The `collect_buffers_for_phase` system tries to reuse these buffers, but
its efforts are stymied by the fact that
`clear_batched_gpu_instance_buffers` clears the containing hash table
and therefore frees the buffers. This patch makes
`clear_batched_gpu_instance_buffers` stop doing that so that the
allocations can be reused.
There was nonsense code in `batch_and_prepare_sorted_render_phase` that
created temporary buffers to add objects to instead of using the correct
ones. I think this was debug code. This commit removes that code in
favor of writing to the actual buffers.
Closes#17846.
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
The `output_index` field is only used in direct mode, and the
`indirect_parameters_index` field is only used in indirect mode.
Consequently, we can combine them into a single field, reducing the size
of `PreprocessWorkItem`, which
`batch_and_prepare_{binned,sorted}_render_phase` must construct every
frame for every mesh instance, from 96 bits to 64 bits.
Currently, invocations of `batch_and_prepare_binned_render_phase` and
`batch_and_prepare_sorted_render_phase` can't run in parallel because
they write to scene-global GPU buffers. After PR #17698,
`batch_and_prepare_binned_render_phase` started accounting for the
lion's share of the CPU time, causing us to be strongly CPU bound on
scenes like Caldera when occlusion culling was on (because of the
overhead of batching for the Z-prepass). Although I eventually plan to
optimize `batch_and_prepare_binned_render_phase`, we can obtain
significant wins now by parallelizing that system across phases.
This commit splits all GPU buffers that
`batch_and_prepare_binned_render_phase` and
`batch_and_prepare_sorted_render_phase` touches into separate buffers
for each phase so that the scheduler will run those phases in parallel.
At the end of batch preparation, we gather the render phases up into a
single resource with a new *collection* phase. Because we already run
mesh preprocessing separately for each phase in order to make occlusion
culling work, this is actually a cleaner separation. For example, mesh
output indices (the unique ID that identifies each mesh instance on GPU)
are now guaranteed to be sequential starting from 0, which will simplify
the forthcoming work to remove them in favor of the compute dispatch ID.
On Caldera, this brings the frame time down to approximately 9.1 ms with
occlusion culling on.

Conceptually, bins are ordered hash maps. We currently implement these
as a list of keys with an associated hash map. But we already have a
data type that implements ordered hash maps directly: `IndexMap`. This
patch switches Bevy to use `IndexMap`s for bins. Because we're memory
bound, this doesn't affect performance much, but it is cleaner.
Currently, we look up each `MeshInputUniform` index in a hash table that
maps the main entity ID to the index every frame. This is inefficient,
cache unfriendly, and unnecessary, as the `MeshInputUniform` index for
an entity remains the same from frame to frame (even if the input
uniform changes). This commit changes the `IndexSet` in the `RenderBin`
to an `IndexMap` that maps the `MainEntity` to `MeshInputUniformIndex`
(a new type that this patch adds for more type safety).
On Caldera with parallel `batch_and_prepare_binned_render_phase`, this
patch improves that function from 3.18 ms to 2.42 ms, a 31% speedup.
Didn't remove WgpuWrapper. Not sure if it's needed or not still.
## Testing
- Did you test these changes? If so, how? Example runner
- Are there any parts that need more testing? Web (portable atomics
thingy?), DXC.
## Migration Guide
- Bevy has upgraded to [wgpu
v24](https://github.com/gfx-rs/wgpu/blob/trunk/CHANGELOG.md#v2400-2025-01-15).
- When using the DirectX 12 rendering backend, the new priority system
for choosing a shader compiler is as follows:
- If the `WGPU_DX12_COMPILER` environment variable is set at runtime, it
is used
- Else if the new `statically-linked-dxc` feature is enabled, a custom
version of DXC will be statically linked into your app at compile time.
- Else Bevy will look in the app's working directory for
`dxcompiler.dll` and `dxil.dll` at runtime.
- Else if they are missing, Bevy will fall back to FXC (not recommended)
---------
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: IceSentry <c.giguere42@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: François Mockers <francois.mockers@vleue.com>
PR #17684 broke occlusion culling because it neglected to set the
indirect parameter offsets for the late mesh preprocessing stage if the
work item buffers were already set. This PR moves the update of those
values to a new function, `init_work_item_buffers`, which is
unconditionally called for every phase every frame.
Note that there's some complexity in order to handle the case in which
occlusion culling was enabled on one frame and disabled on the next, or
vice versa. This was necessary in order to make the occlusion culling
toggle in the `occlusion_culling` example work again.
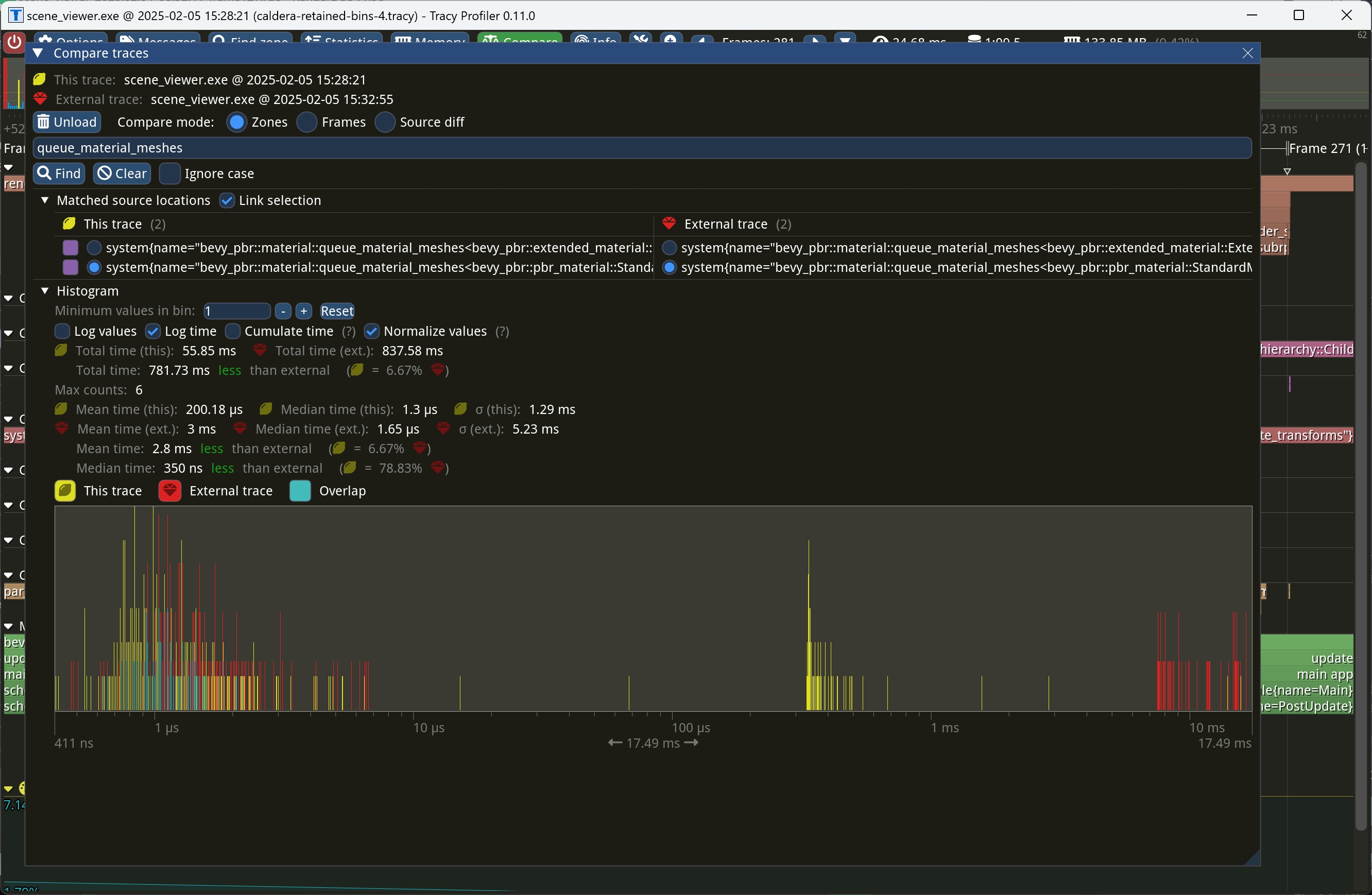
This PR makes Bevy keep entities in bins from frame to frame if they
haven't changed. This reduces the time spent in `queue_material_meshes`
and related functions to near zero for static geometry. This patch uses
the same change tick technique that #17567 uses to detect when meshes
have changed in such a way as to require re-binning.
In order to quickly find the relevant bin for an entity when that entity
has changed, we introduce a new type of cache, the *bin key cache*. This
cache stores a mapping from main world entity ID to cached bin key, as
well as the tick of the most recent change to the entity. As we iterate
through the visible entities in `queue_material_meshes`, we check the
cache to see whether the entity needs to be re-binned. If it doesn't,
then we mark it as clean in the `valid_cached_entity_bin_keys` bit set.
If it does, then we insert it into the correct bin, and then mark the
entity as clean. At the end, all entities not marked as clean are
removed from the bins.
This patch has a dramatic effect on the rendering performance of most
benchmarks, as it effectively eliminates `queue_material_meshes` from
the profile. Note, however, that it generally simultaneously regresses
`batch_and_prepare_binned_render_phase` by a bit (not by enough to
outweigh the win, however). I believe that's because, before this patch,
`queue_material_meshes` put the bins in the CPU cache for
`batch_and_prepare_binned_render_phase` to use, while with this patch,
`batch_and_prepare_binned_render_phase` must load the bins into the CPU
cache itself.
On Caldera, this reduces the time spent in `queue_material_meshes` from
5+ ms to 0.2ms-0.3ms. Note that benchmarking on that scene is very noisy
right now because of https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/17535.
We were calling `clear()` on the work item buffer table, which caused us
to deallocate all the CPU side buffers. This patch changes the logic to
instead just clear the buffers individually, but leave their backing
stores. This has two consequences:
1. To effectively retain work item buffers from frame to frame, we need
to key them off `RetainedViewEntity` values and not the render world
`Entity`, which is transient. This PR changes those buffers accordingly.
2. We need to clean up work item buffers that belong to views that went
away. Amusingly enough, we actually have a system,
`delete_old_work_item_buffers`, that tries to do this already, but it
wasn't doing anything because the `clear_batched_gpu_instance_buffers`
system already handled that. This patch actually makes the
`delete_old_work_item_buffers` system useful, by removing the clearing
behavior from `clear_batched_gpu_instance_buffers` and instead making
`delete_old_work_item_buffers` delete buffers corresponding to
nonexistent views.
On Bistro, this PR improves the performance of
`batch_and_prepare_binned_render_phase` from 61.2 us to 47.8 us, a 28%
speedup.

Data for the other batches is only accessed by the GPU, not the CPU, so
it's a waste of time and memory to store information relating to those
other batches.
On Bistro, this reduces time spent in
`batch_and_prepare_binned_render_phase` from 85.9 us to 61.2 us, a 40%
speedup.

*Occlusion culling* allows the GPU to skip the vertex and fragment
shading overhead for objects that can be quickly proved to be invisible
because they're behind other geometry. A depth prepass already
eliminates most fragment shading overhead for occluded objects, but the
vertex shading overhead, as well as the cost of testing and rejecting
fragments against the Z-buffer, is presently unavoidable for standard
meshes. We currently perform occlusion culling only for meshlets. But
other meshes, such as skinned meshes, can benefit from occlusion culling
too in order to avoid the transform and skinning overhead for unseen
meshes.
This commit adapts the same [*two-phase occlusion culling*] technique
that meshlets use to Bevy's standard 3D mesh pipeline when the new
`OcclusionCulling` component, as well as the `DepthPrepass` component,
are present on the camera. It has these steps:
1. *Early depth prepass*: We use the hierarchical Z-buffer from the
previous frame to cull meshes for the initial depth prepass, effectively
rendering only the meshes that were visible in the last frame.
2. *Early depth downsample*: We downsample the depth buffer to create
another hierarchical Z-buffer, this time with the current view
transform.
3. *Late depth prepass*: We use the new hierarchical Z-buffer to test
all meshes that weren't rendered in the early depth prepass. Any meshes
that pass this check are rendered.
4. *Late depth downsample*: Again, we downsample the depth buffer to
create a hierarchical Z-buffer in preparation for the early depth
prepass of the next frame. This step is done after all the rendering, in
order to account for custom phase items that might write to the depth
buffer.
Note that this patch has no effect on the per-mesh CPU overhead for
occluded objects, which remains high for a GPU-driven renderer due to
the lack of `cold-specialization` and retained bins. If
`cold-specialization` and retained bins weren't on the horizon, then a
more traditional approach like potentially visible sets (PVS) or low-res
CPU rendering would probably be more efficient than the GPU-driven
approach that this patch implements for most scenes. However, at this
point the amount of effort required to implement a PVS baking tool or a
low-res CPU renderer would probably be greater than landing
`cold-specialization` and retained bins, and the GPU driven approach is
the more modern one anyway. It does mean that the performance
improvements from occlusion culling as implemented in this patch *today*
are likely to be limited, because of the high CPU overhead for occluded
meshes.
Note also that this patch currently doesn't implement occlusion culling
for 2D objects or shadow maps. Those can be addressed in a follow-up.
Additionally, note that the techniques in this patch require compute
shaders, which excludes support for WebGL 2.
This PR is marked experimental because of known precision issues with
the downsampling approach when applied to non-power-of-two framebuffer
sizes (i.e. most of them). These precision issues can, in rare cases,
cause objects to be judged occluded that in fact are not. (I've never
seen this in practice, but I know it's possible; it tends to be likelier
to happen with small meshes.) As a follow-up to this patch, we desire to
switch to the [SPD-based hi-Z buffer shader from the Granite engine],
which doesn't suffer from these problems, at which point we should be
able to graduate this feature from experimental status. I opted not to
include that rewrite in this patch for two reasons: (1) @JMS55 is
planning on doing the rewrite to coincide with the new availability of
image atomic operations in Naga; (2) to reduce the scope of this patch.
A new example, `occlusion_culling`, has been added. It demonstrates
objects becoming quickly occluded and disoccluded by dynamic geometry
and shows the number of objects that are actually being rendered. Also,
a new `--occlusion-culling` switch has been added to `scene_viewer`, in
order to make it easy to test this patch with large scenes like Bistro.
[*two-phase occlusion culling*]:
https://medium.com/@mil_kru/two-pass-occlusion-culling-4100edcad501
[Aaltonen SIGGRAPH 2015]:
https://www.advances.realtimerendering.com/s2015/aaltonenhaar_siggraph2015_combined_final_footer_220dpi.pdf
[Some literature]:
https://gist.github.com/reduz/c5769d0e705d8ab7ac187d63be0099b5?permalink_comment_id=5040452#gistcomment-5040452
[SPD-based hi-Z buffer shader from the Granite engine]:
https://github.com/Themaister/Granite/blob/master/assets/shaders/post/hiz.comp
## Migration guide
* When enqueuing a custom mesh pipeline, work item buffers are now
created with
`bevy::render::batching::gpu_preprocessing::get_or_create_work_item_buffer`,
not `PreprocessWorkItemBuffers::new`. See the
`specialized_mesh_pipeline` example.
## Showcase
Occlusion culling example:

Bistro zoomed out, before occlusion culling:

Bistro zoomed out, after occlusion culling:

In this scene, occlusion culling reduces the number of meshes Bevy has
to render from 1591 to 585.
# Objective
`bevy_ecs`'s `system` module is something of a grab bag, and *very*
large. This is particularly true for the `system_param` module, which is
more than 2k lines long!
While it could be defensible to put `Res` and `ResMut` there (lol no
they're in change_detection.rs, obviously), it doesn't make any sense to
put the `Resource` trait there. This is confusing to navigate (and
painful to work on and review).
## Solution
- Create a root level `bevy_ecs/resource.rs` module to mirror
`bevy_ecs/component.rs`
- move the `Resource` trait to that module
- move the `Resource` derive macro to that module as well (Rust really
likes when you pun on the names of the derive macro and trait and put
them in the same path)
- fix all of the imports
## Notes to reviewers
- We could probably move more stuff into here, but I wanted to keep this
PR as small as possible given the absurd level of import changes.
- This PR is ground work for my upcoming attempts to store resource data
on components (resources-as-entities). Splitting this code out will make
the work and review a bit easier, and is the sort of overdue refactor
that's good to do as part of more meaningful work.
## Testing
cargo build works!
## Migration Guide
`bevy_ecs::system::Resource` has been moved to
`bevy_ecs::resource::Resource`.
# Objective
The existing `RelationshipSourceCollection` uses `Vec` as the only
possible backing for our relationships. While a reasonable choice,
benchmarking use cases might reveal that a different data type is better
or faster.
For example:
- Not all relationships require a stable ordering between the
relationship sources (i.e. children). In cases where we a) have many
such relations and b) don't care about the ordering between them, a hash
set is likely a better datastructure than a `Vec`.
- The number of children-like entities may be small on average, and a
`smallvec` may be faster
## Solution
- Implement `RelationshipSourceCollection` for `EntityHashSet`, our
custom entity-optimized `HashSet`.
-~~Implement `DoubleEndedIterator` for `EntityHashSet` to make things
compile.~~
- This implementation was cursed and very surprising.
- Instead, by moving the iterator type on `RelationshipSourceCollection`
from an erased RPTIT to an explicit associated type we can add a trait
bound on the offending methods!
- Implement `RelationshipSourceCollection` for `SmallVec`
## Testing
I've added a pair of new tests to make sure this pattern compiles
successfully in practice!
## Migration Guide
`EntityHashSet` and `EntityHashMap` are no longer re-exported in
`bevy_ecs::entity` directly. If you were not using `bevy_ecs` / `bevy`'s
`prelude`, you can access them through their now-public modules,
`hash_set` and `hash_map` instead.
## Notes to reviewers
The `EntityHashSet::Iter` type needs to be public for this impl to be
allowed. I initially renamed it to something that wasn't ambiguous and
re-exported it, but as @Victoronz pointed out, that was somewhat
unidiomatic.
In
1a8564898f,
I instead made the `entity_hash_set` public (and its `entity_hash_set`)
sister public, and removed the re-export. I prefer this design (give me
module docs please), but it leads to a lot of churn in this PR.
Let me know which you'd prefer, and if you'd like me to split that
change out into its own micro PR.
This commit allows Bevy to use `multi_draw_indirect_count` for drawing
meshes. The `multi_draw_indirect_count` feature works just like
`multi_draw_indirect`, but it takes the number of indirect parameters
from a GPU buffer rather than specifying it on the CPU.
Currently, the CPU constructs the list of indirect draw parameters with
the instance count for each batch set to zero, uploads the resulting
buffer to the GPU, and dispatches a compute shader that bumps the
instance count for each mesh that survives culling. Unfortunately, this
is inefficient when we support `multi_draw_indirect_count`. Draw
commands corresponding to meshes for which all instances were culled
will remain present in the list when calling
`multi_draw_indirect_count`, causing overhead. Proper use of
`multi_draw_indirect_count` requires eliminating these empty draw
commands.
To address this inefficiency, this PR makes Bevy fully construct the
indirect draw commands on the GPU instead of on the CPU. Instead of
writing instance counts to the draw command buffer, the mesh
preprocessing shader now writes them to a separate *indirect metadata
buffer*. A second compute dispatch known as the *build indirect
parameters* shader runs after mesh preprocessing and converts the
indirect draw metadata into actual indirect draw commands for the GPU.
The build indirect parameters shader operates on a batch at a time,
rather than an instance at a time, and as such each thread writes only 0
or 1 indirect draw parameters, simplifying the current logic in
`mesh_preprocessing`, which currently has to have special cases for the
first mesh in each batch. The build indirect parameters shader emits
draw commands in a tightly packed manner, enabling maximally efficient
use of `multi_draw_indirect_count`.
Along the way, this patch switches mesh preprocessing to dispatch one
compute invocation per render phase per view, instead of dispatching one
compute invocation per view. This is preparation for two-phase occlusion
culling, in which we will have two mesh preprocessing stages. In that
scenario, the first mesh preprocessing stage must only process opaque
and alpha tested objects, so the work items must be separated into those
that are opaque or alpha tested and those that aren't. Thus this PR
splits out the work items into a separate buffer for each phase. As this
patch rewrites so much of the mesh preprocessing infrastructure, it was
simpler to just fold the change into this patch instead of deferring it
to the forthcoming occlusion culling PR.
Finally, this patch changes mesh preprocessing so that it runs
separately for indexed and non-indexed meshes. This is because draw
commands for indexed and non-indexed meshes have different sizes and
layouts. *The existing code is actually broken for non-indexed meshes*,
as it attempts to overlay the indirect parameters for non-indexed meshes
on top of those for indexed meshes. Consequently, right now the
parameters will be read incorrectly when multiple non-indexed meshes are
multi-drawn together. *This is a bug fix* and, as with the change to
dispatch phases separately noted above, was easiest to include in this
patch as opposed to separately.
## Migration Guide
* Systems that add custom phase items now need to populate the indirect
drawing-related buffers. See the `specialized_mesh_pipeline` example for
an example of how this is done.
We won't be able to retain render phases from frame to frame if the keys
are unstable. It's not as simple as simply keying off the main world
entity, however, because some main world entities extract to multiple
render world entities. For example, directional lights extract to
multiple shadow cascades, and point lights extract to one view per
cubemap face. Therefore, we key off a new type, `RetainedViewEntity`,
which contains the main entity plus a *subview ID*.
This is part of the preparation for retained bins.
---------
Co-authored-by: ickshonpe <david.curthoys@googlemail.com>
# Objective
the `get` function on [`InstanceInputUniformBuffer`] seems very
error-prone. This PR hopes to fix this.
## Solution
Do a few checks to ensure the index is in bounds and that the `BDI` is
not removed.
Return `Option<BDI>` instead of `BDI`.
## Testing
- Did you test these changes? If so, how?
added a test to verify that the instance buffer works correctly
## Future Work
Performance decreases when using .binary_search(). However this is
likely due to the fact that [`InstanceInputUniformBuffer::get`] for now
is never used, and only get_unchecked.
## Migration Guide
`InstanceInputUniformBuffer::get` now returns `Option<BDI>` instead of
`BDI` to reduce panics. If you require the old functionality of
`InstanceInputUniformBuffer::get` consider using
`InstanceInputUniformBuffer::get_unchecked`.
---------
Co-authored-by: Tim Overbeek <oorbeck@gmail.com>
Currently, our batchable binned items are stored in a hash table that
maps bin key, which includes the batch set key, to a list of entities.
Multidraw is handled by sorting the bin keys and accumulating adjacent
bins that can be multidrawn together (i.e. have the same batch set key)
into multidraw commands during `batch_and_prepare_binned_render_phase`.
This is reasonably efficient right now, but it will complicate future
work to retain indirect draw parameters from frame to frame. Consider
what must happen when we have retained indirect draw parameters and the
application adds a bin (i.e. a new mesh) that shares a batch set key
with some pre-existing meshes. (That is, the new mesh can be multidrawn
with the pre-existing meshes.) To be maximally efficient, our goal in
that scenario will be to update *only* the indirect draw parameters for
the batch set (i.e. multidraw command) containing the mesh that was
added, while leaving the others alone. That means that we have to
quickly locate all the bins that belong to the batch set being modified.
In the existing code, we would have to sort the list of bin keys so that
bins that can be multidrawn together become adjacent to one another in
the list. Then we would have to do a binary search through the sorted
list to find the location of the bin that was just added. Next, we would
have to widen our search to adjacent indexes that contain the same batch
set, doing expensive comparisons against the batch set key every time.
Finally, we would reallocate the indirect draw parameters and update the
stored pointers to the indirect draw parameters that the bins store.
By contrast, it'd be dramatically simpler if we simply changed the way
bins are stored to first map from batch set key (i.e. multidraw command)
to the bins (i.e. meshes) within that batch set key, and then from each
individual bin to the mesh instances. That way, the scenario above in
which we add a new mesh will be simpler to handle. First, we will look
up the batch set key corresponding to that mesh in the outer map to find
an inner map corresponding to the single multidraw command that will
draw that batch set. We will know how many meshes the multidraw command
is going to draw by the size of that inner map. Then we simply need to
reallocate the indirect draw parameters and update the pointers to those
parameters within the bins as necessary. There will be no need to do any
binary search or expensive batch set key comparison: only a single hash
lookup and an iteration over the inner map to update the pointers.
This patch implements the above technique. Because we don't have
retained bins yet, this PR provides no performance benefits. However, it
opens the door to maximally efficient updates when only a small number
of meshes change from frame to frame.
The main churn that this patch causes is that the *batch set key* (which
uniquely specifies a multidraw command) and *bin key* (which uniquely
specifies a mesh *within* that multidraw command) are now separate,
instead of the batch set key being embedded *within* the bin key.
In order to isolate potential regressions, I think that at least #16890,
#16836, and #16825 should land before this PR does.
## Migration Guide
* The *batch set key* is now separate from the *bin key* in
`BinnedPhaseItem`. The batch set key is used to collect multidrawable
meshes together. If you aren't using the multidraw feature, you can
safely set the batch set key to `()`.
# Objective
- Contributes to #11478
## Solution
- Made `bevy_utils::tracing` `doc(hidden)`
- Re-exported `tracing` from `bevy_log` for end-users
- Added `tracing` directly to crates that need it.
## Testing
- CI
---
## Migration Guide
If you were importing `tracing` via `bevy::utils::tracing`, instead use
`bevy::log::tracing`. Note that many items within `tracing` are also
directly re-exported from `bevy::log` as well, so you may only need
`bevy::log` for the most common items (e.g., `warn!`, `trace!`, etc.).
This also applies to the `log_once!` family of macros.
## Notes
- While this doesn't reduce the line-count in `bevy_utils`, it further
decouples the internal crates from `bevy_utils`, making its eventual
removal more feasible in the future.
- I have just imported `tracing` as we do for all dependencies. However,
a workspace dependency may be more appropriate for version management.
This commit makes the following changes:
* `IndirectParametersBuffer` has been changed from a `BufferVec` to a
`RawBufferVec`. This won about 20us or so on Bistro by avoiding `encase`
overhead.
* The methods on the `GetFullBatchData` trait no longer have the
`entity` parameter, as it was unused.
* `PreprocessWorkItem`, which specifies a transform-and-cull operation,
now supplies the mesh instance uniform output index directly instead of
having the shader look it up from the indirect draw parameters.
Accordingly, the responsibility of writing the output index to the
indirect draw parameters has been moved from the CPU to the GPU. This is
in preparation for retained indirect instance draw commands, where the
mesh instance uniform output index may change from frame to frame, while
the indirect instance draw commands will be cached. We won't want the
CPU to have to upload the same indirect draw parameters again and again
if a batch didn't change from frame to frame.
* `batch_and_prepare_binned_render_phase` and
`batch_and_prepare_sorted_render_phase` now allocate indirect draw
commands for an entire batch set at a time when possible, instead of one
batch at a time. This change will allow us to retain the indirect draw
commands for whole batch sets.
* `GetFullBatchData::get_batch_indirect_parameters_index` has been
replaced with `GetFullBatchData::write_batch_indirect_parameters`, which
takes an offset and writes into it instead of allocating. This is
necessary in order to use the optimization mentioned in the previous
point.
* At the WGSL level, `IndirectParameters` has been factored out into
`mesh_preprocess_types.wgsl`. This is because we'll need a new compute
shader that zeroes out the instance counts in preparation for a new
frame. That shader will need to access `IndirectParameters`, so it was
moved to a separate file.
* Bins are no longer raw vectors but are instances of a separate type,
`RenderBin`. This is so that the bin can eventually contain its retained
batches.
OK, so this is tricky. Every frame, `delete_old_work_item_buffers`
deletes the mesh preprocessing index buffers (a.k.a. work item buffers)
for views that don't have `ViewTarget`s. This was always wrong for
shadow map views, as shadow maps only have `ExtractedView` components,
not `ViewTarget`s. However, before #16836, the problem was masked,
because uploading the mesh preprocessing index buffers for shadow views
had already completed by the time `delete_old_work_item_buffers` ran.
But PR #16836 moved `delete_old_work_item_buffers` from the
`ManageViews` phase to `PrepareResources`, which runs before
`write_batched_instance_buffers` uploads the work item buffers to the
GPU.
This itself isn't wrong, but it exposed the bug, because now it's
possible for work item buffers to get deleted before they're uploaded in
`write_batched_instance_buffers`. This is actually intermittent! It's
possible for the old work item buffers to get deleted, and then
*recreated* in `batch_and_prepare_binned_render_phase`, which runs
during `PrepareResources` as well, and under that system ordering, there
will be no problem other than a little inefficiency arising from
recreating the buffers every frame. But, if
`delete_old_work_item_buffers` runs *after*
`batch_and_prepare_render_phase`, then the work item buffers
corresponding to shadow views will get deleted, and then the shadows
will disappear.
The fact that this is racy is what made it look like #16922 solved the
issue. In fact, it didn't: it just perturbed the ordering on the build
bots enough that the issue stopped appearing. However, on my system, the
shadows still don't appear with #16922.
This commit solves the problem by making `delete_old_work_item_buffers`
look at `ExtractedView`s, not `ViewTarget`s, preventing work item
buffers corresponding to live shadow map views from being deleted.
This commit fixes the following regressions:
1. Transmission-specific calls to shader lighting functions didn't pass
the `enable_diffuse` parameter, breaking the `transmission` example.
2. The combination of bindless `StandardMaterial` and bindless lightmaps
caused us to blow past the 128 texture limit on M1/M2 chips in some
cases, in particular the `depth_of_field` example.
https://github.com/gfx-rs/wgpu/issues/3334 should fix this, but in the
meantime this patch reduces the number of bindless lightmaps from 16 to
4 in order to stay under the limit.
3. The renderer was crashing on startup on Adreno 610 chips. This PR
simply disables bindless on Adreno 610 and lower.
This patch replaces the undocumented `NoGpuCulling` component with a new
component, `NoIndirectDrawing`, effectively turning indirect drawing on
by default. Indirect mode is needed for the recently-landed multidraw
feature (#16427). Since multidraw is such a win for performance, when
that feature is supported the small performance tax that indirect mode
incurs is virtually always worth paying.
To ensure that custom drawing code such as that in the
`custom_shader_instancing` example continues to function, this commit
additionally makes GPU culling take the `NoFrustumCulling` component
into account.
This PR is an alternative to #16670 that doesn't break the
`custom_shader_instancing` example. **PR #16755 should land first in
order to avoid breaking deferred rendering, as multidraw currently
breaks it**.
## Migration Guide
* Indirect drawing (GPU culling) is now enabled by default, so the
`GpuCulling` component is no longer available. To disable indirect mode,
which may be useful with custom render nodes, add the new
`NoIndirectDrawing` component to your camera.
This commit resolves most of the failures seen in #16670. It contains
two major fixes:
1. The prepass shaders weren't updated for bindless mode, so they were
accessing `material` as a single element instead of as an array. I added
the needed `BINDLESS` check.
2. If the mesh didn't support batch set keys (i.e. `get_batch_set_key()`
returns `None`), and multidraw was enabled, the batching logic would try
to multidraw all the meshes in a bin together instead of disabling
multidraw. This is because we checked whether the `Option<BatchSetKey>`
for the previous batch was equal to the `Option<BatchSetKey>` for the
next batch to determine whether objects could be multidrawn together,
which would return true if batch set keys were absent, causing an entire
bin to be multidrawn together. This patch fixes the logic so that
multidraw is only enabled if the batch set keys match *and are `Some`*.
Additionally, this commit adds batch key support for bins that use
`Opaque3dNoLightmapBinKey`, which in practice means prepasses.
Consequently, this patch enables multidraw for the prepass when GPU
culling is enabled.
When testing this patch, try adding `GpuCulling` to the camera in the
`deferred_rendering` and `ssr` examples. You can see that these examples
break without this patch and work properly with it.
---------
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
This commit removes the logic that attempted to keep the
`MeshInputUniform` buffer contiguous. Not only was it slow and complex,
but it was also incorrect, which caused #16686 and #16690. I changed the
logic to simply maintain a free list of unused slots in the buffer and
preferentially fill them when pushing new mesh input uniforms.
Closes#16686.
Closes#16690.
This commit adds support for *multidraw*, which is a feature that allows
multiple meshes to be drawn in a single drawcall. `wgpu` currently
implements multidraw on Vulkan, so this feature is only enabled there.
Multiple meshes can be drawn at once if they're in the same vertex and
index buffers and are otherwise placed in the same bin. (Thus, for
example, at present the materials and textures must be identical, but
see #16368.) Multidraw is a significant performance improvement during
the draw phase because it reduces the number of rebindings, as well as
the number of drawcalls.
This feature is currently only enabled when GPU culling is used: i.e.
when `GpuCulling` is present on a camera. Therefore, if you run for
example `scene_viewer`, you will not see any performance improvements,
because `scene_viewer` doesn't add the `GpuCulling` component to its
camera.
Additionally, the multidraw feature is only implemented for opaque 3D
meshes and not for shadows or 2D meshes. I plan to make GPU culling the
default and to extend the feature to shadows in the future. Also, in the
future I suspect that polyfilling multidraw on APIs that don't support
it will be fruitful, as even without driver-level support use of
multidraw allows us to avoid expensive `wgpu` rebindings.
This commit moves the front end of the rendering pipeline to a retained
model when GPU preprocessing is in use (i.e. by default, except in
constrained environments). `RenderMeshInstance` and `MeshUniformData`
are stored from frame to frame and are updated only for the entities
that changed state. This was rather tricky and requires some careful
surgery to keep the data valid in the case of removals.
This patch is built on top of Bevy's change detection. Generally, this
worked, except that `ViewVisibility` isn't currently properly tracked.
Therefore, this commit adds proper change tracking for `ViewVisibility`.
Doing this required adding a new system that runs after all
`check_visibility` invocations, as no single `check_visibility`
invocation has enough global information to detect changes.
On the Bistro exterior scene, with all textures forced to opaque, this
patch improves steady-state `extract_meshes_for_gpu_building` from
93.8us to 34.5us and steady-state `collect_meshes_for_gpu_building` from
195.7us to 4.28us. Altogether this constitutes an improvement from 290us
to 38us, which is a 7.46x speedup.


This patch is only lightly tested and shouldn't land before 0.15 is
released anyway, so I'm releasing it as a draft.
# Objective
In the Render World, there are a number of collections that are derived
from Main World entities and are used to drive rendering. The most
notable are:
- `VisibleEntities`, which is generated in the `check_visibility` system
and contains visible entities for a view.
- `ExtractedInstances`, which maps entity ids to asset ids.
In the old model, these collections were trivially kept in sync -- any
extracted phase item could look itself up because the render entity id
was guaranteed to always match the corresponding main world id.
After #15320, this became much more complicated, and was leading to a
number of subtle bugs in the Render World. The main rendering systems,
i.e. `queue_material_meshes` and `queue_material2d_meshes`, follow a
similar pattern:
```rust
for visible_entity in visible_entities.iter::<With<Mesh2d>>() {
let Some(mesh_instance) = render_mesh_instances.get_mut(visible_entity) else {
continue;
};
// Look some more stuff up and specialize the pipeline...
let bin_key = Opaque2dBinKey {
pipeline: pipeline_id,
draw_function: draw_opaque_2d,
asset_id: mesh_instance.mesh_asset_id.into(),
material_bind_group_id: material_2d.get_bind_group_id().0,
};
opaque_phase.add(
bin_key,
*visible_entity,
BinnedRenderPhaseType::mesh(mesh_instance.automatic_batching),
);
}
```
In this case, `visible_entities` and `render_mesh_instances` are both
collections that are created and keyed by Main World entity ids, and so
this lookup happens to work by coincidence. However, there is a major
unintentional bug here: namely, because `visible_entities` is a
collection of Main World ids, the phase item being queued is created
with a Main World id rather than its correct Render World id.
This happens to not break mesh rendering because the render commands
used for drawing meshes do not access the `ItemQuery` parameter, but
demonstrates the confusion that is now possible: our UI phase items are
correctly being queued with Render World ids while our meshes aren't.
Additionally, this makes it very easy and error prone to use the wrong
entity id to look up things like assets. For example, if instead we
ignored visibility checks and queued our meshes via a query, we'd have
to be extra careful to use `&MainEntity` instead of the natural
`Entity`.
## Solution
Make all collections that are derived from Main World data use
`MainEntity` as their key, to ensure type safety and avoid accidentally
looking up data with the wrong entity id:
```rust
pub type MainEntityHashMap<V> = hashbrown::HashMap<MainEntity, V, EntityHash>;
```
Additionally, we make all `PhaseItem` be able to provide both their Main
and Render World ids, to allow render phase implementors maximum
flexibility as to what id should be used to look up data.
You can think of this like tracking at the type level whether something
in the Render World should use it's "primary key", i.e. entity id, or
needs to use a foreign key, i.e. `MainEntity`.
## Testing
##### TODO:
This will require extensive testing to make sure things didn't break!
Additionally, some extraction logic has become more complicated and
needs to be checked for regressions.
## Migration Guide
With the advent of the retained render world, collections that contain
references to `Entity` that are extracted into the render world have
been changed to contain `MainEntity` in order to prevent errors where a
render world entity id is used to look up an item by accident. Custom
rendering code may need to be changed to query for `&MainEntity` in
order to look up the correct item from such a collection. Additionally,
users who implement their own extraction logic for collections of main
world entity should strongly consider extracting into a different
collection that uses `MainEntity` as a key.
Additionally, render phases now require specifying both the `Entity` and
`MainEntity` for a given `PhaseItem`. Custom render phases should ensure
`MainEntity` is available when queuing a phase item.
# Objective
`EntityHash` and related types were moved from `bevy_utils` to
`bevy_ecs` in #11498, but seemed to have been accidentally reintroduced
a week later in #11707.
## Solution
Remove the old leftover code.
---
## Migration Guide
- Uses of `bevy::utils::{EntityHash, EntityHasher, EntityHashMap,
EntityHashSet}` now have to be imported from `bevy::ecs::entity`.
# Objective
The Android example on Adreno 642L currently crashes on startup.
Previous PRs #14176 and #13323 have adressed this specific crash
occurring on some Adreno GPUs, that fix works as it should but isn't
applied when to the GPU name contains a suffix like in the case of
`642L`.
## Solution
- Amending the logic to filter out any parts of the GPU name not
containing digits thus enabling the fix on `642L`.
## Testing
- Ran the Android example on a Nothing Phone 1. Before this change it
crashed, after it works as intended.
---------
Co-authored-by: Sam Pettersson <sam.pettersson@geoguessr.com>
# Objective
- Fix#14295
## Solution
- Early out when `GFBD::get_index_and_compare_data` returns None.
## Testing
- Tested on a selection of examples including `many_foxes` and
`3d_shapes`.
- Resolved the original issue in `bevy_vector_shapes`.
This commit uses the [`offset-allocator`] crate to combine vertex and
index arrays from different meshes into single buffers. Since the
primary source of `wgpu` overhead is from validation and synchronization
when switching buffers, this significantly improves Bevy's rendering
performance on many scenes.
This patch is a more flexible version of #13218, which also used slabs.
Unlike #13218, which used slabs of a fixed size, this commit implements
slabs that start small and can grow. In addition to reducing memory
usage, supporting slab growth reduces the number of vertex and index
buffer switches that need to happen during rendering, leading to
improved performance. To prevent pathological fragmentation behavior,
slabs are capped to a maximum size, and mesh arrays that are too large
get their own dedicated slabs.
As an additional improvement over #13218, this commit allows the
application to customize all allocator heuristics. The
`MeshAllocatorSettings` resource contains values that adjust the minimum
and maximum slab sizes, the cutoff point at which meshes get their own
dedicated slabs, and the rate at which slabs grow. Hopefully-sensible
defaults have been chosen for each value.
Unfortunately, WebGL 2 doesn't support the *base vertex* feature, which
is necessary to pack vertex arrays from different meshes into the same
buffer. `wgpu` represents this restriction as the downlevel flag
`BASE_VERTEX`. This patch detects that bit and ensures that all vertex
buffers get dedicated slabs on that platform. Even on WebGL 2, though,
we can combine all *index* arrays into single buffers to reduce buffer
changes, and we do so.
The following measurements are on Bistro:
Overall frame time improves from 8.74 ms to 5.53 ms (1.58x speedup):

Render system time improves from 6.57 ms to 3.54 ms (1.86x speedup):

Opaque pass time improves from 4.64 ms to 2.33 ms (1.99x speedup):

## Migration Guide
### Changed
* Vertex and index buffers for meshes may now be packed alongside other
buffers, for performance.
* `GpuMesh` has been renamed to `RenderMesh`, to reflect the fact that
it no longer directly stores handles to GPU objects.
* Because meshes no longer have their own vertex and index buffers, the
responsibility for the buffers has moved from `GpuMesh` (now called
`RenderMesh`) to the `MeshAllocator` resource. To access the vertex data
for a mesh, use `MeshAllocator::mesh_vertex_slice`. To access the index
data for a mesh, use `MeshAllocator::mesh_index_slice`.
[`offset-allocator`]: https://github.com/pcwalton/offset-allocator
# Objective
Fix#14146
## Solution
Expansion of #13323 , excluded Adreno 730 and earlier.
## Testing
Tested on android device(Adreno 730) that used to crash
As reported in #14004, many third-party plugins, such as Hanabi, enqueue
entities that don't have meshes into render phases. However, the
introduction of indirect mode added a dependency on mesh-specific data,
breaking this workflow. This is because GPU preprocessing requires that
the render phases manage indirect draw parameters, which don't apply to
objects that aren't meshes. The existing code skips over binned entities
that don't have indirect draw parameters, which causes the rendering to
be skipped for such objects.
To support this workflow, this commit adds a new field,
`non_mesh_items`, to `BinnedRenderPhase`. This field contains a simple
list of (bin key, entity) pairs. After drawing batchable and unbatchable
objects, the non-mesh items are drawn one after another. Bevy itself
doesn't enqueue any items into this list; it exists solely for the
application and/or plugins to use.
Additionally, this commit switches the asset ID in the standard bin keys
to be an untyped asset ID rather than that of a mesh. This allows more
flexibility, allowing bins to be keyed off any type of asset.
This patch adds a new example, `custom_phase_item`, which simultaneously
serves to demonstrate how to use this new feature and to act as a
regression test so this doesn't break again.
Fixes#14004.
## Changelog
### Added
* `BinnedRenderPhase` now contains a `non_mesh_items` field for plugins
to add custom items to.
# Objective
- Fixes#13728
## Solution
- add a new feature `smaa_luts`. if enables, it also enables `ktx2` and
`zstd`. if not, it doesn't load the files but use placeholders instead
- adds all the resources needed in the same places that system that uses
them are added.
# Objective
- Fixes#13038
## Solution
- Disable gpu preprocessing when feature
`SAMPLED_TEXTURE_AND_STORAGE_BUFFER_ARRAY_NON_UNIFORM_INDEXING` is not
available
## Testing
- Tested on android device that used to crash
This commit makes us stop using the render world ECS for
`BinnedRenderPhase` and `SortedRenderPhase` and instead use resources
with `EntityHashMap`s inside. There are three reasons to do this:
1. We can use `clear()` to clear out the render phase collections
instead of recreating the components from scratch, allowing us to reuse
allocations.
2. This is a prerequisite for retained bins, because components can't be
retained from frame to frame in the render world, but resources can.
3. We want to move away from storing anything in components in the
render world ECS, and this is a step in that direction.
This patch results in a small performance benefit, due to point (1)
above.
## Changelog
### Changed
* The `BinnedRenderPhase` and `SortedRenderPhase` render world
components have been replaced with `ViewBinnedRenderPhases` and
`ViewSortedRenderPhases` resources.
## Migration Guide
* The `BinnedRenderPhase` and `SortedRenderPhase` render world
components have been replaced with `ViewBinnedRenderPhases` and
`ViewSortedRenderPhases` resources. Instead of querying for the
components, look the camera entity up in the
`ViewBinnedRenderPhases`/`ViewSortedRenderPhases` tables.
This is an adoption of #12670 plus some documentation fixes. See that PR
for more details.
---
## Changelog
* Renamed `BufferVec` to `RawBufferVec` and added a new `BufferVec`
type.
## Migration Guide
`BufferVec` has been renamed to `RawBufferVec` and a new similar type
has taken the `BufferVec` name.
---------
Co-authored-by: Patrick Walton <pcwalton@mimiga.net>
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: IceSentry <IceSentry@users.noreply.github.com>
In #12889, I mistakenly started dropping unbatchable sorted items on the
floor instead of giving them solitary batches. This caused the objects
in the `shader_instancing` demo to stop showing up. This patch fixes the
issue by giving those items their own batches as expected.
Fixes#13130.
This commit implements opt-in GPU frustum culling, built on top of the
infrastructure in https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/12773. To
enable it on a camera, add the `GpuCulling` component to it. To
additionally disable CPU frustum culling, add the `NoCpuCulling`
component. Note that adding `GpuCulling` without `NoCpuCulling`
*currently* does nothing useful. The reason why `GpuCulling` doesn't
automatically imply `NoCpuCulling` is that I intend to follow this patch
up with GPU two-phase occlusion culling, and CPU frustum culling plus
GPU occlusion culling seems like a very commonly-desired mode.
Adding the `GpuCulling` component to a view puts that view into
*indirect mode*. This mode makes all drawcalls indirect, relying on the
mesh preprocessing shader to allocate instances dynamically. In indirect
mode, the `PreprocessWorkItem` `output_index` points not to a
`MeshUniform` instance slot but instead to a set of `wgpu`
`IndirectParameters`, from which it allocates an instance slot
dynamically if frustum culling succeeds. Batch building has been updated
to allocate and track indirect parameter slots, and the AABBs are now
supplied to the GPU as `MeshCullingData`.
A small amount of code relating to the frustum culling has been borrowed
from meshlets and moved into `maths.wgsl`. Note that standard Bevy
frustum culling uses AABBs, while meshlets use bounding spheres; this
means that not as much code can be shared as one might think.
This patch doesn't provide any way to perform GPU culling on shadow
maps, to avoid making this patch bigger than it already is. That can be
a followup.
## Changelog
### Added
* Frustum culling can now optionally be done on the GPU. To enable it,
add the `GpuCulling` component to a camera.
* To disable CPU frustum culling, add `NoCpuCulling` to a camera. Note
that `GpuCulling` doesn't automatically imply `NoCpuCulling`.
# Objective
- `cargo run --release --example bevymark -- --benchmark --waves 160
--per-wave 1000 --mode mesh2d` runs slower and slower over time due to
`no_gpu_preprocessing::write_batched_instance_buffer<bevy_sprite::mesh2d::mesh::Mesh2dPipeline>`
taking longer and longer because the `BatchedInstanceBuffer` is not
cleared
## Solution
- Split the `clear_batched_instance_buffers` system into CPU and GPU
versions
- Use the CPU version for 2D meshes
Currently, `MeshUniform`s are rather large: 160 bytes. They're also
somewhat expensive to compute, because they involve taking the inverse
of a 3x4 matrix. Finally, if a mesh is present in multiple views, that
mesh will have a separate `MeshUniform` for each and every view, which
is wasteful.
This commit fixes these issues by introducing the concept of a *mesh
input uniform* and adding a *mesh uniform building* compute shader pass.
The `MeshInputUniform` is simply the minimum amount of data needed for
the GPU to compute the full `MeshUniform`. Most of this data is just the
transform and is therefore only 64 bytes. `MeshInputUniform`s are
computed during the *extraction* phase, much like skins are today, in
order to avoid needlessly copying transforms around on CPU. (In fact,
the render app has been changed to only store the translation of each
mesh; it no longer cares about any other part of the transform, which is
stored only on the GPU and the main world.) Before rendering, the
`build_mesh_uniforms` pass runs to expand the `MeshInputUniform`s to the
full `MeshUniform`.
The mesh uniform building pass does the following, all on GPU:
1. Copy the appropriate fields of the `MeshInputUniform` to the
`MeshUniform` slot. If a single mesh is present in multiple views, this
effectively duplicates it into each view.
2. Compute the inverse transpose of the model transform, used for
transforming normals.
3. If applicable, copy the mesh's transform from the previous frame for
TAA. To support this, we double-buffer the `MeshInputUniform`s over two
frames and swap the buffers each frame. The `MeshInputUniform`s for the
current frame contain the index of that mesh's `MeshInputUniform` for
the previous frame.
This commit produces wins in virtually every CPU part of the pipeline:
`extract_meshes`, `queue_material_meshes`,
`batch_and_prepare_render_phase`, and especially
`write_batched_instance_buffer` are all faster. Shrinking the amount of
CPU data that has to be shuffled around speeds up the entire rendering
process.
| Benchmark | This branch | `main` | Speedup |
|------------------------|-------------|---------|---------|
| `many_cubes -nfc` | 17.259 | 24.529 | 42.12% |
| `many_cubes -nfc -vpi` | 302.116 | 312.123 | 3.31% |
| `many_foxes` | 3.227 | 3.515 | 8.92% |
Because mesh uniform building requires compute shader, and WebGL 2 has
no compute shader, the existing CPU mesh uniform building code has been
left as-is. Many types now have both CPU mesh uniform building and GPU
mesh uniform building modes. Developers can opt into the old CPU mesh
uniform building by setting the `use_gpu_uniform_builder` option on
`PbrPlugin` to `false`.
Below are graphs of the CPU portions of `many-cubes
--no-frustum-culling`. Yellow is this branch, red is `main`.
`extract_meshes`:

It's notable that we get a small win even though we're now writing to a
GPU buffer.
`queue_material_meshes`:

There's a bit of a regression here; not sure what's causing it. In any
case it's very outweighed by the other gains.
`batch_and_prepare_render_phase`:

There's a huge win here, enough to make batching basically drop off the
profile.
`write_batched_instance_buffer`:

There's a massive improvement here, as expected. Note that a lot of it
simply comes from the fact that `MeshInputUniform` is `Pod`. (This isn't
a maintainability problem in my view because `MeshInputUniform` is so
simple: just 16 tightly-packed words.)
## Changelog
### Added
* Per-mesh instance data is now generated on GPU with a compute shader
instead of CPU, resulting in rendering performance improvements on
platforms where compute shaders are supported.
## Migration guide
* Custom render phases now need multiple systems beyond just
`batch_and_prepare_render_phase`. Code that was previously creating
custom render phases should now add a `BinnedRenderPhasePlugin` or
`SortedRenderPhasePlugin` as appropriate instead of directly adding
`batch_and_prepare_render_phase`.