" alt="Screenshot 2023-09-03 at 23 42 10" src="https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/assets/302146/2088716a-c918-486c-8129-090b26fd2bc4"> The mesh and material are the same for all instances. This is basically the best case for the initial batching implementation as it results in 1 draw for the ~11.7k visible meshes. It gives a ~30% reduction in median frame time. The 1000th frame is identical using the flip tool:  ``` Mean: 0.000000 Weighted median: 0.000000 1st weighted quartile: 0.000000 3rd weighted quartile: 0.000000 Min: 0.000000 Max: 0.000000 Evaluation time: 0.4615 seconds ``` ### 3D Mesh `many_cubes --benchmark --material-texture-count 10` <img width="1404" alt="Screenshot 2023-09-03 at 23 45 18" src="https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/assets/302146/5ee9c447-5bd2-45c6-9706-ac5ff8916daf"> This run uses 10 different materials by varying their textures. The materials are randomly selected, and there is no sorting by material bind group for opaque 3D so any batching is 'random'. The PR produces a ~5% reduction in median frame time. If we were to sort the opaque phase by the material bind group, then this should be a lot faster. This produces about 10.5k draws for the 11.7k visible entities. This makes sense as randomly selecting from 10 materials gives a chance that two adjacent entities randomly select the same material and can be batched. The 1000th frame is identical in flip:  ``` Mean: 0.000000 Weighted median: 0.000000 1st weighted quartile: 0.000000 3rd weighted quartile: 0.000000 Min: 0.000000 Max: 0.000000 Evaluation time: 0.4537 seconds ``` ### 3D Mesh `many_cubes --benchmark --vary-per-instance` <img width="1394" alt="Screenshot 2023-09-03 at 23 48 44" src="https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/assets/302146/f02a816b-a444-4c18-a96a-63b5436f3b7f"> This run varies the material data per instance by randomly-generating its colour. This is the worst case for batching and that it performs about the same as `main` is a good thing as it demonstrates that the batching has minimal overhead when dealing with ~11k visible mesh entities. The 1000th frame is identical according to flip:  ``` Mean: 0.000000 Weighted median: 0.000000 1st weighted quartile: 0.000000 3rd weighted quartile: 0.000000 Min: 0.000000 Max: 0.000000 Evaluation time: 0.4568 seconds ``` ### 2D Mesh `bevymark --benchmark --waves 160 --per-wave 1000 --mode mesh2d` <img width="1412" alt="Screenshot 2023-09-03 at 23 59 56" src="https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/assets/302146/cb02ae07-237b-4646-ae9f-fda4dafcbad4"> This spawns 160 waves of 1000 quad meshes that are shaded with ColorMaterial. Each wave has a different material so 160 waves currently should result in 160 batches. This results in a 50% reduction in median frame time. Capturing a screenshot of the 1000th frame main vs PR gives:  ``` Mean: 0.001222 Weighted median: 0.750432 1st weighted quartile: 0.453494 3rd weighted quartile: 0.969758 Min: 0.000000 Max: 0.990296 Evaluation time: 0.4255 seconds ``` So they seem to produce the same results. I also double-checked the number of draws. `main` does 160000 draws, and the PR does 160, as expected. ### 2D Mesh `bevymark --benchmark --waves 160 --per-wave 1000 --mode mesh2d --material-texture-count 10` <img width="1392" alt="Screenshot 2023-09-04 at 00 09 22" src="https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/assets/302146/4358da2e-ce32-4134-82df-3ab74c40849c"> This generates 10 textures and generates materials for each of those and then selects one material per wave. The median frame time is reduced by 50%. Similar to the plain run above, this produces 160 draws on the PR and 160000 on `main` and the 1000th frame is identical (ignoring the fps counter text overlay).  ``` Mean: 0.002877 Weighted median: 0.964980 1st weighted quartile: 0.668871 3rd weighted quartile: 0.982749 Min: 0.000000 Max: 0.992377 Evaluation time: 0.4301 seconds ``` ### 2D Mesh `bevymark --benchmark --waves 160 --per-wave 1000 --mode mesh2d --vary-per-instance` <img width="1396" alt="Screenshot 2023-09-04 at 00 13 53" src="https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/assets/302146/b2198b18-3439-47ad-919a-cdabe190facb"> This creates unique materials per instance by randomly-generating the material's colour. This is the worst case for 2D batching. Somehow, this PR manages a 7% reduction in median frame time. Both main and this PR issue 160000 draws. The 1000th frame is the same:  ``` Mean: 0.001214 Weighted median: 0.937499 1st weighted quartile: 0.635467 3rd weighted quartile: 0.979085 Min: 0.000000 Max: 0.988971 Evaluation time: 0.4462 seconds ``` ### 2D Sprite `bevymark --benchmark --waves 160 --per-wave 1000 --mode sprite` <img width="1396" alt="Screenshot 2023-09-04 at 12 21 12" src="https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/assets/302146/8b31e915-d6be-4cac-abf5-c6a4da9c3d43"> This just spawns 160 waves of 1000 sprites. There should be and is no notable difference between main and the PR. ### 2D Sprite `bevymark --benchmark --waves 160 --per-wave 1000 --mode sprite --material-texture-count 10` <img width="1389" alt="Screenshot 2023-09-04 at 12 36 08" src="https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/assets/302146/45fe8d6d-c901-4062-a349-3693dd044413"> This spawns the sprites selecting a texture at random per instance from the 10 generated textures. This has no significant change vs main and shouldn't. ### 2D Sprite `bevymark --benchmark --waves 160 --per-wave 1000 --mode sprite --vary-per-instance` <img width="1401" alt="Screenshot 2023-09-04 at 12 29 52" src="https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/assets/302146/762c5c60-352e-471f-8dbe-bbf10e24ebd6"> This sets the sprite colour as being unique per instance. This can still all be drawn using one batch. There should be no difference but the PR produces median frame times that are 4% higher. Investigation showed no clear sources of cost, rather a mix of give and take that should not happen. It seems like noise in the results. ### Summary | Benchmark | % change in median frame time | | ------------- | ------------- | | many_cubes | 🟩 -30% | | many_cubes 10 materials | 🟩 -5% | | many_cubes unique materials | 🟩 ~0% | | bevymark mesh2d | 🟩 -50% | | bevymark mesh2d 10 materials | 🟩 -50% | | bevymark mesh2d unique materials | 🟩 -7% | | bevymark sprite | 🟥 2% | | bevymark sprite 10 materials | 🟥 0.6% | | bevymark sprite unique materials | 🟥 4.1% | --- ## Changelog - Added: 2D and 3D mesh entities that share the same mesh and material (same textures, same data) are now batched into the same draw command for better performance. --------- Co-authored-by: robtfm <50659922+robtfm@users.noreply.github.com> Co-authored-by: Nicola Papale <nico@nicopap.ch> |
||
|
|
401b2e77f3
|
renderer init: create a detached task only on wasm, block otherwise (#9830)
# Objective - When initializing the renderer, Bevy currently create a detached task - This is needed on wasm but not on native ## Solution - Don't create a detached task on native but block on the future |
||
|
|
5eb292dc10
|
Bevy Asset V2 (#8624)
# Bevy Asset V2 Proposal ## Why Does Bevy Need A New Asset System? Asset pipelines are a central part of the gamedev process. Bevy's current asset system is missing a number of features that make it non-viable for many classes of gamedev. After plenty of discussions and [a long community feedback period](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/discussions/3972), we've identified a number missing features: * **Asset Preprocessing**: it should be possible to "preprocess" / "compile" / "crunch" assets at "development time" rather than when the game starts up. This enables offloading expensive work from deployed apps, faster asset loading, less runtime memory usage, etc. * **Per-Asset Loader Settings**: Individual assets cannot define their own loaders that override the defaults. Additionally, they cannot provide per-asset settings to their loaders. This is a huge limitation, as many asset types don't provide all information necessary for Bevy _inside_ the asset. For example, a raw PNG image says nothing about how it should be sampled (ex: linear vs nearest). * **Asset `.meta` files**: assets should have configuration files stored adjacent to the asset in question, which allows the user to configure asset-type-specific settings. These settings should be accessible during the pre-processing phase. Modifying a `.meta` file should trigger a re-processing / re-load of the asset. It should be possible to configure asset loaders from the meta file. * **Processed Asset Hot Reloading**: Changes to processed assets (or their dependencies) should result in re-processing them and re-loading the results in live Bevy Apps. * **Asset Dependency Tracking**: The current bevy_asset has no good way to wait for asset dependencies to load. It punts this as an exercise for consumers of the loader apis, which is unreasonable and error prone. There should be easy, ergonomic ways to wait for assets to load and block some logic on an asset's entire dependency tree loading. * **Runtime Asset Loading**: it should be (optionally) possible to load arbitrary assets dynamically at runtime. This necessitates being able to deploy and run the asset server alongside Bevy Apps on _all platforms_. For example, we should be able to invoke the shader compiler at runtime, stream scenes from sources like the internet, etc. To keep deployed binaries (and startup times) small, the runtime asset server configuration should be configurable with different settings compared to the "pre processor asset server". * **Multiple Backends**: It should be possible to load assets from arbitrary sources (filesystems, the internet, remote asset serves, etc). * **Asset Packing**: It should be possible to deploy assets in compressed "packs", which makes it easier and more efficient to distribute assets with Bevy Apps. * **Asset Handoff**: It should be possible to hold a "live" asset handle, which correlates to runtime data, without actually holding the asset in memory. Ex: it must be possible to hold a reference to a GPU mesh generated from a "mesh asset" without keeping the mesh data in CPU memory * **Per-Platform Processed Assets**: Different platforms and app distributions have different capabilities and requirements. Some platforms need lower asset resolutions or different asset formats to operate within the hardware constraints of the platform. It should be possible to define per-platform asset processing profiles. And it should be possible to deploy only the assets required for a given platform. These features have architectural implications that are significant enough to require a full rewrite. The current Bevy Asset implementation got us this far, but it can take us no farther. This PR defines a brand new asset system that implements most of these features, while laying the foundations for the remaining features to be built. ## Bevy Asset V2 Here is a quick overview of the features introduced in this PR. * **Asset Preprocessing**: Preprocess assets at development time into more efficient (and configurable) representations * **Dependency Aware**: Dependencies required to process an asset are tracked. If an asset's processed dependency changes, it will be reprocessed * **Hot Reprocessing/Reloading**: detect changes to asset source files, reprocess them if they have changed, and then hot-reload them in Bevy Apps. * **Only Process Changes**: Assets are only re-processed when their source file (or meta file) has changed. This uses hashing and timestamps to avoid processing assets that haven't changed. * **Transactional and Reliable**: Uses write-ahead logging (a technique commonly used by databases) to recover from crashes / forced-exits. Whenever possible it avoids full-reprocessing / only uncompleted transactions will be reprocessed. When the processor is running in parallel with a Bevy App, processor asset writes block Bevy App asset reads. Reading metadata + asset bytes is guaranteed to be transactional / correctly paired. * **Portable / Run anywhere / Database-free**: The processor does not rely on an in-memory database (although it uses some database techniques for reliability). This is important because pretty much all in-memory databases have unsupported platforms or build complications. * **Configure Processor Defaults Per File Type**: You can say "use this processor for all files of this type". * **Custom Processors**: The `Processor` trait is flexible and unopinionated. It can be implemented by downstream plugins. * **LoadAndSave Processors**: Most asset processing scenarios can be expressed as "run AssetLoader A, save the results using AssetSaver X, and then load the result using AssetLoader B". For example, load this png image using `PngImageLoader`, which produces an `Image` asset and then save it using `CompressedImageSaver` (which also produces an `Image` asset, but in a compressed format), which takes an `Image` asset as input. This means if you have an `AssetLoader` for an asset, you are already half way there! It also means that you can share AssetSavers across multiple loaders. Because `CompressedImageSaver` accepts Bevy's generic Image asset as input, it means you can also use it with some future `JpegImageLoader`. * **Loader and Saver Settings**: Asset Loaders and Savers can now define their own settings types, which are passed in as input when an asset is loaded / saved. Each asset can define its own settings. * **Asset `.meta` files**: configure asset loaders, their settings, enable/disable processing, and configure processor settings * **Runtime Asset Dependency Tracking** Runtime asset dependencies (ex: if an asset contains a `Handle<Image>`) are tracked by the asset server. An event is emitted when an asset and all of its dependencies have been loaded * **Unprocessed Asset Loading**: Assets do not require preprocessing. They can be loaded directly. A processed asset is just a "normal" asset with some extra metadata. Asset Loaders don't need to know or care about whether or not an asset was processed. * **Async Asset IO**: Asset readers/writers use async non-blocking interfaces. Note that because Rust doesn't yet support async traits, there is a bit of manual Boxing / Future boilerplate. This will hopefully be removed in the near future when Rust gets async traits. * **Pluggable Asset Readers and Writers**: Arbitrary asset source readers/writers are supported, both by the processor and the asset server. * **Better Asset Handles** * **Single Arc Tree**: Asset Handles now use a single arc tree that represents the lifetime of the asset. This makes their implementation simpler, more efficient, and allows us to cheaply attach metadata to handles. Ex: the AssetPath of a handle is now directly accessible on the handle itself! * **Const Typed Handles**: typed handles can be constructed in a const context. No more weird "const untyped converted to typed at runtime" patterns! * **Handles and Ids are Smaller / Faster To Hash / Compare**: Typed `Handle<T>` is now much smaller in memory and `AssetId<T>` is even smaller. * **Weak Handle Usage Reduction**: In general Handles are now considered to be "strong". Bevy features that previously used "weak `Handle<T>`" have been ported to `AssetId<T>`, which makes it statically clear that the features do not hold strong handles (while retaining strong type information). Currently Handle::Weak still exists, but it is very possible that we can remove that entirely. * **Efficient / Dense Asset Ids**: Assets now have efficient dense runtime asset ids, which means we can avoid expensive hash lookups. Assets are stored in Vecs instead of HashMaps. There are now typed and untyped ids, which means we no longer need to store dynamic type information in the ID for typed handles. "AssetPathId" (which was a nightmare from a performance and correctness standpoint) has been entirely removed in favor of dense ids (which are retrieved for a path on load) * **Direct Asset Loading, with Dependency Tracking**: Assets that are defined at runtime can still have their dependencies tracked by the Asset Server (ex: if you create a material at runtime, you can still wait for its textures to load). This is accomplished via the (currently optional) "asset dependency visitor" trait. This system can also be used to define a set of assets to load, then wait for those assets to load. * **Async folder loading**: Folder loading also uses this system and immediately returns a handle to the LoadedFolder asset, which means folder loading no longer blocks on directory traversals. * **Improved Loader Interface**: Loaders now have a specific "top level asset type", which makes returning the top-level asset simpler and statically typed. * **Basic Image Settings and Processing**: Image assets can now be processed into the gpu-friendly Basic Universal format. The ImageLoader now has a setting to define what format the image should be loaded as. Note that this is just a minimal MVP ... plenty of additional work to do here. To demo this, enable the `basis-universal` feature and turn on asset processing. * **Simpler Audio Play / AudioSink API**: Asset handle providers are cloneable, which means the Audio resource can mint its own handles. This means you can now do `let sink_handle = audio.play(music)` instead of `let sink_handle = audio_sinks.get_handle(audio.play(music))`. Note that this might still be replaced by https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/8424. **Removed Handle Casting From Engine Features**: Ex: FontAtlases no longer use casting between handle types ## Using The New Asset System ### Normal Unprocessed Asset Loading By default the `AssetPlugin` does not use processing. It behaves pretty much the same way as the old system. If you are defining a custom asset, first derive `Asset`: ```rust #[derive(Asset)] struct Thing { value: String, } ``` Initialize the asset: ```rust app.init_asset:<Thing>() ``` Implement a new `AssetLoader` for it: ```rust #[derive(Default)] struct ThingLoader; #[derive(Serialize, Deserialize, Default)] pub struct ThingSettings { some_setting: bool, } impl AssetLoader for ThingLoader { type Asset = Thing; type Settings = ThingSettings; fn load<'a>( &'a self, reader: &'a mut Reader, settings: &'a ThingSettings, load_context: &'a mut LoadContext, ) -> BoxedFuture<'a, Result<Thing, anyhow::Error>> { Box::pin(async move { let mut bytes = Vec::new(); reader.read_to_end(&mut bytes).await?; // convert bytes to value somehow Ok(Thing { value }) }) } fn extensions(&self) -> &[&str] { &["thing"] } } ``` Note that this interface will get much cleaner once Rust gets support for async traits. `Reader` is an async futures_io::AsyncRead. You can stream bytes as they come in or read them all into a `Vec<u8>`, depending on the context. You can use `let handle = load_context.load(path)` to kick off a dependency load, retrieve a handle, and register the dependency for the asset. Then just register the loader in your Bevy app: ```rust app.init_asset_loader::<ThingLoader>() ``` Now just add your `Thing` asset files into the `assets` folder and load them like this: ```rust fn system(asset_server: Res<AssetServer>) { let handle = Handle<Thing> = asset_server.load("cool.thing"); } ``` You can check load states directly via the asset server: ```rust if asset_server.load_state(&handle) == LoadState::Loaded { } ``` You can also listen for events: ```rust fn system(mut events: EventReader<AssetEvent<Thing>>, handle: Res<SomeThingHandle>) { for event in events.iter() { if event.is_loaded_with_dependencies(&handle) { } } } ``` Note the new `AssetEvent::LoadedWithDependencies`, which only fires when the asset is loaded _and_ all dependencies (and their dependencies) have loaded. Unlike the old asset system, for a given asset path all `Handle<T>` values point to the same underlying Arc. This means Handles can cheaply hold more asset information, such as the AssetPath: ```rust // prints the AssetPath of the handle info!("{:?}", handle.path()) ``` ### Processed Assets Asset processing can be enabled via the `AssetPlugin`. When developing Bevy Apps with processed assets, do this: ```rust app.add_plugins(DefaultPlugins.set(AssetPlugin::processed_dev())) ``` This runs the `AssetProcessor` in the background with hot-reloading. It reads assets from the `assets` folder, processes them, and writes them to the `.imported_assets` folder. Asset loads in the Bevy App will wait for a processed version of the asset to become available. If an asset in the `assets` folder changes, it will be reprocessed and hot-reloaded in the Bevy App. When deploying processed Bevy apps, do this: ```rust app.add_plugins(DefaultPlugins.set(AssetPlugin::processed())) ``` This does not run the `AssetProcessor` in the background. It behaves like `AssetPlugin::unprocessed()`, but reads assets from `.imported_assets`. When the `AssetProcessor` is running, it will populate sibling `.meta` files for assets in the `assets` folder. Meta files for assets that do not have a processor configured look like this: ```rust ( meta_format_version: "1.0", asset: Load( loader: "bevy_render::texture::image_loader::ImageLoader", settings: ( format: FromExtension, ), ), ) ``` This is metadata for an image asset. For example, if you have `assets/my_sprite.png`, this could be the metadata stored at `assets/my_sprite.png.meta`. Meta files are totally optional. If no metadata exists, the default settings will be used. In short, this file says "load this asset with the ImageLoader and use the file extension to determine the image type". This type of meta file is supported in all AssetPlugin modes. If in `Unprocessed` mode, the asset (with the meta settings) will be loaded directly. If in `ProcessedDev` mode, the asset file will be copied directly to the `.imported_assets` folder. The meta will also be copied directly to the `.imported_assets` folder, but with one addition: ```rust ( meta_format_version: "1.0", processed_info: Some(( hash: 12415480888597742505, full_hash: 14344495437905856884, process_dependencies: [], )), asset: Load( loader: "bevy_render::texture::image_loader::ImageLoader", settings: ( format: FromExtension, ), ), ) ``` `processed_info` contains `hash` (a direct hash of the asset and meta bytes), `full_hash` (a hash of `hash` and the hashes of all `process_dependencies`), and `process_dependencies` (the `path` and `full_hash` of every process_dependency). A "process dependency" is an asset dependency that is _directly_ used when processing the asset. Images do not have process dependencies, so this is empty. When the processor is enabled, you can use the `Process` metadata config: ```rust ( meta_format_version: "1.0", asset: Process( processor: "bevy_asset::processor::process::LoadAndSave<bevy_render::texture::image_loader::ImageLoader, bevy_render::texture::compressed_image_saver::CompressedImageSaver>", settings: ( loader_settings: ( format: FromExtension, ), saver_settings: ( generate_mipmaps: true, ), ), ), ) ``` This configures the asset to use the `LoadAndSave` processor, which runs an AssetLoader and feeds the result into an AssetSaver (which saves the given Asset and defines a loader to load it with). (for terseness LoadAndSave will likely get a shorter/friendlier type name when [Stable Type Paths](#7184) lands). `LoadAndSave` is likely to be the most common processor type, but arbitrary processors are supported. `CompressedImageSaver` saves an `Image` in the Basis Universal format and configures the ImageLoader to load it as basis universal. The `AssetProcessor` will read this meta, run it through the LoadAndSave processor, and write the basis-universal version of the image to `.imported_assets`. The final metadata will look like this: ```rust ( meta_format_version: "1.0", processed_info: Some(( hash: 905599590923828066, full_hash: 9948823010183819117, process_dependencies: [], )), asset: Load( loader: "bevy_render::texture::image_loader::ImageLoader", settings: ( format: Format(Basis), ), ), ) ``` To try basis-universal processing out in Bevy examples, (for example `sprite.rs`), change `add_plugins(DefaultPlugins)` to `add_plugins(DefaultPlugins.set(AssetPlugin::processed_dev()))` and run with the `basis-universal` feature enabled: `cargo run --features=basis-universal --example sprite`. To create a custom processor, there are two main paths: 1. Use the `LoadAndSave` processor with an existing `AssetLoader`. Implement the `AssetSaver` trait, register the processor using `asset_processor.register_processor::<LoadAndSave<ImageLoader, CompressedImageSaver>>(image_saver.into())`. 2. Implement the `Process` trait directly and register it using: `asset_processor.register_processor(thing_processor)`. You can configure default processors for file extensions like this: ```rust asset_processor.set_default_processor::<ThingProcessor>("thing") ``` There is one more metadata type to be aware of: ```rust ( meta_format_version: "1.0", asset: Ignore, ) ``` This will ignore the asset during processing / prevent it from being written to `.imported_assets`. The AssetProcessor stores a transaction log at `.imported_assets/log` and uses it to gracefully recover from unexpected stops. This means you can force-quit the processor (and Bevy Apps running the processor in parallel) at arbitrary times! `.imported_assets` is "local state". It should _not_ be checked into source control. It should also be considered "read only". In practice, you _can_ modify processed assets and processed metadata if you really need to test something. But those modifications will not be represented in the hashes of the assets, so the processed state will be "out of sync" with the source assets. The processor _will not_ fix this for you. Either revert the change after you have tested it, or delete the processed files so they can be re-populated. ## Open Questions There are a number of open questions to be discussed. We should decide if they need to be addressed in this PR and if so, how we will address them: ### Implied Dependencies vs Dependency Enumeration There are currently two ways to populate asset dependencies: * **Implied via AssetLoaders**: if an AssetLoader loads an asset (and retrieves a handle), a dependency is added to the list. * **Explicit via the optional Asset::visit_dependencies**: if `server.load_asset(my_asset)` is called, it will call `my_asset.visit_dependencies`, which will grab dependencies that have been manually defined for the asset via the Asset trait impl (which can be derived). This means that defining explicit dependencies is optional for "loaded assets". And the list of dependencies is always accurate because loaders can only produce Handles if they register dependencies. If an asset was loaded with an AssetLoader, it only uses the implied dependencies. If an asset was created at runtime and added with `asset_server.load_asset(MyAsset)`, it will use `Asset::visit_dependencies`. However this can create a behavior mismatch between loaded assets and equivalent "created at runtime" assets if `Assets::visit_dependencies` doesn't exactly match the dependencies produced by the AssetLoader. This behavior mismatch can be resolved by completely removing "implied loader dependencies" and requiring `Asset::visit_dependencies` to supply dependency data. But this creates two problems: * It makes defining loaded assets harder and more error prone: Devs must remember to manually annotate asset dependencies with `#[dependency]` when deriving `Asset`. For more complicated assets (such as scenes), the derive likely wouldn't be sufficient and a manual `visit_dependencies` impl would be required. * Removes the ability to immediately kick off dependency loads: When AssetLoaders retrieve a Handle, they also immediately kick off an asset load for the handle, which means it can start loading in parallel _before_ the asset finishes loading. For large assets, this could be significant. (although this could be mitigated for processed assets if we store dependencies in the processed meta file and load them ahead of time) ### Eager ProcessorDev Asset Loading I made a controversial call in the interest of fast startup times ("time to first pixel") for the "processor dev mode configuration". When initializing the AssetProcessor, current processed versions of unchanged assets are yielded immediately, even if their dependencies haven't been checked yet for reprocessing. This means that non-current-state-of-filesystem-but-previously-valid assets might be returned to the App first, then hot-reloaded if/when their dependencies change and the asset is reprocessed. Is this behavior desirable? There is largely one alternative: do not yield an asset from the processor to the app until all of its dependencies have been checked for changes. In some common cases (load dependency has not changed since last run) this will increase startup time. The main question is "by how much" and is that slower startup time worth it in the interest of only yielding assets that are true to the current state of the filesystem. Should this be configurable? I'm starting to think we should only yield an asset after its (historical) dependencies have been checked for changes + processed as necessary, but I'm curious what you all think. ### Paths Are Currently The Only Canonical ID / Do We Want Asset UUIDs? In this implementation AssetPaths are the only canonical asset identifier (just like the previous Bevy Asset system and Godot). Moving assets will result in re-scans (and currently reprocessing, although reprocessing can easily be avoided with some changes). Asset renames/moves will break code and assets that rely on specific paths, unless those paths are fixed up. Do we want / need "stable asset uuids"? Introducing them is very possible: 1. Generate a UUID and include it in .meta files 2. Support UUID in AssetPath 3. Generate "asset indices" which are loaded on startup and map UUIDs to paths. 4 (maybe). Consider only supporting UUIDs for processed assets so we can generate quick-to-load indices instead of scanning meta files. The main "pro" is that assets referencing UUIDs don't need to be migrated when a path changes. The main "con" is that UUIDs cannot be "lazily resolved" like paths. They need a full view of all assets to answer the question "does this UUID exist". Which means UUIDs require the AssetProcessor to fully finish startup scans before saying an asset doesnt exist. And they essentially require asset pre-processing to use in apps, because scanning all asset metadata files at runtime to resolve a UUID is not viable for medium-to-large apps. It really requires a pre-generated UUID index, which must be loaded before querying for assets. I personally think this should be investigated in a separate PR. Paths aren't going anywhere ... _everyone_ uses filesystems (and filesystem-like apis) to manage their asset source files. I consider them permanent canonical asset information. Additionally, they behave well for both processed and unprocessed asset modes. Given that Bevy is supporting both, this feels like the right canonical ID to start with. UUIDS (and maybe even other indexed-identifier types) can be added later as necessary. ### Folder / File Naming Conventions All asset processing config currently lives in the `.imported_assets` folder. The processor transaction log is in `.imported_assets/log`. Processed assets are added to `.imported_assets/Default`, which will make migrating to processed asset profiles (ex: a `.imported_assets/Mobile` profile) a non-breaking change. It also allows us to create top-level files like `.imported_assets/log` without it being interpreted as an asset. Meta files currently have a `.meta` suffix. Do we like these names and conventions? ### Should the `AssetPlugin::processed_dev` configuration enable `watch_for_changes` automatically? Currently it does (which I think makes sense), but it does make it the only configuration that enables watch_for_changes by default. ### Discuss on_loaded High Level Interface: This PR includes a very rough "proof of concept" `on_loaded` system adapter that uses the `LoadedWithDependencies` event in combination with `asset_server.load_asset` dependency tracking to support this pattern ```rust fn main() { App::new() .init_asset::<MyAssets>() .add_systems(Update, on_loaded(create_array_texture)) .run(); } #[derive(Asset, Clone)] struct MyAssets { #[dependency] picture_of_my_cat: Handle<Image>, #[dependency] picture_of_my_other_cat: Handle<Image>, } impl FromWorld for ArrayTexture { fn from_world(world: &mut World) -> Self { picture_of_my_cat: server.load("meow.png"), picture_of_my_other_cat: server.load("meeeeeeeow.png"), } } fn spawn_cat(In(my_assets): In<MyAssets>, mut commands: Commands) { commands.spawn(SpriteBundle { texture: my_assets.picture_of_my_cat.clone(), ..default() }); commands.spawn(SpriteBundle { texture: my_assets.picture_of_my_other_cat.clone(), ..default() }); } ``` The implementation is _very_ rough. And it is currently unsafe because `bevy_ecs` doesn't expose some internals to do this safely from inside `bevy_asset`. There are plenty of unanswered questions like: * "do we add a Loadable" derive? (effectively automate the FromWorld implementation above) * Should `MyAssets` even be an Asset? (largely implemented this way because it elegantly builds on `server.load_asset(MyAsset { .. })` dependency tracking). We should think hard about what our ideal API looks like (and if this is a pattern we want to support). Not necessarily something we need to solve in this PR. The current `on_loaded` impl should probably be removed from this PR before merging. ## Clarifying Questions ### What about Assets as Entities? This Bevy Asset V2 proposal implementation initially stored Assets as ECS Entities. Instead of `AssetId<T>` + the `Assets<T>` resource it used `Entity` as the asset id and Asset values were just ECS components. There are plenty of compelling reasons to do this: 1. Easier to inline assets in Bevy Scenes (as they are "just" normal entities + components) 2. More flexible queries: use the power of the ECS to filter assets (ex: `Query<Mesh, With<Tree>>`). 3. Extensible. Users can add arbitrary component data to assets. 4. Things like "component visualization tools" work out of the box to visualize asset data. However Assets as Entities has a ton of caveats right now: * We need to be able to allocate entity ids without a direct World reference (aka rework id allocator in Entities ... i worked around this in my prototypes by just pre allocating big chunks of entities) * We want asset change events in addition to ECS change tracking ... how do we populate them when mutations can come from anywhere? Do we use Changed queries? This would require iterating over the change data for all assets every frame. Is this acceptable or should we implement a new "event based" component change detection option? * Reconciling manually created assets with asset-system managed assets has some nuance (ex: are they "loaded" / do they also have that component metadata?) * "how do we handle "static" / default entity handles" (ties in to the Entity Indices discussion: https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/discussions/8319). This is necessary for things like "built in" assets and default handles in things like SpriteBundle. * Storing asset information as a component makes it easy to "invalidate" asset state by removing the component (or forcing modifications). Ideally we have ways to lock this down (some combination of Rust type privacy and ECS validation) In practice, how we store and identify assets is a reasonably superficial change (porting off of Assets as Entities and implementing dedicated storage + ids took less than a day). So once we sort out the remaining challenges the flip should be straightforward. Additionally, I do still have "Assets as Entities" in my commit history, so we can reuse that work. I personally think "assets as entities" is a good endgame, but it also doesn't provide _significant_ value at the moment and it certainly isn't ready yet with the current state of things. ### Why not Distill? [Distill](https://github.com/amethyst/distill) is a high quality fully featured asset system built in Rust. It is very natural to ask "why not just use Distill?". It is also worth calling out that for awhile, [we planned on adopting Distill / I signed off on it](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/708). However I think Bevy has a number of constraints that make Distill adoption suboptimal: * **Architectural Simplicity:** * Distill's processor requires an in-memory database (lmdb) and RPC networked API (using Cap'n Proto). Each of these introduces API complexity that increases maintenance burden and "code grokability". Ignoring tests, documentation, and examples, Distill has 24,237 lines of Rust code (including generated code for RPC + database interactions). If you ignore generated code, it has 11,499 lines. * Bevy builds the AssetProcessor and AssetServer using pluggable AssetReader/AssetWriter Rust traits with simple io interfaces. They do not necessitate databases or RPC interfaces (although Readers/Writers could use them if that is desired). Bevy Asset V2 (at the time of writing this PR) is 5,384 lines of Rust code (ignoring tests, documentation, and examples). Grain of salt: Distill does have more features currently (ex: Asset Packing, GUIDS, remote-out-of-process asset processor). I do plan to implement these features in Bevy Asset V2 and I personally highly doubt they will meaningfully close the 6115 lines-of-code gap. * This complexity gap (which while illustrated by lines of code, is much bigger than just that) is noteworthy to me. Bevy should be hackable and there are pillars of Distill that are very hard to understand and extend. This is a matter of opinion (and Bevy Asset V2 also has complicated areas), but I think Bevy Asset V2 is much more approachable for the average developer. * Necessary disclaimer: counting lines of code is an extremely rough complexity metric. Read the code and form your own opinions. * **Optional Asset Processing:** Not all Bevy Apps (or Bevy App developers) need / want asset preprocessing. Processing increases the complexity of the development environment by introducing things like meta files, imported asset storage, running processors in the background, waiting for processing to finish, etc. Distill _requires_ preprocessing to work. With Bevy Asset V2 processing is fully opt-in. The AssetServer isn't directly aware of asset processors at all. AssetLoaders only care about converting bytes to runtime Assets ... they don't know or care if the bytes were pre-processed or not. Processing is "elegantly" (forgive my self-congratulatory phrasing) layered on top and builds on the existing Asset system primitives. * **Direct Filesystem Access to Processed Asset State:** Distill stores processed assets in a database. This makes debugging / inspecting the processed outputs harder (either requires special tooling to query the database or they need to be "deployed" to be inspected). Bevy Asset V2, on the other hand, stores processed assets in the filesystem (by default ... this is configurable). This makes interacting with the processed state more natural. Note that both Godot and Unity's new asset system store processed assets in the filesystem. * **Portability**: Because Distill's processor uses lmdb and RPC networking, it cannot be run on certain platforms (ex: lmdb is a non-rust dependency that cannot run on the web, some platforms don't support running network servers). Bevy should be able to process assets everywhere (ex: run the Bevy Editor on the web, compile + process shaders on mobile, etc). Distill does partially mitigate this problem by supporting "streaming" assets via the RPC protocol, but this is not a full solve from my perspective. And Bevy Asset V2 can (in theory) also stream assets (without requiring RPC, although this isn't implemented yet) Note that I _do_ still think Distill would be a solid asset system for Bevy. But I think the approach in this PR is a better solve for Bevy's specific "asset system requirements". ### Doesn't async-fs just shim requests to "sync" `std::fs`? What is the point? "True async file io" has limited / spotty platform support. async-fs (and the rust async ecosystem generally ... ex Tokio) currently use async wrappers over std::fs that offload blocking requests to separate threads. This may feel unsatisfying, but it _does_ still provide value because it prevents our task pools from blocking on file system operations (which would prevent progress when there are many tasks to do, but all threads in a pool are currently blocking on file system ops). Additionally, using async APIs for our AssetReaders and AssetWriters also provides value because we can later add support for "true async file io" for platforms that support it. _And_ we can implement other "true async io" asset backends (such as networked asset io). ## Draft TODO - [x] Fill in missing filesystem event APIs: file removed event (which is expressed as dangling RenameFrom events in some cases), file/folder renamed event - [x] Assets without loaders are not moved to the processed folder. This breaks things like referenced `.bin` files for GLTFs. This should be configurable per-non-asset-type. - [x] Initial implementation of Reflect and FromReflect for Handle. The "deserialization" parity bar is low here as this only worked with static UUIDs in the old impl ... this is a non-trivial problem. Either we add a Handle::AssetPath variant that gets "upgraded" to a strong handle on scene load or we use a separate AssetRef type for Bevy scenes (which is converted to a runtime Handle on load). This deserves its own discussion in a different pr. - [x] Populate read_asset_bytes hash when run by the processor (a bit of a special case .. when run by the processor the processed meta will contain the hash so we don't need to compute it on the spot, but we don't want/need to read the meta when run by the main AssetServer) - [x] Delay hot reloading: currently filesystem events are handled immediately, which creates timing issues in some cases. For example hot reloading images can sometimes break because the image isn't finished writing. We should add a delay, likely similar to the [implementation in this PR](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/8503). - [x] Port old platform-specific AssetIo implementations to the new AssetReader interface (currently missing Android and web) - [x] Resolve on_loaded unsafety (either by removing the API entirely or removing the unsafe) - [x] Runtime loader setting overrides - [x] Remove remaining unwraps that should be error-handled. There are number of TODOs here - [x] Pretty AssetPath Display impl - [x] Document more APIs - [x] Resolve spurious "reloading because it has changed" events (to repro run load_gltf with `processed_dev()`) - [x] load_dependency hot reloading currently only works for processed assets. If processing is disabled, load_dependency changes are not hot reloaded. - [x] Replace AssetInfo dependency load/fail counters with `loading_dependencies: HashSet<UntypedAssetId>` to prevent reloads from (potentially) breaking counters. Storing this will also enable "dependency reloaded" events (see [Next Steps](#next-steps)) - [x] Re-add filesystem watcher cargo feature gate (currently it is not optional) - [ ] Migration Guide - [ ] Changelog ## Followup TODO - [ ] Replace "eager unchanged processed asset loading" behavior with "don't returned unchanged processed asset until dependencies have been checked". - [ ] Add true `Ignore` AssetAction that does not copy the asset to the imported_assets folder. - [ ] Finish "live asset unloading" (ex: free up CPU asset memory after uploading an image to the GPU), rethink RenderAssets, and port renderer features. The `Assets` collection uses `Option<T>` for asset storage to support its removal. (1) the Option might not actually be necessary ... might be able to just remove from the collection entirely (2) need to finalize removal apis - [ ] Try replacing the "channel based" asset id recycling with something a bit more efficient (ex: we might be able to use raw atomic ints with some cleverness) - [ ] Consider adding UUIDs to processed assets (scoped just to helping identify moved assets ... not exposed to load queries ... see [Next Steps](#next-steps)) - [ ] Store "last modified" source asset and meta timestamps in processed meta files to enable skipping expensive hashing when the file wasn't changed - [ ] Fix "slow loop" handle drop fix - [ ] Migrate to TypeName - [x] Handle "loader preregistration". See #9429 ## Next Steps * **Configurable per-type defaults for AssetMeta**: It should be possible to add configuration like "all png image meta should default to using nearest sampling" (currently this hard-coded per-loader/processor Settings::default() impls). Also see the "Folder Meta" bullet point. * **Avoid Reprocessing on Asset Renames / Moves**: See the "canonical asset ids" discussion in [Open Questions](#open-questions) and the relevant bullet point in [Draft TODO](#draft-todo). Even without canonical ids, folder renames could avoid reprocessing in some cases. * **Multiple Asset Sources**: Expand AssetPath to support "asset source names" and support multiple AssetReaders in the asset server (ex: `webserver://some_path/image.png` backed by an Http webserver AssetReader). The "default" asset reader would use normal `some_path/image.png` paths. Ideally this works in combination with multiple AssetWatchers for hot-reloading * **Stable Type Names**: this pr removes the TypeUuid requirement from assets in favor of `std::any::type_name`. This makes defining assets easier (no need to generate a new uuid / use weird proc macro syntax). It also makes reading meta files easier (because things have "friendly names"). We also use type names for components in scene files. If they are good enough for components, they are good enough for assets. And consistency across Bevy pillars is desirable. However, `std::any::type_name` is not guaranteed to be stable (although in practice it is). We've developed a [stable type path](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/7184) to resolve this, which should be adopted when it is ready. * **Command Line Interface**: It should be possible to run the asset processor in a separate process from the command line. This will also require building a network-server-backed AssetReader to communicate between the app and the processor. We've been planning to build a "bevy cli" for awhile. This seems like a good excuse to build it. * **Asset Packing**: This is largely an additive feature, so it made sense to me to punt this until we've laid the foundations in this PR. * **Per-Platform Processed Assets**: It should be possible to generate assets for multiple platforms by supporting multiple "processor profiles" per asset (ex: compress with format X on PC and Y on iOS). I think there should probably be arbitrary "profiles" (which can be separate from actual platforms), which are then assigned to a given platform when generating the final asset distribution for that platform. Ex: maybe devs want a "Mobile" profile that is shared between iOS and Android. Or a "LowEnd" profile shared between web and mobile. * **Versioning and Migrations**: Assets, Loaders, Savers, and Processors need to have versions to determine if their schema is valid. If an asset / loader version is incompatible with the current version expected at runtime, the processor should be able to migrate them. I think we should try using Bevy Reflect for this, as it would allow us to load the old version as a dynamic Reflect type without actually having the old Rust type. It would also allow us to define "patches" to migrate between versions (Bevy Reflect devs are currently working on patching). The `.meta` file already has its own format version. Migrating that to new versions should also be possible. * **Real Copy-on-write AssetPaths**: Rust's actual Cow (clone-on-write type) currently used by AssetPath can still result in String clones that aren't actually necessary (cloning an Owned Cow clones the contents). Bevy's asset system requires cloning AssetPaths in a number of places, which result in actual clones of the internal Strings. This is not efficient. AssetPath internals should be reworked to exhibit truer cow-like-behavior that reduces String clones to the absolute minimum. * **Consider processor-less processing**: In theory the AssetServer could run processors "inline" even if the background AssetProcessor is disabled. If we decide this is actually desirable, we could add this. But I don't think its a priority in the short or medium term. * **Pre-emptive dependency loading**: We could encode dependencies in processed meta files, which could then be used by the Asset Server to kick of dependency loads as early as possible (prior to starting the actual asset load). Is this desirable? How much time would this save in practice? * **Optimize Processor With UntypedAssetIds**: The processor exclusively uses AssetPath to identify assets currently. It might be possible to swap these out for UntypedAssetIds in some places, which are smaller / cheaper to hash and compare. * **One to Many Asset Processing**: An asset source file that produces many assets currently must be processed into a single "processed" asset source. If labeled assets can be written separately they can each have their own configured savers _and_ they could be loaded more granularly. Definitely worth exploring! * **Automatically Track "Runtime-only" Asset Dependencies**: Right now, tracking "created at runtime" asset dependencies requires adding them via `asset_server.load_asset(StandardMaterial::default())`. I think with some cleverness we could also do this for `materials.add(StandardMaterial::default())`, making tracking work "everywhere". There are challenges here relating to change detection / ensuring the server is made aware of dependency changes. This could be expensive in some cases. * **"Dependency Changed" events**: Some assets have runtime artifacts that need to be re-generated when one of their dependencies change (ex: regenerate a material's bind group when a Texture needs to change). We are generating the dependency graph so we can definitely produce these events. Buuuuut generating these events will have a cost / they could be high frequency for some assets, so we might want this to be opt-in for specific cases. * **Investigate Storing More Information In Handles**: Handles can now store arbitrary information, which makes it cheaper and easier to access. How much should we move into them? Canonical asset load states (via atomics)? (`handle.is_loaded()` would be very cool). Should we store the entire asset and remove the `Assets<T>` collection? (`Arc<RwLock<Option<Image>>>`?) * **Support processing and loading files without extensions**: This is a pretty arbitrary restriction and could be supported with very minimal changes. * **Folder Meta**: It would be nice if we could define per folder processor configuration defaults (likely in a `.meta` or `.folder_meta` file). Things like "default to linear filtering for all Images in this folder". * **Replace async_broadcast with event-listener?** This might be approximately drop-in for some uses and it feels more light weight * **Support Running the AssetProcessor on the Web**: Most of the hard work is done here, but there are some easy straggling TODOs (make the transaction log an interface instead of a direct file writer so we can write a web storage backend, implement an AssetReader/AssetWriter that reads/writes to something like LocalStorage). * **Consider identifying and preventing circular dependencies**: This is especially important for "processor dependencies", as processing will silently never finish in these cases. * **Built-in/Inlined Asset Hot Reloading**: This PR regresses "built-in/inlined" asset hot reloading (previously provided by the DebugAssetServer). I'm intentionally punting this because I think it can be cleanly implemented with "multiple asset sources" by registering a "debug asset source" (ex: `debug://bevy_pbr/src/render/pbr.wgsl` asset paths) in combination with an AssetWatcher for that asset source and support for "manually loading pats with asset bytes instead of AssetReaders". The old DebugAssetServer was quite nasty and I'd love to avoid that hackery going forward. * **Investigate ways to remove double-parsing meta files**: Parsing meta files currently involves parsing once with "minimal" versions of the meta file to extract the type name of the loader/processor config, then parsing again to parse the "full" meta. This is suboptimal. We should be able to define custom deserializers that (1) assume the loader/processor type name comes first (2) dynamically looks up the loader/processor registrations to deserialize settings in-line (similar to components in the bevy scene format). Another alternative: deserialize as dynamic Reflect objects and then convert. * **More runtime loading configuration**: Support using the Handle type as a hint to select an asset loader (instead of relying on AssetPath extensions) * **More high level Processor trait implementations**: For example, it might be worth adding support for arbitrary chains of "asset transforms" that modify an in-memory asset representation between loading and saving. (ex: load a Mesh, run a `subdivide_mesh` transform, followed by a `flip_normals` transform, then save the mesh to an efficient compressed format). * **Bevy Scene Handle Deserialization**: (see the relevant [Draft TODO item](#draft-todo) for context) * **Explore High Level Load Interfaces**: See [this discussion](#discuss-on_loaded-high-level-interface) for one prototype. * **Asset Streaming**: It would be great if we could stream Assets (ex: stream a long video file piece by piece) * **ID Exchanging**: In this PR Asset Handles/AssetIds are bigger than they need to be because they have a Uuid enum variant. If we implement an "id exchanging" system that trades Uuids for "efficient runtime ids", we can cut down on the size of AssetIds, making them more efficient. This has some open design questions, such as how to spawn entities with "default" handle values (as these wouldn't have access to the exchange api in the current system). * **Asset Path Fixup Tooling**: Assets that inline asset paths inside them will break when an asset moves. The asset system provides the functionality to detect when paths break. We should build a framework that enables formats to define "path migrations". This is especially important for scene files. For editor-generated files, we should also consider using UUIDs (see other bullet point) to avoid the need to migrate in these cases. --------- Co-authored-by: BeastLe9enD <beastle9end@outlook.de> Co-authored-by: Mike <mike.hsu@gmail.com> Co-authored-by: Nicola Papale <nicopap@users.noreply.github.com> |
||
|
|
118509e4aa
|
Replace IntoSystemSetConfig with IntoSystemSetConfigs (#9247)
# Objective - Fixes #9244. ## Solution - Changed the `(Into)SystemSetConfigs` traits and structs be more like the `(Into)SystemConfigs` traits and structs. - Replaced uses of `IntoSystemSetConfig` with `IntoSystemSetConfigs` - Added generic `ItemConfig` and `ItemConfigs` types. - Changed `SystemConfig(s)` and `SystemSetConfig(s)` to be type aliases to `ItemConfig(s)`. - Added generic `process_configs` to `ScheduleGraph`. - Changed `configure_sets_inner` and `add_systems_inner` to reuse `process_configs`. --- ## Changelog - Added `run_if` to `IntoSystemSetConfigs` - Deprecated `Schedule::configure_set` and `App::configure_set` - Removed `IntoSystemSetConfig` ## Migration Guide - Use `App::configure_sets` instead of `App::configure_set` - Use `Schedule::configure_sets` instead of `Schedule::configure_set` --------- Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com> |
||
|
|
4fdea02087
|
Use instancing for sprites (#9597)
# Objective - Supercedes #8872 - Improve sprite rendering performance after the regression in #9236 ## Solution - Use an instance-rate vertex buffer to store per-instance data. - Store color, UV offset and scale, and a transform per instance. - Convert Sprite rect, custom_size, anchor, and flip_x/_y to an affine 3x4 matrix and store the transpose of that in the per-instance data. This is similar to how MeshUniform uses transpose affine matrices. - Use a special index buffer that has batches of 6 indices referencing 4 vertices. The lower 2 bits indicate the x and y of a quad such that the corners are: ``` 10 11 00 01 ``` UVs are implicit but get modified by UV offset and scale The remaining upper bits contain the instance index. ## Benchmarks I will compare versus `main` before #9236 because the results should be as good as or faster than that. Running `bevymark -- 10000 16` on an M1 Max with `main` at `e8b38925` in yellow, this PR in red: 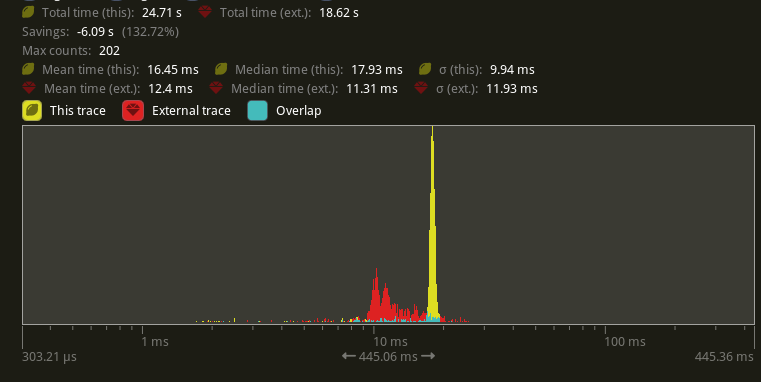 Looking at the median frame times, that's a 37% reduction from before. --- ## Changelog - Changed: Improved sprite rendering performance by leveraging an instance-rate vertex buffer. --------- Co-authored-by: Giacomo Stevanato <giaco.stevanato@gmail.com> |
||
|
|
02b520b4e8
|
Split ComputedVisibility into two components to allow for accurate change detection and speed up visibility propagation (#9497)
# Objective Fix #8267. Fixes half of #7840. The `ComputedVisibility` component contains two flags: hierarchy visibility, and view visibility (whether its visible to any cameras). Due to the modular and open-ended way that view visibility is computed, it triggers change detection every single frame, even when the value does not change. Since hierarchy visibility is stored in the same component as view visibility, this means that change detection for inherited visibility is completely broken. At the company I work for, this has become a real issue. We are using change detection to only re-render scenes when necessary. The broken state of change detection for computed visibility means that we have to to rely on the non-inherited `Visibility` component for now. This is workable in the early stages of our project, but since we will inevitably want to use the hierarchy, we will have to either: 1. Roll our own solution for computed visibility. 2. Fix the issue for everyone. ## Solution Split the `ComputedVisibility` component into two: `InheritedVisibilty` and `ViewVisibility`. This allows change detection to behave properly for `InheritedVisibility`. View visiblity is still erratic, although it is less useful to be able to detect changes for this flavor of visibility. Overall, this actually simplifies the API. Since the visibility system consists of self-explaining components, it is much easier to document the behavior and usage. This approach is more modular and "ECS-like" -- one could strip out the `ViewVisibility` component entirely if it's not needed, and rely only on inherited visibility. --- ## Changelog - `ComputedVisibility` has been removed in favor of: `InheritedVisibility` and `ViewVisiblity`. ## Migration Guide The `ComputedVisibilty` component has been split into `InheritedVisiblity` and `ViewVisibility`. Replace any usages of `ComputedVisibility::is_visible_in_hierarchy` with `InheritedVisibility::get`, and replace `ComputedVisibility::is_visible_in_view` with `ViewVisibility::get`. ```rust // Before: commands.spawn(VisibilityBundle { visibility: Visibility::Inherited, computed_visibility: ComputedVisibility::default(), }); // After: commands.spawn(VisibilityBundle { visibility: Visibility::Inherited, inherited_visibility: InheritedVisibility::default(), view_visibility: ViewVisibility::default(), }); ``` ```rust // Before: fn my_system(q: Query<&ComputedVisibilty>) { for vis in &q { if vis.is_visible_in_hierarchy() { // After: fn my_system(q: Query<&InheritedVisibility>) { for inherited_visibility in &q { if inherited_visibility.get() { ``` ```rust // Before: fn my_system(q: Query<&ComputedVisibilty>) { for vis in &q { if vis.is_visible_in_view() { // After: fn my_system(q: Query<&ViewVisibility>) { for view_visibility in &q { if view_visibility.get() { ``` ```rust // Before: fn my_system(mut q: Query<&mut ComputedVisibilty>) { for vis in &mut q { vis.set_visible_in_view(); // After: fn my_system(mut q: Query<&mut ViewVisibility>) { for view_visibility in &mut q { view_visibility.set(); ``` --------- Co-authored-by: Robert Swain <robert.swain@gmail.com> |
||
|
|
33fdc5f5db
|
Move schedule name into Schedule (#9600)
# Objective - Move schedule name into `Schedule` to allow the schedule name to be used for errors and tracing in Schedule methods - Fixes #9510 ## Solution - Move label onto `Schedule` and adjust api's on `World` and `Schedule` to not pass explicit label where it makes sense to. - add name to errors and tracing. - `Schedule::new` now takes a label so either add the label or use `Schedule::default` which uses a default label. `default` is mostly used in doc examples and tests. --- ## Changelog - move label onto `Schedule` to improve error message and logging for schedules. ## Migration Guide `Schedule::new` and `App::add_schedule` ```rust // old let schedule = Schedule::new(); app.add_schedule(MyLabel, schedule); // new let schedule = Schedule::new(MyLabel); app.add_schedule(schedule); ``` if you aren't using a label and are using the schedule struct directly you can use the default constructor. ```rust // old let schedule = Schedule::new(); schedule.run(world); // new let schedule = Schedule::default(); schedule.run(world); ``` `Schedules:insert` ```rust // old let schedule = Schedule::new(); schedules.insert(MyLabel, schedule); // new let schedule = Schedule::new(MyLabel); schedules.insert(schedule); ``` `World::add_schedule` ```rust // old let schedule = Schedule::new(); world.add_schedule(MyLabel, schedule); // new let schedule = Schedule::new(MyLabel); world.add_schedule(schedule); ``` |
||
|
|
4f1d9a6315
|
Reorder render sets, refactor bevy_sprite to take advantage (#9236)
This is a continuation of this PR: #8062 # Objective - Reorder render schedule sets to allow data preparation when phase item order is known to support improved batching - Part of the batching/instancing etc plan from here: https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/89#issuecomment-1379249074 - The original idea came from @inodentry and proved to be a good one. Thanks! - Refactor `bevy_sprite` and `bevy_ui` to take advantage of the new ordering ## Solution - Move `Prepare` and `PrepareFlush` after `PhaseSortFlush` - Add a `PrepareAssets` set that runs in parallel with other systems and sets in the render schedule. - Put prepare_assets systems in the `PrepareAssets` set - If explicit dependencies are needed on Mesh or Material RenderAssets then depend on the appropriate system. - Add `ManageViews` and `ManageViewsFlush` sets between `ExtractCommands` and Queue - Move `queue_mesh*_bind_group` to the Prepare stage - Rename them to `prepare_` - Put systems that prepare resources (buffers, textures, etc.) into a `PrepareResources` set inside `Prepare` - Put the `prepare_..._bind_group` systems into a `PrepareBindGroup` set after `PrepareResources` - Move `prepare_lights` to the `ManageViews` set - `prepare_lights` creates views and this must happen before `Queue` - This system needs refactoring to stop handling all responsibilities - Gather lights, sort, and create shadow map views. Store sorted light entities in a resource - Remove `BatchedPhaseItem` - Replace `batch_range` with `batch_size` representing how many items to skip after rendering the item or to skip the item entirely if `batch_size` is 0. - `queue_sprites` has been split into `queue_sprites` for queueing phase items and `prepare_sprites` for batching after the `PhaseSort` - `PhaseItem`s are still inserted in `queue_sprites` - After sorting adjacent compatible sprite phase items are accumulated into `SpriteBatch` components on the first entity of each batch, containing a range of vertex indices. The associated `PhaseItem`'s `batch_size` is updated appropriately. - `SpriteBatch` items are then drawn skipping over the other items in the batch based on the value in `batch_size` - A very similar refactor was performed on `bevy_ui` --- ## Changelog Changed: - Reordered and reworked render app schedule sets. The main change is that data is extracted, queued, sorted, and then prepared when the order of data is known. - Refactor `bevy_sprite` and `bevy_ui` to take advantage of the reordering. ## Migration Guide - Assets such as materials and meshes should now be created in `PrepareAssets` e.g. `prepare_assets<Mesh>` - Queueing entities to `RenderPhase`s continues to be done in `Queue` e.g. `queue_sprites` - Preparing resources (textures, buffers, etc.) should now be done in `PrepareResources`, e.g. `prepare_prepass_textures`, `prepare_mesh_uniforms` - Prepare bind groups should now be done in `PrepareBindGroups` e.g. `prepare_mesh_bind_group` - Any batching or instancing can now be done in `Prepare` where the order of the phase items is known e.g. `prepare_sprites` ## Next Steps - Introduce some generic mechanism to ensure items that can be batched are grouped in the phase item order, currently you could easily have `[sprite at z 0, mesh at z 0, sprite at z 0]` preventing batching. - Investigate improved orderings for building the MeshUniform buffer - Implementing batching across the rest of bevy --------- Co-authored-by: Robert Swain <robert.swain@gmail.com> Co-authored-by: robtfm <50659922+robtfm@users.noreply.github.com> |
||
|
|
c1a5428f8e
|
Work around naga/wgpu WGSL instance_index -> GLSL gl_InstanceID bug on WebGL2 (#9383)
naga and wgpu should polyfill WGSL instance_index functionality where it is not available in GLSL. Until that is done, we can work around it in bevy using a push constant which is converted to a uniform by naga and wgpu. # Objective - Fixes #9375 ## Solution - Use a push constant to pass in the base instance to the shader on WebGL2 so that base instance + gl_InstanceID is used to correctly represent the instance index. ## TODO - [ ] Benchmark vs per-object dynamic offset MeshUniform as this will now push a uniform value per-draw as well as update the dynamic offset per-batch. - [x] Test on DX12 AMD/NVIDIA to check that this PR does not regress any problems that were observed there. (@Elabajaba @robtfm were testing that last time - help appreciated. <3 ) --- ## Changelog - Added: `bevy_render::instance_index` shader import which includes a workaround for the lack of a WGSL `instance_index` polyfill for WebGL2 in naga and wgpu for the time being. It uses a push_constant which gets converted to a plain uniform by naga and wgpu. ## Migration Guide Shader code before: ``` struct Vertex { @builtin(instance_index) instance_index: u32, ... } @vertex fn vertex(vertex_no_morph: Vertex) -> VertexOutput { ... var model = mesh[vertex_no_morph.instance_index].model; ``` After: ``` #import bevy_render::instance_index struct Vertex { @builtin(instance_index) instance_index: u32, ... } @vertex fn vertex(vertex_no_morph: Vertex) -> VertexOutput { ... var model = mesh[bevy_render::instance_index::get_instance_index(vertex_no_morph.instance_index)].model; ``` |
||
|
|
ad011d0455
|
Add GpuArrayBuffer and BatchedUniformBuffer (#8204)
# Objective - Add a type for uploading a Rust `Vec<T>` to a GPU `array<T>`. - Makes progress towards https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/89. ## Solution - Port @superdump's `BatchedUniformBuffer` to bevy main, as a fallback for WebGL2, which doesn't support storage buffers. - Rather than getting an `array<T>` in a shader, you get an `array<T, N>`, and have to rebind every N elements via dynamic offsets. - Add `GpuArrayBuffer` to abstract over `StorageBuffer<Vec<T>>`/`BatchedUniformBuffer`. ## Future Work Add a shader macro kinda thing to abstract over the following automatically: https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/8204#pullrequestreview-1396911727 --- ## Changelog * Added `GpuArrayBuffer`, `GpuComponentArrayBufferPlugin`, `GpuArrayBufferable`, and `GpuArrayBufferIndex` types. * Added `DynamicUniformBuffer::new_with_alignment()`. --------- Co-authored-by: Robert Swain <robert.swain@gmail.com> Co-authored-by: François <mockersf@gmail.com> Co-authored-by: Teodor Tanasoaia <28601907+teoxoy@users.noreply.github.com> Co-authored-by: IceSentry <IceSentry@users.noreply.github.com> Co-authored-by: Vincent <9408210+konsolas@users.noreply.github.com> Co-authored-by: robtfm <50659922+robtfm@users.noreply.github.com> |
||
|
|
608367f905
|
Remove unused dependency on once_cell in bevy_render (#9039)
# Objective bevy_render currently has a dependency on a random older version of once_cell which is not used anywhere. ## Solution Remove the dependency ## Changelog N/A ## Migration Guide N/A |
||
|
|
c6170d48f9
|
Add morph targets (#8158)
# Objective - Add morph targets to `bevy_pbr` (closes #5756) & load them from glTF - Supersedes #3722 - Fixes #6814 [Morph targets][1] (also known as shape interpolation, shape keys, or blend shapes) allow animating individual vertices with fine grained controls. This is typically used for facial expressions. By specifying multiple poses as vertex offset, and providing a set of weight of each pose, it is possible to define surprisingly realistic transitions between poses. Blending between multiple poses also allow composition. Morph targets are part of the [gltf standard][2] and are a feature of Unity and Unreal, and babylone.js, it is only natural to implement them in bevy. ## Solution This implementation of morph targets uses a 3d texture where each pixel is a component of an animated attribute. Each layer is a different target. We use a 2d texture for each target, because the number of attribute×components×animated vertices is expected to always exceed the maximum pixel row size limit of webGL2. It copies fairly closely the way skinning is implemented on the CPU side, while on the GPU side, the shader morph target implementation is a relatively trivial detail. We add an optional `morph_texture` to the `Mesh` struct. The `morph_texture` is built through a method that accepts an iterator over attribute buffers. The `MorphWeights` component, user-accessible, controls the blend of poses used by mesh instances (so that multiple copy of the same mesh may have different weights), all the weights are uploaded to a uniform buffer of 256 `f32`. We limit to 16 poses per mesh, and a total of 256 poses. More literature: * Old babylone.js implementation (vertex attribute-based): https://www.eternalcoding.com/dev-log-1-morph-targets/ * Babylone.js implementation (similar to ours): https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=LBPRmGgU0PE * GPU gems 3: https://developer.nvidia.com/gpugems/gpugems3/part-i-geometry/chapter-3-directx-10-blend-shapes-breaking-limits * Development discord thread https://discord.com/channels/691052431525675048/1083325980615114772 https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/26321040/231181046-3bca2ab2-d4d9-472e-8098-639f1871ce2e.mp4 https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/assets/26321040/d2a0c544-0ef8-45cf-9f99-8c3792f5a258 ## Acknowledgements * Thanks to `storytold` for sponsoring the feature * Thanks to `superdump` and `james7132` for guidance and help figuring out stuff ## Future work - Handling of less and more attributes (eg: animated uv, animated arbitrary attributes) - Dynamic pose allocation (so that zero-weighted poses aren't uploaded to GPU for example, enables much more total poses) - Better animation API, see #8357 ---- ## Changelog - Add morph targets to bevy meshes - Support up to 64 poses per mesh of individually up to 116508 vertices, animation currently strictly limited to the position, normal and tangent attributes. - Load a morph target using `Mesh::set_morph_targets` - Add `VisitMorphTargets` and `VisitMorphAttributes` traits to `bevy_render`, this allows defining morph targets (a fairly complex and nested data structure) through iterators (ie: single copy instead of passing around buffers), see documentation of those traits for details - Add `MorphWeights` component exported by `bevy_render` - `MorphWeights` control mesh's morph target weights, blending between various poses defined as morph targets. - `MorphWeights` are directly inherited by direct children (single level of hierarchy) of an entity. This allows controlling several mesh primitives through a unique entity _as per GLTF spec_. - Add `MorphTargetNames` component, naming each indices of loaded morph targets. - Load morph targets weights and buffers in `bevy_gltf` - handle morph targets animations in `bevy_animation` (previously, it was a `warn!` log) - Add the `MorphStressTest.gltf` asset for morph targets testing, taken from the glTF samples repo, CC0. - Add morph target manipulation to `scene_viewer` - Separate the animation code in `scene_viewer` from the rest of the code, reducing `#[cfg(feature)]` noise - Add the `morph_targets.rs` example to show off how to manipulate morph targets, loading `MorpStressTest.gltf` ## Migration Guide - (very specialized, unlikely to be touched by 3rd parties) - `MeshPipeline` now has a single `mesh_layouts` field rather than separate `mesh_layout` and `skinned_mesh_layout` fields. You should handle all possible mesh bind group layouts in your implementation - You should also handle properly the new `MORPH_TARGETS` shader def and mesh pipeline key. A new function is exposed to make this easier: `setup_moprh_and_skinning_defs` - The `MeshBindGroup` is now `MeshBindGroups`, cached bind groups are now accessed through the `get` method. [1]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Morph_target_animation [2]: https://registry.khronos.org/glTF/specs/2.0/glTF-2.0.html#morph-targets --------- Co-authored-by: François <mockersf@gmail.com> Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com> |
||
|
|
f18f28874a
|
Allow tuples and single plugins in add_plugins, deprecate add_plugin (#8097)
# Objective - Better consistency with `add_systems`. - Deprecating `add_plugin` in favor of a more powerful `add_plugins`. - Allow passing `Plugin` to `add_plugins`. - Allow passing tuples to `add_plugins`. ## Solution - `App::add_plugins` now takes an `impl Plugins` parameter. - `App::add_plugin` is deprecated. - `Plugins` is a new sealed trait that is only implemented for `Plugin`, `PluginGroup` and tuples over `Plugins`. - All examples, benchmarks and tests are changed to use `add_plugins`, using tuples where appropriate. --- ## Changelog ### Changed - `App::add_plugins` now accepts all types that implement `Plugins`, which is implemented for: - Types that implement `Plugin`. - Types that implement `PluginGroup`. - Tuples (up to 16 elements) over types that implement `Plugins`. - Deprecated `App::add_plugin` in favor of `App::add_plugins`. ## Migration Guide - Replace `app.add_plugin(plugin)` calls with `app.add_plugins(plugin)`. --------- Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com> |
||
|
|
cbd4abf0fc
|
Rename apply_system_buffers to apply_deferred (#8726)
# Objective - `apply_system_buffers` is an unhelpful name: it introduces a new internal-only concept - this is particularly rough for beginners as reasoning about how commands work is a critical stumbling block ## Solution - rename `apply_system_buffers` to the more descriptive `apply_deferred` - rename related fields, arguments and methods in the internals fo bevy_ecs for consistency - update the docs ## Changelog `apply_system_buffers` has been renamed to `apply_deferred`, to more clearly communicate its intent and relation to `Deferred` system parameters like `Commands`. ## Migration Guide - `apply_system_buffers` has been renamed to `apply_deferred` - the `apply_system_buffers` method on the `System` trait has been renamed to `apply_deferred` - the `is_apply_system_buffers` function has been replaced by `is_apply_deferred` - `Executor::set_apply_final_buffers` is now `Executor::set_apply_final_deferred` - `Schedule::apply_system_buffers` is now `Schedule::apply_deferred` --------- Co-authored-by: JoJoJet <21144246+JoJoJet@users.noreply.github.com> |
||
|
|
71842c5ac9
|
Webgpu support (#8336)
# Objective - Support WebGPU - alternative to #5027 that doesn't need any async / await - fixes #8315 - Surprise fix #7318 ## Solution ### For async renderer initialisation - Update the plugin lifecycle: - app builds the plugin - calls `plugin.build` - registers the plugin - app starts the event loop - event loop waits for `ready` of all registered plugins in the same order - returns `true` by default - then call all `finish` then all `cleanup` in the same order as registered - then execute the schedule In the case of the renderer, to avoid anything async: - building the renderer plugin creates a detached task that will send back the initialised renderer through a mutex in a resource - `ready` will wait for the renderer to be present in the resource - `finish` will take that renderer and place it in the expected resources by other plugins - other plugins (that expect the renderer to be available) `finish` are called and they are able to set up their pipelines - `cleanup` is called, only custom one is still for pipeline rendering ### For WebGPU support - update the `build-wasm-example` script to support passing `--api webgpu` that will build the example with WebGPU support - feature for webgl2 was always enabled when building for wasm. it's now in the default feature list and enabled on all platforms, so check for this feature must also check that the target_arch is `wasm32` --- ## Migration Guide - `Plugin::setup` has been renamed `Plugin::cleanup` - `Plugin::finish` has been added, and plugins adding pipelines should do it in this function instead of `Plugin::build` ```rust // Before impl Plugin for MyPlugin { fn build(&self, app: &mut App) { app.insert_resource::<MyResource> .add_systems(Update, my_system); let render_app = match app.get_sub_app_mut(RenderApp) { Ok(render_app) => render_app, Err(_) => return, }; render_app .init_resource::<RenderResourceNeedingDevice>() .init_resource::<OtherRenderResource>(); } } // After impl Plugin for MyPlugin { fn build(&self, app: &mut App) { app.insert_resource::<MyResource> .add_systems(Update, my_system); let render_app = match app.get_sub_app_mut(RenderApp) { Ok(render_app) => render_app, Err(_) => return, }; render_app .init_resource::<OtherRenderResource>(); } fn finish(&self, app: &mut App) { let render_app = match app.get_sub_app_mut(RenderApp) { Ok(render_app) => render_app, Err(_) => return, }; render_app .init_resource::<RenderResourceNeedingDevice>(); } } ``` |
||
|
|
abf12f3b3b
|
Fixed several missing links in docs. (#8117)
Links in the api docs are nice. I noticed that there were several places where structs / functions and other things were referenced in the docs, but weren't linked. I added the links where possible / logical. --------- Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com> Co-authored-by: François <mockersf@gmail.com> |
||
|
|
3ead10a3e0
|
Suppress the clippy::type_complexity lint (#8313)
# Objective The clippy lint `type_complexity` is known not to play well with bevy. It frequently triggers when writing complex queries, and taking the lint's advice of using a type alias almost always just obfuscates the code with no benefit. Because of this, this lint is currently ignored in CI, but unfortunately it still shows up when viewing bevy code in an IDE. As someone who's made a fair amount of pull requests to this repo, I will say that this issue has been a consistent thorn in my side. Since bevy code is filled with spurious, ignorable warnings, it can be very difficult to spot the *real* warnings that must be fixed -- most of the time I just ignore all warnings, only to later find out that one of them was real after I'm done when CI runs. ## Solution Suppress this lint in all bevy crates. This was previously attempted in #7050, but the review process ended up making it more complicated than it needs to be and landed on a subpar solution. The discussion in https://github.com/rust-lang/rust-clippy/pull/10571 explores some better long-term solutions to this problem. Since there is no timeline on when these solutions may land, we should resolve this issue in the meantime by locally suppressing these lints. ### Unresolved issues Currently, these lints are not suppressed in our examples, since that would require suppressing the lint in every single source file. They are still ignored in CI. |
||
|
|
464d35aef5
|
docs: update docs and comments that still refer to stages (#8156)
# Objective Documentation should no longer be using pre-stageless terminology to avoid confusion. ## Solution - update all docs referring to stages to instead refer to sets/schedules where appropriate - also mention `apply_system_buffers` for anything system-buffer-related that previously referred to buffers being applied "at the end of a stage" |
||
|
|
aefe1f0739
|
Schedule-First: the new and improved add_systems (#8079)
Co-authored-by: Mike <mike.hsu@gmail.com> |
||
|
|
fd1af7c8b8
|
Replace multiple calls to add_system with add_systems (#8001)
|
||
|
|
b39f83640f |
Fix some typos (#7763)
# Objective Stumbled on a typo and went on a typo hunt. ## Solution Fix em |
||
|
|
0bce78439b |
Cleanup system sets called labels (#7678)
# Objective We have a few old system labels that are now system sets but are still named or documented as labels. Documentation also generally mentioned system labels in some places. ## Solution - Clean up naming and documentation regarding system sets ## Migration Guide `PrepareAssetLabel` is now called `PrepareAssetSet` |
||
|
|
cd447fb4e6 |
Cleanup render schedule (#7589)
# Objective - Fixes https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/7531 ## Solution - Add systems to prepare set - Also remove a unnecessary apply_systems_buffers from ExtractCommands set. |
||
|
|
aa4170d9a4 |
Rename schedule v3 to schedule (#7519)
# Objective - Follow up of https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/7267 ## Solution - Rename schedule_v3 to schedule - Suppress "module inception" lint |
||
|
|
206c7ce219 |
Migrate engine to Schedule v3 (#7267)
Huge thanks to @maniwani, @devil-ira, @hymm, @cart, @superdump and @jakobhellermann for the help with this PR. # Objective - Followup #6587. - Minimal integration for the Stageless Scheduling RFC: https://github.com/bevyengine/rfcs/pull/45 ## Solution - [x] Remove old scheduling module - [x] Migrate new methods to no longer use extension methods - [x] Fix compiler errors - [x] Fix benchmarks - [x] Fix examples - [x] Fix docs - [x] Fix tests ## Changelog ### Added - a large number of methods on `App` to work with schedules ergonomically - the `CoreSchedule` enum - `App::add_extract_system` via the `RenderingAppExtension` trait extension method - the private `prepare_view_uniforms` system now has a public system set for scheduling purposes, called `ViewSet::PrepareUniforms` ### Removed - stages, and all code that mentions stages - states have been dramatically simplified, and no longer use a stack - `RunCriteriaLabel` - `AsSystemLabel` trait - `on_hierarchy_reports_enabled` run criteria (now just uses an ad hoc resource checking run condition) - systems in `RenderSet/Stage::Extract` no longer warn when they do not read data from the main world - `RunCriteriaLabel` - `transform_propagate_system_set`: this was a nonstandard pattern that didn't actually provide enough control. The systems are already `pub`: the docs have been updated to ensure that the third-party usage is clear. ### Changed - `System::default_labels` is now `System::default_system_sets`. - `App::add_default_labels` is now `App::add_default_sets` - `CoreStage` and `StartupStage` enums are now `CoreSet` and `StartupSet` - `App::add_system_set` was renamed to `App::add_systems` - The `StartupSchedule` label is now defined as part of the `CoreSchedules` enum - `.label(SystemLabel)` is now referred to as `.in_set(SystemSet)` - `SystemLabel` trait was replaced by `SystemSet` - `SystemTypeIdLabel<T>` was replaced by `SystemSetType<T>` - The `ReportHierarchyIssue` resource now has a public constructor (`new`), and implements `PartialEq` - Fixed time steps now use a schedule (`CoreSchedule::FixedTimeStep`) rather than a run criteria. - Adding rendering extraction systems now panics rather than silently failing if no subapp with the `RenderApp` label is found. - the `calculate_bounds` system, with the `CalculateBounds` label, is now in `CoreSet::Update`, rather than in `CoreSet::PostUpdate` before commands are applied. - `SceneSpawnerSystem` now runs under `CoreSet::Update`, rather than `CoreStage::PreUpdate.at_end()`. - `bevy_pbr::add_clusters` is no longer an exclusive system - the top level `bevy_ecs::schedule` module was replaced with `bevy_ecs::scheduling` - `tick_global_task_pools_on_main_thread` is no longer run as an exclusive system. Instead, it has been replaced by `tick_global_task_pools`, which uses a `NonSend` resource to force running on the main thread. ## Migration Guide - Calls to `.label(MyLabel)` should be replaced with `.in_set(MySet)` - Stages have been removed. Replace these with system sets, and then add command flushes using the `apply_system_buffers` exclusive system where needed. - The `CoreStage`, `StartupStage, `RenderStage` and `AssetStage` enums have been replaced with `CoreSet`, `StartupSet, `RenderSet` and `AssetSet`. The same scheduling guarantees have been preserved. - Systems are no longer added to `CoreSet::Update` by default. Add systems manually if this behavior is needed, although you should consider adding your game logic systems to `CoreSchedule::FixedTimestep` instead for more reliable framerate-independent behavior. - Similarly, startup systems are no longer part of `StartupSet::Startup` by default. In most cases, this won't matter to you. - For example, `add_system_to_stage(CoreStage::PostUpdate, my_system)` should be replaced with - `add_system(my_system.in_set(CoreSet::PostUpdate)` - When testing systems or otherwise running them in a headless fashion, simply construct and run a schedule using `Schedule::new()` and `World::run_schedule` rather than constructing stages - Run criteria have been renamed to run conditions. These can now be combined with each other and with states. - Looping run criteria and state stacks have been removed. Use an exclusive system that runs a schedule if you need this level of control over system control flow. - For app-level control flow over which schedules get run when (such as for rollback networking), create your own schedule and insert it under the `CoreSchedule::Outer` label. - Fixed timesteps are now evaluated in a schedule, rather than controlled via run criteria. The `run_fixed_timestep` system runs this schedule between `CoreSet::First` and `CoreSet::PreUpdate` by default. - Command flush points introduced by `AssetStage` have been removed. If you were relying on these, add them back manually. - Adding extract systems is now typically done directly on the main app. Make sure the `RenderingAppExtension` trait is in scope, then call `app.add_extract_system(my_system)`. - the `calculate_bounds` system, with the `CalculateBounds` label, is now in `CoreSet::Update`, rather than in `CoreSet::PostUpdate` before commands are applied. You may need to order your movement systems to occur before this system in order to avoid system order ambiguities in culling behavior. - the `RenderLabel` `AppLabel` was renamed to `RenderApp` for clarity - `App::add_state` now takes 0 arguments: the starting state is set based on the `Default` impl. - Instead of creating `SystemSet` containers for systems that run in stages, simply use `.on_enter::<State::Variant>()` or its `on_exit` or `on_update` siblings. - `SystemLabel` derives should be replaced with `SystemSet`. You will also need to add the `Debug`, `PartialEq`, `Eq`, and `Hash` traits to satisfy the new trait bounds. - `with_run_criteria` has been renamed to `run_if`. Run criteria have been renamed to run conditions for clarity, and should now simply return a bool. - States have been dramatically simplified: there is no longer a "state stack". To queue a transition to the next state, call `NextState::set` ## TODO - [x] remove dead methods on App and World - [x] add `App::add_system_to_schedule` and `App::add_systems_to_schedule` - [x] avoid adding the default system set at inappropriate times - [x] remove any accidental cycles in the default plugins schedule - [x] migrate benchmarks - [x] expose explicit labels for the built-in command flush points - [x] migrate engine code - [x] remove all mentions of stages from the docs - [x] verify docs for States - [x] fix uses of exclusive systems that use .end / .at_start / .before_commands - [x] migrate RenderStage and AssetStage - [x] migrate examples - [x] ensure that transform propagation is exported in a sufficiently public way (the systems are already pub) - [x] ensure that on_enter schedules are run at least once before the main app - [x] re-enable opt-in to execution order ambiguities - [x] revert change to `update_bounds` to ensure it runs in `PostUpdate` - [x] test all examples - [x] unbreak directional lights - [x] unbreak shadows (see 3d_scene, 3d_shape, lighting, transparaency_3d examples) - [x] game menu example shows loading screen and menu simultaneously - [x] display settings menu is a blank screen - [x] `without_winit` example panics - [x] ensure all tests pass - [x] SubApp doc test fails - [x] runs_spawn_local tasks fails - [x] [Fix panic_when_hierachy_cycle test hanging](https://github.com/alice-i-cecile/bevy/pull/120) ## Points of Difficulty and Controversy **Reviewers, please give feedback on these and look closely** 1. Default sets, from the RFC, have been removed. These added a tremendous amount of implicit complexity and result in hard to debug scheduling errors. They're going to be tackled in the form of "base sets" by @cart in a followup. 2. The outer schedule controls which schedule is run when `App::update` is called. 3. I implemented `Label for `Box<dyn Label>` for our label types. This enables us to store schedule labels in concrete form, and then later run them. I ran into the same set of problems when working with one-shot systems. We've previously investigated this pattern in depth, and it does not appear to lead to extra indirection with nested boxes. 4. `SubApp::update` simply runs the default schedule once. This sucks, but this whole API is incomplete and this was the minimal changeset. 5. `time_system` and `tick_global_task_pools_on_main_thread` no longer use exclusive systems to attempt to force scheduling order 6. Implemetnation strategy for fixed timesteps 7. `AssetStage` was migrated to `AssetSet` without reintroducing command flush points. These did not appear to be used, and it's nice to remove these bottlenecks. 8. Migration of `bevy_render/lib.rs` and pipelined rendering. The logic here is unusually tricky, as we have complex scheduling requirements. ## Future Work (ideally before 0.10) - Rename schedule_v3 module to schedule or scheduling - Add a derive macro to states, and likely a `EnumIter` trait of some form - Figure out what exactly to do with the "systems added should basically work by default" problem - Improve ergonomics for working with fixed timesteps and states - Polish FixedTime API to match Time - Rebase and merge #7415 - Resolve all internal ambiguities (blocked on better tools, especially #7442) - Add "base sets" to replace the removed default sets. |
||
|
|
bfd1d4b0a7 |
Wgpu 0.15 (#7356)
# Objective Update Bevy to wgpu 0.15. ## Changelog - Update to wgpu 0.15, wgpu-hal 0.15.1, and naga 0.11 - Users can now use the [DirectX Shader Compiler](https://github.com/microsoft/DirectXShaderCompiler) (DXC) on Windows with DX12 for faster shader compilation and ShaderModel 6.0+ support (requires `dxcompiler.dll` and `dxil.dll`, which are included in DXC downloads from [here](https://github.com/microsoft/DirectXShaderCompiler/releases/latest)) ## Migration Guide ### WGSL Top-Level `let` is now `const` All top level constants are now declared with `const`, catching up with the wgsl spec. `let` is no longer allowed at the global scope, only within functions. ```diff -let SOME_CONSTANT = 12.0; +const SOME_CONSTANT = 12.0; ``` #### `TextureDescriptor` and `SurfaceConfiguration` now requires a `view_formats` field The new `view_formats` field in the `TextureDescriptor` is used to specify a list of formats the texture can be re-interpreted to in a texture view. Currently only changing srgb-ness is allowed (ex. `Rgba8Unorm` <=> `Rgba8UnormSrgb`). You should set `view_formats` to `&[]` (empty) unless you have a specific reason not to. #### The DirectX Shader Compiler (DXC) is now supported on DX12 DXC is now the default shader compiler when using the DX12 backend. DXC is Microsoft's replacement for their legacy FXC compiler, and is faster, less buggy, and allows for modern shader features to be used (ShaderModel 6.0+). DXC requires `dxcompiler.dll` and `dxil.dll` to be available, otherwise it will log a warning and fall back to FXC. You can get `dxcompiler.dll` and `dxil.dll` by downloading the latest release from [Microsoft's DirectXShaderCompiler github repo](https://github.com/microsoft/DirectXShaderCompiler/releases/latest) and copying them into your project's root directory. These must be included when you distribute your Bevy game/app/etc if you plan on supporting the DX12 backend and are using DXC. `WgpuSettings` now has a `dx12_shader_compiler` field which can be used to choose between either FXC or DXC (if you pass None for the paths for DXC, it will check for the .dlls in the working directory). |
||
|
|
c3a46822e1 |
Cascaded shadow maps. (#7064)
Co-authored-by: Robert Swain <robert.swain@gmail.com> # Objective Implements cascaded shadow maps for directional lights, which produces better quality shadows without needing excessively large shadow maps. Fixes #3629 Before  After  ## Solution Rather than rendering a single shadow map for directional light, the view frustum is divided into a series of cascades, each of which gets its own shadow map. The correct cascade is then sampled for shadow determination. --- ## Changelog Directional lights now use cascaded shadow maps for improved shadow quality. ## Migration Guide You no longer have to manually specify a `shadow_projection` for a directional light, and these settings should be removed. If customization of how cascaded shadow maps work is desired, modify the `CascadeShadowConfig` component instead. |
||
|
|
958a898b4a |
Remove App::add_sub_app (#7290)
# Objective Fixes #7286. Both `App::add_sub_app` and `App::insert_sub_app` are rather redundant. Before 0.10 is shipped, one of them should be removed. ## Solution Remove `App::add_sub_app` to prefer `App::insert_sub_app`. Also hid away `SubApp::extract` since that can be a footgun if someone mutates it for whatever reason. Willing to revert this change if there are objections. Perhaps we should make `SubApp: Deref<Target=App>`? Might change if we decide to move `!Send` resources into it. --- ## Changelog Added: `SubApp::new` Removed: `App::add_sub_app` ## Migration Guide `App::add_sub_app` has been removed in favor of `App::insert_sub_app`. Use `SubApp::new` and insert it via `App::add_sub_app` Old: ```rust let mut sub_app = App::new() // Build subapp here app.add_sub_app(MySubAppLabel, sub_app); ``` New: ```rust let mut sub_app = App::new() // Build subapp here app.insert_sub_app(MySubAppLabel, SubApp::new(sub_app, extract_fn)); ``` |
||
|
|
2027af4c54 |
Pipelined Rendering (#6503)
# Objective - Implement pipelined rendering - Fixes #5082 - Fixes #4718 ## User Facing Description Bevy now implements piplelined rendering! Pipelined rendering allows the app logic and rendering logic to run on different threads leading to large gains in performance.  *tracy capture of many_foxes example* To use pipelined rendering, you just need to add the `PipelinedRenderingPlugin`. If you're using `DefaultPlugins` then it will automatically be added for you on all platforms except wasm. Bevy does not currently support multithreading on wasm which is needed for this feature to work. If you aren't using `DefaultPlugins` you can add the plugin manually. ```rust use bevy::prelude::*; use bevy::render::pipelined_rendering::PipelinedRenderingPlugin; fn main() { App::new() // whatever other plugins you need .add_plugin(RenderPlugin) // needs to be added after RenderPlugin .add_plugin(PipelinedRenderingPlugin) .run(); } ``` If for some reason pipelined rendering needs to be removed. You can also disable the plugin the normal way. ```rust use bevy::prelude::*; use bevy::render::pipelined_rendering::PipelinedRenderingPlugin; fn main() { App::new.add_plugins(DefaultPlugins.build().disable::<PipelinedRenderingPlugin>()); } ``` ### A setup function was added to plugins A optional plugin lifecycle function was added to the `Plugin trait`. This function is called after all plugins have been built, but before the app runner is called. This allows for some final setup to be done. In the case of pipelined rendering, the function removes the sub app from the main app and sends it to the render thread. ```rust struct MyPlugin; impl Plugin for MyPlugin { fn build(&self, app: &mut App) { } // optional function fn setup(&self, app: &mut App) { // do some final setup before runner is called } } ``` ### A Stage for Frame Pacing In the `RenderExtractApp` there is a stage labelled `BeforeIoAfterRenderStart` that systems can be added to. The specific use case for this stage is for a frame pacing system that can delay the start of main app processing in render bound apps to reduce input latency i.e. "frame pacing". This is not currently built into bevy, but exists as `bevy` ```text |-------------------------------------------------------------------| | | BeforeIoAfterRenderStart | winit events | main schedule | | extract |---------------------------------------------------------| | | extract commands | rendering schedule | |-------------------------------------------------------------------| ``` ### Small API additions * `Schedule::remove_stage` * `App::insert_sub_app` * `App::remove_sub_app` * `TaskPool::scope_with_executor` ## Problems and Solutions ### Moving render app to another thread Most of the hard bits for this were done with the render redo. This PR just sends the render app back and forth through channels which seems to work ok. I originally experimented with using a scope to run the render task. It was cuter, but that approach didn't allow render to start before i/o processing. So I switched to using channels. There is much complexity in the coordination that needs to be done, but it's worth it. By moving rendering during i/o processing the frame times should be much more consistent in render bound apps. See https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/4691. ### Unsoundness with Sending World with NonSend resources Dropping !Send things on threads other than the thread they were spawned on is considered unsound. The render world doesn't have any nonsend resources. So if we tell the users to "pretty please don't spawn nonsend resource on the render world", we can avoid this problem. More seriously there is this https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/6534 pr, which patches the unsoundness by aborting the app if a nonsend resource is dropped on the wrong thread. ~~That PR should probably be merged before this one.~~ For a longer term solution we have this discussion going https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/discussions/6552. ### NonSend Systems in render world The render world doesn't have any !Send resources, but it does have a non send system. While Window is Send, winit does have some API's that can only be accessed on the main thread. `prepare_windows` in the render schedule thus needs to be scheduled on the main thread. Currently we run nonsend systems by running them on the thread the TaskPool::scope runs on. When we move render to another thread this no longer works. To fix this, a new `scope_with_executor` method was added that takes a optional `TheadExecutor` that can only be ticked on the thread it was initialized on. The render world then holds a `MainThreadExecutor` resource which can be passed to the scope in the parallel executor that it uses to spawn it's non send systems on. ### Scopes executors between render and main should not share tasks Since the render world and the app world share the `ComputeTaskPool`. Because `scope` has executors for the ComputeTaskPool a system from the main world could run on the render thread or a render system could run on the main thread. This can cause performance problems because it can delay a stage from finishing. See https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/6503#issuecomment-1309791442 for more details. To avoid this problem, `TaskPool::scope` has been changed to not tick the ComputeTaskPool when it's used by the parallel executor. In the future when we move closer to the 1 thread to 1 logical core model we may want to overprovide threads, because the render and main app threads don't do much when executing the schedule. ## Performance My machine is Windows 11, AMD Ryzen 5600x, RX 6600 ### Examples #### This PR with pipelining vs Main > Note that these were run on an older version of main and the performance profile has probably changed due to optimizations Seeing a perf gain from 29% on many lights to 7% on many sprites. <html> <body> <!--StartFragment--><google-sheets-html-origin> | percent | | | Diff | | | Main | | | PR | | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- tracy frame time | mean | median | sigma | mean | median | sigma | mean | median | sigma | mean | median | sigma many foxes | 27.01% | 27.34% | -47.09% | 1.58 | 1.55 | -1.78 | 5.85 | 5.67 | 3.78 | 4.27 | 4.12 | 5.56 many lights | 29.35% | 29.94% | -10.84% | 3.02 | 3.03 | -0.57 | 10.29 | 10.12 | 5.26 | 7.27 | 7.09 | 5.83 many animated sprites | 13.97% | 15.69% | 14.20% | 3.79 | 4.17 | 1.41 | 27.12 | 26.57 | 9.93 | 23.33 | 22.4 | 8.52 3d scene | 25.79% | 26.78% | 7.46% | 0.49 | 0.49 | 0.15 | 1.9 | 1.83 | 2.01 | 1.41 | 1.34 | 1.86 many cubes | 11.97% | 11.28% | 14.51% | 1.93 | 1.78 | 1.31 | 16.13 | 15.78 | 9.03 | 14.2 | 14 | 7.72 many sprites | 7.14% | 9.42% | -85.42% | 1.72 | 2.23 | -6.15 | 24.09 | 23.68 | 7.2 | 22.37 | 21.45 | 13.35 <!--EndFragment--> </body> </html> #### This PR with pipelining disabled vs Main Mostly regressions here. I don't think this should be a problem as users that are disabling pipelined rendering are probably running single threaded and not using the parallel executor. The regression is probably mostly due to the switch to use `async_executor::run` instead of `try_tick` and also having one less thread to run systems on. I'll do a writeup on why switching to `run` causes regressions, so we can try to eventually fix it. Using try_tick causes issues when pipeline rendering is enable as seen [here](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/6503#issuecomment-1380803518) <html> <body> <!--StartFragment--><google-sheets-html-origin> | percent | | | Diff | | | Main | | | PR no pipelining | | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- tracy frame time | mean | median | sigma | mean | median | sigma | mean | median | sigma | mean | median | sigma many foxes | -3.72% | -4.42% | -1.07% | -0.21 | -0.24 | -0.04 | 5.64 | 5.43 | 3.74 | 5.85 | 5.67 | 3.78 many lights | 0.29% | -0.30% | 4.75% | 0.03 | -0.03 | 0.25 | 10.29 | 10.12 | 5.26 | 10.26 | 10.15 | 5.01 many animated sprites | 0.22% | 1.81% | -2.72% | 0.06 | 0.48 | -0.27 | 27.12 | 26.57 | 9.93 | 27.06 | 26.09 | 10.2 3d scene | -15.79% | -14.75% | -31.34% | -0.3 | -0.27 | -0.63 | 1.9 | 1.83 | 2.01 | 2.2 | 2.1 | 2.64 many cubes | -2.85% | -3.30% | 0.00% | -0.46 | -0.52 | 0 | 16.13 | 15.78 | 9.03 | 16.59 | 16.3 | 9.03 many sprites | 2.49% | 2.41% | 0.69% | 0.6 | 0.57 | 0.05 | 24.09 | 23.68 | 7.2 | 23.49 | 23.11 | 7.15 <!--EndFragment--> </body> </html> ### Benchmarks Mostly the same except empty_systems has got a touch slower. The maybe_pipelining+1 column has the compute task pool with an extra thread over default added. This is because pipelining loses one thread over main to execute systems on, since the main thread no longer runs normal systems. <details> <summary>Click Me</summary> ```text group main maybe-pipelining+1 ----- ------------------------- ------------------ busy_systems/01x_entities_03_systems 1.07 30.7±1.32µs ? ?/sec 1.00 28.6±1.35µs ? ?/sec busy_systems/01x_entities_06_systems 1.10 52.1±1.10µs ? ?/sec 1.00 47.2±1.08µs ? ?/sec busy_systems/01x_entities_09_systems 1.00 74.6±1.36µs ? ?/sec 1.00 75.0±1.93µs ? ?/sec busy_systems/01x_entities_12_systems 1.03 100.6±6.68µs ? ?/sec 1.00 98.0±1.46µs ? ?/sec busy_systems/01x_entities_15_systems 1.11 128.5±3.53µs ? ?/sec 1.00 115.5±1.02µs ? ?/sec busy_systems/02x_entities_03_systems 1.16 50.4±2.56µs ? ?/sec 1.00 43.5±3.00µs ? ?/sec busy_systems/02x_entities_06_systems 1.00 87.1±1.27µs ? ?/sec 1.05 91.5±7.15µs ? ?/sec busy_systems/02x_entities_09_systems 1.04 139.9±6.37µs ? ?/sec 1.00 134.0±1.06µs ? ?/sec busy_systems/02x_entities_12_systems 1.05 179.2±3.47µs ? ?/sec 1.00 170.1±3.17µs ? ?/sec busy_systems/02x_entities_15_systems 1.01 219.6±3.75µs ? ?/sec 1.00 218.1±2.55µs ? ?/sec busy_systems/03x_entities_03_systems 1.10 70.6±2.33µs ? ?/sec 1.00 64.3±0.69µs ? ?/sec busy_systems/03x_entities_06_systems 1.02 130.2±3.11µs ? ?/sec 1.00 128.0±1.34µs ? ?/sec busy_systems/03x_entities_09_systems 1.00 195.0±10.11µs ? ?/sec 1.00 194.8±1.41µs ? ?/sec busy_systems/03x_entities_12_systems 1.01 261.7±4.05µs ? ?/sec 1.00 259.8±4.11µs ? ?/sec busy_systems/03x_entities_15_systems 1.00 318.0±3.04µs ? ?/sec 1.06 338.3±20.25µs ? ?/sec busy_systems/04x_entities_03_systems 1.00 82.9±0.63µs ? ?/sec 1.02 84.3±0.63µs ? ?/sec busy_systems/04x_entities_06_systems 1.01 181.7±3.65µs ? ?/sec 1.00 179.8±1.76µs ? ?/sec busy_systems/04x_entities_09_systems 1.04 265.0±4.68µs ? ?/sec 1.00 255.3±1.98µs ? ?/sec busy_systems/04x_entities_12_systems 1.00 335.9±3.00µs ? ?/sec 1.05 352.6±15.84µs ? ?/sec busy_systems/04x_entities_15_systems 1.00 418.6±10.26µs ? ?/sec 1.08 450.2±39.58µs ? ?/sec busy_systems/05x_entities_03_systems 1.07 114.3±0.95µs ? ?/sec 1.00 106.9±1.52µs ? ?/sec busy_systems/05x_entities_06_systems 1.08 229.8±2.90µs ? ?/sec 1.00 212.3±4.18µs ? ?/sec busy_systems/05x_entities_09_systems 1.03 329.3±1.99µs ? ?/sec 1.00 319.2±2.43µs ? ?/sec busy_systems/05x_entities_12_systems 1.06 454.7±6.77µs ? ?/sec 1.00 430.1±3.58µs ? ?/sec busy_systems/05x_entities_15_systems 1.03 554.6±6.15µs ? ?/sec 1.00 538.4±23.87µs ? ?/sec contrived/01x_entities_03_systems 1.00 14.0±0.15µs ? ?/sec 1.08 15.1±0.21µs ? ?/sec contrived/01x_entities_06_systems 1.04 28.5±0.37µs ? ?/sec 1.00 27.4±0.44µs ? ?/sec contrived/01x_entities_09_systems 1.00 41.5±4.38µs ? ?/sec 1.02 42.2±2.24µs ? ?/sec contrived/01x_entities_12_systems 1.06 55.9±1.49µs ? ?/sec 1.00 52.6±1.36µs ? ?/sec contrived/01x_entities_15_systems 1.02 68.0±2.00µs ? ?/sec 1.00 66.5±0.78µs ? ?/sec contrived/02x_entities_03_systems 1.03 25.2±0.38µs ? ?/sec 1.00 24.6±0.52µs ? ?/sec contrived/02x_entities_06_systems 1.00 46.3±0.49µs ? ?/sec 1.04 48.1±4.13µs ? ?/sec contrived/02x_entities_09_systems 1.02 70.4±0.99µs ? ?/sec 1.00 68.8±1.04µs ? ?/sec contrived/02x_entities_12_systems 1.06 96.8±1.49µs ? ?/sec 1.00 91.5±0.93µs ? ?/sec contrived/02x_entities_15_systems 1.02 116.2±0.95µs ? ?/sec 1.00 114.2±1.42µs ? ?/sec contrived/03x_entities_03_systems 1.00 33.2±0.38µs ? ?/sec 1.01 33.6±0.45µs ? ?/sec contrived/03x_entities_06_systems 1.00 62.4±0.73µs ? ?/sec 1.01 63.3±1.05µs ? ?/sec contrived/03x_entities_09_systems 1.02 96.4±0.85µs ? ?/sec 1.00 94.8±3.02µs ? ?/sec contrived/03x_entities_12_systems 1.01 126.3±4.67µs ? ?/sec 1.00 125.6±2.27µs ? ?/sec contrived/03x_entities_15_systems 1.03 160.2±9.37µs ? ?/sec 1.00 156.0±1.53µs ? ?/sec contrived/04x_entities_03_systems 1.02 41.4±3.39µs ? ?/sec 1.00 40.5±0.52µs ? ?/sec contrived/04x_entities_06_systems 1.00 78.9±1.61µs ? ?/sec 1.02 80.3±1.06µs ? ?/sec contrived/04x_entities_09_systems 1.02 121.8±3.97µs ? ?/sec 1.00 119.2±1.46µs ? ?/sec contrived/04x_entities_12_systems 1.00 157.8±1.48µs ? ?/sec 1.01 160.1±1.72µs ? ?/sec contrived/04x_entities_15_systems 1.00 197.9±1.47µs ? ?/sec 1.08 214.2±34.61µs ? ?/sec contrived/05x_entities_03_systems 1.00 49.1±0.33µs ? ?/sec 1.01 49.7±0.75µs ? ?/sec contrived/05x_entities_06_systems 1.00 95.0±0.93µs ? ?/sec 1.00 94.6±0.94µs ? ?/sec contrived/05x_entities_09_systems 1.01 143.2±1.68µs ? ?/sec 1.00 142.2±2.00µs ? ?/sec contrived/05x_entities_12_systems 1.00 191.8±2.03µs ? ?/sec 1.01 192.7±7.88µs ? ?/sec contrived/05x_entities_15_systems 1.02 239.7±3.71µs ? ?/sec 1.00 235.8±4.11µs ? ?/sec empty_systems/000_systems 1.01 47.8±0.67ns ? ?/sec 1.00 47.5±2.02ns ? ?/sec empty_systems/001_systems 1.00 1743.2±126.14ns ? ?/sec 1.01 1761.1±70.10ns ? ?/sec empty_systems/002_systems 1.01 2.2±0.04µs ? ?/sec 1.00 2.2±0.02µs ? ?/sec empty_systems/003_systems 1.02 2.7±0.09µs ? ?/sec 1.00 2.7±0.16µs ? ?/sec empty_systems/004_systems 1.00 3.1±0.11µs ? ?/sec 1.00 3.1±0.24µs ? ?/sec empty_systems/005_systems 1.00 3.5±0.05µs ? ?/sec 1.11 3.9±0.70µs ? ?/sec empty_systems/010_systems 1.00 5.5±0.12µs ? ?/sec 1.03 5.7±0.17µs ? ?/sec empty_systems/015_systems 1.00 7.9±0.19µs ? ?/sec 1.06 8.4±0.16µs ? ?/sec empty_systems/020_systems 1.00 10.4±1.25µs ? ?/sec 1.02 10.6±0.18µs ? ?/sec empty_systems/025_systems 1.00 12.4±0.39µs ? ?/sec 1.14 14.1±1.07µs ? ?/sec empty_systems/030_systems 1.00 15.1±0.39µs ? ?/sec 1.05 15.8±0.62µs ? ?/sec empty_systems/035_systems 1.00 16.9±0.47µs ? ?/sec 1.07 18.0±0.37µs ? ?/sec empty_systems/040_systems 1.00 19.3±0.41µs ? ?/sec 1.05 20.3±0.39µs ? ?/sec empty_systems/045_systems 1.00 22.4±1.67µs ? ?/sec 1.02 22.9±0.51µs ? ?/sec empty_systems/050_systems 1.00 24.4±1.67µs ? ?/sec 1.01 24.7±0.40µs ? ?/sec empty_systems/055_systems 1.05 28.6±5.27µs ? ?/sec 1.00 27.2±0.70µs ? ?/sec empty_systems/060_systems 1.02 29.9±1.64µs ? ?/sec 1.00 29.3±0.66µs ? ?/sec empty_systems/065_systems 1.02 32.7±3.15µs ? ?/sec 1.00 32.1±0.98µs ? ?/sec empty_systems/070_systems 1.00 33.0±1.42µs ? ?/sec 1.03 34.1±1.44µs ? ?/sec empty_systems/075_systems 1.00 34.8±0.89µs ? ?/sec 1.04 36.2±0.70µs ? ?/sec empty_systems/080_systems 1.00 37.0±1.82µs ? ?/sec 1.05 38.7±1.37µs ? ?/sec empty_systems/085_systems 1.00 38.7±0.76µs ? ?/sec 1.05 40.8±0.83µs ? ?/sec empty_systems/090_systems 1.00 41.5±1.09µs ? ?/sec 1.04 43.2±0.82µs ? ?/sec empty_systems/095_systems 1.00 43.6±1.10µs ? ?/sec 1.04 45.2±0.99µs ? ?/sec empty_systems/100_systems 1.00 46.7±2.27µs ? ?/sec 1.03 48.1±1.25µs ? ?/sec ``` </details> ## Migration Guide ### App `runner` and SubApp `extract` functions are now required to be Send This was changed to enable pipelined rendering. If this breaks your use case please report it as these new bounds might be able to be relaxed. ## ToDo * [x] redo benchmarking * [x] reinvestigate the perf of the try_tick -> run change for task pool scope |
||
|
|
ddfafab971 |
Windows as Entities (#5589)
# Objective Fix https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/4530 - Make it easier to open/close/modify windows by setting them up as `Entity`s with a `Window` component. - Make multiple windows very simple to set up. (just add a `Window` component to an entity and it should open) ## Solution - Move all properties of window descriptor to ~components~ a component. - Replace `WindowId` with `Entity`. - ~Use change detection for components to update backend rather than events/commands. (The `CursorMoved`/`WindowResized`/... events are kept for user convenience.~ Check each field individually to see what we need to update, events are still kept for user convenience. --- ## Changelog - `WindowDescriptor` renamed to `Window`. - Width/height consolidated into a `WindowResolution` component. - Requesting maximization/minimization is done on the [`Window::state`] field. - `WindowId` is now `Entity`. ## Migration Guide - Replace `WindowDescriptor` with `Window`. - Change `width` and `height` fields in a `WindowResolution`, either by doing ```rust WindowResolution::new(width, height) // Explicitly // or using From<_> for tuples for convenience (1920., 1080.).into() ``` - Replace any `WindowCommand` code to just modify the `Window`'s fields directly and creating/closing windows is now by spawning/despawning an entity with a `Window` component like so: ```rust let window = commands.spawn(Window { ... }).id(); // open window commands.entity(window).despawn(); // close window ``` ## Unresolved - ~How do we tell when a window is minimized by a user?~ ~Currently using the `Resize(0, 0)` as an indicator of minimization.~ No longer attempting to tell given how finnicky this was across platforms, now the user can only request that a window be maximized/minimized. ## Future work - Move `exit_on_close` functionality out from windowing and into app(?) - https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/5621 - https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/7099 - https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/7098 Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com> |
||
|
|
517deda215 |
Make PipelineCache internally mutable. (#7205)
# Objective - Allow rendering queue systems to use a `Res<PipelineCache>` even for queueing up new rendering pipelines. This is part of unblocking parallel execution queue systems. ## Solution - Make `PipelineCache` internally mutable w.r.t to queueing new pipelines. Pipelines are no longer immediately updated into the cache state, but rather queued into a Vec. The Vec of pending new pipelines is then later processed at the same time we actually create the queued pipelines on the GPU device. --- ## Changelog `PipelineCache` no longer requires mutable access in order to queue render / compute pipelines. ## Migration Guide * Most usages of `resource_mut::<PipelineCache>` and `ResMut<PipelineCache>` can be changed to `resource::<PipelineCache>` and `Res<PipelineCache>` as long as they don't use any methods requiring mutability - the only public method requiring it is `process_queue`. |
||
|
|
76de9f9407 |
Improve render phase documentation (#7016)
# Objective The documentation of the bevy_render crate is still pretty incomplete. This PR follows up on #6885 and improves the documentation of the `render_phase` module. This module contains one of our most important rendering abstractions and the current documentation is pretty confusing. This PR tries to clarify what all of these pieces are for and how they work together to form bevy`s modular rendering logic. ## Solution ### Code Reformating - I have moved the `rangefinder` into the `render_phase` module since it is only used there. - I have moved the `PhaseItem` (and the `BatchedPhaseItem`) from `render_phase::draw` over to `render_phase::mod`. This does not change the public-facing API since they are reexported anyway, but this change makes the relation between `RenderPhase` and `PhaseItem` clear and easier to discover. ### Documentation - revised all documentation in the `render_phase` module - added a module-level explanation of how `RenderPhase`s, `RenderPass`es, `PhaseItem`s, `Draw` functions, and `RenderCommands` relate to each other and how they are used --- ## Changelog - The `rangefinder` module has been moved into the `render_phase` module. ## Migration Guide - The `rangefinder` module has been moved into the `render_phase` module. ```rust //old use bevy::render::rangefinder::*; // new use bevy::render::render_phase::rangefinder::*; ``` |
||
|
|
d76b53bf4d |
Separate Extract from Sub App Schedule (#7046)
# Objective
- This pulls out some of the changes to Plugin setup and sub apps from #6503 to make that PR easier to review.
- Separate the extract stage from running the sub app's schedule to allow for them to be run on separate threads in the future
- Fixes #6990
## Solution
- add a run method to `SubApp` that runs the schedule
- change the name of `sub_app_runner` to extract to make it clear that this function is only for extracting data between the main app and the sub app
- remove the extract stage from the sub app schedule so it can be run separately. This is done by adding a `setup` method to the `Plugin` trait that runs after all plugin build methods run. This is required to allow the extract stage to be removed from the schedule after all the plugins have added their systems to the stage. We will also need the setup method for pipelined rendering to setup the render thread. See
|
||
|
|
15b19b930c |
Move 'startup' Resource WgpuSettings into the RenderPlugin (#6946)
# Objective
The `WgpuSettings` resource is only used during plugin build. Move it into the `RenderPlugin` struct.
Changing these settings requires re-initializing the render context, which is currently not supported.
If it is supported in the future it should probably be more explicit than changing a field on a resource, maybe something similar to the `CreateWindow` event.
## Migration Guide
```rust
// Before (0.9)
App::new()
.insert_resource(WgpuSettings { .. })
.add_plugins(DefaultPlugins)
// After (0.10)
App::new()
.add_plugins(DefaultPlugins.set(RenderPlugin {
wgpu_settings: WgpuSettings { .. },
}))
```
Co-authored-by: devil-ira <justthecooldude@gmail.com>
|
||
|
|
bd615cbf8c |
Shrink DrawFunctionId (#6944)
# Objective This includes one part of #4899. The aim is to improve CPU-side rendering performance by reducing the memory footprint and bandwidth required. ## Solution Shrink `DrawFunctionId` to `u32`. Enforce that `u32 as usize` conversions are always safe by forbidding compilation on 16-bit platforms. This shouldn't be a breaking change since #4736 disabled compilation of `bevy_ecs` on those platforms. Shrinking `DrawFunctionId` shrinks all of the `PhaseItem` types, which is integral to sort and render phase performance. Testing against `many_cubes`, the sort phase improved by 22% (174.21us -> 141.76us per frame). 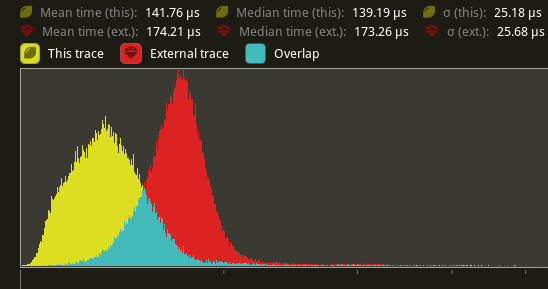 The main opaque pass also imrproved by 9% (5.49ms -> 5.03ms) 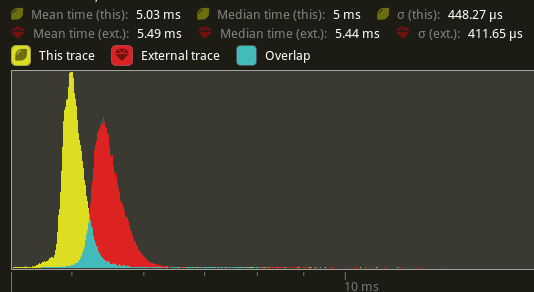 Overall frame time improved by 5% (14.85ms -> 14.09ms) 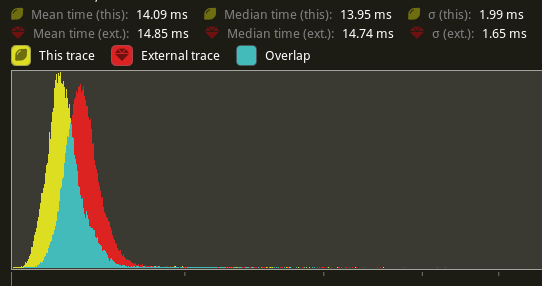 There will be a followup PR that likewise shrinks `CachedRenderPipelineId` which should yield similar results on top of these improvements. |
||
|
|
e954b8573c |
Lock down access to Entities (#6740)
# Objective The soundness of the ECS `World` partially relies on the correctness of the state of `Entities` stored within it. We're currently allowing users to (unsafely) mutate it, as well as readily construct it without using a `World`. While this is not strictly unsound so long as users (including `bevy_render`) safely use the APIs, it's a fairly easy path to unsoundness without much of a guard rail. Addresses #3362 for `bevy_ecs::entity`. Incorporates the changes from #3985. ## Solution Remove `Entities`'s `Default` implementation and force access to the type to only be through a properly constructed `World`. Additional cleanup for other parts of `bevy_ecs::entity`: - `Entity::index` and `Entity::generation` are no longer `pub(crate)`, opting to force the rest of bevy_ecs to use the public interface to access these values. - `EntityMeta` is no longer `pub` and also not `pub(crate)` to attempt to cut down on updating `generation` without going through an `Entities` API. It's currently inaccessible except via the `pub(crate)` Vec on `Entities`, there was no way for an outside user to use it. - Added `Entities::set`, an unsafe `pub(crate)` API for setting the location of an Entity (parallel to `Entities::get`) that replaces the internal case where we need to set the location of an entity when it's been spawned, moved, or despawned. - `Entities::alloc_at_without_replacement` is only used in `World::get_or_spawn` within the first party crates, and I cannot find a public use of this API in any ecosystem crate that I've checked (via GitHub search). - Attempted to document the few remaining undocumented public APIs in the module. --- ## Changelog Removed: `Entities`'s `Default` implementation. Removed: `EntityMeta` Removed: `Entities::alloc_at_without_replacement` and `AllocAtWithoutReplacement`. Co-authored-by: james7132 <contact@jamessliu.com> Co-authored-by: James Liu <contact@jamessliu.com> |
||
|
|
3827316100 |
bevy_reflect: Register missing reflected types for bevy_render (#6725)
# Objective Many types in `bevy_render` implemented `Reflect` but were not registered. ## Solution Register all types in `bevy_render` that impl `Reflect`. This also registers additional dependent types (i.e. field types). > Note: Adding these dependent types would not be needed using something like #5781 😉 --- ## Changelog - Register missing `bevy_render` types in the `TypeRegistry`: - `camera::RenderTarget` - `globals::GlobalsUniform` - `texture::Image` - `view::ComputedVisibility` - `view::Visibility` - `view::VisibleEntities` - Register additional dependent types: - `view::ComputedVisibilityFlags` - `Vec<Entity>` |
||
|
|
ed2ea0d417 |
The update_frame_count system should be placed in CorePlugin (#6676)
# Objective Latest Release, "bevy 0.9" move the FrameCount updater into RenderPlugin, it leads to user who only run app with Core/Minimal Plugin cannot get the right number of FrameCount, it always return 0. As for use cases like a server app, we don't want to add render dependencies to the app. More detail in #6656 ## Solution - Move the `update_frame_count` into CorePlugin |
||
|
|
334e09892b |
Revert "Show prelude re-exports in docs (#6448)" (#6449)
This reverts commit
|
||
|
|
53d387f340 |
Show prelude re-exports in docs (#6448)
# Objective - Right now re-exports are completely hidden in prelude docs. - Fixes #6433 ## Solution - We could show the re-exports without inlining their documentation. |
||
|
|
4d3d3c869e |
Support arbitrary RenderTarget texture formats (#6380)
# Objective Currently, Bevy only supports rendering to the current "surface texture format". This means that "render to texture" scenarios must use the exact format the primary window's surface uses, or Bevy will crash. This is even harder than it used to be now that we detect preferred surface formats at runtime instead of using hard coded BevyDefault values. ## Solution 1. Look up and store each window surface's texture format alongside other extracted window information 2. Specialize the upscaling pass on the current `RenderTarget`'s texture format, now that we can cheaply correlate render targets to their current texture format 3. Remove the old `SurfaceTextureFormat` and `AvailableTextureFormats`: these are now redundant with the information stored on each extracted window, and probably should not have been globals in the first place (as in theory each surface could have a different format). This means you can now use any texture format you want when rendering to a texture! For example, changing the `render_to_texture` example to use `R16Float` now doesn't crash / properly only stores the red component:  |
||
|
|
838b318863 |
separate tonemapping and upscaling passes (#3425)
Attempt to make features like bloom https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/2876 easier to implement. **This PR:** - Moves the tonemapping from `pbr.wgsl` into a separate pass - also add a separate upscaling pass after the tonemapping which writes to the swap chain (enables resolution-independant rendering and post-processing after tonemapping) - adds a `hdr` bool to the camera which controls whether the pbr and sprite shaders render into a `Rgba16Float` texture **Open questions:** - ~should the 2d graph work the same as the 3d one?~ it is the same now - ~The current solution is a bit inflexible because while you can add a post processing pass that writes to e.g. the `hdr_texture`, you can't write to a separate `user_postprocess_texture` while reading the `hdr_texture` and tell the tone mapping pass to read from the `user_postprocess_texture` instead. If the tonemapping and upscaling render graph nodes were to take in a `TextureView` instead of the view entity this would almost work, but the bind groups for their respective input textures are already created in the `Queue` render stage in the hardcoded order.~ solved by creating bind groups in render node **New render graph:** 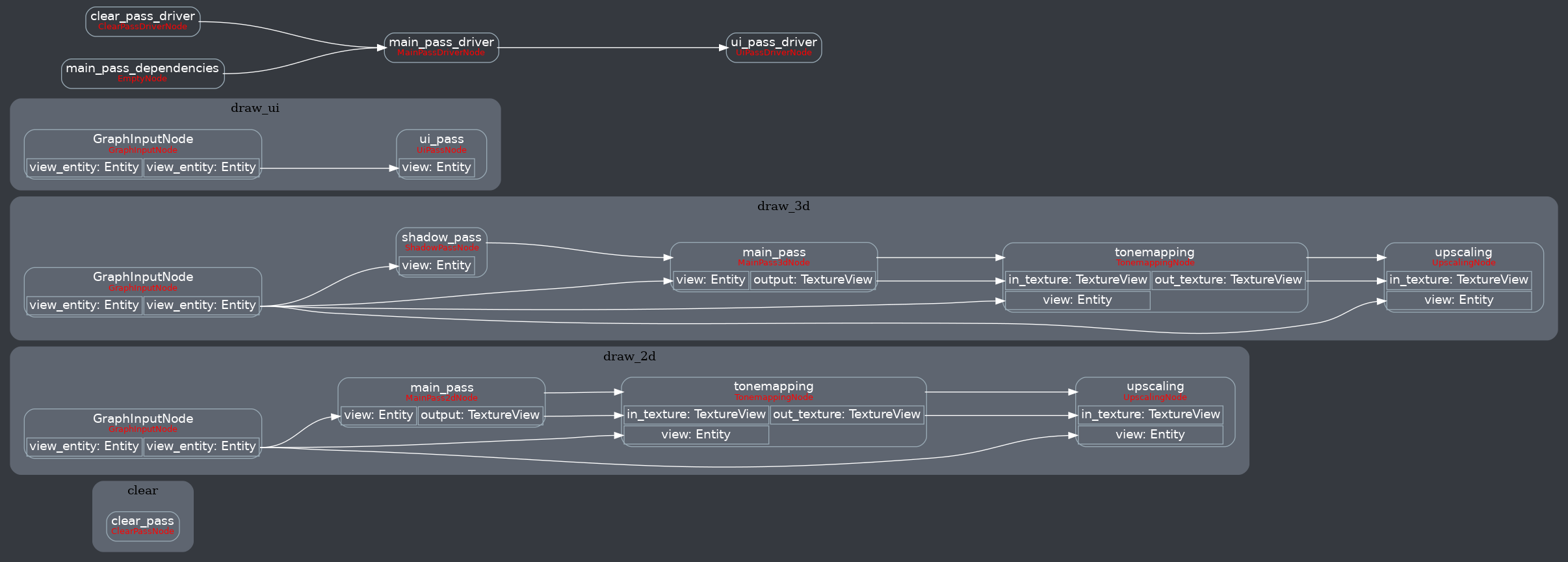 <details> <summary>Before</summary> 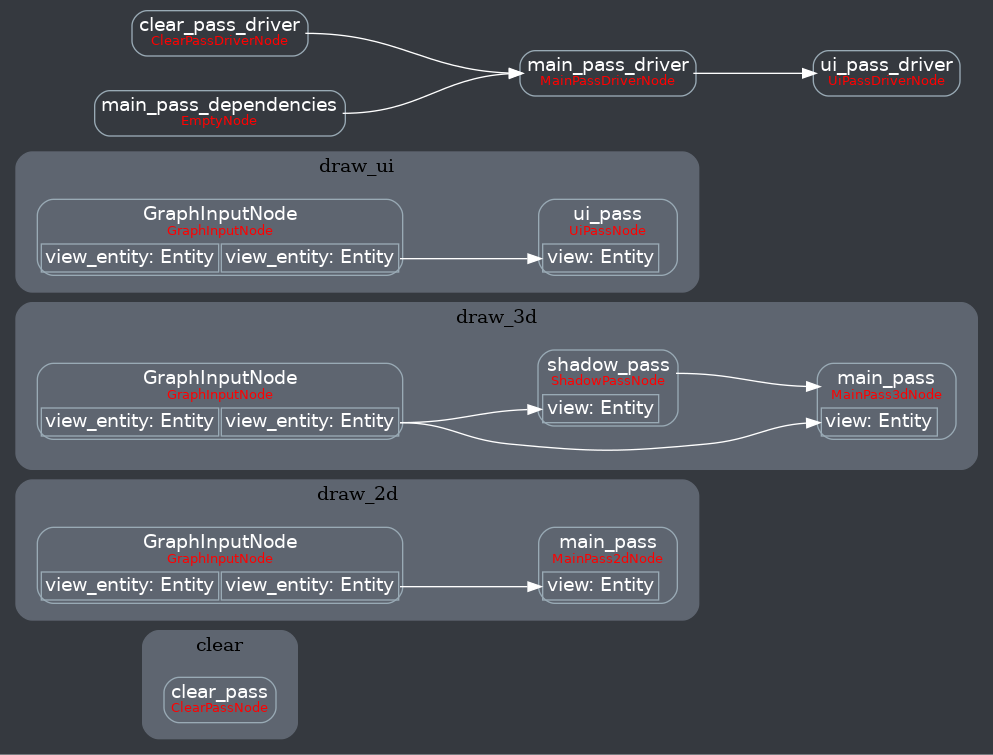 </details> Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com> |
||
|
|
5622d56be1 |
Use plugin setup for resource only used at setup time (#6360)
# Objective - Build on #6336 for more plugin configurations ## Solution - `LogSettings`, `ImageSettings` and `DefaultTaskPoolOptions` are now plugins settings rather than resources --- ## Changelog - `LogSettings` plugin settings have been move to `LogPlugin`, `ImageSettings` to `ImagePlugin` and `DefaultTaskPoolOptions` to `CorePlugin` ## Migration Guide The `LogSettings` settings have been moved from a resource to `LogPlugin` configuration: ```rust // Old (Bevy 0.8) app .insert_resource(LogSettings { level: Level::DEBUG, filter: "wgpu=error,bevy_render=info,bevy_ecs=trace".to_string(), }) .add_plugins(DefaultPlugins) // New (Bevy 0.9) app.add_plugins(DefaultPlugins.set(LogPlugin { level: Level::DEBUG, filter: "wgpu=error,bevy_render=info,bevy_ecs=trace".to_string(), })) ``` The `ImageSettings` settings have been moved from a resource to `ImagePlugin` configuration: ```rust // Old (Bevy 0.8) app .insert_resource(ImageSettings::default_nearest()) .add_plugins(DefaultPlugins) // New (Bevy 0.9) app.add_plugins(DefaultPlugins.set(ImagePlugin::default_nearest())) ``` The `DefaultTaskPoolOptions` settings have been moved from a resource to `CorePlugin::task_pool_options`: ```rust // Old (Bevy 0.8) app .insert_resource(DefaultTaskPoolOptions::with_num_threads(4)) .add_plugins(DefaultPlugins) // New (Bevy 0.9) app.add_plugins(DefaultPlugins.set(CorePlugin { task_pool_options: TaskPoolOptions::with_num_threads(4), })) ``` |
||
|
|
3c13c75036 |
Optimize rendering slow-down at high entity counts (#5509)
# Objective - Improve #3953 ## Solution - The very specific circumstances under which the render world is reset meant that the flush_as_invalid function could be replaced with one that had a noop as its init method. - This removes a double-writing issue leading to greatly increased performance. Running the reproduction code in the linked issue, this change nearly doubles the framerate. Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com> |
||
|
|
c313e21d65 |
Update wgpu to 0.14.0, naga to 0.10.0, winit to 0.27.4, raw-window-handle to 0.5.0, ndk to 0.7 (#6218)
# Objective - Update `wgpu` to 0.14.0, `naga` to `0.10.0`, `winit` to 0.27.4, `raw-window-handle` to 0.5.0, `ndk` to 0.7. ## Solution --- ## Changelog ### Changed - Changed `RawWindowHandleWrapper` to `RawHandleWrapper` which wraps both `RawWindowHandle` and `RawDisplayHandle`, which satisfies the `impl HasRawWindowHandle and HasRawDisplayHandle` that `wgpu` 0.14.0 requires. - Changed `bevy_window::WindowDescriptor`'s `cursor_locked` to `cursor_grab_mode`, change its type from `bool` to `bevy_window::CursorGrabMode`. ## Migration Guide - Adjust usage of `bevy_window::WindowDescriptor`'s `cursor_locked` to `cursor_grab_mode`, and adjust its type from `bool` to `bevy_window::CursorGrabMode`. |
||
|
|
b840ba3eaf |
Tidy up surface creation in RenderPlugin (#6276)
# Objective Tidy up a bit |
||
|
|
964b047466 |
Make raw_window_handle field in Window and ExtractedWindow an Option. (#6114)
# Objective - Trying to make it possible to do write tests that don't require a raw window handle. - Fixes https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/6106. ## Solution - Make the interface and type changes. Avoid accessing `None`. --- ## Changelog - Converted `raw_window_handle` field in both `Window` and `ExtractedWindow` to `Option<RawWindowHandleWrapper>`. - Revised accessor function `Window::raw_window_handle()` to return `Option<RawWindowHandleWrapper>`. - Skip conditions in loops that would require a raw window handle (to create a `Surface`, for example). ## Migration Guide `Window::raw_window_handle()` now returns `Option<RawWindowHandleWrapper>`. Co-authored-by: targrub <62773321+targrub@users.noreply.github.com> |
||
|
|
13dcdba05f |
use bevy default texture format if the surface is not yet available (#6233)
# Objective - Fix #6231 ## Solution - In case no supported format is found, try to use Bevy default instead of panicking |
||
|
|
f5322cd757 |
get proper texture format after the renderer is initialized, fix #3897 (#5413)
# Objective There is no Srgb support on some GPU and display protocols with `winit` (for example, Nvidia's GPUs with Wayland). Thus `TextureFormat::bevy_default()` which returns `Rgba8UnormSrgb` or `Bgra8UnormSrgb` will cause panics on such platforms. This patch will resolve this problem. Fix https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/3897. ## Solution Make `initialize_renderer` expose `wgpu::Adapter` and `first_available_texture_format`, use the `first_available_texture_format` by default. ## Changelog * Fixed https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/3897. |
||
|
|
8073362039 |
add globals to mesh view bind group (#5409)
# Objective - It's often really useful to have access to the time when writing shaders. ## Solution - Add a UnifformBuffer in the mesh view bind group - This buffer contains the time, delta time and a wrapping frame count https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/8348954/180130314-97948c2a-2d11-423d-a9c4-fb5c9d1892c7.mp4 --- ## Changelog - Added a `GlobalsUniform` at position 9 of the mesh view bind group ## Notes The implementation is currently split between bevy_render and bevy_pbr because I was basing my implementation on the `ViewPlugin`. I'm not sure if that's the right way to structure it. I named this `globals` instead of just time because we could potentially add more things to it. ## References in other engines - Godot: <https://docs.godotengine.org/en/stable/tutorials/shaders/shader_reference/canvas_item_shader.html#global-built-ins> - Global time since startup, in seconds, by default resets to 0 after 3600 seconds - Doesn't seem to have anything else - Unreal: <https://docs.unrealengine.com/4.26/en-US/RenderingAndGraphics/Materials/ExpressionReference/Constant/> - Generic time value that updates every frame. Can be paused or scaled. - Frame count node, doesn't seem to be an equivalent for shaders: <https://docs.unrealengine.com/4.26/en-US/BlueprintAPI/Utilities/GetFrameCount/> - Unity: <https://docs.unity3d.com/Manual/SL-UnityShaderVariables.html> - time since startup in seconds. No mention of time wrapping. Stored as a `vec4(t/20, t, t*2, t*3)` where `t` is the value in seconds - Also has delta time, sin time and cos time - ShaderToy: <https://www.shadertoy.com/howto> - iTime is the time since startup in seconds. - iFrameRate - iTimeDelta - iFrame frame counter Co-authored-by: Charles <IceSentry@users.noreply.github.com> |
||
|
|
dc3f801239 |
Exclusive Systems Now Implement System. Flexible Exclusive System Params (#6083)
# Objective The [Stageless RFC](https://github.com/bevyengine/rfcs/pull/45) involves allowing exclusive systems to be referenced and ordered relative to parallel systems. We've agreed that unifying systems under `System` is the right move. This is an alternative to #4166 (see rationale in the comments I left there). Note that this builds on the learnings established there (and borrows some patterns). ## Solution This unifies parallel and exclusive systems under the shared `System` trait, removing the old `ExclusiveSystem` trait / impls. This is accomplished by adding a new `ExclusiveFunctionSystem` impl similar to `FunctionSystem`. It is backed by `ExclusiveSystemParam`, which is similar to `SystemParam`. There is a new flattened out SystemContainer api (which cuts out a lot of trait and type complexity). This means you can remove all cases of `exclusive_system()`: ```rust // before commands.add_system(some_system.exclusive_system()); // after commands.add_system(some_system); ``` I've also implemented `ExclusiveSystemParam` for `&mut QueryState` and `&mut SystemState`, which makes this possible in exclusive systems: ```rust fn some_exclusive_system( world: &mut World, transforms: &mut QueryState<&Transform>, state: &mut SystemState<(Res<Time>, Query<&Player>)>, ) { for transform in transforms.iter(world) { println!("{transform:?}"); } let (time, players) = state.get(world); for player in players.iter() { println!("{player:?}"); } } ``` Note that "exclusive function systems" assume `&mut World` is present (and the first param). I think this is a fair assumption, given that the presence of `&mut World` is what defines the need for an exclusive system. I added some targeted SystemParam `static` constraints, which removed the need for this: ``` rust fn some_exclusive_system(state: &mut SystemState<(Res<'static, Time>, Query<&'static Player>)>) {} ``` ## Related - #2923 - #3001 - #3946 ## Changelog - `ExclusiveSystem` trait (and implementations) has been removed in favor of sharing the `System` trait. - `ExclusiveFunctionSystem` and `ExclusiveSystemParam` were added, enabling flexible exclusive function systems - `&mut SystemState` and `&mut QueryState` now implement `ExclusiveSystemParam` - Exclusive and parallel System configuration is now done via a unified `SystemDescriptor`, `IntoSystemDescriptor`, and `SystemContainer` api. ## Migration Guide Calling `.exclusive_system()` is no longer required (or supported) for converting exclusive system functions to exclusive systems: ```rust // Old (0.8) app.add_system(some_exclusive_system.exclusive_system()); // New (0.9) app.add_system(some_exclusive_system); ``` Converting "normal" parallel systems to exclusive systems is done by calling the exclusive ordering apis: ```rust // Old (0.8) app.add_system(some_system.exclusive_system().at_end()); // New (0.9) app.add_system(some_system.at_end()); ``` Query state in exclusive systems can now be cached via ExclusiveSystemParams, which should be preferred for clarity and performance reasons: ```rust // Old (0.8) fn some_system(world: &mut World) { let mut transforms = world.query::<&Transform>(); for transform in transforms.iter(world) { } } // New (0.9) fn some_system(world: &mut World, transforms: &mut QueryState<&Transform>) { for transform in transforms.iter(world) { } } ``` |
||
|
|
6c5403cf47 |
Add warning when a hierarchy component is missing (#5590)
# Objective A common pitfall since 0.8 is the requirement on `ComputedVisibility` being present on all ancestors of an entity that itself has `ComputedVisibility`, without which, the entity becomes invisible. I myself hit the issue and got very confused, and saw a few people hit it as well, so it makes sense to provide a hint of what to do when such a situation is encountered. - Fixes #5849 - Closes #5616 - Closes #2277 - Closes #5081 ## Solution We now check that all entities with both a `Parent` and a `ComputedVisibility` component have parents that themselves have a `ComputedVisibility` component. Note that the warning is only printed once. We also add a similar warning to `GlobalTransform`. This only emits a warning. Because sometimes it could be an intended behavior. Alternatives: - Do nothing and keep repeating to newcomers how to avoid recurring pitfalls - Make the transform and visibility propagation tolerant to missing components (#5616) - Probably archetype invariants, though the current draft would not allow detecting that kind of errors --- ## Changelog - Add a warning when encountering dubious component hierarchy structure Co-authored-by: Nicola Papale <nicopap@users.noreply.github.com> |
||
|
|
3221e569e0 |
Remove an outdated workaround for impl Trait (#5659)
# Objective Rust 1.63 resolved [an issue](https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/83701) that prevents you from combining explicit generic arguments with `impl Trait` arguments. Now, we no longer need to use dynamic dispatch to work around this. ## Migration Guide The methods `Schedule::get_stage` and `get_stage_mut` now accept `impl StageLabel` instead of `&dyn StageLabel`. ### Before ```rust let stage = schedule.get_stage_mut::<SystemStage>(&MyLabel)?; ``` ### After ```rust let stage = schedule.get_stage_mut::<SystemStage>(MyLabel)?; ``` |
||
|
|
992681b59b |
Make Resource trait opt-in, requiring #[derive(Resource)] V2 (#5577)
*This PR description is an edited copy of #5007, written by @alice-i-cecile.* # Objective Follow-up to https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/2254. The `Resource` trait currently has a blanket implementation for all types that meet its bounds. While ergonomic, this results in several drawbacks: * it is possible to make confusing, silent mistakes such as inserting a function pointer (Foo) rather than a value (Foo::Bar) as a resource * it is challenging to discover if a type is intended to be used as a resource * we cannot later add customization options (see the [RFC](https://github.com/bevyengine/rfcs/blob/main/rfcs/27-derive-component.md) for the equivalent choice for Component). * dependencies can use the same Rust type as a resource in invisibly conflicting ways * raw Rust types used as resources cannot preserve privacy appropriately, as anyone able to access that type can read and write to internal values * we cannot capture a definitive list of possible resources to display to users in an editor ## Notes to reviewers * Review this commit-by-commit; there's effectively no back-tracking and there's a lot of churn in some of these commits. *ira: My commits are not as well organized :')* * I've relaxed the bound on Local to Send + Sync + 'static: I don't think these concerns apply there, so this can keep things simple. Storing e.g. a u32 in a Local is fine, because there's a variable name attached explaining what it does. * I think this is a bad place for the Resource trait to live, but I've left it in place to make reviewing easier. IMO that's best tackled with https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/4981. ## Changelog `Resource` is no longer automatically implemented for all matching types. Instead, use the new `#[derive(Resource)]` macro. ## Migration Guide Add `#[derive(Resource)]` to all types you are using as a resource. If you are using a third party type as a resource, wrap it in a tuple struct to bypass orphan rules. Consider deriving `Deref` and `DerefMut` to improve ergonomics. `ClearColor` no longer implements `Component`. Using `ClearColor` as a component in 0.8 did nothing. Use the `ClearColorConfig` in the `Camera3d` and `Camera2d` components instead. Co-authored-by: Alice <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com> Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com> Co-authored-by: devil-ira <justthecooldude@gmail.com> Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com> |
||
|
|
90d1dc8820 |
Add bevy_render::texture::ImageSettings to prelude (#5566)
# Objective In Bevy 0.8, the default filter mode was changed to linear (#4465). I believe this is a sensible default, but it's also very common to want to use point filtering (e.g. for pixel art games). ## Solution I am proposing including `bevy_render::texture::ImageSettings` in the Bevy prelude so it is more ergonomic to change the filtering in such cases. --- ## Changelog ### Added - Added `bevy_render::texture::ImageSettings` to prelude. |
||
|
|
13b4a7daaa |
Add Projection component to prelude. (#5557)
:) Co-authored-by: Devil Ira <justthecooldude@gmail.com> |
||
|
|
fdcffb885f |
Remove duplicate RenderGraph insertion to render world (#5551)
# Objective - Remove unnecessary duplicate `init_resource` call for `RenderGraph`. ## Solution - Remove unnecessary duplicate `init_resource` call for `RenderGraph`. |
||
|
|
4affc8cd93 |
add a SpatialBundle with visibility and transform components (#5344)
# Objective - Help user when they need to add both a `TransformBundle` and a `VisibilityBundle` ## Solution - Add a `SpatialBundle` adding all components |
||
|
|
a63d761aa3 |
Add VisibilityBundle and use it to fix gltfs, scenes, and examples (#5335)
# Objective Gltfs, and a few examples were broken by #5310. Fix em. Closes #5334 ## Solution Add `VisibilityBundle` as described here: https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/5334#issuecomment-1186050778 and sprinkle it around where needed. |
||
|
|
a1d3f1b3b4 |
Update time by sending frame instant through a channel (#4744)
# Objective - The time update is currently done in the wrong part of the schedule. For a single frame the current order of things is update input, update time (First stage), other stages, render stage (frame presentation). So when we update the time it includes the input processing of the current frame and the frame presentation of the previous frame. This is a problem when vsync is on. When input processing takes a longer amount of time for a frame, the vsync wait time gets shorter. So when these are not paired correctly we can potentially have a long input processing time added to the normal vsync wait time in the previous frame. This leads to inaccurate frame time reporting and more variance of the time than actually exists. For more details of why this is an issue see the linked issue below. - Helps with https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/4669 - Supercedes https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/4728 and https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/4735. This PR should be less controversial than those because it doesn't add to the API surface. ## Solution - The most accurate frame time would come from hardware. We currently don't have access to that for multiple reasons, so the next best thing we can do is measure the frame time as close to frame presentation as possible. This PR gets the Instant::now() for the time immediately after frame presentation in the render system and then sends that time to the app world through a channel. - implements suggestion from @aevyrie from here https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/4728#discussion_r872010606 ## Statistics 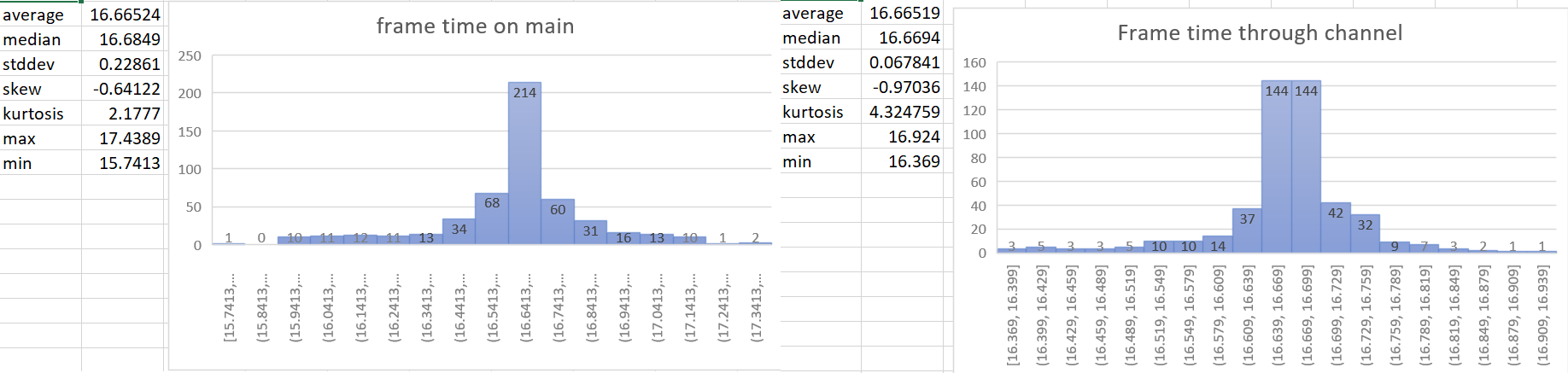 --- ## Changelog - Make frame time reporting more accurate. ## Migration Guide `time.delta()` now reports zero for 2 frames on startup instead of 1 frame. |
||
|
|
7b2cf98896 |
Make RenderStage::Extract run on the render world (#4402)
# Objective - Currently, the `Extract` `RenderStage` is executed on the main world, with the render world available as a resource. - However, when needing access to resources in the render world (e.g. to mutate them), the only way to do so was to get exclusive access to the whole `RenderWorld` resource. - This meant that effectively only one extract which wrote to resources could run at a time. - We didn't previously make `Extract`ing writing to the world a non-happy path, even though we want to discourage that. ## Solution - Move the extract stage to run on the render world. - Add the main world as a `MainWorld` resource. - Add an `Extract` `SystemParam` as a convenience to access a (read only) `SystemParam` in the main world during `Extract`. ## Future work It should be possible to avoid needing to use `get_or_spawn` for the render commands, since now the `Commands`' `Entities` matches up with the world being executed on. We need to determine how this interacts with https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/3519 It's theoretically possible to remove the need for the `value` method on `Extract`. However, that requires slightly changing the `SystemParam` interface, which would make it more complicated. That would probably mess up the `SystemState` api too. ## Todo I still need to add doc comments to `Extract`. --- ## Changelog ### Changed - The `Extract` `RenderStage` now runs on the render world (instead of the main world as before). You must use the `Extract` `SystemParam` to access the main world during the extract phase. Resources on the render world can now be accessed using `ResMut` during extract. ### Removed - `Commands::spawn_and_forget`. Use `Commands::get_or_spawn(e).insert_bundle(bundle)` instead ## Migration Guide The `Extract` `RenderStage` now runs on the render world (instead of the main world as before). You must use the `Extract` `SystemParam` to access the main world during the extract phase. `Extract` takes a single type parameter, which is any system parameter (such as `Res`, `Query` etc.). It will extract this from the main world, and returns the result of this extraction when `value` is called on it. For example, if previously your extract system looked like: ```rust fn extract_clouds(mut commands: Commands, clouds: Query<Entity, With<Cloud>>) { for cloud in clouds.iter() { commands.get_or_spawn(cloud).insert(Cloud); } } ``` the new version would be: ```rust fn extract_clouds(mut commands: Commands, mut clouds: Extract<Query<Entity, With<Cloud>>>) { for cloud in clouds.value().iter() { commands.get_or_spawn(cloud).insert(Cloud); } } ``` The diff is: ```diff --- a/src/clouds.rs +++ b/src/clouds.rs @@ -1,5 +1,5 @@ -fn extract_clouds(mut commands: Commands, clouds: Query<Entity, With<Cloud>>) { - for cloud in clouds.iter() { +fn extract_clouds(mut commands: Commands, mut clouds: Extract<Query<Entity, With<Cloud>>>) { + for cloud in clouds.value().iter() { commands.get_or_spawn(cloud).insert(Cloud); } } ``` You can now also access resources from the render world using the normal system parameters during `Extract`: ```rust fn extract_assets(mut render_assets: ResMut<MyAssets>, source_assets: Extract<Res<MyAssets>>) { *render_assets = source_assets.clone(); } ``` Please note that all existing extract systems need to be updated to match this new style; even if they currently compile they will not run as expected. A warning will be emitted on a best-effort basis if this is not met. Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com> |
||
|
|
5b5013d540 |
Add ViewRangefinder3d to reduce boilerplate when enqueuing standard 3D PhaseItems. (#5014)
# Objective Reduce the boilerplate code needed to make draw order sorting work correctly when queuing items through new common functionality. Also fix several instances in the bevy code-base (mostly examples) where this boilerplate appears to be incorrect. ## Solution - Moved the logic for handling back-to-front vs front-to-back draw ordering into the PhaseItems by inverting the sort key ordering of Opaque3d and AlphaMask3d. The means that all the standard 3d rendering phases measure distance in the same way. Clients of these structs no longer need to know to negate the distance. - Added a new utility struct, ViewRangefinder3d, which encapsulates the maths needed to calculate a "distance" from an ExtractedView and a mesh's transform matrix. - Converted all the occurrences of the distance calculations in Bevy and its examples to use ViewRangefinder3d. Several of these occurrences appear to be buggy because they don't invert the view matrix or don't negate the distance where appropriate. This leads me to the view that Bevy should expose a facility to correctly perform this calculation. ## Migration Guide Code which creates Opaque3d, AlphaMask3d, or Transparent3d phase items _should_ use ViewRangefinder3d to calculate the distance value. Code which manually calculated the distance for Opaque3d or AlphaMask3d phase items and correctly negated the z value will no longer depth sort correctly. However, incorrect depth sorting for these types will not impact the rendered output as sorting is only a performance optimisation when drawing with depth-testing enabled. Code which manually calculated the distance for Transparent3d phase items will continue to work as before. |
||
|
|
772d15238c |
Change default Image FilterMode to Linear (#4465)
# Objective - Closes #4464 ## Solution - Specify default mag and min filter types for `Image` instead of using `wgpu`'s defaults. --- ## Changelog ### Changed - Default `Image` filtering changed from `Nearest` to `Linear`. Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com> |
||
|
|
f487407e07 |
Camera Driven Rendering (#4745)
This adds "high level camera driven rendering" to Bevy. The goal is to give users more control over what gets rendered (and where) without needing to deal with render logic. This will make scenarios like "render to texture", "multiple windows", "split screen", "2d on 3d", "3d on 2d", "pass layering", and more significantly easier. Here is an [example of a 2d render sandwiched between two 3d renders (each from a different perspective)](https://gist.github.com/cart/4fe56874b2e53bc5594a182fc76f4915):  Users can now spawn a camera, point it at a RenderTarget (a texture or a window), and it will "just work". Rendering to a second window is as simple as spawning a second camera and assigning it to a specific window id: ```rust // main camera (main window) commands.spawn_bundle(Camera2dBundle::default()); // second camera (other window) commands.spawn_bundle(Camera2dBundle { camera: Camera { target: RenderTarget::Window(window_id), ..default() }, ..default() }); ``` Rendering to a texture is as simple as pointing the camera at a texture: ```rust commands.spawn_bundle(Camera2dBundle { camera: Camera { target: RenderTarget::Texture(image_handle), ..default() }, ..default() }); ``` Cameras now have a "render priority", which controls the order they are drawn in. If you want to use a camera's output texture as a texture in the main pass, just set the priority to a number lower than the main pass camera (which defaults to `0`). ```rust // main pass camera with a default priority of 0 commands.spawn_bundle(Camera2dBundle::default()); commands.spawn_bundle(Camera2dBundle { camera: Camera { target: RenderTarget::Texture(image_handle.clone()), priority: -1, ..default() }, ..default() }); commands.spawn_bundle(SpriteBundle { texture: image_handle, ..default() }) ``` Priority can also be used to layer to cameras on top of each other for the same RenderTarget. This is what "2d on top of 3d" looks like in the new system: ```rust commands.spawn_bundle(Camera3dBundle::default()); commands.spawn_bundle(Camera2dBundle { camera: Camera { // this will render 2d entities "on top" of the default 3d camera's render priority: 1, ..default() }, ..default() }); ``` There is no longer the concept of a global "active camera". Resources like `ActiveCamera<Camera2d>` and `ActiveCamera<Camera3d>` have been replaced with the camera-specific `Camera::is_active` field. This does put the onus on users to manage which cameras should be active. Cameras are now assigned a single render graph as an "entry point", which is configured on each camera entity using the new `CameraRenderGraph` component. The old `PerspectiveCameraBundle` and `OrthographicCameraBundle` (generic on camera marker components like Camera2d and Camera3d) have been replaced by `Camera3dBundle` and `Camera2dBundle`, which set 3d and 2d default values for the `CameraRenderGraph` and projections. ```rust // old 3d perspective camera commands.spawn_bundle(PerspectiveCameraBundle::default()) // new 3d perspective camera commands.spawn_bundle(Camera3dBundle::default()) ``` ```rust // old 2d orthographic camera commands.spawn_bundle(OrthographicCameraBundle::new_2d()) // new 2d orthographic camera commands.spawn_bundle(Camera2dBundle::default()) ``` ```rust // old 3d orthographic camera commands.spawn_bundle(OrthographicCameraBundle::new_3d()) // new 3d orthographic camera commands.spawn_bundle(Camera3dBundle { projection: OrthographicProjection { scale: 3.0, scaling_mode: ScalingMode::FixedVertical, ..default() }.into(), ..default() }) ``` Note that `Camera3dBundle` now uses a new `Projection` enum instead of hard coding the projection into the type. There are a number of motivators for this change: the render graph is now a part of the bundle, the way "generic bundles" work in the rust type system prevents nice `..default()` syntax, and changing projections at runtime is much easier with an enum (ex for editor scenarios). I'm open to discussing this choice, but I'm relatively certain we will all come to the same conclusion here. Camera2dBundle and Camera3dBundle are much clearer than being generic on marker components / using non-default constructors. If you want to run a custom render graph on a camera, just set the `CameraRenderGraph` component: ```rust commands.spawn_bundle(Camera3dBundle { camera_render_graph: CameraRenderGraph::new(some_render_graph_name), ..default() }) ``` Just note that if the graph requires data from specific components to work (such as `Camera3d` config, which is provided in the `Camera3dBundle`), make sure the relevant components have been added. Speaking of using components to configure graphs / passes, there are a number of new configuration options: ```rust commands.spawn_bundle(Camera3dBundle { camera_3d: Camera3d { // overrides the default global clear color clear_color: ClearColorConfig::Custom(Color::RED), ..default() }, ..default() }) commands.spawn_bundle(Camera3dBundle { camera_3d: Camera3d { // disables clearing clear_color: ClearColorConfig::None, ..default() }, ..default() }) ``` Expect to see more of the "graph configuration Components on Cameras" pattern in the future. By popular demand, UI no longer requires a dedicated camera. `UiCameraBundle` has been removed. `Camera2dBundle` and `Camera3dBundle` now both default to rendering UI as part of their own render graphs. To disable UI rendering for a camera, disable it using the CameraUi component: ```rust commands .spawn_bundle(Camera3dBundle::default()) .insert(CameraUi { is_enabled: false, ..default() }) ``` ## Other Changes * The separate clear pass has been removed. We should revisit this for things like sky rendering, but I think this PR should "keep it simple" until we're ready to properly support that (for code complexity and performance reasons). We can come up with the right design for a modular clear pass in a followup pr. * I reorganized bevy_core_pipeline into Core2dPlugin and Core3dPlugin (and core_2d / core_3d modules). Everything is pretty much the same as before, just logically separate. I've moved relevant types (like Camera2d, Camera3d, Camera3dBundle, Camera2dBundle) into their relevant modules, which is what motivated this reorganization. * I adapted the `scene_viewer` example (which relied on the ActiveCameras behavior) to the new system. I also refactored bits and pieces to be a bit simpler. * All of the examples have been ported to the new camera approach. `render_to_texture` and `multiple_windows` are now _much_ simpler. I removed `two_passes` because it is less relevant with the new approach. If someone wants to add a new "layered custom pass with CameraRenderGraph" example, that might fill a similar niche. But I don't feel much pressure to add that in this pr. * Cameras now have `target_logical_size` and `target_physical_size` fields, which makes finding the size of a camera's render target _much_ simpler. As a result, the `Assets<Image>` and `Windows` parameters were removed from `Camera::world_to_screen`, making that operation much more ergonomic. * Render order ambiguities between cameras with the same target and the same priority now produce a warning. This accomplishes two goals: 1. Now that there is no "global" active camera, by default spawning two cameras will result in two renders (one covering the other). This would be a silent performance killer that would be hard to detect after the fact. By detecting ambiguities, we can provide a helpful warning when this occurs. 2. Render order ambiguities could result in unexpected / unpredictable render results. Resolving them makes sense. ## Follow Up Work * Per-Camera viewports, which will make it possible to render to a smaller area inside of a RenderTarget (great for something like splitscreen) * Camera-specific MSAA config (should use the same "overriding" pattern used for ClearColor) * Graph Based Camera Ordering: priorities are simple, but they make complicated ordering constraints harder to express. We should consider adopting a "graph based" camera ordering model with "before" and "after" relationships to other cameras (or build it "on top" of the priority system). * Consider allowing graphs to run subgraphs from any nest level (aka a global namespace for graphs). Right now the 2d and 3d graphs each need their own UI subgraph, which feels "fine" in the short term. But being able to share subgraphs between other subgraphs seems valuable. * Consider splitting `bevy_core_pipeline` into `bevy_core_2d` and `bevy_core_3d` packages. Theres a shared "clear color" dependency here, which would need a new home. |
||
|
|
a0a3d8798b |
ExtractResourcePlugin (#3745)
# Objective - Add an `ExtractResourcePlugin` for convenience and consistency ## Solution - Add an `ExtractResourcePlugin` similar to `ExtractComponentPlugin` but for ECS `Resource`s. The system that is executed simply clones the main world resource into a render world resource, if and only if the main world resource was either added or changed since the last execution of the system. - Add an `ExtractResource` trait with a `fn extract_resource(res: &Self) -> Self` function. This is used by the `ExtractResourcePlugin` to extract the resource - Add a derive macro for `ExtractResource` on a `Resource` with the `Clone` trait, that simply returns `res.clone()` - Use `ExtractResourcePlugin` wherever both possible and appropriate |
||
|
|
b1b3bd533b |
Skip drop when needs_drop is false (#4773)
# Objective - We do a lot of function pointer calls in a hot loop (clearing entities in render). This is slow, since calling function pointers cannot be optimised out. We can avoid that in the cases where the function call is a no-op. - Alternative to https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/2897 - On my machine, in `many_cubes`, this reduces dropping time from ~150μs to ~80μs. ## Solution - Make `drop` in `BlobVec` an `Option`, recording whether the given drop impl is required or not. - Note that this does add branching in some cases - we could consider splitting this into two fields, i.e. unconditionally call the `drop` fn pointer. - My intuition of how often types stored in `World` should have non-trivial drops makes me think that would be slower, however. N.B. Even once this lands, we should still test having a 'drop_multiple' variant - for types with a real `Drop` impl, the current implementation is definitely optimal. |
||
|
|
637a149910 |
unsafeify World::entities_mut (#4093)
# Objective
make bevy ecs a lil bit less unsound
## Solution
make unsound API unsafe so that there is an unsafe block to blame:
```rust
use bevy_ecs::prelude::*;
#[derive(Debug, Component)]
struct Foo(u8);
fn main() {
let mut world = World::new();
let e1 = world.spawn().id();
let e2 = world.spawn().insert(Foo(2)).id();
world.entities_mut().meta[0] = world.entities_mut().meta[1].clone();
let foo = world.entity(e1).get::<Foo>().unwrap();
// whoo i love having components i dont have
dbg!(foo);
}
```
This is not _strictly_ speaking UB, however:
- `Query::get_multiple` cannot work if this is allowed
- bevy_ecs is a pile of unsafe code whose soundness generally depends on the world being in a "correct" state with "no funny business" so it seems best to disallow this
- it is trivial to get bevy to panic inside of functions with safety invariants that have been violated (the entity location is not valid)
- it seems to violate what the safety invariant on `Entities::flush` is trying to ensure
|
||
|
|
9e450f2827 |
Compute Pipeline Specialization (#3979)
# Objective - Fixes #3970 - To support Bevy's shader abstraction(shader defs, shader imports and hot shader reloading) for compute shaders, I have followed carts advice and change the `PipelinenCache` to accommodate both compute and render pipelines. ## Solution - renamed `RenderPipelineCache` to `PipelineCache` - Cached Pipelines are now represented by an enum (render, compute) - split the `SpecializedPipelines` into `SpecializedRenderPipelines` and `SpecializedComputePipelines` - updated the game of life example ## Open Questions - should `SpecializedRenderPipelines` and `SpecializedComputePipelines` be merged and how would we do that? - should the `get_render_pipeline` and `get_compute_pipeline` methods be merged? - is pipeline specialization for different entry points a good pattern Co-authored-by: Kurt Kühnert <51823519+Ku95@users.noreply.github.com> Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com> |
||
|
|
de677dbfc9 |
Use more ergonomic span syntax (#4246)
Tracing added support for "inline span entering", which cuts down on a lot of complexity:
```rust
let span = info_span!("my_span").entered();
```
This adapts our code to use this pattern where possible, and updates our docs to recommend it.
This produces equivalent tracing behavior. Here is a side by side profile of "before" and "after" these changes.
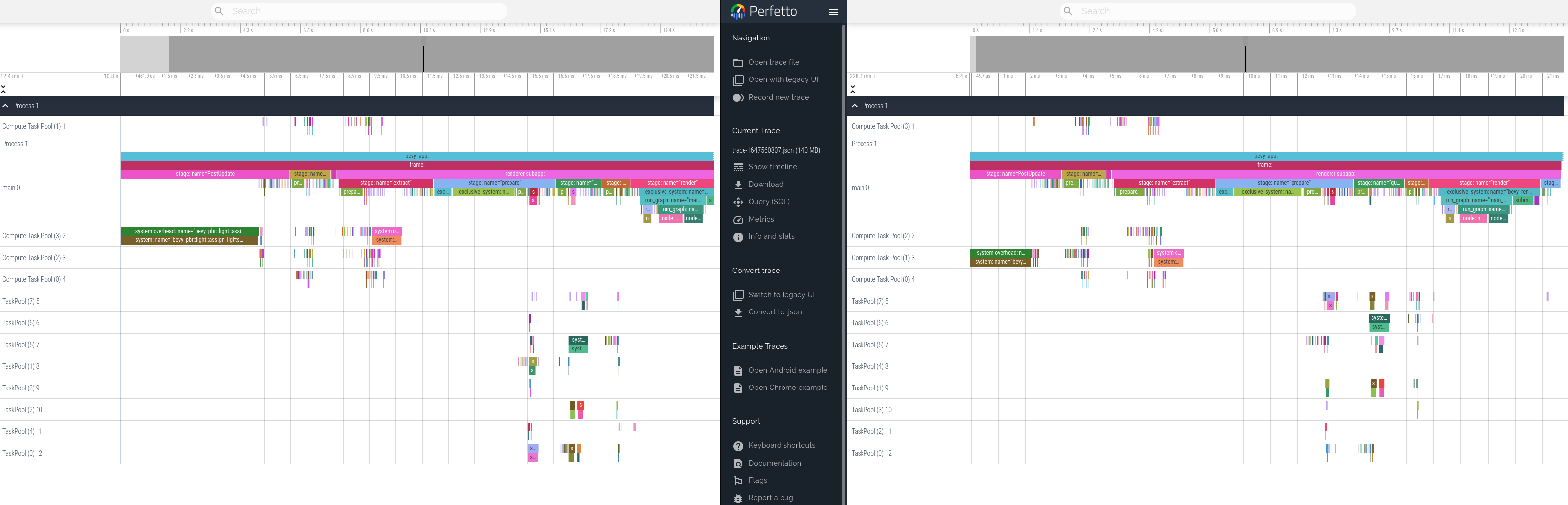
|
||
|
|
0529f633f9 |
KTX2/DDS/.basis compressed texture support (#3884)
# Objective - Support compressed textures including 'universal' formats (ETC1S, UASTC) and transcoding of them to - Support `.dds`, `.ktx2`, and `.basis` files ## Solution - Fixes https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/3608 Look there for more details. - Note that the functionality is all enabled through non-default features. If it is desirable to enable some by default, I can do that. - The `basis-universal` crate, used for `.basis` file support and for transcoding, is built on bindings against a C++ library. It's not feasible to rewrite in Rust in a short amount of time. There are no Rust alternatives of which I am aware and it's specialised code. In its current state it doesn't support the wasm target, but I don't know for sure. However, it is possible to build the upstream C++ library with emscripten, so there is perhaps a way to add support for web too with some shenanigans. - There's no support for transcoding from BasisLZ/ETC1S in KTX2 files as it was quite non-trivial to implement and didn't feel important given people could use `.basis` files for ETC1S. |
||
|
|
557ab9897a |
Make get_resource (and friends) infallible (#4047)
# Objective - In the large majority of cases, users were calling `.unwrap()` immediately after `.get_resource`. - Attempting to add more helpful error messages here resulted in endless manual boilerplate (see #3899 and the linked PRs). ## Solution - Add an infallible variant named `.resource` and so on. - Use these infallible variants over `.get_resource().unwrap()` across the code base. ## Notes I did not provide equivalent methods on `WorldCell`, in favor of removing it entirely in #3939. ## Migration Guide Infallible variants of `.get_resource` have been added that implicitly panic, rather than needing to be unwrapped. Replace `world.get_resource::<Foo>().unwrap()` with `world.resource::<Foo>()`. ## Impact - `.unwrap` search results before: 1084 - `.unwrap` search results after: 942 - internal `unwrap_or_else` calls added: 4 - trivial unwrap calls removed from tests and code: 146 - uses of the new `try_get_resource` API: 11 - percentage of the time the unwrapping API was used internally: 93% |
||
|
|
98938a8555 |
Internal Asset Hot Reloading (#3966)
Adds "hot reloading" of internal assets, which is normally not possible because they are loaded using `include_str` / direct Asset collection access. This is accomplished via the following: * Add a new `debug_asset_server` feature flag * When that feature flag is enabled, create a second App with a second AssetServer that points to a configured location (by default the `crates` folder). Plugins that want to add hot reloading support for their assets can call the new `app.add_debug_asset::<T>()` and `app.init_debug_asset_loader::<T>()` functions. * Load "internal" assets using the new `load_internal_asset` macro. By default this is identical to the current "include_str + register in asset collection" approach. But if the `debug_asset_server` feature flag is enabled, it will also load the asset dynamically in the debug asset server using the file path. It will then set up a correlation between the "debug asset" and the "actual asset" by listening for asset change events. This is an alternative to #3673. The goal was to keep the boilerplate and features flags to a minimum for bevy plugin authors, and allow them to home their shaders near relevant code. This is a draft because I haven't done _any_ quality control on this yet. I'll probably rename things and remove a bunch of unwraps. I just got it working and wanted to use it to start a conversation. Fixes #3660 |
||
|
|
936468aa1e |
bevy_render: Use RenderDevice to get limits/features and expose AdapterInfo (#3931)
# Objective - `WgpuOptions` is mutated to be updated with the actual device limits and features, but this information is readily available to both the main and render worlds through the `RenderDevice` which has .limits() and .features() methods - Information about the adapter in terms of its name, the backend in use, etc were not being exposed but have clear use cases for being used to take decisions about what rendering code to use. For example, if something works well on AMD GPUs but poorly on Intel GPUs. Or perhaps something works well in Vulkan but poorly in DX12. ## Solution - Stop mutating `WgpuOptions `and don't insert the updated values into the main and render worlds - Return `AdapterInfo` from `initialize_renderer` and insert it into the main and render worlds - Use `RenderDevice` limits in the lighting code that was using `WgpuOptions.limits`. - Renamed `WgpuOptions` to `WgpuSettings` |
||
|
|
458cb7a9e9 |
Add headless mode (#3439)
# Objective In this PR I added the ability to opt-out graphical backends. Closes #3155. ## Solution I turned backends into `Option` ~~and removed panicking sub app API to force users handle the error (was suggested by `@cart`)~~. |
||
|
|
b9c623e4f3 |
Configurable wgpu features/limits priority (#3452)
# Objective - Allow the user to specify the priority when configuring wgpu features/limits and by default use the maximum capabilities of the chosen adapter. ## Solution - Add a `WgpuOptionsPriority` enum with `Compatibility`, `Functionality` and `WebGL2` options. - Add a `priority: WgpuOptionsPriority` member to `WgpuOptions`. - When initialising the renderer, if `WgpuOptions::priority == WgpuOptionsPriority::Functionality`, query the adapter for the available features and limits, use them when creating a device, and update `WgpuOptions` with those values. If `Compatibility` use the behaviour as before this PR. If `WebGL2` then use the WebGL2 downlevel limits as used when when building for wasm, for convenience of testing WebGL2 limits without having to build for wasm. - Add an environment variable `WGPU_OPTIONS_PRIO` that takes `compatibility`, `functionality`, `webgl2`. - Default to `WgpuOptionsPriority::Functionality`. - Insert updated `WgpuOptions` into render app world as well. This is useful for applying the limits when rendering, such as limiting the directional light shadow map texture to 2048x2048 when using WebGL2 downlevel limits but not on wasm. - Reduced `draw_state` logs from `debug` to `trace` and added `debug` level logs for the wgpu features and limits. Use `RUST_LOG=bevy_render=debug` to see the output. |
||
|
|
85b7589388 |
bevy_gltf: Add support for loading lights (#3506)
# Objective - Add support for loading lights from glTF 2.0 files ## Solution - This adds support for the KHR_punctual_lights extension which supports point, directional, and spot lights, though we don't yet support spot lights. - Inserting light bundles when creating scenes required registering some more light bundle component types. |
||
|
|
ffecb05a0a |
Replace old renderer with new renderer (#3312)
This makes the [New Bevy Renderer](#2535) the default (and only) renderer. The new renderer isn't _quite_ ready for the final release yet, but I want as many people as possible to start testing it so we can identify bugs and address feedback prior to release. The examples are all ported over and operational with a few exceptions: * I removed a good portion of the examples in the `shader` folder. We still have some work to do in order to make these examples possible / ergonomic / worthwhile: #3120 and "high level shader material plugins" are the big ones. This is a temporary measure. * Temporarily removed the multiple_windows example: doing this properly in the new renderer will require the upcoming "render targets" changes. Same goes for the render_to_texture example. * Removed z_sort_debug: entity visibility sort info is no longer available in app logic. we could do this on the "render app" side, but i dont consider it a priority. |
||
|
|
c6fec1f0c2 |
Fix clippy lints for 1.57 (#3238)
# Objective - New clippy lints with rust 1.57 are failing ## Solution - Fixed clippy lints following suggestions - I ignored clippy in old renderer because there was many and it will be removed soon |
||
|
|
b724a0f586 |
Down with the system! (#2496)
# Objective - Remove all the `.system()` possible. - Check for remaining missing cases. ## Solution - Remove all `.system()`, fix compile errors - 32 calls to `.system()` remains, mostly internals, the few others should be removed after #2446 |
||
|
|
6d6bc2a8b4 |
Merge AppBuilder into App (#2531)
This is extracted out of eb8f973646476b4a4926ba644a77e2b3a5772159 and includes some additional changes to remove all references to AppBuilder and fix examples that still used App::build() instead of App::new(). In addition I didn't extract the sub app feature as it isn't ready yet. You can use `git diff --diff-filter=M eb8f973646476b4a4926ba644a77e2b3a5772159` to find all differences in this PR. The `--diff-filtered=M` filters all files added in the original commit but not in this commit away. Co-Authored-By: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com> |
||
|
|
4fed2ee858 |
Use cfg attribute to filter supported extensions (#2297)
When implementing `AssetLoader ` you need to specify which File extensions are supported by that loader. Currently, Bevy always says it supports extensions that actually require activating a Feature beforehand. This PR adds cf attributes, so Bevy only tries to load those Extensions whose Features were activated. This prevents Bevy from Panicking and reports such a warning: ``` Jun 02 23:05:57.139 WARN bevy_asset::asset_server: no `AssetLoader` found for the following extension: ogg ``` This also fixes the Bug, that the `png Feature had to be activated even if you wanted to load a different image format. Fixes #640 |
||
|
|
b1ed28e17e |
Hide re-exported docs (#1985)
Solves #1957 Co-authored-by: caelumLaron <caelum.laron@gmail.com> |
||
|
|
30c6ca6166 |
don't panic when no RenderResourceContext can be found (#1971)
In bevy_webgl2, the `RenderResourceContext` is created after startup as it needs to first wait for an event from js side:
|
||
|
|
80df583a21 | When missing a render backend also mention the bevy_wgpu feature (#1970) | ||
|
|
ad43f52bd2 |
Provide better error message when missing a render backend (#1965)
Fixes #626 |
||
|
|
b65ec82d46 |
Frustum Culling (for Sprites) (#1492)
This PR adds two systems to the sprite module that culls Sprites and AtlasSprites that are not within the camera's view. This is achieved by removing / adding a new `Viewable` Component dynamically. Some of the render queries now use a `With<Viewable>` filter to only process the sprites that are actually on screen, which improves performance drastically for scene swith a large amount of sprites off-screen. https://streamable.com/vvzh2u This scene shows a map with a 320x320 tiles, with a grid size of 64p. This is exactly 102400 Sprites in the entire scene. Without this PR, this scene runs with 1 to 4 FPS. With this PR.. .. at 720p, there are around 600 visible sprites and runs at ~215 FPS .. at 1440p there are around 2000 visible sprites and runs at ~135 FPS The Systems this PR adds take around 1.2ms (with 100K+ sprites in the scene) Note: This is only implemented for Sprites and AtlasTextureSprites. There is no culling for 3D in this PR. Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com> |
||
|
|
b17f8a4bce |
format comments (#1612)
Uses the new unstable comment formatting features added to rustfmt.toml. |
||
|
|
be1c317d4e |
Resolve (most) internal system ambiguities (#1606)
* Adds labels and orderings to systems that need them (uses the new many-to-many labels for InputSystem) * Removes the Event, PreEvent, Scene, and Ui stages in favor of First, PreUpdate, and PostUpdate (there is more collapsing potential, such as the Asset stages and _maybe_ removing First, but those have more nuance so they should be handled separately) * Ambiguity detection now prints component conflicts * Removed broken change filters from flex calculation (which implicitly relied on the z-update system always modifying translation.z). This will require more work to make it behave as expected so i just removed it (and it was already doing this work every frame). |
||
|
|
faeccd7a09 |
Reflection cleanup (#1536)
This is an effort to provide the correct `#[reflect_value(...)]` attributes where they are needed. Supersedes #1533 and resolves #1528. --- I am working under the following assumptions (thanks to @bjorn3 and @Davier for advice here): - Any `enum` that derives `Reflect` and one or more of { `Serialize`, `Deserialize`, `PartialEq`, `Hash` } needs a `#[reflect_value(...)]` attribute containing the same subset of { `Serialize`, `Deserialize`, `PartialEq`, `Hash` } that is present on the derive. - Same as above for `struct` and `#[reflect(...)]`, respectively. - If a `struct` is used as a component, it should also have `#[reflect(Component)]` - All reflected types should be registered in their plugins I treated the following as components (added `#[reflect(Component)]` if necessary): - `bevy_render` - `struct RenderLayers` - `bevy_transform` - `struct GlobalTransform` - `struct Parent` - `struct Transform` - `bevy_ui` - `struct Style` Not treated as components: - `bevy_math` - `struct Size<T>` - `struct Rect<T>` - Note: The updates for `Size<T>` and `Rect<T>` in `bevy::math::geometry` required using @Davier's suggestion to add `+ PartialEq` to the trait bound. I then registered the specific types used over in `bevy_ui` such as `Size<Val>`, etc. in `bevy_ui`'s plugin, since `bevy::math` does not contain a plugin. - `bevy_render` - `struct Color` - `struct PipelineSpecialization` - `struct ShaderSpecialization` - `enum PrimitiveTopology` - `enum IndexFormat` Not Addressed: - I am not searching for components in Bevy that are _not_ reflected. So if there are components that are not reflected that should be reflected, that will need to be figured out in another PR. - I only added `#[reflect(...)]` or `#[reflect_value(...)]` entries for the set of four traits { `Serialize`, `Deserialize`, `PartialEq`, `Hash` } _if they were derived via `#[derive(...)]`_. I did not look for manual trait implementations of the same set of four, nor did I consider any traits outside the four. Are those other possibilities something that needs to be looked into? |
||
|
|
3a2a68852c |
Bevy ECS V2 (#1525)
# Bevy ECS V2
This is a rewrite of Bevy ECS (basically everything but the new executor/schedule, which are already awesome). The overall goal was to improve the performance and versatility of Bevy ECS. Here is a quick bulleted list of changes before we dive into the details:
* Complete World rewrite
* Multiple component storage types:
* Tables: fast cache friendly iteration, slower add/removes (previously called Archetypes)
* Sparse Sets: fast add/remove, slower iteration
* Stateful Queries (caches query results for faster iteration. fragmented iteration is _fast_ now)
* Stateful System Params (caches expensive operations. inspired by @DJMcNab's work in #1364)
* Configurable System Params (users can set configuration when they construct their systems. once again inspired by @DJMcNab's work)
* Archetypes are now "just metadata", component storage is separate
* Archetype Graph (for faster archetype changes)
* Component Metadata
* Configure component storage type
* Retrieve information about component size/type/name/layout/send-ness/etc
* Components are uniquely identified by a densely packed ComponentId
* TypeIds are now totally optional (which should make implementing scripting easier)
* Super fast "for_each" query iterators
* Merged Resources into World. Resources are now just a special type of component
* EntityRef/EntityMut builder apis (more efficient and more ergonomic)
* Fast bitset-backed `Access<T>` replaces old hashmap-based approach everywhere
* Query conflicts are determined by component access instead of archetype component access (to avoid random failures at runtime)
* With/Without are still taken into account for conflicts, so this should still be comfy to use
* Much simpler `IntoSystem` impl
* Significantly reduced the amount of hashing throughout the ecs in favor of Sparse Sets (indexed by densely packed ArchetypeId, ComponentId, BundleId, and TableId)
* Safety Improvements
* Entity reservation uses a normal world reference instead of unsafe transmute
* QuerySets no longer transmute lifetimes
* Made traits "unsafe" where relevant
* More thorough safety docs
* WorldCell
* Exposes safe mutable access to multiple resources at a time in a World
* Replaced "catch all" `System::update_archetypes(world: &World)` with `System::new_archetype(archetype: &Archetype)`
* Simpler Bundle implementation
* Replaced slow "remove_bundle_one_by_one" used as fallback for Commands::remove_bundle with fast "remove_bundle_intersection"
* Removed `Mut<T>` query impl. it is better to only support one way: `&mut T`
* Removed with() from `Flags<T>` in favor of `Option<Flags<T>>`, which allows querying for flags to be "filtered" by default
* Components now have is_send property (currently only resources support non-send)
* More granular module organization
* New `RemovedComponents<T>` SystemParam that replaces `query.removed::<T>()`
* `world.resource_scope()` for mutable access to resources and world at the same time
* WorldQuery and QueryFilter traits unified. FilterFetch trait added to enable "short circuit" filtering. Auto impled for cases that don't need it
* Significantly slimmed down SystemState in favor of individual SystemParam state
* System Commands changed from `commands: &mut Commands` back to `mut commands: Commands` (to allow Commands to have a World reference)
Fixes #1320
## `World` Rewrite
This is a from-scratch rewrite of `World` that fills the niche that `hecs` used to. Yes, this means Bevy ECS is no longer a "fork" of hecs. We're going out our own!
(the only shared code between the projects is the entity id allocator, which is already basically ideal)
A huge shout out to @SanderMertens (author of [flecs](https://github.com/SanderMertens/flecs)) for sharing some great ideas with me (specifically hybrid ecs storage and archetype graphs). He also helped advise on a number of implementation details.
## Component Storage (The Problem)
Two ECS storage paradigms have gained a lot of traction over the years:
* **Archetypal ECS**:
* Stores components in "tables" with static schemas. Each "column" stores components of a given type. Each "row" is an entity.
* Each "archetype" has its own table. Adding/removing an entity's component changes the archetype.
* Enables super-fast Query iteration due to its cache-friendly data layout
* Comes at the cost of more expensive add/remove operations for an Entity's components, because all components need to be copied to the new archetype's "table"
* **Sparse Set ECS**:
* Stores components of the same type in densely packed arrays, which are sparsely indexed by densely packed unsigned integers (Entity ids)
* Query iteration is slower than Archetypal ECS because each entity's component could be at any position in the sparse set. This "random access" pattern isn't cache friendly. Additionally, there is an extra layer of indirection because you must first map the entity id to an index in the component array.
* Adding/removing components is a cheap, constant time operation
Bevy ECS V1, hecs, legion, flec, and Unity DOTS are all "archetypal ecs-es". I personally think "archetypal" storage is a good default for game engines. An entity's archetype doesn't need to change frequently in general, and it creates "fast by default" query iteration (which is a much more common operation). It is also "self optimizing". Users don't need to think about optimizing component layouts for iteration performance. It "just works" without any extra boilerplate.
Shipyard and EnTT are "sparse set ecs-es". They employ "packing" as a way to work around the "suboptimal by default" iteration performance for specific sets of components. This helps, but I didn't think this was a good choice for a general purpose engine like Bevy because:
1. "packs" conflict with each other. If bevy decides to internally pack the Transform and GlobalTransform components, users are then blocked if they want to pack some custom component with Transform.
2. users need to take manual action to optimize
Developers selecting an ECS framework are stuck with a hard choice. Select an "archetypal" framework with "fast iteration everywhere" but without the ability to cheaply add/remove components, or select a "sparse set" framework to cheaply add/remove components but with slower iteration performance.
## Hybrid Component Storage (The Solution)
In Bevy ECS V2, we get to have our cake and eat it too. It now has _both_ of the component storage types above (and more can be added later if needed):
* **Tables** (aka "archetypal" storage)
* The default storage. If you don't configure anything, this is what you get
* Fast iteration by default
* Slower add/remove operations
* **Sparse Sets**
* Opt-in
* Slower iteration
* Faster add/remove operations
These storage types complement each other perfectly. By default Query iteration is fast. If developers know that they want to add/remove a component at high frequencies, they can set the storage to "sparse set":
```rust
world.register_component(
ComponentDescriptor:🆕:<MyComponent>(StorageType::SparseSet)
).unwrap();
```
## Archetypes
Archetypes are now "just metadata" ... they no longer store components directly. They do store:
* The `ComponentId`s of each of the Archetype's components (and that component's storage type)
* Archetypes are uniquely defined by their component layouts
* For example: entities with "table" components `[A, B, C]` _and_ "sparse set" components `[D, E]` will always be in the same archetype.
* The `TableId` associated with the archetype
* For now each archetype has exactly one table (which can have no components),
* There is a 1->Many relationship from Tables->Archetypes. A given table could have any number of archetype components stored in it:
* Ex: an entity with "table storage" components `[A, B, C]` and "sparse set" components `[D, E]` will share the same `[A, B, C]` table as an entity with `[A, B, C]` table component and `[F]` sparse set components.
* This 1->Many relationship is how we preserve fast "cache friendly" iteration performance when possible (more on this later)
* A list of entities that are in the archetype and the row id of the table they are in
* ArchetypeComponentIds
* unique densely packed identifiers for (ArchetypeId, ComponentId) pairs
* used by the schedule executor for cheap system access control
* "Archetype Graph Edges" (see the next section)
## The "Archetype Graph"
Archetype changes in Bevy (and a number of other archetypal ecs-es) have historically been expensive to compute. First, you need to allocate a new vector of the entity's current component ids, add or remove components based on the operation performed, sort it (to ensure it is order-independent), then hash it to find the archetype (if it exists). And thats all before we get to the _already_ expensive full copy of all components to the new table storage.
The solution is to build a "graph" of archetypes to cache these results. @SanderMertens first exposed me to the idea (and he got it from @gjroelofs, who came up with it). They propose adding directed edges between archetypes for add/remove component operations. If `ComponentId`s are densely packed, you can use sparse sets to cheaply jump between archetypes.
Bevy takes this one step further by using add/remove `Bundle` edges instead of `Component` edges. Bevy encourages the use of `Bundles` to group add/remove operations. This is largely for "clearer game logic" reasons, but it also helps cut down on the number of archetype changes required. `Bundles` now also have densely-packed `BundleId`s. This allows us to use a _single_ edge for each bundle operation (rather than needing to traverse N edges ... one for each component). Single component operations are also bundles, so this is strictly an improvement over a "component only" graph.
As a result, an operation that used to be _heavy_ (both for allocations and compute) is now two dirt-cheap array lookups and zero allocations.
## Stateful Queries
World queries are now stateful. This allows us to:
1. Cache archetype (and table) matches
* This resolves another issue with (naive) archetypal ECS: query performance getting worse as the number of archetypes goes up (and fragmentation occurs).
2. Cache Fetch and Filter state
* The expensive parts of fetch/filter operations (such as hashing the TypeId to find the ComponentId) now only happen once when the Query is first constructed
3. Incrementally build up state
* When new archetypes are added, we only process the new archetypes (no need to rebuild state for old archetypes)
As a result, the direct `World` query api now looks like this:
```rust
let mut query = world.query::<(&A, &mut B)>();
for (a, mut b) in query.iter_mut(&mut world) {
}
```
Requiring `World` to generate stateful queries (rather than letting the `QueryState` type be constructed separately) allows us to ensure that _all_ queries are properly initialized (and the relevant world state, such as ComponentIds). This enables QueryState to remove branches from its operations that check for initialization status (and also enables query.iter() to take an immutable world reference because it doesn't need to initialize anything in world).
However in systems, this is a non-breaking change. State management is done internally by the relevant SystemParam.
## Stateful SystemParams
Like Queries, `SystemParams` now also cache state. For example, `Query` system params store the "stateful query" state mentioned above. Commands store their internal `CommandQueue`. This means you can now safely use as many separate `Commands` parameters in your system as you want. `Local<T>` system params store their `T` value in their state (instead of in Resources).
SystemParam state also enabled a significant slim-down of SystemState. It is much nicer to look at now.
Per-SystemParam state naturally insulates us from an "aliased mut" class of errors we have hit in the past (ex: using multiple `Commands` system params).
(credit goes to @DJMcNab for the initial idea and draft pr here #1364)
## Configurable SystemParams
@DJMcNab also had the great idea to make SystemParams configurable. This allows users to provide some initial configuration / values for system parameters (when possible). Most SystemParams have no config (the config type is `()`), but the `Local<T>` param now supports user-provided parameters:
```rust
fn foo(value: Local<usize>) {
}
app.add_system(foo.system().config(|c| c.0 = Some(10)));
```
## Uber Fast "for_each" Query Iterators
Developers now have the choice to use a fast "for_each" iterator, which yields ~1.5-3x iteration speed improvements for "fragmented iteration", and minor ~1.2x iteration speed improvements for unfragmented iteration.
```rust
fn system(query: Query<(&A, &mut B)>) {
// you now have the option to do this for a speed boost
query.for_each_mut(|(a, mut b)| {
});
// however normal iterators are still available
for (a, mut b) in query.iter_mut() {
}
}
```
I think in most cases we should continue to encourage "normal" iterators as they are more flexible and more "rust idiomatic". But when that extra "oomf" is needed, it makes sense to use `for_each`.
We should also consider using `for_each` for internal bevy systems to give our users a nice speed boost (but that should be a separate pr).
## Component Metadata
`World` now has a `Components` collection, which is accessible via `world.components()`. This stores mappings from `ComponentId` to `ComponentInfo`, as well as `TypeId` to `ComponentId` mappings (where relevant). `ComponentInfo` stores information about the component, such as ComponentId, TypeId, memory layout, send-ness (currently limited to resources), and storage type.
## Significantly Cheaper `Access<T>`
We used to use `TypeAccess<TypeId>` to manage read/write component/archetype-component access. This was expensive because TypeIds must be hashed and compared individually. The parallel executor got around this by "condensing" type ids into bitset-backed access types. This worked, but it had to be re-generated from the `TypeAccess<TypeId>`sources every time archetypes changed.
This pr removes TypeAccess in favor of faster bitset access everywhere. We can do this thanks to the move to densely packed `ComponentId`s and `ArchetypeComponentId`s.
## Merged Resources into World
Resources had a lot of redundant functionality with Components. They stored typed data, they had access control, they had unique ids, they were queryable via SystemParams, etc. In fact the _only_ major difference between them was that they were unique (and didn't correlate to an entity).
Separate resources also had the downside of requiring a separate set of access controls, which meant the parallel executor needed to compare more bitsets per system and manage more state.
I initially got the "separate resources" idea from `legion`. I think that design was motivated by the fact that it made the direct world query/resource lifetime interactions more manageable. It certainly made our lives easier when using Resources alongside hecs/bevy_ecs. However we already have a construct for safely and ergonomically managing in-world lifetimes: systems (which use `Access<T>` internally).
This pr merges Resources into World:
```rust
world.insert_resource(1);
world.insert_resource(2.0);
let a = world.get_resource::<i32>().unwrap();
let mut b = world.get_resource_mut::<f64>().unwrap();
*b = 3.0;
```
Resources are now just a special kind of component. They have their own ComponentIds (and their own resource TypeId->ComponentId scope, so they don't conflict wit components of the same type). They are stored in a special "resource archetype", which stores components inside the archetype using a new `unique_components` sparse set (note that this sparse set could later be used to implement Tags). This allows us to keep the code size small by reusing existing datastructures (namely Column, Archetype, ComponentFlags, and ComponentInfo). This allows us the executor to use a single `Access<ArchetypeComponentId>` per system. It should also make scripting language integration easier.
_But_ this merge did create problems for people directly interacting with `World`. What if you need mutable access to multiple resources at the same time? `world.get_resource_mut()` borrows World mutably!
## WorldCell
WorldCell applies the `Access<ArchetypeComponentId>` concept to direct world access:
```rust
let world_cell = world.cell();
let a = world_cell.get_resource_mut::<i32>().unwrap();
let b = world_cell.get_resource_mut::<f64>().unwrap();
```
This adds cheap runtime checks (a sparse set lookup of `ArchetypeComponentId` and a counter) to ensure that world accesses do not conflict with each other. Each operation returns a `WorldBorrow<'w, T>` or `WorldBorrowMut<'w, T>` wrapper type, which will release the relevant ArchetypeComponentId resources when dropped.
World caches the access sparse set (and only one cell can exist at a time), so `world.cell()` is a cheap operation.
WorldCell does _not_ use atomic operations. It is non-send, does a mutable borrow of world to prevent other accesses, and uses a simple `Rc<RefCell<ArchetypeComponentAccess>>` wrapper in each WorldBorrow pointer.
The api is currently limited to resource access, but it can and should be extended to queries / entity component access.
## Resource Scopes
WorldCell does not yet support component queries, and even when it does there are sometimes legitimate reasons to want a mutable world ref _and_ a mutable resource ref (ex: bevy_render and bevy_scene both need this). In these cases we could always drop down to the unsafe `world.get_resource_unchecked_mut()`, but that is not ideal!
Instead developers can use a "resource scope"
```rust
world.resource_scope(|world: &mut World, a: &mut A| {
})
```
This temporarily removes the `A` resource from `World`, provides mutable pointers to both, and re-adds A to World when finished. Thanks to the move to ComponentIds/sparse sets, this is a cheap operation.
If multiple resources are required, scopes can be nested. We could also consider adding a "resource tuple" to the api if this pattern becomes common and the boilerplate gets nasty.
## Query Conflicts Use ComponentId Instead of ArchetypeComponentId
For safety reasons, systems cannot contain queries that conflict with each other without wrapping them in a QuerySet. On bevy `main`, we use ArchetypeComponentIds to determine conflicts. This is nice because it can take into account filters:
```rust
// these queries will never conflict due to their filters
fn filter_system(a: Query<&mut A, With<B>>, b: Query<&mut B, Without<B>>) {
}
```
But it also has a significant downside:
```rust
// these queries will not conflict _until_ an entity with A, B, and C is spawned
fn maybe_conflicts_system(a: Query<(&mut A, &C)>, b: Query<(&mut A, &B)>) {
}
```
The system above will panic at runtime if an entity with A, B, and C is spawned. This makes it hard to trust that your game logic will run without crashing.
In this pr, I switched to using `ComponentId` instead. This _is_ more constraining. `maybe_conflicts_system` will now always fail, but it will do it consistently at startup. Naively, it would also _disallow_ `filter_system`, which would be a significant downgrade in usability. Bevy has a number of internal systems that rely on disjoint queries and I expect it to be a common pattern in userspace.
To resolve this, I added a new `FilteredAccess<T>` type, which wraps `Access<T>` and adds with/without filters. If two `FilteredAccess` have with/without values that prove they are disjoint, they will no longer conflict.
## EntityRef / EntityMut
World entity operations on `main` require that the user passes in an `entity` id to each operation:
```rust
let entity = world.spawn((A, )); // create a new entity with A
world.get::<A>(entity);
world.insert(entity, (B, C));
world.insert_one(entity, D);
```
This means that each operation needs to look up the entity location / verify its validity. The initial spawn operation also requires a Bundle as input. This can be awkward when no components are required (or one component is required).
These operations have been replaced by `EntityRef` and `EntityMut`, which are "builder-style" wrappers around world that provide read and read/write operations on a single, pre-validated entity:
```rust
// spawn now takes no inputs and returns an EntityMut
let entity = world.spawn()
.insert(A) // insert a single component into the entity
.insert_bundle((B, C)) // insert a bundle of components into the entity
.id() // id returns the Entity id
// Returns EntityMut (or panics if the entity does not exist)
world.entity_mut(entity)
.insert(D)
.insert_bundle(SomeBundle::default());
{
// returns EntityRef (or panics if the entity does not exist)
let d = world.entity(entity)
.get::<D>() // gets the D component
.unwrap();
// world.get still exists for ergonomics
let d = world.get::<D>(entity).unwrap();
}
// These variants return Options if you want to check existence instead of panicing
world.get_entity_mut(entity)
.unwrap()
.insert(E);
if let Some(entity_ref) = world.get_entity(entity) {
let d = entity_ref.get::<D>().unwrap();
}
```
This _does not_ affect the current Commands api or terminology. I think that should be a separate conversation as that is a much larger breaking change.
## Safety Improvements
* Entity reservation in Commands uses a normal world borrow instead of an unsafe transmute
* QuerySets no longer transmutes lifetimes
* Made traits "unsafe" when implementing a trait incorrectly could cause unsafety
* More thorough safety docs
## RemovedComponents SystemParam
The old approach to querying removed components: `query.removed:<T>()` was confusing because it had no connection to the query itself. I replaced it with the following, which is both clearer and allows us to cache the ComponentId mapping in the SystemParamState:
```rust
fn system(removed: RemovedComponents<T>) {
for entity in removed.iter() {
}
}
```
## Simpler Bundle implementation
Bundles are no longer responsible for sorting (or deduping) TypeInfo. They are just a simple ordered list of component types / data. This makes the implementation smaller and opens the door to an easy "nested bundle" implementation in the future (which i might even add in this pr). Duplicate detection is now done once per bundle type by World the first time a bundle is used.
## Unified WorldQuery and QueryFilter types
(don't worry they are still separate type _parameters_ in Queries .. this is a non-breaking change)
WorldQuery and QueryFilter were already basically identical apis. With the addition of `FetchState` and more storage-specific fetch methods, the overlap was even clearer (and the redundancy more painful).
QueryFilters are now just `F: WorldQuery where F::Fetch: FilterFetch`. FilterFetch requires `Fetch<Item = bool>` and adds new "short circuit" variants of fetch methods. This enables a filter tuple like `(With<A>, Without<B>, Changed<C>)` to stop evaluating the filter after the first mismatch is encountered. FilterFetch is automatically implemented for `Fetch` implementations that return bool.
This forces fetch implementations that return things like `(bool, bool, bool)` (such as the filter above) to manually implement FilterFetch and decide whether or not to short-circuit.
## More Granular Modules
World no longer globs all of the internal modules together. It now exports `core`, `system`, and `schedule` separately. I'm also considering exporting `core` submodules directly as that is still pretty "glob-ey" and unorganized (feedback welcome here).
## Remaining Draft Work (to be done in this pr)
* ~~panic on conflicting WorldQuery fetches (&A, &mut A)~~
* ~~bevy `main` and hecs both currently allow this, but we should protect against it if possible~~
* ~~batch_iter / par_iter (currently stubbed out)~~
* ~~ChangedRes~~
* ~~I skipped this while we sort out #1313. This pr should be adapted to account for whatever we land on there~~.
* ~~The `Archetypes` and `Tables` collections use hashes of sorted lists of component ids to uniquely identify each archetype/table. This hash is then used as the key in a HashMap to look up the relevant ArchetypeId or TableId. (which doesn't handle hash collisions properly)~~
* ~~It is currently unsafe to generate a Query from "World A", then use it on "World B" (despite the api claiming it is safe). We should probably close this gap. This could be done by adding a randomly generated WorldId to each world, then storing that id in each Query. They could then be compared to each other on each `query.do_thing(&world)` operation. This _does_ add an extra branch to each query operation, so I'm open to other suggestions if people have them.~~
* ~~Nested Bundles (if i find time)~~
## Potential Future Work
* Expand WorldCell to support queries.
* Consider not allocating in the empty archetype on `world.spawn()`
* ex: return something like EntityMutUninit, which turns into EntityMut after an `insert` or `insert_bundle` op
* this actually regressed performance last time i tried it, but in theory it should be faster
* Optimize SparseSet::insert (see `PERF` comment on insert)
* Replace SparseArray `Option<T>` with T::MAX to cut down on branching
* would enable cheaper get_unchecked() operations
* upstream fixedbitset optimizations
* fixedbitset could be allocation free for small block counts (store blocks in a SmallVec)
* fixedbitset could have a const constructor
* Consider implementing Tags (archetype-specific by-value data that affects archetype identity)
* ex: ArchetypeA could have `[A, B, C]` table components and `[D(1)]` "tag" component. ArchetypeB could have `[A, B, C]` table components and a `[D(2)]` tag component. The archetypes are different, despite both having D tags because the value inside D is different.
* this could potentially build on top of the `archetype.unique_components` added in this pr for resource storage.
* Consider reverting `all_tuples` proc macro in favor of the old `macro_rules` implementation
* all_tuples is more flexible and produces cleaner documentation (the macro_rules version produces weird type parameter orders due to parser constraints)
* but unfortunately all_tuples also appears to make Rust Analyzer sad/slow when working inside of `bevy_ecs` (does not affect user code)
* Consider "resource queries" and/or "mixed resource and entity component queries" as an alternative to WorldCell
* this is basically just "systems" so maybe it's not worth it
* Add more world ops
* `world.clear()`
* `world.reserve<T: Bundle>(count: usize)`
* Try using the old archetype allocation strategy (allocate new memory on resize and copy everything over). I expect this to improve batch insertion performance at the cost of unbatched performance. But thats just a guess. I'm not an allocation perf pro :)
* Adapt Commands apis for consistency with new World apis
## Benchmarks
key:
* `bevy_old`: bevy `main` branch
* `bevy`: this branch
* `_foreach`: uses an optimized for_each iterator
* ` _sparse`: uses sparse set storage (if unspecified assume table storage)
* `_system`: runs inside a system (if unspecified assume test happens via direct world ops)
### Simple Insert (from ecs_bench_suite)
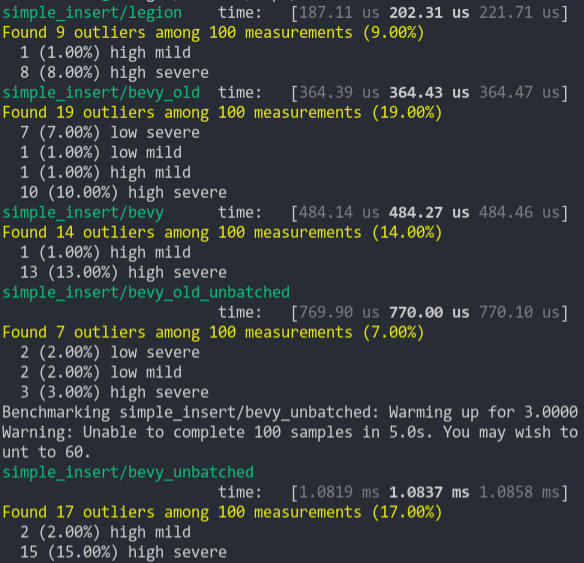
### Simpler Iter (from ecs_bench_suite)
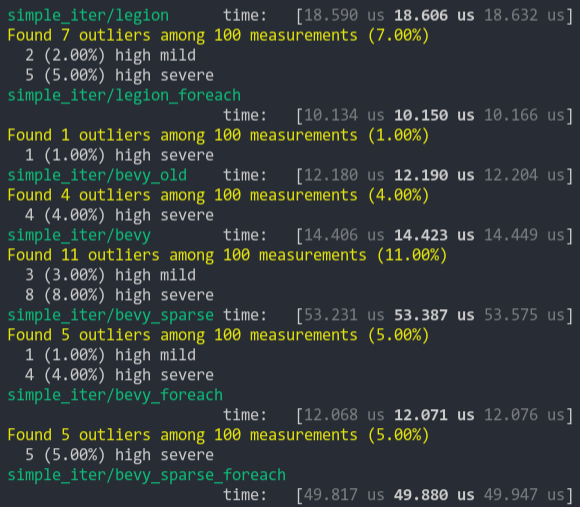
### Fragment Iter (from ecs_bench_suite)
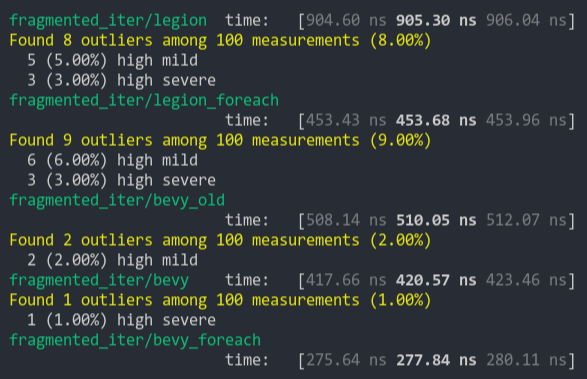
### Sparse Fragmented Iter
Iterate a query that matches 5 entities from a single matching archetype, but there are 100 unmatching archetypes
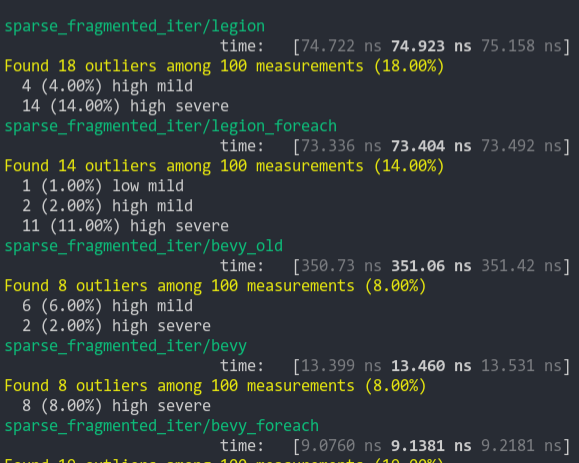
### Schedule (from ecs_bench_suite)
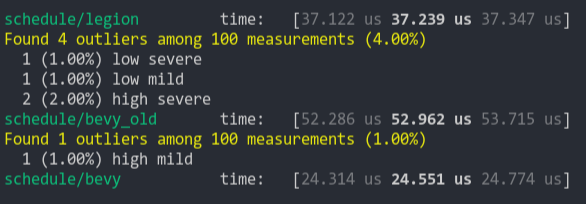
### Add Remove Component (from ecs_bench_suite)
### Add Remove Component Big
Same as the test above, but each entity has 5 "large" matrix components and 1 "large" matrix component is added and removed
### Get Component
Looks up a single component value a large number of times
|