# Objective
https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/17746
## Solution
- Change `Image.data` from being a `Vec<u8>` to a `Option<Vec<u8>>`
- Added functions to help with creating images
## Testing
- Did you test these changes? If so, how?
All current tests pass
Tested a variety of existing examples to make sure they don't crash
(they don't)
- If relevant, what platforms did you test these changes on, and are
there any important ones you can't test?
Linux x86 64-bit NixOS
---
## Migration Guide
Code that directly access `Image` data will now need to use unwrap or
handle the case where no data is provided.
Behaviour of new_fill slightly changed, but not in a way that is likely
to affect anything. It no longer panics and will fill the whole texture
instead of leaving black pixels if the data provided is not a nice
factor of the size of the image.
---------
Co-authored-by: IceSentry <IceSentry@users.noreply.github.com>
## Objective
A major critique of Bevy at the moment is how boilerplatey it is to
compose (and read) entity hierarchies:
```rust
commands
.spawn(Foo)
.with_children(|p| {
p.spawn(Bar).with_children(|p| {
p.spawn(Baz);
});
p.spawn(Bar).with_children(|p| {
p.spawn(Baz);
});
});
```
There is also currently no good way to statically define and return an
entity hierarchy from a function. Instead, people often do this
"internally" with a Commands function that returns nothing, making it
impossible to spawn the hierarchy in other cases (direct World spawns,
ChildSpawner, etc).
Additionally, because this style of API results in creating the
hierarchy bits _after_ the initial spawn of a bundle, it causes ECS
archetype changes (and often expensive table moves).
Because children are initialized after the fact, we also can't count
them to pre-allocate space. This means each time a child inserts itself,
it has a high chance of overflowing the currently allocated capacity in
the `RelationshipTarget` collection, causing literal worst-case
reallocations.
We can do better!
## Solution
The Bundle trait has been extended to support an optional
`BundleEffect`. This is applied directly to World immediately _after_
the Bundle has fully inserted. Note that this is
[intentionally](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/discussions/16920)
_not done via a deferred Command_, which would require repeatedly
copying each remaining subtree of the hierarchy to a new command as we
walk down the tree (_not_ good performance).
This allows us to implement the new `SpawnRelated` trait for all
`RelationshipTarget` impls, which looks like this in practice:
```rust
world.spawn((
Foo,
Children::spawn((
Spawn((
Bar,
Children::spawn(Spawn(Baz)),
)),
Spawn((
Bar,
Children::spawn(Spawn(Baz)),
)),
))
))
```
`Children::spawn` returns `SpawnRelatedBundle<Children, L:
SpawnableList>`, which is a `Bundle` that inserts `Children`
(preallocated to the size of the `SpawnableList::size_hint()`).
`Spawn<B: Bundle>(pub B)` implements `SpawnableList` with a size of 1.
`SpawnableList` is also implemented for tuples of `SpawnableList` (same
general pattern as the Bundle impl).
There are currently three built-in `SpawnableList` implementations:
```rust
world.spawn((
Foo,
Children::spawn((
Spawn(Name::new("Child1")),
SpawnIter(["Child2", "Child3"].into_iter().map(Name::new),
SpawnWith(|parent: &mut ChildSpawner| {
parent.spawn(Name::new("Child4"));
parent.spawn(Name::new("Child5"));
})
)),
))
```
We get the benefits of "structured init", but we have nice flexibility
where it is required!
Some readers' first instinct might be to try to remove the need for the
`Spawn` wrapper. This is impossible in the Rust type system, as a tuple
of "child Bundles to be spawned" and a "tuple of Components to be added
via a single Bundle" is ambiguous in the Rust type system. There are two
ways to resolve that ambiguity:
1. By adding support for variadics to the Rust type system (removing the
need for nested bundles). This is out of scope for this PR :)
2. Using wrapper types to resolve the ambiguity (this is what I did in
this PR).
For the single-entity spawn cases, `Children::spawn_one` does also
exist, which removes the need for the wrapper:
```rust
world.spawn((
Foo,
Children::spawn_one(Bar),
))
```
## This works for all Relationships
This API isn't just for `Children` / `ChildOf` relationships. It works
for any relationship type, and they can be mixed and matched!
```rust
world.spawn((
Foo,
Observers::spawn((
Spawn(Observer::new(|trigger: Trigger<FuseLit>| {})),
Spawn(Observer::new(|trigger: Trigger<Exploded>| {})),
)),
OwnerOf::spawn(Spawn(Bar))
Children::spawn(Spawn(Baz))
))
```
## Macros
While `Spawn` is necessary to satisfy the type system, we _can_ remove
the need to express it via macros. The example above can be expressed
more succinctly using the new `children![X]` macro, which internally
produces `Children::spawn(Spawn(X))`:
```rust
world.spawn((
Foo,
children![
(
Bar,
children![Baz],
),
(
Bar,
children![Baz],
),
]
))
```
There is also a `related!` macro, which is a generic version of the
`children!` macro that supports any relationship type:
```rust
world.spawn((
Foo,
related!(Children[
(
Bar,
related!(Children[Baz]),
),
(
Bar,
related!(Children[Baz]),
),
])
))
```
## Returning Hierarchies from Functions
Thanks to these changes, the following pattern is now possible:
```rust
fn button(text: &str, color: Color) -> impl Bundle {
(
Node {
width: Val::Px(300.),
height: Val::Px(100.),
..default()
},
BackgroundColor(color),
children![
Text::new(text),
]
)
}
fn ui() -> impl Bundle {
(
Node {
width: Val::Percent(100.0),
height: Val::Percent(100.0),
..default(),
},
children![
button("hello", BLUE),
button("world", RED),
]
)
}
// spawn from a system
fn system(mut commands: Commands) {
commands.spawn(ui());
}
// spawn directly on World
world.spawn(ui());
```
## Additional Changes and Notes
* `Bundle::from_components` has been split out into
`BundleFromComponents::from_components`, enabling us to implement
`Bundle` for types that cannot be "taken" from the ECS (such as the new
`SpawnRelatedBundle`).
* The `NoBundleEffect` trait (which implements `BundleEffect`) is
implemented for empty tuples (and tuples of empty tuples), which allows
us to constrain APIs to only accept bundles that do not have effects.
This is critical because the current batch spawn APIs cannot efficiently
apply BundleEffects in their current form (as doing so in-place could
invalidate the cached raw pointers). We could consider allocating a
buffer of the effects to be applied later, but that does have
performance implications that could offset the balance and value of the
batched APIs (and would likely require some refactors to the underlying
code). I've decided to be conservative here. We can consider relaxing
that requirement on those APIs later, but that should be done in a
followup imo.
* I've ported a few examples to illustrate real-world usage. I think in
a followup we should port all examples to the `children!` form whenever
possible (and for cases that require things like SpawnIter, use the raw
APIs).
* Some may ask "why not use the `Relationship` to spawn (ex:
`ChildOf::spawn(Foo)`) instead of the `RelationshipTarget` (ex:
`Children::spawn(Spawn(Foo))`)?". That _would_ allow us to remove the
`Spawn` wrapper. I've explicitly chosen to disallow this pattern.
`Bundle::Effect` has the ability to create _significant_ weirdness.
Things in `Bundle` position look like components. For example
`world.spawn((Foo, ChildOf::spawn(Bar)))` _looks and reads_ like Foo is
a child of Bar. `ChildOf` is in Foo's "component position" but it is not
a component on Foo. This is a huge problem. Now that `Bundle::Effect`
exists, we should be _very_ principled about keeping the "weird and
unintuitive behavior" to a minimum. Things that read like components
_should be the components they appear to be".
## Remaining Work
* The macros are currently trivially implemented using macro_rules and
are currently limited to the max tuple length. They will require a
proc_macro implementation to work around the tuple length limit.
## Next Steps
* Port the remaining examples to use `children!` where possible and raw
`Spawn` / `SpawnIter` / `SpawnWith` where the flexibility of the raw API
is required.
## Migration Guide
Existing spawn patterns will continue to work as expected.
Manual Bundle implementations now require a `BundleEffect` associated
type. Exisiting bundles would have no bundle effect, so use `()`.
Additionally `Bundle::from_components` has been moved to the new
`BundleFromComponents` trait.
```rust
// Before
unsafe impl Bundle for X {
unsafe fn from_components<T, F>(ctx: &mut T, func: &mut F) -> Self {
}
/* remaining bundle impl here */
}
// After
unsafe impl Bundle for X {
type Effect = ();
/* remaining bundle impl here */
}
unsafe impl BundleFromComponents for X {
unsafe fn from_components<T, F>(ctx: &mut T, func: &mut F) -> Self {
}
}
```
---------
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Gino Valente <49806985+MrGVSV@users.noreply.github.com>
Co-authored-by: Emerson Coskey <emerson@coskey.dev>
This pr uses the `extern crate self as` trick to make proc macros behave
the same way inside and outside bevy.
# Objective
- Removes noise introduced by `crate as` in the whole bevy repo.
- Fixes#17004.
- Hardens proc macro path resolution.
## TODO
- [x] `BevyManifest` needs cleanup.
- [x] Cleanup remaining `crate as`.
- [x] Add proper integration tests to the ci.
## Notes
- `cargo-manifest-proc-macros` is written by me and based/inspired by
the old `BevyManifest` implementation and
[`bkchr/proc-macro-crate`](https://github.com/bkchr/proc-macro-crate).
- What do you think about the new integration test machinery I added to
the `ci`?
More and better integration tests can be added at a later stage.
The goal of these integration tests is to simulate an actual separate
crate that uses bevy. Ideally they would lightly touch all bevy crates.
## Testing
- Needs RA test
- Needs testing from other users
- Others need to run at least `cargo run -p ci integration-test` and
verify that they work.
---------
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
Didn't remove WgpuWrapper. Not sure if it's needed or not still.
## Testing
- Did you test these changes? If so, how? Example runner
- Are there any parts that need more testing? Web (portable atomics
thingy?), DXC.
## Migration Guide
- Bevy has upgraded to [wgpu
v24](https://github.com/gfx-rs/wgpu/blob/trunk/CHANGELOG.md#v2400-2025-01-15).
- When using the DirectX 12 rendering backend, the new priority system
for choosing a shader compiler is as follows:
- If the `WGPU_DX12_COMPILER` environment variable is set at runtime, it
is used
- Else if the new `statically-linked-dxc` feature is enabled, a custom
version of DXC will be statically linked into your app at compile time.
- Else Bevy will look in the app's working directory for
`dxcompiler.dll` and `dxil.dll` at runtime.
- Else if they are missing, Bevy will fall back to FXC (not recommended)
---------
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: IceSentry <c.giguere42@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: François Mockers <francois.mockers@vleue.com>
# Objective
- publish script copy the license files to all subcrates, meaning that
all publish are dirty. this breaks git verification of crates
- the order and list of crates to publish is manually maintained,
leading to error. cargo 1.84 is more strict and the list is currently
wrong
## Solution
- duplicate all the licenses to all crates and remove the
`--allow-dirty` flag
- instead of a manual list of crates, get it from `cargo package
--workspace`
- remove the `--no-verify` flag to... verify more things?
PR #17684 broke occlusion culling because it neglected to set the
indirect parameter offsets for the late mesh preprocessing stage if the
work item buffers were already set. This PR moves the update of those
values to a new function, `init_work_item_buffers`, which is
unconditionally called for every phase every frame.
Note that there's some complexity in order to handle the case in which
occlusion culling was enabled on one frame and disabled on the next, or
vice versa. This was necessary in order to make the occlusion culling
toggle in the `occlusion_culling` example work again.
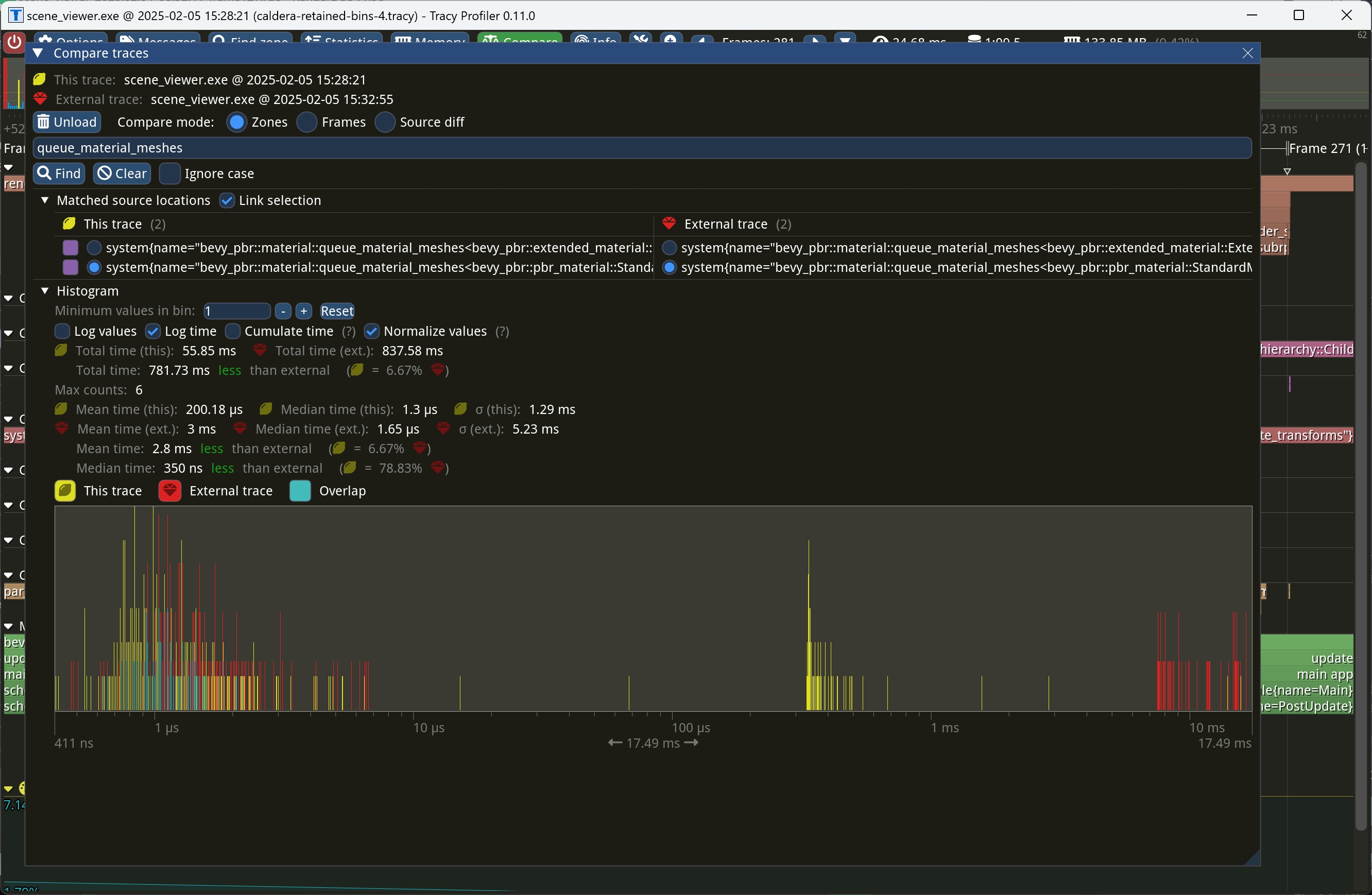
This PR makes Bevy keep entities in bins from frame to frame if they
haven't changed. This reduces the time spent in `queue_material_meshes`
and related functions to near zero for static geometry. This patch uses
the same change tick technique that #17567 uses to detect when meshes
have changed in such a way as to require re-binning.
In order to quickly find the relevant bin for an entity when that entity
has changed, we introduce a new type of cache, the *bin key cache*. This
cache stores a mapping from main world entity ID to cached bin key, as
well as the tick of the most recent change to the entity. As we iterate
through the visible entities in `queue_material_meshes`, we check the
cache to see whether the entity needs to be re-binned. If it doesn't,
then we mark it as clean in the `valid_cached_entity_bin_keys` bit set.
If it does, then we insert it into the correct bin, and then mark the
entity as clean. At the end, all entities not marked as clean are
removed from the bins.
This patch has a dramatic effect on the rendering performance of most
benchmarks, as it effectively eliminates `queue_material_meshes` from
the profile. Note, however, that it generally simultaneously regresses
`batch_and_prepare_binned_render_phase` by a bit (not by enough to
outweigh the win, however). I believe that's because, before this patch,
`queue_material_meshes` put the bins in the CPU cache for
`batch_and_prepare_binned_render_phase` to use, while with this patch,
`batch_and_prepare_binned_render_phase` must load the bins into the CPU
cache itself.
On Caldera, this reduces the time spent in `queue_material_meshes` from
5+ ms to 0.2ms-0.3ms. Note that benchmarking on that scene is very noisy
right now because of https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/17535.
# Objective
- Make use of the new `weak_handle!` macro added in
https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/17384
## Solution
- Migrate bevy from `Handle::weak_from_u128` to the new `weak_handle!`
macro that takes a random UUID
- Deprecate `Handle::weak_from_u128`, since there are no remaining use
cases that can't also be addressed by constructing the type manually
## Testing
- `cargo run -p ci -- test`
---
## Migration Guide
Replace `Handle::weak_from_u128` with `weak_handle!` and a random UUID.
# Objective
Fixes#17662
## Solution
Moved `Item` and `fetch` from `WorldQuery` to `QueryData`, and adjusted
their implementations accordingly.
Currently, documentation related to `fetch` is written under
`WorldQuery`. It would be more appropriate to move it to the `QueryData`
documentation for clarity.
I am not very experienced with making contributions. If there are any
mistakes or areas for improvement, I would appreciate any suggestions
you may have.
## Migration Guide
The `WorldQuery::Item` type and `WorldQuery::fetch` method have been
moved to `QueryData`, as they were not useful for `QueryFilter` types.
---------
Co-authored-by: Chris Russell <8494645+chescock@users.noreply.github.com>
# Objective
Simplify and expand the API for `QueryState`.
`QueryState` has a lot of methods that mirror those on `Query`. These
are then multiplied by variants that take `&World`, `&mut World`, and
`UnsafeWorldCell`. In addition, many of them have `_manual` variants
that take `&QueryState` and avoid calling `update_archetypes()`. Not all
of the combinations exist, however, so some operations are not possible.
## Solution
Introduce methods to get a `Query` from a `QueryState`. That will reduce
duplication between the types, and ensure that the full `Query` API is
always available for `QueryState`.
Introduce methods on `Query` that consume the query to return types with
the full `'w` lifetime. This avoids issues with borrowing where things
like `query_state.query(&world).get(entity)` don't work because they
borrow from the temporary `Query`.
Finally, implement `Copy` for read-only `Query`s. `get_inner` and
`iter_inner` currently take `&self`, so changing them to consume `self`
would be a breaking change. By making `Query: Copy`, they can consume a
copy of `self` and continue to work.
The consuming methods also let us simplify the implementation of methods
on `Query`, by doing `fn foo(&self) { self.as_readonly().foo_inner() }`
and `fn foo_mut(&mut self) { self.reborrow().foo_inner() }`. That
structure makes it more difficult to accidentally extend lifetimes,
since the safe `as_readonly()` and `reborrow()` methods shrink them
appropriately. The optimizer is able to see that they are both identity
functions and inline them, so there should be no performance cost.
Note that this change would conflict with #15848. If `QueryState` is
stored as a `Cow`, then the consuming methods cannot be implemented, and
`Copy` cannot be implemented.
## Future Work
The next step is to mark the methods on `QueryState` as `#[deprecated]`,
and move the implementations into `Query`.
## Migration Guide
`Query::to_readonly` has been renamed to `Query::as_readonly`.
# Cold Specialization
## Objective
An ongoing part of our quest to retain everything in the render world,
cold-specialization aims to cache pipeline specialization so that
pipeline IDs can be recomputed only when necessary, rather than every
frame. This approach reduces redundant work in stable scenes, while
still accommodating scenarios in which materials, views, or visibility
might change, as well as unlocking future optimization work like
retaining render bins.
## Solution
Queue systems are split into a specialization system and queue system,
the former of which only runs when necessary to compute a new pipeline
id. Pipelines are invalidated using a combination of change detection
and ECS ticks.
### The difficulty with change detection
Detecting “what changed” can be tricky because pipeline specialization
depends not only on the entity’s components (e.g., mesh, material, etc.)
but also on which view (camera) it is rendering in. In other words, the
cache key for a given pipeline id is a view entity/render entity pair.
As such, it's not sufficient simply to react to change detection in
order to specialize -- an entity could currently be out of view or could
be rendered in the future in camera that is currently disabled or hasn't
spawned yet.
### Why ticks?
Ticks allow us to ensure correctness by allowing us to compare the last
time a view or entity was updated compared to the cached pipeline id.
This ensures that even if an entity was out of view or has never been
seen in a given camera before we can still correctly determine whether
it needs to be re-specialized or not.
## Testing
TODO: Tested a bunch of different examples, need to test more.
## Migration Guide
TODO
- `AssetEvents` has been moved into the `PostUpdate` schedule.
---------
Co-authored-by: Patrick Walton <pcwalton@mimiga.net>
We were calling `clear()` on the work item buffer table, which caused us
to deallocate all the CPU side buffers. This patch changes the logic to
instead just clear the buffers individually, but leave their backing
stores. This has two consequences:
1. To effectively retain work item buffers from frame to frame, we need
to key them off `RetainedViewEntity` values and not the render world
`Entity`, which is transient. This PR changes those buffers accordingly.
2. We need to clean up work item buffers that belong to views that went
away. Amusingly enough, we actually have a system,
`delete_old_work_item_buffers`, that tries to do this already, but it
wasn't doing anything because the `clear_batched_gpu_instance_buffers`
system already handled that. This patch actually makes the
`delete_old_work_item_buffers` system useful, by removing the clearing
behavior from `clear_batched_gpu_instance_buffers` and instead making
`delete_old_work_item_buffers` delete buffers corresponding to
nonexistent views.
On Bistro, this PR improves the performance of
`batch_and_prepare_binned_render_phase` from 61.2 us to 47.8 us, a 28%
speedup.

Data for the other batches is only accessed by the GPU, not the CPU, so
it's a waste of time and memory to store information relating to those
other batches.
On Bistro, this reduces time spent in
`batch_and_prepare_binned_render_phase` from 85.9 us to 61.2 us, a 40%
speedup.

# Objective
- Most of the `*MeshBuilder` classes are not implementing `Reflect`
## Solution
- Implementing `Reflect` for all `*MeshBuilder` were is possible.
- Make sure all `*MeshBuilder` implements `Default`.
- Adding new `MeshBuildersPlugin` that registers all `*MeshBuilder`
types.
## Testing
- `cargo run -p ci`
- Tested some examples like `3d_scene` just in case something was
broken.
# Objective
- Fix the atmosphere LUT parameterization in the aerial -view and
sky-view LUTs
- Correct the light accumulation according to a ray-marched reference
- Avoid negative values of the sun disk illuminance when the sun disk is
below the horizon
## Solution
- Adding a Newton's method iteration to `fast_sqrt` function
- Switched to using `fast_acos_4` for better precision of the sun angle
towards the horizon (view mu angle = 0)
- Simplified the function for mapping to and from the Sky View UV
coordinates by removing an if statement and correctly apply the method
proposed by the [Hillarie
paper](https://sebh.github.io/publications/egsr2020.pdf) detailed in
section 5.3 and 5.4.
- Replaced the `ray_dir_ws.y` term with a shadow factor in the
`sample_sun_illuminance` function that correctly approximates the sun
disk occluded by the earth from any view point
## Testing
- Ran the atmosphere and SSAO examples to make sure the shaders still
compile and run as expected.
---
## Showcase
<img width="1151" alt="showcase-img"
src="https://github.com/user-attachments/assets/de875533-42bd-41f9-9fd0-d7cc57d6e51c"
/>
---------
Co-authored-by: Emerson Coskey <emerson@coskey.dev>
# Objective
- Linking to a specific AsBindGroup attribute is hard because it doesn't
use any headers and all the docs is in a giant block
## Solution
- Make each attribute it's own sub-header so they can be easily linked
---
## Showcase
Here's what the rustdoc output looks like with this change

## Notes
I kept the bullet point so the text is still indented like before. Not
sure if we should keep that or not
Minor improvement to the render_resource doc comments; specifically, the
gpu buffer types
- makes them consistently reference each other
- reorders them to be alphabetical
- removes duplicated entries
*Occlusion culling* allows the GPU to skip the vertex and fragment
shading overhead for objects that can be quickly proved to be invisible
because they're behind other geometry. A depth prepass already
eliminates most fragment shading overhead for occluded objects, but the
vertex shading overhead, as well as the cost of testing and rejecting
fragments against the Z-buffer, is presently unavoidable for standard
meshes. We currently perform occlusion culling only for meshlets. But
other meshes, such as skinned meshes, can benefit from occlusion culling
too in order to avoid the transform and skinning overhead for unseen
meshes.
This commit adapts the same [*two-phase occlusion culling*] technique
that meshlets use to Bevy's standard 3D mesh pipeline when the new
`OcclusionCulling` component, as well as the `DepthPrepass` component,
are present on the camera. It has these steps:
1. *Early depth prepass*: We use the hierarchical Z-buffer from the
previous frame to cull meshes for the initial depth prepass, effectively
rendering only the meshes that were visible in the last frame.
2. *Early depth downsample*: We downsample the depth buffer to create
another hierarchical Z-buffer, this time with the current view
transform.
3. *Late depth prepass*: We use the new hierarchical Z-buffer to test
all meshes that weren't rendered in the early depth prepass. Any meshes
that pass this check are rendered.
4. *Late depth downsample*: Again, we downsample the depth buffer to
create a hierarchical Z-buffer in preparation for the early depth
prepass of the next frame. This step is done after all the rendering, in
order to account for custom phase items that might write to the depth
buffer.
Note that this patch has no effect on the per-mesh CPU overhead for
occluded objects, which remains high for a GPU-driven renderer due to
the lack of `cold-specialization` and retained bins. If
`cold-specialization` and retained bins weren't on the horizon, then a
more traditional approach like potentially visible sets (PVS) or low-res
CPU rendering would probably be more efficient than the GPU-driven
approach that this patch implements for most scenes. However, at this
point the amount of effort required to implement a PVS baking tool or a
low-res CPU renderer would probably be greater than landing
`cold-specialization` and retained bins, and the GPU driven approach is
the more modern one anyway. It does mean that the performance
improvements from occlusion culling as implemented in this patch *today*
are likely to be limited, because of the high CPU overhead for occluded
meshes.
Note also that this patch currently doesn't implement occlusion culling
for 2D objects or shadow maps. Those can be addressed in a follow-up.
Additionally, note that the techniques in this patch require compute
shaders, which excludes support for WebGL 2.
This PR is marked experimental because of known precision issues with
the downsampling approach when applied to non-power-of-two framebuffer
sizes (i.e. most of them). These precision issues can, in rare cases,
cause objects to be judged occluded that in fact are not. (I've never
seen this in practice, but I know it's possible; it tends to be likelier
to happen with small meshes.) As a follow-up to this patch, we desire to
switch to the [SPD-based hi-Z buffer shader from the Granite engine],
which doesn't suffer from these problems, at which point we should be
able to graduate this feature from experimental status. I opted not to
include that rewrite in this patch for two reasons: (1) @JMS55 is
planning on doing the rewrite to coincide with the new availability of
image atomic operations in Naga; (2) to reduce the scope of this patch.
A new example, `occlusion_culling`, has been added. It demonstrates
objects becoming quickly occluded and disoccluded by dynamic geometry
and shows the number of objects that are actually being rendered. Also,
a new `--occlusion-culling` switch has been added to `scene_viewer`, in
order to make it easy to test this patch with large scenes like Bistro.
[*two-phase occlusion culling*]:
https://medium.com/@mil_kru/two-pass-occlusion-culling-4100edcad501
[Aaltonen SIGGRAPH 2015]:
https://www.advances.realtimerendering.com/s2015/aaltonenhaar_siggraph2015_combined_final_footer_220dpi.pdf
[Some literature]:
https://gist.github.com/reduz/c5769d0e705d8ab7ac187d63be0099b5?permalink_comment_id=5040452#gistcomment-5040452
[SPD-based hi-Z buffer shader from the Granite engine]:
https://github.com/Themaister/Granite/blob/master/assets/shaders/post/hiz.comp
## Migration guide
* When enqueuing a custom mesh pipeline, work item buffers are now
created with
`bevy::render::batching::gpu_preprocessing::get_or_create_work_item_buffer`,
not `PreprocessWorkItemBuffers::new`. See the
`specialized_mesh_pipeline` example.
## Showcase
Occlusion culling example:

Bistro zoomed out, before occlusion culling:

Bistro zoomed out, after occlusion culling:

In this scene, occlusion culling reduces the number of meshes Bevy has
to render from 1591 to 585.
# Objective
Implement `Eq` and `Hash` for the `BindGroup` and `BindGroupLayout`
wrappers.
## Solution
Implement based on the same assumption that the ID is unique, for
consistency with `PartialEq`.
## Testing
None; this should be straightforward. If there's an issue that would be
a design one.
Implement procedural atmospheric scattering from [Sebastien Hillaire's
2020 paper](https://sebh.github.io/publications/egsr2020.pdf). This
approach should scale well even down to mobile hardware, and is
physically accurate.
## Co-author: @mate-h
He helped massively with getting this over the finish line, ensuring
everything was physically correct, correcting several places where I had
misunderstood or misapplied the paper, and improving the performance in
several places as well. Thanks!
## Credits
@aevyrie: helped find numerous bugs and improve the example to best show
off this feature :)
Built off of @mtsr's original branch, which handled the transmittance
lut (arguably the most important part)
## Showcase:


## For followup
- Integrate with pcwalton's volumetrics code
- refactor/reorganize for better integration with other effects
- have atmosphere transmittance affect directional lights
- add support for generating skybox/environment map
---------
Co-authored-by: Emerson Coskey <56370779+EmersonCoskey@users.noreply.github.com>
Co-authored-by: atlv <email@atlasdostal.com>
Co-authored-by: JMS55 <47158642+JMS55@users.noreply.github.com>
Co-authored-by: Emerson Coskey <coskey@emerlabs.net>
Co-authored-by: Máté Homolya <mate.homolya@gmail.com>
# Objective
- Contributes to #16877
## Solution
- Moved `hashbrown`, `foldhash`, and related types out of `bevy_utils`
and into `bevy_platform_support`
- Refactored the above to match the layout of these types in `std`.
- Updated crates as required.
## Testing
- CI
---
## Migration Guide
- The following items were moved out of `bevy_utils` and into
`bevy_platform_support::hash`:
- `FixedState`
- `DefaultHasher`
- `RandomState`
- `FixedHasher`
- `Hashed`
- `PassHash`
- `PassHasher`
- `NoOpHash`
- The following items were moved out of `bevy_utils` and into
`bevy_platform_support::collections`:
- `HashMap`
- `HashSet`
- `bevy_utils::hashbrown` has been removed. Instead, import from
`bevy_platform_support::collections` _or_ take a dependency on
`hashbrown` directly.
- `bevy_utils::Entry` has been removed. Instead, import from
`bevy_platform_support::collections::hash_map` or
`bevy_platform_support::collections::hash_set` as appropriate.
- All of the above equally apply to `bevy::utils` and
`bevy::platform_support`.
## Notes
- I left `PreHashMap`, `PreHashMapExt`, and `TypeIdMap` in `bevy_utils`
as they might be candidates for micro-crating. They can always be moved
into `bevy_platform_support` at a later date if desired.
# Objective
- Make the function signature for `ComponentHook` less verbose
## Solution
- Refactored `Entity`, `ComponentId`, and `Option<&Location>` into a new
`HookContext` struct.
## Testing
- CI
---
## Migration Guide
Update the function signatures for your component hooks to only take 2
arguments, `world` and `context`. Note that because `HookContext` is
plain data with all members public, you can use de-structuring to
simplify migration.
```rust
// Before
fn my_hook(
mut world: DeferredWorld,
entity: Entity,
component_id: ComponentId,
) { ... }
// After
fn my_hook(
mut world: DeferredWorld,
HookContext { entity, component_id, caller }: HookContext,
) { ... }
```
Likewise, if you were discarding certain parameters, you can use `..` in
the de-structuring:
```rust
// Before
fn my_hook(
mut world: DeferredWorld,
entity: Entity,
_: ComponentId,
) { ... }
// After
fn my_hook(
mut world: DeferredWorld,
HookContext { entity, .. }: HookContext,
) { ... }
```
# Objective
Fixes#14708
Also fixes some commands not updating tracked location.
## Solution
`ObserverTrigger` has a new `caller` field with the
`track_change_detection` feature;
hooks take an additional caller parameter (which is `Some(…)` or `None`
depending on the feature).
## Testing
See the new tests in `src/observer/mod.rs`
---
## Showcase
Observers now know from where they were triggered (if
`track_change_detection` is enabled):
```rust
world.observe(move |trigger: Trigger<OnAdd, Foo>| {
println!("Added Foo from {}", trigger.caller());
});
```
## Migration
- hooks now take an additional `Option<&'static Location>` argument
---------
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
This commit makes Bevy use change detection to only update
`RenderMaterialInstances` and `RenderMeshMaterialIds` when meshes have
been added, changed, or removed. `extract_mesh_materials`, the system
that extracts these, now follows the pattern that
`extract_meshes_for_gpu_building` established.
This improves frame time of `many_cubes` from 3.9ms to approximately
3.1ms, which slightly surpasses the performance of Bevy 0.14.
(Resubmitted from #16878 to clean up history.)

---------
Co-authored-by: Charlotte McElwain <charlotte.c.mcelwain@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
# Objective
`bevy_ecs`'s `system` module is something of a grab bag, and *very*
large. This is particularly true for the `system_param` module, which is
more than 2k lines long!
While it could be defensible to put `Res` and `ResMut` there (lol no
they're in change_detection.rs, obviously), it doesn't make any sense to
put the `Resource` trait there. This is confusing to navigate (and
painful to work on and review).
## Solution
- Create a root level `bevy_ecs/resource.rs` module to mirror
`bevy_ecs/component.rs`
- move the `Resource` trait to that module
- move the `Resource` derive macro to that module as well (Rust really
likes when you pun on the names of the derive macro and trait and put
them in the same path)
- fix all of the imports
## Notes to reviewers
- We could probably move more stuff into here, but I wanted to keep this
PR as small as possible given the absurd level of import changes.
- This PR is ground work for my upcoming attempts to store resource data
on components (resources-as-entities). Splitting this code out will make
the work and review a bit easier, and is the sort of overdue refactor
that's good to do as part of more meaningful work.
## Testing
cargo build works!
## Migration Guide
`bevy_ecs::system::Resource` has been moved to
`bevy_ecs::resource::Resource`.
Fixes#17412
## Objective
`Parent` uses the "has a X" naming convention. There is increasing
sentiment that we should use the "is a X" naming convention for
relationships (following #17398). This leaves `Children` as-is because
there is prevailing sentiment that `Children` is clearer than `ParentOf`
in many cases (especially when treating it like a collection).
This renames `Parent` to `ChildOf`.
This is just the implementation PR. To discuss the path forward, do so
in #17412.
## Migration Guide
- The `Parent` component has been renamed to `ChildOf`.
# Objective
Diagnostics for labels don't suggest how to best implement them.
```
error[E0277]: the trait bound `Label: ScheduleLabel` is not satisfied
--> src/main.rs:15:35
|
15 | let mut sched = Schedule::new(Label);
| ------------- ^^^^^ the trait `ScheduleLabel` is not implemented for `Label`
| |
| required by a bound introduced by this call
|
= help: the trait `ScheduleLabel` is implemented for `Interned<(dyn ScheduleLabel + 'static)>`
note: required by a bound in `bevy_ecs::schedule::Schedule::new`
--> /home/vj/workspace/rust/bevy/crates/bevy_ecs/src/schedule/schedule.rs:297:28
|
297 | pub fn new(label: impl ScheduleLabel) -> Self {
| ^^^^^^^^^^^^^ required by this bound in `Schedule::new`
```
## Solution
`diagnostics::on_unimplemented` and `diagnostics::do_not_recommend`
## Showcase
New error message:
```
error[E0277]: the trait bound `Label: ScheduleLabel` is not satisfied
--> src/main.rs:15:35
|
15 | let mut sched = Schedule::new(Label);
| ------------- ^^^^^ the trait `ScheduleLabel` is not implemented for `Label`
| |
| required by a bound introduced by this call
|
= note: consider annotating `Label` with `#[derive(ScheduleLabel)]`
note: required by a bound in `bevy_ecs::schedule::Schedule::new`
--> /home/vj/workspace/rust/bevy/crates/bevy_ecs/src/schedule/schedule.rs:297:28
|
297 | pub fn new(label: impl ScheduleLabel) -> Self {
| ^^^^^^^^^^^^^ required by this bound in `Schedule::new`
```
# Objective
The existing `RelationshipSourceCollection` uses `Vec` as the only
possible backing for our relationships. While a reasonable choice,
benchmarking use cases might reveal that a different data type is better
or faster.
For example:
- Not all relationships require a stable ordering between the
relationship sources (i.e. children). In cases where we a) have many
such relations and b) don't care about the ordering between them, a hash
set is likely a better datastructure than a `Vec`.
- The number of children-like entities may be small on average, and a
`smallvec` may be faster
## Solution
- Implement `RelationshipSourceCollection` for `EntityHashSet`, our
custom entity-optimized `HashSet`.
-~~Implement `DoubleEndedIterator` for `EntityHashSet` to make things
compile.~~
- This implementation was cursed and very surprising.
- Instead, by moving the iterator type on `RelationshipSourceCollection`
from an erased RPTIT to an explicit associated type we can add a trait
bound on the offending methods!
- Implement `RelationshipSourceCollection` for `SmallVec`
## Testing
I've added a pair of new tests to make sure this pattern compiles
successfully in practice!
## Migration Guide
`EntityHashSet` and `EntityHashMap` are no longer re-exported in
`bevy_ecs::entity` directly. If you were not using `bevy_ecs` / `bevy`'s
`prelude`, you can access them through their now-public modules,
`hash_set` and `hash_map` instead.
## Notes to reviewers
The `EntityHashSet::Iter` type needs to be public for this impl to be
allowed. I initially renamed it to something that wasn't ambiguous and
re-exported it, but as @Victoronz pointed out, that was somewhat
unidiomatic.
In
1a8564898f,
I instead made the `entity_hash_set` public (and its `entity_hash_set`)
sister public, and removed the re-export. I prefer this design (give me
module docs please), but it leads to a lot of churn in this PR.
Let me know which you'd prefer, and if you'd like me to split that
change out into its own micro PR.
# Objective
- Contributes to #16877
## Solution
- Initial creation of `bevy_platform_support` crate.
- Moved `bevy_utils::Instant` into new `bevy_platform_support` crate.
- Moved `portable-atomic`, `portable-atomic-util`, and
`critical-section` into new `bevy_platform_support` crate.
## Testing
- CI
---
## Showcase
Instead of needing code like this to import an `Arc`:
```rust
#[cfg(feature = "portable-atomic")]
use portable_atomic_util::Arc;
#[cfg(not(feature = "portable-atomic"))]
use alloc::sync::Arc;
```
We can now use:
```rust
use bevy_platform_support::sync::Arc;
```
This applies to many other types, but the goal is overall the same:
allowing crates to use `std`-like types without the boilerplate of
conditional compilation and platform-dependencies.
## Migration Guide
- Replace imports of `bevy_utils::Instant` with
`bevy_platform_support::time::Instant`
- Replace imports of `bevy::utils::Instant` with
`bevy::platform_support::time::Instant`
## Notes
- `bevy_platform_support` hasn't been reserved on `crates.io`
- ~~`bevy_platform_support` is not re-exported from `bevy` at this time.
It may be worthwhile exporting this crate, but I am unsure of a
reasonable name to export it under (`platform_support` may be a bit
wordy for user-facing).~~
- I've included an implementation of `Instant` which is suitable for
`no_std` platforms that are not Wasm for the sake of eliminating feature
gates around its use. It may be a controversial inclusion, so I'm happy
to remove it if required.
- There are many other items (`spin`, `bevy_utils::Sync(Unsafe)Cell`,
etc.) which should be added to this crate. I have kept the initial scope
small to demonstrate utility without making this too unwieldy.
---------
Co-authored-by: TimJentzsch <TimJentzsch@users.noreply.github.com>
Co-authored-by: Chris Russell <8494645+chescock@users.noreply.github.com>
Co-authored-by: François Mockers <francois.mockers@vleue.com>
This adds support for one-to-many non-fragmenting relationships (with
planned paths for fragmenting and non-fragmenting many-to-many
relationships). "Non-fragmenting" means that entities with the same
relationship type, but different relationship targets, are not forced
into separate tables (which would cause "table fragmentation").
Functionally, this fills a similar niche as the current Parent/Children
system. The biggest differences are:
1. Relationships have simpler internals and significantly improved
performance and UX. Commands and specialized APIs are no longer
necessary to keep everything in sync. Just spawn entities with the
relationship components you want and everything "just works".
2. Relationships are generalized. Bevy can provide additional built in
relationships, and users can define their own.
**REQUEST TO REVIEWERS**: _please don't leave top level comments and
instead comment on specific lines of code. That way we can take
advantage of threaded discussions. Also dont leave comments simply
pointing out CI failures as I can read those just fine._
## Built on top of what we have
Relationships are implemented on top of the Bevy ECS features we already
have: components, immutability, and hooks. This makes them immediately
compatible with all of our existing (and future) APIs for querying,
spawning, removing, scenes, reflection, etc. The fewer specialized APIs
we need to build, maintain, and teach, the better.
## Why focus on one-to-many non-fragmenting first?
1. This allows us to improve Parent/Children relationships immediately,
in a way that is reasonably uncontroversial. Switching our hierarchy to
fragmenting relationships would have significant performance
implications. ~~Flecs is heavily considering a switch to non-fragmenting
relations after careful considerations of the performance tradeoffs.~~
_(Correction from @SanderMertens: Flecs is implementing non-fragmenting
storage specialized for asset hierarchies, where asset hierarchies are
many instances of small trees that have a well defined structure)_
2. Adding generalized one-to-many relationships is currently a priority
for the [Next Generation Scene / UI
effort](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/discussions/14437).
Specifically, we're interested in building reactions and observers on
top.
## The changes
This PR does the following:
1. Adds a generic one-to-many Relationship system
3. Ports the existing Parent/Children system to Relationships, which now
lives in `bevy_ecs::hierarchy`. The old `bevy_hierarchy` crate has been
removed.
4. Adds on_despawn component hooks
5. Relationships can opt-in to "despawn descendants" behavior, meaning
that the entire relationship hierarchy is despawned when
`entity.despawn()` is called. The built in Parent/Children hierarchies
enable this behavior, and `entity.despawn_recursive()` has been removed.
6. `world.spawn` now applies commands after spawning. This ensures that
relationship bookkeeping happens immediately and removes the need to
manually flush. This is in line with the equivalent behaviors recently
added to the other APIs (ex: insert).
7. Removes the ValidParentCheckPlugin (system-driven / poll based) in
favor of a `validate_parent_has_component` hook.
## Using Relationships
The `Relationship` trait looks like this:
```rust
pub trait Relationship: Component + Sized {
type RelationshipSources: RelationshipSources<Relationship = Self>;
fn get(&self) -> Entity;
fn from(entity: Entity) -> Self;
}
```
A relationship is a component that:
1. Is a simple wrapper over a "target" Entity.
2. Has a corresponding `RelationshipSources` component, which is a
simple wrapper over a collection of entities. Every "target entity"
targeted by a "source entity" with a `Relationship` has a
`RelationshipSources` component, which contains every "source entity"
that targets it.
For example, the `Parent` component (as it currently exists in Bevy) is
the `Relationship` component and the entity containing the Parent is the
"source entity". The entity _inside_ the `Parent(Entity)` component is
the "target entity". And that target entity has a `Children` component
(which implements `RelationshipSources`).
In practice, the Parent/Children relationship looks like this:
```rust
#[derive(Relationship)]
#[relationship(relationship_sources = Children)]
pub struct Parent(pub Entity);
#[derive(RelationshipSources)]
#[relationship_sources(relationship = Parent)]
pub struct Children(Vec<Entity>);
```
The Relationship and RelationshipSources derives automatically implement
Component with the relevant configuration (namely, the hooks necessary
to keep everything in sync).
The most direct way to add relationships is to spawn entities with
relationship components:
```rust
let a = world.spawn_empty().id();
let b = world.spawn(Parent(a)).id();
assert_eq!(world.entity(a).get::<Children>().unwrap(), &[b]);
```
There are also convenience APIs for spawning more than one entity with
the same relationship:
```rust
world.spawn_empty().with_related::<Children>(|s| {
s.spawn_empty();
s.spawn_empty();
})
```
The existing `with_children` API is now a simpler wrapper over
`with_related`. This makes this change largely non-breaking for existing
spawn patterns.
```rust
world.spawn_empty().with_children(|s| {
s.spawn_empty();
s.spawn_empty();
})
```
There are also other relationship APIs, such as `add_related` and
`despawn_related`.
## Automatic recursive despawn via the new on_despawn hook
`RelationshipSources` can opt-in to "despawn descendants" behavior,
which will despawn all related entities in the relationship hierarchy:
```rust
#[derive(RelationshipSources)]
#[relationship_sources(relationship = Parent, despawn_descendants)]
pub struct Children(Vec<Entity>);
```
This means that `entity.despawn_recursive()` is no longer required.
Instead, just use `entity.despawn()` and the relevant related entities
will also be despawned.
To despawn an entity _without_ despawning its parent/child descendants,
you should remove the `Children` component first, which will also remove
the related `Parent` components:
```rust
entity
.remove::<Children>()
.despawn()
```
This builds on the on_despawn hook introduced in this PR, which is fired
when an entity is despawned (before other hooks).
## Relationships are the source of truth
`Relationship` is the _single_ source of truth component.
`RelationshipSources` is merely a reflection of what all the
`Relationship` components say. By embracing this, we are able to
significantly improve the performance of the system as a whole. We can
rely on component lifecycles to protect us against duplicates, rather
than needing to scan at runtime to ensure entities don't already exist
(which results in quadratic runtime). A single source of truth gives us
constant-time inserts. This does mean that we cannot directly spawn
populated `Children` components (or directly add or remove entities from
those components). I personally think this is a worthwhile tradeoff,
both because it makes the performance much better _and_ because it means
theres exactly one way to do things (which is a philosophy we try to
employ for Bevy APIs).
As an aside: treating both sides of the relationship as "equivalent
source of truth relations" does enable building simple and flexible
many-to-many relationships. But this introduces an _inherent_ need to
scan (or hash) to protect against duplicates.
[`evergreen_relations`](https://github.com/EvergreenNest/evergreen_relations)
has a very nice implementation of the "symmetrical many-to-many"
approach. Unfortunately I think the performance issues inherent to that
approach make it a poor choice for Bevy's default relationship system.
## Followup Work
* Discuss renaming `Parent` to `ChildOf`. I refrained from doing that in
this PR to keep the diff reasonable, but I'm personally biased toward
this change (and using that naming pattern generally for relationships).
* [Improved spawning
ergonomics](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/discussions/16920)
* Consider adding relationship observers/triggers for "relationship
targets" whenever a source is added or removed. This would replace the
current "hierarchy events" system, which is unused upstream but may have
existing users downstream. I think triggers are the better fit for this
than a buffered event queue, and would prefer not to add that back.
* Fragmenting relations: My current idea hinges on the introduction of
"value components" (aka: components whose type _and_ value determines
their ComponentId, via something like Hashing / PartialEq). By labeling
a Relationship component such as `ChildOf(Entity)` as a "value
component", `ChildOf(e1)` and `ChildOf(e2)` would be considered
"different components". This makes the transition between fragmenting
and non-fragmenting a single flag, and everything else continues to work
as expected.
* Many-to-many support
* Non-fragmenting: We can expand Relationship to be a list of entities
instead of a single entity. I have largely already written the code for
this.
* Fragmenting: With the "value component" impl mentioned above, we get
many-to-many support "for free", as it would allow inserting multiple
copies of a Relationship component with different target entities.
Fixes#3742 (If this PR is merged, I think we should open more targeted
followup issues for the work above, with a fresh tracking issue free of
the large amount of less-directed historical context)
Fixes#17301Fixes#12235Fixes#15299Fixes#15308
## Migration Guide
* Replace `ChildBuilder` with `ChildSpawnerCommands`.
* Replace calls to `.set_parent(parent_id)` with
`.insert(Parent(parent_id))`.
* Replace calls to `.replace_children()` with `.remove::<Children>()`
followed by `.add_children()`. Note that you'll need to manually despawn
any children that are not carried over.
* Replace calls to `.despawn_recursive()` with `.despawn()`.
* Replace calls to `.despawn_descendants()` with
`.despawn_related::<Children>()`.
* If you have any calls to `.despawn()` which depend on the children
being preserved, you'll need to remove the `Children` component first.
---------
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
# Objective
Fixes https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/17111
## Solution
Move `#![warn(clippy::allow_attributes,
clippy::allow_attributes_without_reason)]` to the workspace `Cargo.toml`
## Testing
Lots of CI testing, and local testing too.
---------
Co-authored-by: Benjamin Brienen <benjamin.brienen@outlook.com>
This commit allows Bevy to use `multi_draw_indirect_count` for drawing
meshes. The `multi_draw_indirect_count` feature works just like
`multi_draw_indirect`, but it takes the number of indirect parameters
from a GPU buffer rather than specifying it on the CPU.
Currently, the CPU constructs the list of indirect draw parameters with
the instance count for each batch set to zero, uploads the resulting
buffer to the GPU, and dispatches a compute shader that bumps the
instance count for each mesh that survives culling. Unfortunately, this
is inefficient when we support `multi_draw_indirect_count`. Draw
commands corresponding to meshes for which all instances were culled
will remain present in the list when calling
`multi_draw_indirect_count`, causing overhead. Proper use of
`multi_draw_indirect_count` requires eliminating these empty draw
commands.
To address this inefficiency, this PR makes Bevy fully construct the
indirect draw commands on the GPU instead of on the CPU. Instead of
writing instance counts to the draw command buffer, the mesh
preprocessing shader now writes them to a separate *indirect metadata
buffer*. A second compute dispatch known as the *build indirect
parameters* shader runs after mesh preprocessing and converts the
indirect draw metadata into actual indirect draw commands for the GPU.
The build indirect parameters shader operates on a batch at a time,
rather than an instance at a time, and as such each thread writes only 0
or 1 indirect draw parameters, simplifying the current logic in
`mesh_preprocessing`, which currently has to have special cases for the
first mesh in each batch. The build indirect parameters shader emits
draw commands in a tightly packed manner, enabling maximally efficient
use of `multi_draw_indirect_count`.
Along the way, this patch switches mesh preprocessing to dispatch one
compute invocation per render phase per view, instead of dispatching one
compute invocation per view. This is preparation for two-phase occlusion
culling, in which we will have two mesh preprocessing stages. In that
scenario, the first mesh preprocessing stage must only process opaque
and alpha tested objects, so the work items must be separated into those
that are opaque or alpha tested and those that aren't. Thus this PR
splits out the work items into a separate buffer for each phase. As this
patch rewrites so much of the mesh preprocessing infrastructure, it was
simpler to just fold the change into this patch instead of deferring it
to the forthcoming occlusion culling PR.
Finally, this patch changes mesh preprocessing so that it runs
separately for indexed and non-indexed meshes. This is because draw
commands for indexed and non-indexed meshes have different sizes and
layouts. *The existing code is actually broken for non-indexed meshes*,
as it attempts to overlay the indirect parameters for non-indexed meshes
on top of those for indexed meshes. Consequently, right now the
parameters will be read incorrectly when multiple non-indexed meshes are
multi-drawn together. *This is a bug fix* and, as with the change to
dispatch phases separately noted above, was easiest to include in this
patch as opposed to separately.
## Migration Guide
* Systems that add custom phase items now need to populate the indirect
drawing-related buffers. See the `specialized_mesh_pipeline` example for
an example of how this is done.
We won't be able to retain render phases from frame to frame if the keys
are unstable. It's not as simple as simply keying off the main world
entity, however, because some main world entities extract to multiple
render world entities. For example, directional lights extract to
multiple shadow cascades, and point lights extract to one view per
cubemap face. Therefore, we key off a new type, `RetainedViewEntity`,
which contains the main entity plus a *subview ID*.
This is part of the preparation for retained bins.
---------
Co-authored-by: ickshonpe <david.curthoys@googlemail.com>
# Objective
I realized that setting these to `deny` may have been a little
aggressive - especially since we upgrade warnings to denies in CI.
## Solution
Downgrades these lints to `warn`, so that compiles can work locally. CI
will still treat these as denies.
# Objective
Stumbled upon a `from <-> form` transposition while reviewing a PR,
thought it was interesting, and went down a bit of a rabbit hole.
## Solution
Fix em
# Objective
Many instances of `clippy::too_many_arguments` linting happen to be on
systems - functions which we don't call manually, and thus there's not
much reason to worry about the argument count.
## Solution
Allow `clippy::too_many_arguments` globally, and remove all lint
attributes related to it.
# Objective
In my crusade to give every lint attribute a reason, it appears I got
too complacent and copy-pasted this expect onto non-system functions.
## Solution
Fix up the reason on those non-system functions
## Testing
N/A
# Objective
- Commands like `cargo bench -- --save-baseline before` do not work
because the default `libtest` is intercepting Criterion-specific CLI
arguments.
- Fixes#17200.
## Solution
- Disable the default `libtest` benchmark harness for the library crate,
as per [the Criterion
book](https://bheisler.github.io/criterion.rs/book/faq.html#cargo-bench-gives-unrecognized-option-errors-for-valid-command-line-options).
## Testing
- `cargo bench -p benches -- --save-baseline before`
- You don't need to run the entire benchmarks, just make sure that they
start without any errors. :)
# Objective & Solution
- Update `downcast-rs` to the latest version, 2.
- Disable (new) `sync` feature to improve compatibility with atomically
challenged platforms.
- Remove stub `downcast-rs` alternative code from `bevy_app`
## Testing
- CI
## Notes
The only change from version 1 to version 2 is the addition of a new
`sync` feature, which allows disabling the `DowncastSync` parts of
`downcast-rs`, which require access to `alloc::sync::Arc`, which is not
available on atomically challenged platforms. Since Bevy makes no use of
the functionality provided by the `sync` feature, I've disabled it in
all crates. Further details can be found
[here](https://github.com/marcianx/downcast-rs/pull/22).
# Objective
- https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/17111
## Solution
Set the `clippy::allow_attributes` and
`clippy::allow_attributes_without_reason` lints to `deny`, and bring
`bevy_render` in line with the new restrictions.
## Testing
`cargo clippy` and `cargo test --package bevy_render` were run, and no
errors were encountered.
# Objective
the `get` function on [`InstanceInputUniformBuffer`] seems very
error-prone. This PR hopes to fix this.
## Solution
Do a few checks to ensure the index is in bounds and that the `BDI` is
not removed.
Return `Option<BDI>` instead of `BDI`.
## Testing
- Did you test these changes? If so, how?
added a test to verify that the instance buffer works correctly
## Future Work
Performance decreases when using .binary_search(). However this is
likely due to the fact that [`InstanceInputUniformBuffer::get`] for now
is never used, and only get_unchecked.
## Migration Guide
`InstanceInputUniformBuffer::get` now returns `Option<BDI>` instead of
`BDI` to reduce panics. If you require the old functionality of
`InstanceInputUniformBuffer::get` consider using
`InstanceInputUniformBuffer::get_unchecked`.
---------
Co-authored-by: Tim Overbeek <oorbeck@gmail.com>
Currently, our batchable binned items are stored in a hash table that
maps bin key, which includes the batch set key, to a list of entities.
Multidraw is handled by sorting the bin keys and accumulating adjacent
bins that can be multidrawn together (i.e. have the same batch set key)
into multidraw commands during `batch_and_prepare_binned_render_phase`.
This is reasonably efficient right now, but it will complicate future
work to retain indirect draw parameters from frame to frame. Consider
what must happen when we have retained indirect draw parameters and the
application adds a bin (i.e. a new mesh) that shares a batch set key
with some pre-existing meshes. (That is, the new mesh can be multidrawn
with the pre-existing meshes.) To be maximally efficient, our goal in
that scenario will be to update *only* the indirect draw parameters for
the batch set (i.e. multidraw command) containing the mesh that was
added, while leaving the others alone. That means that we have to
quickly locate all the bins that belong to the batch set being modified.
In the existing code, we would have to sort the list of bin keys so that
bins that can be multidrawn together become adjacent to one another in
the list. Then we would have to do a binary search through the sorted
list to find the location of the bin that was just added. Next, we would
have to widen our search to adjacent indexes that contain the same batch
set, doing expensive comparisons against the batch set key every time.
Finally, we would reallocate the indirect draw parameters and update the
stored pointers to the indirect draw parameters that the bins store.
By contrast, it'd be dramatically simpler if we simply changed the way
bins are stored to first map from batch set key (i.e. multidraw command)
to the bins (i.e. meshes) within that batch set key, and then from each
individual bin to the mesh instances. That way, the scenario above in
which we add a new mesh will be simpler to handle. First, we will look
up the batch set key corresponding to that mesh in the outer map to find
an inner map corresponding to the single multidraw command that will
draw that batch set. We will know how many meshes the multidraw command
is going to draw by the size of that inner map. Then we simply need to
reallocate the indirect draw parameters and update the pointers to those
parameters within the bins as necessary. There will be no need to do any
binary search or expensive batch set key comparison: only a single hash
lookup and an iteration over the inner map to update the pointers.
This patch implements the above technique. Because we don't have
retained bins yet, this PR provides no performance benefits. However, it
opens the door to maximally efficient updates when only a small number
of meshes change from frame to frame.
The main churn that this patch causes is that the *batch set key* (which
uniquely specifies a multidraw command) and *bin key* (which uniquely
specifies a mesh *within* that multidraw command) are now separate,
instead of the batch set key being embedded *within* the bin key.
In order to isolate potential regressions, I think that at least #16890,
#16836, and #16825 should land before this PR does.
## Migration Guide
* The *batch set key* is now separate from the *bin key* in
`BinnedPhaseItem`. The batch set key is used to collect multidrawable
meshes together. If you aren't using the multidraw feature, you can
safely set the batch set key to `()`.
Bump version after release
This PR has been auto-generated
---------
Co-authored-by: Bevy Auto Releaser <41898282+github-actions[bot]@users.noreply.github.com>
Co-authored-by: François Mockers <mockersf@gmail.com>
# Objective
- Contributes to #11478
## Solution
- Made `bevy_utils::tracing` `doc(hidden)`
- Re-exported `tracing` from `bevy_log` for end-users
- Added `tracing` directly to crates that need it.
## Testing
- CI
---
## Migration Guide
If you were importing `tracing` via `bevy::utils::tracing`, instead use
`bevy::log::tracing`. Note that many items within `tracing` are also
directly re-exported from `bevy::log` as well, so you may only need
`bevy::log` for the most common items (e.g., `warn!`, `trace!`, etc.).
This also applies to the `log_once!` family of macros.
## Notes
- While this doesn't reduce the line-count in `bevy_utils`, it further
decouples the internal crates from `bevy_utils`, making its eventual
removal more feasible in the future.
- I have just imported `tracing` as we do for all dependencies. However,
a workspace dependency may be more appropriate for version management.
Some hardware and driver combos, such as Intel Iris Xe, have low limits
on the numbers of samplers per shader, causing an overflow. With
first-class bindless arrays, `wgpu` should be able to work around this
limitation eventually, but for now we need to disable bindless materials
on those platforms.
This is an alternative to PR #17107 that calculates the precise number
of samplers needed and compares to the hardware sampler limit,
transparently falling back to non-bindless if the limit is exceeded.
Fixes#16988.
Derived `Default` for all public unit structs that already derive from
`Component`. This allows them to be used more easily as required
components.
To avoid clutter in tests/examples, only public components were
affected, but this could easily be expanded to affect all unit
components.
Fixes#17052.
# Objective
- Fixes https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/16556
- Closes https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/11807
## Solution
- Simplify custom projections by using a single source of truth -
`Projection`, removing all existing generic systems and types.
- Existing perspective and orthographic structs are no longer components
- I could dissolve these to simplify further, but keeping them around
was the fast way to implement this.
- Instead of generics, introduce a third variant, with a trait object.
- Do an object safety dance with an intermediate trait to allow cloning
boxed camera projections. This is a normal rust polymorphism papercut.
You can do this with a crate but a manual impl is short and sweet.
## Testing
- Added a custom projection example
---
## Showcase
- Custom projections and projection handling has been simplified.
- Projection systems are no longer generic, with the potential for many
different projection components on the same camera.
- Instead `Projection` is now the single source of truth for camera
projections, and is the only projection component.
- Custom projections are still supported, and can be constructed with
`Projection::custom()`.
## Migration Guide
- `PerspectiveProjection` and `OrthographicProjection` are no longer
components. Use `Projection` instead.
- Custom projections should no longer be inserted as a component.
Instead, simply set the custom projection as a value of `Projection`
with `Projection::custom()`.
# Objective
Some sort calls and `Ord` impls are unnecessarily complex.
## Solution
Rewrite the "match on cmp, if equal do another cmp" as either a
comparison on tuples, or `Ordering::then_with`, depending on whether the
compare keys need construction.
`sort_by` -> `sort_by_key` when symmetrical. Do the same for
`min_by`/`max_by`.
Note that `total_cmp` can only work with `sort_by`, and not on tuples.
When sorting collected query results that contain
`Entity`/`MainEntity`/`RenderEntity` in their `QueryData`, with that
`Entity` in the sort key:
stable -> unstable sort (all queried entities are unique)
If key construction is not simple, switch to `sort_by_cached_key` when
possible.
Sorts that are only performed to discover the maximal element are
replaced by `max_by_key`.
Dedicated comparison functions and structs are removed where simple.
Derive `PartialOrd`/`Ord` when useful.
Misc. closure style inconsistencies.
## Testing
- Existing tests.
# Objective
Fixes#17024
## Solution
## Testing
By adding
```
if let Some(mut cmd) = commands.get_entity( *equipment_link_node ){
cmd.insert(Visibility::Inherited); // a hack for now
}
```
in my build after .set_parent() , this fixes the issue. This is why i
think that this change will fix the issue. Unfortunately i was not able
to test the Changed (parent ) , this actual code change, because no
matter how i 'patch', it breaks my project. I got super close but still
had 23 errors due to Reflect being angry.
---
This commit makes the following changes:
* `IndirectParametersBuffer` has been changed from a `BufferVec` to a
`RawBufferVec`. This won about 20us or so on Bistro by avoiding `encase`
overhead.
* The methods on the `GetFullBatchData` trait no longer have the
`entity` parameter, as it was unused.
* `PreprocessWorkItem`, which specifies a transform-and-cull operation,
now supplies the mesh instance uniform output index directly instead of
having the shader look it up from the indirect draw parameters.
Accordingly, the responsibility of writing the output index to the
indirect draw parameters has been moved from the CPU to the GPU. This is
in preparation for retained indirect instance draw commands, where the
mesh instance uniform output index may change from frame to frame, while
the indirect instance draw commands will be cached. We won't want the
CPU to have to upload the same indirect draw parameters again and again
if a batch didn't change from frame to frame.
* `batch_and_prepare_binned_render_phase` and
`batch_and_prepare_sorted_render_phase` now allocate indirect draw
commands for an entire batch set at a time when possible, instead of one
batch at a time. This change will allow us to retain the indirect draw
commands for whole batch sets.
* `GetFullBatchData::get_batch_indirect_parameters_index` has been
replaced with `GetFullBatchData::write_batch_indirect_parameters`, which
takes an offset and writes into it instead of allocating. This is
necessary in order to use the optimization mentioned in the previous
point.
* At the WGSL level, `IndirectParameters` has been factored out into
`mesh_preprocess_types.wgsl`. This is because we'll need a new compute
shader that zeroes out the instance counts in preparation for a new
frame. That shader will need to access `IndirectParameters`, so it was
moved to a separate file.
* Bins are no longer raw vectors but are instances of a separate type,
`RenderBin`. This is so that the bin can eventually contain its retained
batches.
OK, so this is tricky. Every frame, `delete_old_work_item_buffers`
deletes the mesh preprocessing index buffers (a.k.a. work item buffers)
for views that don't have `ViewTarget`s. This was always wrong for
shadow map views, as shadow maps only have `ExtractedView` components,
not `ViewTarget`s. However, before #16836, the problem was masked,
because uploading the mesh preprocessing index buffers for shadow views
had already completed by the time `delete_old_work_item_buffers` ran.
But PR #16836 moved `delete_old_work_item_buffers` from the
`ManageViews` phase to `PrepareResources`, which runs before
`write_batched_instance_buffers` uploads the work item buffers to the
GPU.
This itself isn't wrong, but it exposed the bug, because now it's
possible for work item buffers to get deleted before they're uploaded in
`write_batched_instance_buffers`. This is actually intermittent! It's
possible for the old work item buffers to get deleted, and then
*recreated* in `batch_and_prepare_binned_render_phase`, which runs
during `PrepareResources` as well, and under that system ordering, there
will be no problem other than a little inefficiency arising from
recreating the buffers every frame. But, if
`delete_old_work_item_buffers` runs *after*
`batch_and_prepare_render_phase`, then the work item buffers
corresponding to shadow views will get deleted, and then the shadows
will disappear.
The fact that this is racy is what made it look like #16922 solved the
issue. In fact, it didn't: it just perturbed the ordering on the build
bots enough that the issue stopped appearing. However, on my system, the
shadows still don't appear with #16922.
This commit solves the problem by making `delete_old_work_item_buffers`
look at `ExtractedView`s, not `ViewTarget`s, preventing work item
buffers corresponding to live shadow map views from being deleted.
# Objective
Fix alignment calculations in our rendering code.
Fixes#16992
The `gpu_readback::align_byte_size` function incorrectly rounds aligned
values to the next alignment.
If we assume the alignment to be 256 (because that's what wgpu says it
its) the function would align 0 to 256, 256 to 512, etc...
## Solution
Forward the `gpu_readback::align_byte_size` to
`RenderDevice::align_copy_bytes_per_row` so we don't implement the same
method twice.
Simplify `RenderDevice::align_copy_bytes_per_row`.
## Testing
Ran the code provided in #16992 to see if the issue has been solved +
added a test to check if `align_copy_bytes_per_row` returns the correct
values.
# Objective
Fixes#16683
## Solution
Make all fields ine `RawHandleWrapper` private.
## Testing
- CI
- `cargo clippy`
- The lightmaps example
---
## Migration Guide
The `window_handle` and `dispay_handle` fields on `RawHandleWrapper` are
no longer public. Use the newly added getters and setters to manipulate
them instead.
# Objective
- Related to https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/11478
## Solution
- Moved `futures.rs`, `ConditionalSend` `ConditionalSendFuture` and
`BoxedFuture` from `bevy_utils` to `bevy_tasks`.
## Testing
- CI checks
## Migration Guide
- Several modules were moved from `bevy_utils` into `bevy_tasks`:
- Replace `bevy_utils::futures` imports with `bevy_tasks::futures`.
- Replace `bevy_utils::ConditionalSend` with
`bevy_tasks::ConditionalSend`.
- Replace `bevy_utils::ConditionalSendFuture` with
`bevy_tasks::ConditionalSendFuture`.
- Replace `bevy_utils::BoxedFuture` with `bevy_tasks::BoxedFuture`.
# Objective
Fixes#16104
## Solution
I removed all instances of `:?` and put them back one by one where it
caused an error.
I removed some bevy_utils helper functions that were only used in 2
places and don't add value. See: #11478
## Testing
CI should catch the mistakes
## Migration Guide
`bevy::utils::{dbg,info,warn,error}` were removed. Use
`bevy::utils::tracing::{debug,info,warn,error}` instead.
---------
Co-authored-by: SpecificProtagonist <vincentjunge@posteo.net>
# Objective
Some types like `RenderEntity` and `MainEntity` are just wrappers around
`Entity`, so they should be able to implement
`EntityBorrow`/`TrustedEntityBorrow`. This allows using them with
`EntitySet` functionality.
The `EntityRef` family are more than direct wrappers around `Entity`,
but can still benefit from being unique in a collection.
## Solution
Implement `EntityBorrow` and `TrustedEntityBorrow` for simple `Entity`
newtypes and `EntityRef` types.
These impls are an explicit decision to have the `EntityRef` types
compare like just `Entity`.
`EntityWorldMut` is omitted from this impl, because it explicitly
contains a `&mut World` as well, and we do not ever use more than one at
a time.
Add `EntityBorrow` to the `bevy_ecs` prelude.
## Migration Guide
`NormalizedWindowRef::entity` has been replaced with an
`EntityBorrow::entity` impl.
This commit fixes the following regressions:
1. Transmission-specific calls to shader lighting functions didn't pass
the `enable_diffuse` parameter, breaking the `transmission` example.
2. The combination of bindless `StandardMaterial` and bindless lightmaps
caused us to blow past the 128 texture limit on M1/M2 chips in some
cases, in particular the `depth_of_field` example.
https://github.com/gfx-rs/wgpu/issues/3334 should fix this, but in the
meantime this patch reduces the number of bindless lightmaps from 16 to
4 in order to stay under the limit.
3. The renderer was crashing on startup on Adreno 610 chips. This PR
simply disables bindless on Adreno 610 and lower.
# Objective
- Fixes#16892
## Solution
- Removed `TypeRegistryPlugin` (`Name` is now automatically registered
with a default `App`)
- Moved `TaskPoolPlugin` to `bevy_app`
- Moved `FrameCountPlugin` to `bevy_diagnostic`
- Deleted now-empty `bevy_core`
## Testing
- CI
## Migration Guide
- `TypeRegistryPlugin` no longer exists. If you can't use a default
`App` but still need `Name` registered, do so manually with
`app.register_type::<Name>()`.
- References to `TaskPoolPlugin` and associated types will need to
import it from `bevy_app` instead of `bevy_core`
- References to `FrameCountPlugin` and associated types will need to
import it from `bevy_diagnostic` instead of `bevy_core`
## Notes
This strategy was agreed upon by Cart and several other members in
[Discord](https://discord.com/channels/691052431525675048/692572690833473578/1319137218312278077).
# Objective
Simplify the code by using `macro_rules` instead of a proc macro where
possible.
## Solution
Replace `impl_param_set` proc macro with a `macro_rules` macro.
# Objective
I have something of a niche use case. I have a camera rendering pixel
art with a scale factor set, and another camera that renders to an
off-screen texture which is supposed to match the main camera exactly.
However, when computing camera target info, Bevy [hardcodes a scale
factor of
1.0](116c2b02fe/crates/bevy_render/src/camera/camera.rs (L828))
for image targets which means that my main camera and my image target
camera get different `OrthographicProjections` calculated.
## Solution
This PR adds an `ImageRenderTarget` struct which allows scale factors to
be specified.
## Testing
I tested the affected examples on macOS and they still work. This is an
additive change and should not break any existing code, apart from what
is trivially fixable by following compiler error messages.
---
## Migration Guide
`RenderTarget::Image` now takes an `ImageRenderTarget` instead of a
`Handle<Image>`. You can call `handle.into()` to construct an
`ImageRenderTarget` using the same settings as before.
# Objective
When preparing `GpuImage`s, we currently discard the
`depth_or_array_layers` of the `Image`'s size by converting it into a
`UVec2`.
Fixes#16715.
## Solution
Change `GpuImage::size` to `Extent3d`, and just pass that through when
creating `GpuImage`s.
Also copy the `aspect_ratio`, and `size` (now `size_2d` for
disambiguation from the field) functions from `Image` to `GpuImage` for
ease of use with 2D textures.
I originally copied all size-related functions (like `width`, and
`height`), but i think they are unnecessary considering how visible the
`size` field on `GpuImage` is compared to `Image`.
## Testing
Tested via `cargo r -p ci` for everything except docs, when generating
docs it keeps spitting out a ton of
```
error[E0554]: `#![feature]` may not be used on the stable release channel
--> crates/bevy_dylib/src/lib.rs:1:21
|
1 | #![cfg_attr(docsrs, feature(doc_auto_cfg))]
|
```
Not sure why this is happening, but it also happens without my changes,
so it's almost certainly some strange issue specific to my machine.
## Migration Guide
- `GpuImage::size` is now an `Extent3d`. To easily get 2D size, use
`size_2d()`.
# Objective
Expand `track_change_detection` feature to also track entity spawns and
despawns. Use this to create better error messages.
# Solution
Adds `Entities::entity_get_spawned_or_despawned_by` as well as `{all
entity reference types}::spawned_by`.
This also removes the deprecated `get_many_entities_mut` & co (and
therefore can't land in 0.15) because we don't yet have no Polonius.
## Testing
Added a test that checks that the locations get updated and these
updates are ordered correctly vs hooks & observers.
---
## Showcase
Access location:
```rust
let mut world = World::new();
let entity = world.spawn_empty().id();
println!("spawned by: {}", world.entity(entity).spawned_by());
```
```
spawned by: src/main.rs:5:24
```
Error message (with `track_change_detection`):
```rust
world.despawn(entity);
world.entity(entity);
```
```
thread 'main' panicked at src/main.rs:11:11:
Entity 0v1#4294967296 was despawned by src/main.rs:10:11
```
and without:
```
thread 'main' panicked at src/main.rs:11:11:
Entity 0v1#4294967296 does not exist (enable `track_change_detection` feature for more details)
```
Similar error messages now also exists for `Query::get`,
`World::entity_mut`, `EntityCommands` creation and everything that
causes `B0003`, e.g.
```
error[B0003]: Could not insert a bundle (of type `MaterialMeshBundle<StandardMaterial>`) for entity Entity { index: 7, generation: 1 }, which was despawned by src/main.rs:10:11. See: https://bevyengine.org/learn/errors/#b0003
```
---------
Co-authored-by: kurk070ff <108901106+kurk070ff@users.noreply.github.com>
Co-authored-by: Freya Pines <freya@MacBookAir.lan>
Co-authored-by: Freya Pines <freya@Freyas-MacBook-Air.local>
Co-authored-by: Matty Weatherley <weatherleymatthew@gmail.com>
Currently, `check_visibility` is parameterized over a query filter that
specifies the type of potentially-visible object. This has the
unfortunate side effect that we need a separate system,
`mark_view_visibility_as_changed_if_necessary`, to trigger view
visibility change detection. That system is quite slow because it must
iterate sequentially over all entities in the scene.
This PR moves the query filter from `check_visibility` to a new
component, `VisibilityClass`. `VisibilityClass` stores a list of type
IDs, each corresponding to one of the query filters we used to use.
Because `check_visibility` is no longer specialized to the query filter
at the type level, Bevy now only needs to invoke it once, leading to
better performance as `check_visibility` can do change detection on the
fly rather than delegating it to a separate system.
This commit also has ergonomic improvements, as there's no need for
applications that want to add their own custom renderable components to
add specializations of the `check_visibility` system to the schedule.
Instead, they only need to ensure that the `ViewVisibility` component is
properly kept up to date. The recommended way to do this, and the way
that's demonstrated in the `custom_phase_item` and
`specialized_mesh_pipeline` examples, is to make `ViewVisibility` a
required component and to add the type ID to it in a component add hook.
This patch does this for `Mesh3d`, `Mesh2d`, `Sprite`, `Light`, and
`Node`, which means that most app code doesn't need to change at all.
Note that, although this patch has a large impact on the performance of
visibility determination, it doesn't actually improve the end-to-end
frame time of `many_cubes`. That's because the render world was already
effectively hiding the latency from
`mark_view_visibility_as_changed_if_necessary`. This patch is, however,
necessary for *further* improvements to `many_cubes` performance.
`many_cubes` trace before:

`many_cubes` trace after:

## Migration Guide
* `check_visibility` no longer takes a `QueryFilter`, and there's no
need to add it manually to your app schedule anymore for custom
rendering items. Instead, entities with custom renderable components
should add the appropriate type IDs to `VisibilityClass`. See
`custom_phase_item` for an example.
# Objective
- Wgpu barrier tracking is expensive. Making buffers read-only makes
ideally lets wgpu skip worrying about barriers, although in wgpu 23 it
apparently won't yet.
## Solution
- Remove COPY_DST usage from AsBindGroup uniform buffers to allow future
wgpu versions to make this cheaper.
- AsBindGroup never updates buffers, so there's no need for COPY_DST. We
always recreate all buffers and the bind group every time data changes,
which yeah is also expensive.
## Testing
- Ran the animated materials example with/without bindless enabled. No
crashes.
This commit allows Bevy to bind 16 lightmaps at a time, if the current
platform supports bindless textures. Naturally, if bindless textures
aren't supported, Bevy falls back to binding only a single lightmap at a
time. As lightmaps are usually heavily atlased, I doubt many scenes will
use more than 16 lightmap textures.
This has little performance impact now, but it's desirable for us to
reap the benefits of multidraw and bindless textures on scenes that use
lightmaps. Otherwise, we might have to break batches in order to switch
those lightmaps.
Additionally, this PR slightly reduces the cost of binning because it
makes the lightmap index in `Opaque3dBinKey` 32 bits instead of an
`AssetId`.
## Migration Guide
* The `Opaque3dBinKey::lightmap_image` field is now
`Opaque3dBinKey::lightmap_slab`, which is a lightweight identifier for
an entire binding array of lightmaps.
# Objective
We were waiting for 1.83 to address most of these, due to a bug with
`missing_docs` and `expect`. Relates to, but does not entirely complete,
#15059.
## Solution
- Upgrade to 1.83
- Switch `allow(missing_docs)` to `expect(missing_docs)`
- Remove a few now-unused `allow`s along the way, or convert to `expect`
# Objective
Fixes#16659
## Solution
- I just added all the `#[reflect(Component)]` attributes where
necessary.
## Testing
I wrote a small program that scans the bevy code for all structs and
enums that derive `Component` and `Reflect`, but don't have the
attribute `#[reflect(Component)]`.
I don't know if this testing program should be part of the testing suite
of bevy. It takes a bit of time to scan the whole codebase. In any case,
I've published it [here](https://github.com/anlumo/bevy-reflect-check).
---------
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
I forgot to set `BINDLESS_SLOT_COUNT` in `ExtendedMaterial`'s
implementation of `AsBindGroup`, so it didn't actually become bindless.
In fact, it would usually crash with a shader/bind group layout
mismatch, because some parts of Bevy's renderer thought that the
resulting material was bindless while other parts didn't. This commit
corrects the situation.
I had to make `BINDLESS_SLOT_COUNT` a function instead of a constant
because the `ExtendedMaterial` version needs some logic. Unfortunately,
trait methods can't be `const fn`s, so it has to be a runtime function.
# Objective
- Minor consistency improvement in proc macro code.
- Remove `get_path_direct` since it was only used once anyways and
doesn't add much.
## Solution
- Possibly a minor performance improvement since the `Cargo.toml` wont
be parsed as often.
## Testing
- I don't think it breaks anything.
- This is my first time working on bevy itself. Is there a script to do
a quick verify of my pr?
## Other PR
Similar to #7536 but has no extra dependencies.
Co-authored-by: François Mockers <mockersf@gmail.com>
# Objective
- Describe the objective or issue this PR addresses.
- If you're fixing a specific issue, say "Fixes #X".
## Solution
- Describe the solution used to achieve the objective above.
## Testing
- Did you test these changes? If so, how?
- Are there any parts that need more testing?
- How can other people (reviewers) test your changes? Is there anything
specific they need to know?
- If relevant, what platforms did you test these changes on, and are
there any important ones you can't test?
---
## Showcase
> This section is optional. If this PR does not include a visual change
or does not add a new feature, you can delete this section.
- Help others understand the result of this PR by showcasing your
awesome work!
- If this PR adds a new feature or public API, consider adding a brief
pseudo-code snippet of it in action
- If this PR includes a visual change, consider adding a screenshot,
GIF, or video
- If you want, you could even include a before/after comparison!
- If the Migration Guide adequately covers the changes, you can delete
this section
While a showcase should aim to be brief and digestible, you can use a
toggleable section to save space on longer showcases:
<details>
<summary>Click to view showcase</summary>
```rust
println!("My super cool code.");
```
</details>
## Migration Guide
> This section is optional. If there are no breaking changes, you can
delete this section.
- If this PR is a breaking change (relative to the last release of
Bevy), describe how a user might need to migrate their code to support
these changes
- Simply adding new functionality is not a breaking change.
- Fixing behavior that was definitely a bug, rather than a questionable
design choice is not a breaking change.
This patch replaces the undocumented `NoGpuCulling` component with a new
component, `NoIndirectDrawing`, effectively turning indirect drawing on
by default. Indirect mode is needed for the recently-landed multidraw
feature (#16427). Since multidraw is such a win for performance, when
that feature is supported the small performance tax that indirect mode
incurs is virtually always worth paying.
To ensure that custom drawing code such as that in the
`custom_shader_instancing` example continues to function, this commit
additionally makes GPU culling take the `NoFrustumCulling` component
into account.
This PR is an alternative to #16670 that doesn't break the
`custom_shader_instancing` example. **PR #16755 should land first in
order to avoid breaking deferred rendering, as multidraw currently
breaks it**.
## Migration Guide
* Indirect drawing (GPU culling) is now enabled by default, so the
`GpuCulling` component is no longer available. To disable indirect mode,
which may be useful with custom render nodes, add the new
`NoIndirectDrawing` component to your camera.
This commit resolves most of the failures seen in #16670. It contains
two major fixes:
1. The prepass shaders weren't updated for bindless mode, so they were
accessing `material` as a single element instead of as an array. I added
the needed `BINDLESS` check.
2. If the mesh didn't support batch set keys (i.e. `get_batch_set_key()`
returns `None`), and multidraw was enabled, the batching logic would try
to multidraw all the meshes in a bin together instead of disabling
multidraw. This is because we checked whether the `Option<BatchSetKey>`
for the previous batch was equal to the `Option<BatchSetKey>` for the
next batch to determine whether objects could be multidrawn together,
which would return true if batch set keys were absent, causing an entire
bin to be multidrawn together. This patch fixes the logic so that
multidraw is only enabled if the batch set keys match *and are `Some`*.
Additionally, this commit adds batch key support for bins that use
`Opaque3dNoLightmapBinKey`, which in practice means prepasses.
Consequently, this patch enables multidraw for the prepass when GPU
culling is enabled.
When testing this patch, try adding `GpuCulling` to the camera in the
`deferred_rendering` and `ssr` examples. You can see that these examples
break without this patch and work properly with it.
---------
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
Updating dependencies; adopted version of #15696. (Supercedes #15696.)
Long answer: hashbrown is no longer using ahash by default, meaning that
we can't use the default-hasher methods with ahasher. So, we have to use
the longer-winded versions instead. This takes the opportunity to also
switch our default hasher as well, but without actually enabling the
default-hasher feature for hashbrown, meaning that we'll be able to
change our hasher more easily at the cost of all of these method calls
being obnoxious forever.
One large change from 0.15 is that `insert_unique_unchecked` is now
`unsafe`, and for cases where unsafe code was denied at the crate level,
I replaced it with `insert`.
## Migration Guide
`bevy_utils` has updated its version of `hashbrown` to 0.15 and now
defaults to `foldhash` instead of `ahash`. This means that if you've
hard-coded your hasher to `bevy_utils::AHasher` or separately used the
`ahash` crate in your code, you may need to switch to `foldhash` to
ensure that everything works like it does in Bevy.
This commit makes `StandardMaterial` use bindless textures, as
implemented in PR #16368. Non-bindless mode, as used for example in
Metal and WebGL 2, remains fully supported via a plethora of `#ifdef
BINDLESS` preprocessor definitions.
Unfortunately, this PR introduces quite a bit of unsightliness into the
PBR shaders. This is a result of the fact that WGSL supports neither
passing binding arrays to functions nor passing individual *elements* of
binding arrays to functions, except directly to texture sample
functions. Thus we're unable to use the `sample_texture` abstraction
that helped abstract over the meshlet and non-meshlet paths. I don't
think there's anything we can do to help this other than to suggest
improvements to upstream Naga.
PR #15756 made us create temporary render entities for all visible
objects, even if they had no render world counterpart. This regressed
our `many_cubes` time from about 3.59 ms/frame to 4.66 ms/frame.
This commit changes that behavior to use `Entity::PLACEHOLDER` instead
of creating a temporary render entity. This improves our `many_cubes`
time from 5.66 ms/frame to 3.96 ms/frame, a 43% speedup.
I tested 3D, 2D gizmos, and UI and they seem to work.
See the following graph of `many_cubes` frame time (lower is better). PR
#15756 is the one in October.

This commit removes the logic that attempted to keep the
`MeshInputUniform` buffer contiguous. Not only was it slow and complex,
but it was also incorrect, which caused #16686 and #16690. I changed the
logic to simply maintain a free list of unused slots in the buffer and
preferentially fill them when pushing new mesh input uniforms.
Closes#16686.
Closes#16690.
# Objective
- A `Trigger` has multiple associated `Entity`s - the entity observing
the event, and the entity that was targeted by the event.
- The field `entity: Entity` encodes no semantic information about what
the entity is used for, you can already tell that it's an `Entity` by
the type signature!
## Solution
- Rename `trigger.entity()` to `trigger.target()`
---
## Changelog
- `Trigger`s are associated with multiple entities. `Trigger::entity()`
has been renamed to `Trigger::target()` to reflect the semantics of the
entity being returned.
## Migration Guide
- Rename `Trigger::entity()` to `Trigger::target()`.
- Rename `ObserverTrigger::entity` to `ObserverTrigger::target`
This commit adds support for *multidraw*, which is a feature that allows
multiple meshes to be drawn in a single drawcall. `wgpu` currently
implements multidraw on Vulkan, so this feature is only enabled there.
Multiple meshes can be drawn at once if they're in the same vertex and
index buffers and are otherwise placed in the same bin. (Thus, for
example, at present the materials and textures must be identical, but
see #16368.) Multidraw is a significant performance improvement during
the draw phase because it reduces the number of rebindings, as well as
the number of drawcalls.
This feature is currently only enabled when GPU culling is used: i.e.
when `GpuCulling` is present on a camera. Therefore, if you run for
example `scene_viewer`, you will not see any performance improvements,
because `scene_viewer` doesn't add the `GpuCulling` component to its
camera.
Additionally, the multidraw feature is only implemented for opaque 3D
meshes and not for shadows or 2D meshes. I plan to make GPU culling the
default and to extend the feature to shadows in the future. Also, in the
future I suspect that polyfilling multidraw on APIs that don't support
it will be fruitful, as even without driver-level support use of
multidraw allows us to avoid expensive `wgpu` rebindings.
# Objective
- Remove `derive_more`'s error derivation and replace it with
`thiserror`
## Solution
- Added `derive_more`'s `error` feature to `deny.toml` to prevent it
sneaking back in.
- Reverted to `thiserror` error derivation
## Notes
Merge conflicts were too numerous to revert the individual changes, so
this reversion was done manually. Please scrutinise carefully during
review.
The bindless PR (#16368) broke some examples:
* `specialized_mesh_pipeline` and `custom_shader_instancing` failed
because they expect to be able to render a mesh with no material, by
overriding enough of the render pipeline to be able to do so. This PR
fixes the issue by restoring the old behavior in which we extract meshes
even if they have no material.
* `texture_binding_array` broke because it doesn't implement
`AsBindGroup::unprepared_bind_group`. This was tricky to fix because
there's a very good reason why `texture_binding_array` doesn't implement
that method: there's no sensible way to do so with `wgpu`'s current
bindless API, due to its multiple levels of borrowed references. To fix
the example, I split `MaterialBindGroup` into
`MaterialBindlessBindGroup` and `MaterialNonBindlessBindGroup`, and
allow direct custom implementations of `AsBindGroup::as_bind_group` for
the latter type of bind groups. To opt in to the new behavior, return
the `AsBindGroupError::CreateBindGroupDirectly` error from your
`AsBindGroup::unprepared_bind_group` implementation, and Bevy will call
your custom `AsBindGroup::as_bind_group` method as before.
## Migration Guide
* Bevy will now unconditionally call
`AsBindGroup::unprepared_bind_group` for your materials, so you must no
longer panic in that function. Instead, return the new
`AsBindGroupError::CreateBindGroupDirectly` error, and Bevy will fall
back to calling `AsBindGroup::as_bind_group` as before.
This commit moves the front end of the rendering pipeline to a retained
model when GPU preprocessing is in use (i.e. by default, except in
constrained environments). `RenderMeshInstance` and `MeshUniformData`
are stored from frame to frame and are updated only for the entities
that changed state. This was rather tricky and requires some careful
surgery to keep the data valid in the case of removals.
This patch is built on top of Bevy's change detection. Generally, this
worked, except that `ViewVisibility` isn't currently properly tracked.
Therefore, this commit adds proper change tracking for `ViewVisibility`.
Doing this required adding a new system that runs after all
`check_visibility` invocations, as no single `check_visibility`
invocation has enough global information to detect changes.
On the Bistro exterior scene, with all textures forced to opaque, this
patch improves steady-state `extract_meshes_for_gpu_building` from
93.8us to 34.5us and steady-state `collect_meshes_for_gpu_building` from
195.7us to 4.28us. Altogether this constitutes an improvement from 290us
to 38us, which is a 7.46x speedup.


This patch is only lightly tested and shouldn't land before 0.15 is
released anyway, so I'm releasing it as a draft.
# Objective
- Required by #16622 due to differing implementations of `System` by
`FunctionSystem` and `ExclusiveFunctionSystem`.
- Optimize the memory usage of instances of `apply_deferred` in system
schedules.
## Solution
By changing `apply_deferred` from being an ordinary system that ends up
as an `ExclusiveFunctionSystem`, and instead into a ZST struct that
implements `System` manually, we save ~320 bytes per instance of
`apply_deferred` in any schedule.
## Testing
- All current tests pass.
---
## Migration Guide
- If you were previously calling the special `apply_deferred` system via
`apply_deferred(world)`, don't.
# Objective
- Fixes#16208
## Solution
- Added an associated type to `Component`, `Mutability`, which flags
whether a component is mutable, or immutable. If `Mutability= Mutable`,
the component is mutable. If `Mutability= Immutable`, the component is
immutable.
- Updated `derive_component` to default to mutable unless an
`#[component(immutable)]` attribute is added.
- Updated `ReflectComponent` to check if a component is mutable and, if
not, panic when attempting to mutate.
## Testing
- CI
- `immutable_components` example.
---
## Showcase
Users can now mark a component as `#[component(immutable)]` to prevent
safe mutation of a component while it is attached to an entity:
```rust
#[derive(Component)]
#[component(immutable)]
struct Foo {
// ...
}
```
This prevents creating an exclusive reference to the component while it
is attached to an entity. This is particularly powerful when combined
with component hooks, as you can now fully track a component's value,
ensuring whatever invariants you desire are upheld. Before this would be
done my making a component private, and manually creating a `QueryData`
implementation which only permitted read access.
<details>
<summary>Using immutable components as an index</summary>
```rust
/// This is an example of a component like [`Name`](bevy::prelude::Name), but immutable.
#[derive(Clone, Copy, PartialEq, Eq, PartialOrd, Ord, Hash, Component)]
#[component(
immutable,
on_insert = on_insert_name,
on_replace = on_replace_name,
)]
pub struct Name(pub &'static str);
/// This index allows for O(1) lookups of an [`Entity`] by its [`Name`].
#[derive(Resource, Default)]
struct NameIndex {
name_to_entity: HashMap<Name, Entity>,
}
impl NameIndex {
fn get_entity(&self, name: &'static str) -> Option<Entity> {
self.name_to_entity.get(&Name(name)).copied()
}
}
fn on_insert_name(mut world: DeferredWorld<'_>, entity: Entity, _component: ComponentId) {
let Some(&name) = world.entity(entity).get::<Name>() else {
unreachable!()
};
let Some(mut index) = world.get_resource_mut::<NameIndex>() else {
return;
};
index.name_to_entity.insert(name, entity);
}
fn on_replace_name(mut world: DeferredWorld<'_>, entity: Entity, _component: ComponentId) {
let Some(&name) = world.entity(entity).get::<Name>() else {
unreachable!()
};
let Some(mut index) = world.get_resource_mut::<NameIndex>() else {
return;
};
index.name_to_entity.remove(&name);
}
// Setup our name index
world.init_resource::<NameIndex>();
// Spawn some entities!
let alyssa = world.spawn(Name("Alyssa")).id();
let javier = world.spawn(Name("Javier")).id();
// Check our index
let index = world.resource::<NameIndex>();
assert_eq!(index.get_entity("Alyssa"), Some(alyssa));
assert_eq!(index.get_entity("Javier"), Some(javier));
// Changing the name of an entity is also fully capture by our index
world.entity_mut(javier).insert(Name("Steven"));
// Javier changed their name to Steven
let steven = javier;
// Check our index
let index = world.resource::<NameIndex>();
assert_eq!(index.get_entity("Javier"), None);
assert_eq!(index.get_entity("Steven"), Some(steven));
```
</details>
Additionally, users can use `Component<Mutability = ...>` in trait
bounds to enforce that a component _is_ mutable or _is_ immutable. When
using `Component` as a trait bound without specifying `Mutability`, any
component is applicable. However, methods which only work on mutable or
immutable components are unavailable, since the compiler must be
pessimistic about the type.
## Migration Guide
- When implementing `Component` manually, you must now provide a type
for `Mutability`. The type `Mutable` provides equivalent behaviour to
earlier versions of `Component`:
```rust
impl Component for Foo {
type Mutability = Mutable;
// ...
}
```
- When working with generic components, you may need to specify that
your generic parameter implements `Component<Mutability = Mutable>`
rather than `Component` if you require mutable access to said component.
- The entity entry API has had to have some changes made to minimise
friction when working with immutable components. Methods which
previously returned a `Mut<T>` will now typically return an
`OccupiedEntry<T>` instead, requiring you to add an `into_mut()` to get
the `Mut<T>` item again.
## Draft Release Notes
Components can now be made immutable while stored within the ECS.
Components are the fundamental unit of data within an ECS, and Bevy
provides a number of ways to work with them that align with Rust's rules
around ownership and borrowing. One part of this is hooks, which allow
for defining custom behavior at key points in a component's lifecycle,
such as addition and removal. However, there is currently no way to
respond to _mutation_ of a component using hooks. The reasons for this
are quite technical, but to summarize, their addition poses a
significant challenge to Bevy's core promises around performance.
Without mutation hooks, it's relatively trivial to modify a component in
such a way that breaks invariants it intends to uphold. For example, you
can use `core::mem::swap` to swap the components of two entities,
bypassing the insertion and removal hooks.
This means the only way to react to this modification is via change
detection in a system, which then begs the question of what happens
_between_ that alteration and the next run of that system?
Alternatively, you could make your component private to prevent
mutation, but now you need to provide commands and a custom `QueryData`
implementation to allow users to interact with your component at all.
Immutable components solve this problem by preventing the creation of an
exclusive reference to the component entirely. Without an exclusive
reference, the only way to modify an immutable component is via removal
or replacement, which is fully captured by component hooks. To make a
component immutable, simply add `#[component(immutable)]`:
```rust
#[derive(Component)]
#[component(immutable)]
struct Foo {
// ...
}
```
When implementing `Component` manually, there is an associated type
`Mutability` which controls this behavior:
```rust
impl Component for Foo {
type Mutability = Mutable;
// ...
}
```
Note that this means when working with generic components, you may need
to specify that a component is mutable to gain access to certain
methods:
```rust
// Before
fn bar<C: Component>() {
// ...
}
// After
fn bar<C: Component<Mutability = Mutable>>() {
// ...
}
```
With this new tool, creating index components, or caching data on an
entity should be more user friendly, allowing libraries to provide APIs
relying on components and hooks to uphold their invariants.
## Notes
- ~~I've done my best to implement this feature, but I'm not happy with
how reflection has turned out. If any reflection SMEs know a way to
improve this situation I'd greatly appreciate it.~~ There is an
outstanding issue around the fallibility of mutable methods on
`ReflectComponent`, but the DX is largely unchanged from `main` now.
- I've attempted to prevent all safe mutable access to a component that
does not implement `Component<Mutability = Mutable>`, but there may
still be some methods I have missed. Please indicate so and I will
address them, as they are bugs.
- Unsafe is an escape hatch I am _not_ attempting to prevent. Whatever
you do with unsafe is between you and your compiler.
- I am marking this PR as ready, but I suspect it will undergo fairly
major revisions based on SME feedback.
- I've marked this PR as _Uncontroversial_ based on the feature, not the
implementation.
---------
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Benjamin Brienen <benjamin.brienen@outlook.com>
Co-authored-by: Gino Valente <49806985+MrGVSV@users.noreply.github.com>
Co-authored-by: Nuutti Kotivuori <naked@iki.fi>
# Objective
Make documentation of a component's required components more visible by
moving it to the type's docs
## Solution
Change `#[require]` from a derive macro helper to an attribute macro.
Disadvantages:
- this silences any unused code warnings on the component, as it is used
by the macro!
- need to import `require` if not using the ecs prelude (I have not
included this in the migration guilde as Rust tooling already suggests
the fix)
---
## Showcase

---------
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: JMS55 <47158642+JMS55@users.noreply.github.com>
This patch adds the infrastructure necessary for Bevy to support
*bindless resources*, by adding a new `#[bindless]` attribute to
`AsBindGroup`.
Classically, only a single texture (or sampler, or buffer) can be
attached to each shader binding. This means that switching materials
requires breaking a batch and issuing a new drawcall, even if the mesh
is otherwise identical. This adds significant overhead not only in the
driver but also in `wgpu`, as switching bind groups increases the amount
of validation work that `wgpu` must do.
*Bindless resources* are the typical solution to this problem. Instead
of switching bindings between each texture, the renderer instead
supplies a large *array* of all textures in the scene up front, and the
material contains an index into that array. This pattern is repeated for
buffers and samplers as well. The renderer now no longer needs to switch
binding descriptor sets while drawing the scene.
Unfortunately, as things currently stand, this approach won't quite work
for Bevy. Two aspects of `wgpu` conspire to make this ideal approach
unacceptably slow:
1. In the DX12 backend, all binding arrays (bindless resources) must
have a constant size declared in the shader, and all textures in an
array must be bound to actual textures. Changing the size requires a
recompile.
2. Changing even one texture incurs revalidation of all textures, a
process that takes time that's linear in the total size of the binding
array.
This means that declaring a large array of textures big enough to
encompass the entire scene is presently unacceptably slow. For example,
if you declare 4096 textures, then `wgpu` will have to revalidate all
4096 textures if even a single one changes. This process can take
multiple frames.
To work around this problem, this PR groups bindless resources into
small *slabs* and maintains a free list for each. The size of each slab
for the bindless arrays associated with a material is specified via the
`#[bindless(N)]` attribute. For instance, consider the following
declaration:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
#[bindless(16)]
struct MyMaterial {
#[buffer(0)]
color: Vec4,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
diffuse: Handle<Image>,
}
```
The `#[bindless(N)]` attribute specifies that, if bindless arrays are
supported on the current platform, each resource becomes a binding array
of N instances of that resource. So, for `MyMaterial` above, the `color`
attribute is exposed to the shader as `binding_array<vec4<f32>, 16>`,
the `diffuse` texture is exposed to the shader as
`binding_array<texture_2d<f32>, 16>`, and the `diffuse` sampler is
exposed to the shader as `binding_array<sampler, 16>`. Inside the
material's vertex and fragment shaders, the applicable index is
available via the `material_bind_group_slot` field of the `Mesh`
structure. So, for instance, you can access the current color like so:
```wgsl
// `uniform` binding arrays are a non-sequitur, so `uniform` is automatically promoted
// to `storage` in bindless mode.
@group(2) @binding(0) var<storage> material_color: binding_array<Color, 4>;
...
@fragment
fn fragment(in: VertexOutput) -> @location(0) vec4<f32> {
let color = material_color[mesh[in.instance_index].material_bind_group_slot];
...
}
```
Note that portable shader code can't guarantee that the current platform
supports bindless textures. Indeed, bindless mode is only available in
Vulkan and DX12. The `BINDLESS` shader definition is available for your
use to determine whether you're on a bindless platform or not. Thus a
portable version of the shader above would look like:
```wgsl
#ifdef BINDLESS
@group(2) @binding(0) var<storage> material_color: binding_array<Color, 4>;
#else // BINDLESS
@group(2) @binding(0) var<uniform> material_color: Color;
#endif // BINDLESS
...
@fragment
fn fragment(in: VertexOutput) -> @location(0) vec4<f32> {
#ifdef BINDLESS
let color = material_color[mesh[in.instance_index].material_bind_group_slot];
#else // BINDLESS
let color = material_color;
#endif // BINDLESS
...
}
```
Importantly, this PR *doesn't* update `StandardMaterial` to be bindless.
So, for example, `scene_viewer` will currently not run any faster. I
intend to update `StandardMaterial` to use bindless mode in a follow-up
patch.
A new example, `shaders/shader_material_bindless`, has been added to
demonstrate how to use this new feature.
Here's a Tracy profile of `submit_graph_commands` of this patch and an
additional patch (not submitted yet) that makes `StandardMaterial` use
bindless. Red is those patches; yellow is `main`. The scene was Bistro
Exterior with a hack that forces all textures to opaque. You can see a
1.47x mean speedup.

## Migration Guide
* `RenderAssets::prepare_asset` now takes an `AssetId` parameter.
* Bin keys now have Bevy-specific material bind group indices instead of
`wgpu` material bind group IDs, as part of the bindless change. Use the
new `MaterialBindGroupAllocator` to map from bind group index to bind
group ID.
# Objective
Fixes#15941
## Solution
Created https://crates.io/crates/variadics_please and moved the code
there; updating references
`bevy_utils/macros` is deleted.
## Testing
cargo check
## Migration Guide
Use `variadics_please::{all_tuples, all_tuples_with_size}` instead of
`bevy::utils::{all_tuples, all_tuples_with_size}`.
# Objective
- Fixes: #15663
## Solution
- Add an `is_forward_plane` method to `Aabb`, and a `contains_aabb`
method to `Frustum`.
## Test
- I have created a frustum with an offset along with three unit tests to
evaluate the `contains_aabb` algorithm.
## Explanation for the Test Cases
- To facilitate the code review, I will explain how the frustum is
created. Initially, we create a frustum without any offset and then
create a cuboid that is just contained within it.
<img width="714" alt="image"
src="https://github.com/user-attachments/assets/a9ac53a2-f8a3-4e09-b20b-4ee71b27a099">
- Secondly, we move the cuboid by 2 units along both the x-axis and the
y-axis to make it more general.
## Reference
- [Frustum
Culling](https://learnopengl.com/Guest-Articles/2021/Scene/Frustum-Culling#)
- [AABB Plane
intersection](https://gdbooks.gitbooks.io/3dcollisions/content/Chapter2/static_aabb_plane.html)
---------
Co-authored-by: IQuick 143 <IQuick143cz@gmail.com>
# Objective
- Fixes#16363
- Ensure that someone using minimum version doesn't get the bugs that
were fixed in the 23.0.1 patch
## Solution
- Use wgpu 23.0.1
# Objective
- Refactor
## Solution
- Refactor
## Testing
- Ran 3d_scene
---
## Migration Guide
`RenderCreation::Manual` variant fields are now wrapped in a struct
called `RenderResources`