# Objective Currently, Bevy only supports rendering to the current "surface texture format". This means that "render to texture" scenarios must use the exact format the primary window's surface uses, or Bevy will crash. This is even harder than it used to be now that we detect preferred surface formats at runtime instead of using hard coded BevyDefault values. ## Solution 1. Look up and store each window surface's texture format alongside other extracted window information 2. Specialize the upscaling pass on the current `RenderTarget`'s texture format, now that we can cheaply correlate render targets to their current texture format 3. Remove the old `SurfaceTextureFormat` and `AvailableTextureFormats`: these are now redundant with the information stored on each extracted window, and probably should not have been globals in the first place (as in theory each surface could have a different format). This means you can now use any texture format you want when rendering to a texture! For example, changing the `render_to_texture` example to use `R16Float` now doesn't crash / properly only stores the red component: 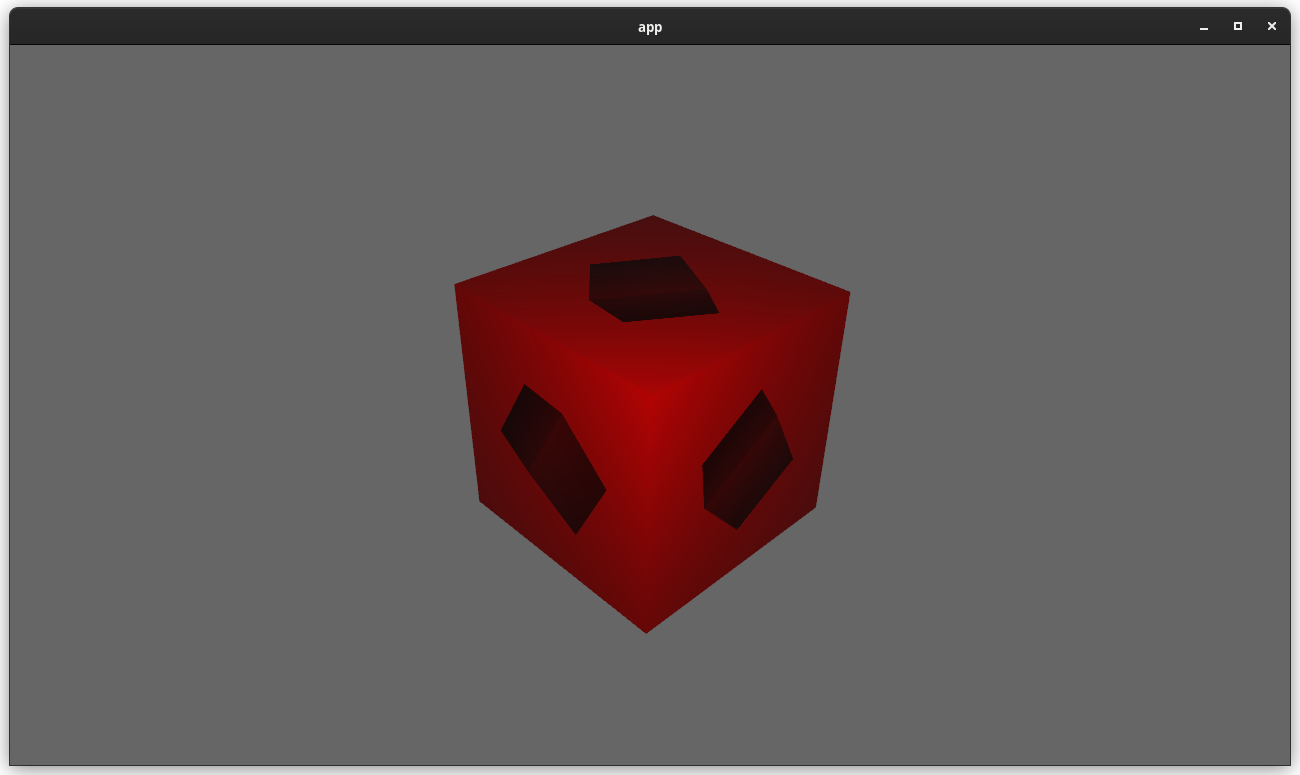
517 lines
20 KiB
Rust
517 lines
20 KiB
Rust
use crate::{
|
|
camera::CameraProjection,
|
|
prelude::Image,
|
|
render_asset::RenderAssets,
|
|
render_resource::TextureView,
|
|
view::{ExtractedView, ExtractedWindows, VisibleEntities},
|
|
Extract,
|
|
};
|
|
use bevy_asset::{AssetEvent, Assets, Handle};
|
|
use bevy_derive::{Deref, DerefMut};
|
|
use bevy_ecs::{
|
|
change_detection::DetectChanges,
|
|
component::Component,
|
|
entity::Entity,
|
|
event::EventReader,
|
|
query::Added,
|
|
reflect::ReflectComponent,
|
|
system::{Commands, ParamSet, Query, Res},
|
|
};
|
|
use bevy_math::{Mat4, Ray, UVec2, UVec4, Vec2, Vec3};
|
|
use bevy_reflect::prelude::*;
|
|
use bevy_reflect::FromReflect;
|
|
use bevy_transform::components::GlobalTransform;
|
|
use bevy_utils::HashSet;
|
|
use bevy_window::{WindowCreated, WindowId, WindowResized, Windows};
|
|
use std::{borrow::Cow, ops::Range};
|
|
use wgpu::{Extent3d, TextureFormat};
|
|
|
|
/// Render viewport configuration for the [`Camera`] component.
|
|
///
|
|
/// The viewport defines the area on the render target to which the camera renders its image.
|
|
/// You can overlay multiple cameras in a single window using viewports to create effects like
|
|
/// split screen, minimaps, and character viewers.
|
|
#[derive(Reflect, FromReflect, Debug, Clone)]
|
|
#[reflect(Default)]
|
|
pub struct Viewport {
|
|
/// The physical position to render this viewport to within the [`RenderTarget`] of this [`Camera`].
|
|
/// (0,0) corresponds to the top-left corner
|
|
pub physical_position: UVec2,
|
|
/// The physical size of the viewport rectangle to render to within the [`RenderTarget`] of this [`Camera`].
|
|
/// The origin of the rectangle is in the top-left corner.
|
|
pub physical_size: UVec2,
|
|
/// The minimum and maximum depth to render (on a scale from 0.0 to 1.0).
|
|
pub depth: Range<f32>,
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
impl Default for Viewport {
|
|
fn default() -> Self {
|
|
Self {
|
|
physical_position: Default::default(),
|
|
physical_size: Default::default(),
|
|
depth: 0.0..1.0,
|
|
}
|
|
}
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
/// Information about the current [`RenderTarget`].
|
|
#[derive(Default, Debug, Clone)]
|
|
pub struct RenderTargetInfo {
|
|
/// The physical size of this render target (ignores scale factor).
|
|
pub physical_size: UVec2,
|
|
/// The scale factor of this render target.
|
|
pub scale_factor: f64,
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
/// Holds internally computed [`Camera`] values.
|
|
#[derive(Default, Debug, Clone)]
|
|
pub struct ComputedCameraValues {
|
|
projection_matrix: Mat4,
|
|
target_info: Option<RenderTargetInfo>,
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
/// The defining component for camera entities, storing information about how and what to render
|
|
/// through this camera.
|
|
///
|
|
/// The [`Camera`] component is added to an entity to define the properties of the viewpoint from
|
|
/// which rendering occurs. It defines the position of the view to render, the projection method
|
|
/// to transform the 3D objects into a 2D image, as well as the render target into which that image
|
|
/// is produced.
|
|
///
|
|
/// Adding a camera is typically done by adding a bundle, either the `Camera2dBundle` or the
|
|
/// `Camera3dBundle`.
|
|
#[derive(Component, Debug, Reflect, FromReflect, Clone)]
|
|
#[reflect(Component)]
|
|
pub struct Camera {
|
|
/// If set, this camera will render to the given [`Viewport`] rectangle within the configured [`RenderTarget`].
|
|
pub viewport: Option<Viewport>,
|
|
/// Cameras with a lower priority will be rendered before cameras with a higher priority.
|
|
pub priority: isize,
|
|
/// If this is set to `true`, this camera will be rendered to its specified [`RenderTarget`]. If `false`, this
|
|
/// camera will not be rendered.
|
|
pub is_active: bool,
|
|
/// Computed values for this camera, such as the projection matrix and the render target size.
|
|
#[reflect(ignore)]
|
|
pub computed: ComputedCameraValues,
|
|
/// The "target" that this camera will render to.
|
|
#[reflect(ignore)]
|
|
pub target: RenderTarget,
|
|
/// If this is set to `true`, the camera will use an intermediate "high dynamic range" render texture.
|
|
/// Warning: we are still working on this feature. If MSAA is enabled, there will be artifacts in
|
|
/// some cases. When rendering with WebGL, this will crash if MSAA is enabled.
|
|
/// See <https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/3425> for details.
|
|
// TODO: resolve the issues mentioned in the doc comment above, then remove the warning.
|
|
pub hdr: bool,
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
impl Default for Camera {
|
|
fn default() -> Self {
|
|
Self {
|
|
is_active: true,
|
|
priority: 0,
|
|
viewport: None,
|
|
computed: Default::default(),
|
|
target: Default::default(),
|
|
hdr: false,
|
|
}
|
|
}
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
impl Camera {
|
|
/// Converts a physical size in this `Camera` to a logical size.
|
|
#[inline]
|
|
pub fn to_logical(&self, physical_size: UVec2) -> Option<Vec2> {
|
|
let scale = self.computed.target_info.as_ref()?.scale_factor;
|
|
Some((physical_size.as_dvec2() / scale).as_vec2())
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
/// The rendered physical bounds (minimum, maximum) of the camera. If the `viewport` field is
|
|
/// set to [`Some`], this will be the rect of that custom viewport. Otherwise it will default to
|
|
/// the full physical rect of the current [`RenderTarget`].
|
|
#[inline]
|
|
pub fn physical_viewport_rect(&self) -> Option<(UVec2, UVec2)> {
|
|
let min = self
|
|
.viewport
|
|
.as_ref()
|
|
.map(|v| v.physical_position)
|
|
.unwrap_or(UVec2::ZERO);
|
|
let max = min + self.physical_viewport_size()?;
|
|
Some((min, max))
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
/// The rendered logical bounds (minimum, maximum) of the camera. If the `viewport` field is set
|
|
/// to [`Some`], this will be the rect of that custom viewport. Otherwise it will default to the
|
|
/// full logical rect of the current [`RenderTarget`].
|
|
#[inline]
|
|
pub fn logical_viewport_rect(&self) -> Option<(Vec2, Vec2)> {
|
|
let (min, max) = self.physical_viewport_rect()?;
|
|
Some((self.to_logical(min)?, self.to_logical(max)?))
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
/// The logical size of this camera's viewport. If the `viewport` field is set to [`Some`], this
|
|
/// will be the size of that custom viewport. Otherwise it will default to the full logical size
|
|
/// of the current [`RenderTarget`].
|
|
/// For logic that requires the full logical size of the
|
|
/// [`RenderTarget`], prefer [`Camera::logical_target_size`].
|
|
#[inline]
|
|
pub fn logical_viewport_size(&self) -> Option<Vec2> {
|
|
self.viewport
|
|
.as_ref()
|
|
.and_then(|v| self.to_logical(v.physical_size))
|
|
.or_else(|| self.logical_target_size())
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
/// The physical size of this camera's viewport. If the `viewport` field is set to [`Some`], this
|
|
/// will be the size of that custom viewport. Otherwise it will default to the full physical size of
|
|
/// the current [`RenderTarget`].
|
|
/// For logic that requires the full physical size of the [`RenderTarget`], prefer [`Camera::physical_target_size`].
|
|
#[inline]
|
|
pub fn physical_viewport_size(&self) -> Option<UVec2> {
|
|
self.viewport
|
|
.as_ref()
|
|
.map(|v| v.physical_size)
|
|
.or_else(|| self.physical_target_size())
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
/// The full logical size of this camera's [`RenderTarget`], ignoring custom `viewport` configuration.
|
|
/// Note that if the `viewport` field is [`Some`], this will not represent the size of the rendered area.
|
|
/// For logic that requires the size of the actually rendered area, prefer [`Camera::logical_viewport_size`].
|
|
#[inline]
|
|
pub fn logical_target_size(&self) -> Option<Vec2> {
|
|
self.computed
|
|
.target_info
|
|
.as_ref()
|
|
.and_then(|t| self.to_logical(t.physical_size))
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
/// The full physical size of this camera's [`RenderTarget`], ignoring custom `viewport` configuration.
|
|
/// Note that if the `viewport` field is [`Some`], this will not represent the size of the rendered area.
|
|
/// For logic that requires the size of the actually rendered area, prefer [`Camera::physical_viewport_size`].
|
|
#[inline]
|
|
pub fn physical_target_size(&self) -> Option<UVec2> {
|
|
self.computed.target_info.as_ref().map(|t| t.physical_size)
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
/// The projection matrix computed using this camera's [`CameraProjection`].
|
|
#[inline]
|
|
pub fn projection_matrix(&self) -> Mat4 {
|
|
self.computed.projection_matrix
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
/// Given a position in world space, use the camera to compute the viewport-space coordinates.
|
|
///
|
|
/// To get the coordinates in Normalized Device Coordinates, you should use
|
|
/// [`world_to_ndc`](Self::world_to_ndc).
|
|
#[doc(alias = "world_to_screen")]
|
|
pub fn world_to_viewport(
|
|
&self,
|
|
camera_transform: &GlobalTransform,
|
|
world_position: Vec3,
|
|
) -> Option<Vec2> {
|
|
let target_size = self.logical_viewport_size()?;
|
|
let ndc_space_coords = self.world_to_ndc(camera_transform, world_position)?;
|
|
// NDC z-values outside of 0 < z < 1 are outside the camera frustum and are thus not in viewport-space
|
|
if ndc_space_coords.z < 0.0 || ndc_space_coords.z > 1.0 {
|
|
return None;
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
// Once in NDC space, we can discard the z element and rescale x/y to fit the screen
|
|
Some((ndc_space_coords.truncate() + Vec2::ONE) / 2.0 * target_size)
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
/// Returns a ray originating from the camera, that passes through everything beyond `viewport_position`.
|
|
///
|
|
/// The resulting ray starts on the near plane of the camera.
|
|
///
|
|
/// If the camera's projection is orthographic the direction of the ray is always equal to `camera_transform.forward()`.
|
|
///
|
|
/// To get the world space coordinates with Normalized Device Coordinates, you should use
|
|
/// [`ndc_to_world`](Self::ndc_to_world).
|
|
pub fn viewport_to_world(
|
|
&self,
|
|
camera_transform: &GlobalTransform,
|
|
viewport_position: Vec2,
|
|
) -> Option<Ray> {
|
|
let target_size = self.logical_viewport_size()?;
|
|
let ndc = viewport_position * 2. / target_size - Vec2::ONE;
|
|
|
|
let world_near_plane = self.ndc_to_world(camera_transform, ndc.extend(1.))?;
|
|
// Using EPSILON because passing an ndc with Z = 0 returns NaNs.
|
|
let world_far_plane = self.ndc_to_world(camera_transform, ndc.extend(f32::EPSILON))?;
|
|
|
|
Some(Ray {
|
|
origin: world_near_plane,
|
|
direction: (world_far_plane - world_near_plane).normalize(),
|
|
})
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
/// Given a position in world space, use the camera's viewport to compute the Normalized Device Coordinates.
|
|
///
|
|
/// When the position is within the viewport the values returned will be between -1.0 and 1.0 on the X and Y axes,
|
|
/// and between 0.0 and 1.0 on the Z axis.
|
|
/// To get the coordinates in the render target's viewport dimensions, you should use
|
|
/// [`world_to_viewport`](Self::world_to_viewport).
|
|
pub fn world_to_ndc(
|
|
&self,
|
|
camera_transform: &GlobalTransform,
|
|
world_position: Vec3,
|
|
) -> Option<Vec3> {
|
|
// Build a transformation matrix to convert from world space to NDC using camera data
|
|
let world_to_ndc: Mat4 =
|
|
self.computed.projection_matrix * camera_transform.compute_matrix().inverse();
|
|
let ndc_space_coords: Vec3 = world_to_ndc.project_point3(world_position);
|
|
|
|
(!ndc_space_coords.is_nan()).then_some(ndc_space_coords)
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
/// Given a position in Normalized Device Coordinates,
|
|
/// use the camera's viewport to compute the world space position.
|
|
///
|
|
/// When the position is within the viewport the values returned will be between -1.0 and 1.0 on the X and Y axes,
|
|
/// and between 0.0 and 1.0 on the Z axis.
|
|
/// To get the world space coordinates with the viewport position, you should use
|
|
/// [`world_to_viewport`](Self::world_to_viewport).
|
|
pub fn ndc_to_world(&self, camera_transform: &GlobalTransform, ndc: Vec3) -> Option<Vec3> {
|
|
// Build a transformation matrix to convert from NDC to world space using camera data
|
|
let ndc_to_world =
|
|
camera_transform.compute_matrix() * self.computed.projection_matrix.inverse();
|
|
|
|
let world_space_coords = ndc_to_world.project_point3(ndc);
|
|
|
|
(!world_space_coords.is_nan()).then_some(world_space_coords)
|
|
}
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
/// Configures the [`RenderGraph`](crate::render_graph::RenderGraph) name assigned to be run for a given [`Camera`] entity.
|
|
#[derive(Component, Deref, DerefMut, Reflect, Default)]
|
|
#[reflect(Component)]
|
|
pub struct CameraRenderGraph(Cow<'static, str>);
|
|
|
|
impl CameraRenderGraph {
|
|
#[inline]
|
|
pub fn new<T: Into<Cow<'static, str>>>(name: T) -> Self {
|
|
Self(name.into())
|
|
}
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
/// The "target" that a [`Camera`] will render to. For example, this could be a [`Window`](bevy_window::Window)
|
|
/// swapchain or an [`Image`].
|
|
#[derive(Debug, Clone, Reflect, PartialEq, Eq, Hash, PartialOrd, Ord)]
|
|
pub enum RenderTarget {
|
|
/// Window to which the camera's view is rendered.
|
|
Window(WindowId),
|
|
/// Image to which the camera's view is rendered.
|
|
Image(Handle<Image>),
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
impl Default for RenderTarget {
|
|
fn default() -> Self {
|
|
Self::Window(Default::default())
|
|
}
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
impl RenderTarget {
|
|
pub fn get_texture_view<'a>(
|
|
&self,
|
|
windows: &'a ExtractedWindows,
|
|
images: &'a RenderAssets<Image>,
|
|
) -> Option<&'a TextureView> {
|
|
match self {
|
|
RenderTarget::Window(window_id) => windows
|
|
.get(window_id)
|
|
.and_then(|window| window.swap_chain_texture.as_ref()),
|
|
RenderTarget::Image(image_handle) => {
|
|
images.get(image_handle).map(|image| &image.texture_view)
|
|
}
|
|
}
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
/// Retrieves the [`TextureFormat`] of this render target, if it exists.
|
|
pub fn get_texture_format<'a>(
|
|
&self,
|
|
windows: &'a ExtractedWindows,
|
|
images: &'a RenderAssets<Image>,
|
|
) -> Option<TextureFormat> {
|
|
match self {
|
|
RenderTarget::Window(window_id) => windows
|
|
.get(window_id)
|
|
.and_then(|window| window.swap_chain_texture_format),
|
|
RenderTarget::Image(image_handle) => {
|
|
images.get(image_handle).map(|image| image.texture_format)
|
|
}
|
|
}
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
pub fn get_render_target_info(
|
|
&self,
|
|
windows: &Windows,
|
|
images: &Assets<Image>,
|
|
) -> Option<RenderTargetInfo> {
|
|
Some(match self {
|
|
RenderTarget::Window(window_id) => {
|
|
let window = windows.get(*window_id)?;
|
|
RenderTargetInfo {
|
|
physical_size: UVec2::new(window.physical_width(), window.physical_height()),
|
|
scale_factor: window.scale_factor(),
|
|
}
|
|
}
|
|
RenderTarget::Image(image_handle) => {
|
|
let image = images.get(image_handle)?;
|
|
let Extent3d { width, height, .. } = image.texture_descriptor.size;
|
|
RenderTargetInfo {
|
|
physical_size: UVec2::new(width, height),
|
|
scale_factor: 1.0,
|
|
}
|
|
}
|
|
})
|
|
}
|
|
// Check if this render target is contained in the given changed windows or images.
|
|
fn is_changed(
|
|
&self,
|
|
changed_window_ids: &[WindowId],
|
|
changed_image_handles: &HashSet<&Handle<Image>>,
|
|
) -> bool {
|
|
match self {
|
|
RenderTarget::Window(window_id) => changed_window_ids.contains(window_id),
|
|
RenderTarget::Image(image_handle) => changed_image_handles.contains(&image_handle),
|
|
}
|
|
}
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
/// System in charge of updating a [`Camera`] when its window or projection changes.
|
|
///
|
|
/// The system detects window creation and resize events to update the camera projection if
|
|
/// needed. It also queries any [`CameraProjection`] component associated with the same entity
|
|
/// as the [`Camera`] one, to automatically update the camera projection matrix.
|
|
///
|
|
/// The system function is generic over the camera projection type, and only instances of
|
|
/// [`OrthographicProjection`] and [`PerspectiveProjection`] are automatically added to
|
|
/// the app, as well as the runtime-selected [`Projection`]. The system runs during the
|
|
/// [`CoreStage::PostUpdate`] stage.
|
|
///
|
|
/// [`OrthographicProjection`]: crate::camera::OrthographicProjection
|
|
/// [`PerspectiveProjection`]: crate::camera::PerspectiveProjection
|
|
/// [`Projection`]: crate::camera::Projection
|
|
/// [`CoreStage::PostUpdate`]: bevy_app::CoreStage::PostUpdate
|
|
pub fn camera_system<T: CameraProjection + Component>(
|
|
mut window_resized_events: EventReader<WindowResized>,
|
|
mut window_created_events: EventReader<WindowCreated>,
|
|
mut image_asset_events: EventReader<AssetEvent<Image>>,
|
|
windows: Res<Windows>,
|
|
images: Res<Assets<Image>>,
|
|
mut queries: ParamSet<(
|
|
Query<(Entity, &mut Camera, &mut T)>,
|
|
Query<Entity, Added<Camera>>,
|
|
)>,
|
|
) {
|
|
let mut changed_window_ids = Vec::new();
|
|
|
|
// Collect all unique window IDs of changed windows by inspecting created windows
|
|
for event in window_created_events.iter() {
|
|
if changed_window_ids.contains(&event.id) {
|
|
continue;
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
changed_window_ids.push(event.id);
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
// Collect all unique window IDs of changed windows by inspecting resized windows
|
|
for event in window_resized_events.iter() {
|
|
if changed_window_ids.contains(&event.id) {
|
|
continue;
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
changed_window_ids.push(event.id);
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
let changed_image_handles: HashSet<&Handle<Image>> = image_asset_events
|
|
.iter()
|
|
.filter_map(|event| {
|
|
if let AssetEvent::Modified { handle } = event {
|
|
Some(handle)
|
|
} else {
|
|
None
|
|
}
|
|
})
|
|
.collect();
|
|
|
|
let mut added_cameras = vec![];
|
|
for entity in &queries.p1() {
|
|
added_cameras.push(entity);
|
|
}
|
|
for (entity, mut camera, mut camera_projection) in &mut queries.p0() {
|
|
if camera
|
|
.target
|
|
.is_changed(&changed_window_ids, &changed_image_handles)
|
|
|| added_cameras.contains(&entity)
|
|
|| camera_projection.is_changed()
|
|
{
|
|
camera.computed.target_info = camera.target.get_render_target_info(&windows, &images);
|
|
if let Some(size) = camera.logical_viewport_size() {
|
|
camera_projection.update(size.x, size.y);
|
|
camera.computed.projection_matrix = camera_projection.get_projection_matrix();
|
|
}
|
|
}
|
|
}
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
#[derive(Component, Debug)]
|
|
pub struct ExtractedCamera {
|
|
pub target: RenderTarget,
|
|
pub physical_viewport_size: Option<UVec2>,
|
|
pub physical_target_size: Option<UVec2>,
|
|
pub viewport: Option<Viewport>,
|
|
pub render_graph: Cow<'static, str>,
|
|
pub priority: isize,
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
pub fn extract_cameras(
|
|
mut commands: Commands,
|
|
query: Extract<
|
|
Query<(
|
|
Entity,
|
|
&Camera,
|
|
&CameraRenderGraph,
|
|
&GlobalTransform,
|
|
&VisibleEntities,
|
|
)>,
|
|
>,
|
|
) {
|
|
for (entity, camera, camera_render_graph, transform, visible_entities) in query.iter() {
|
|
if !camera.is_active {
|
|
continue;
|
|
}
|
|
if let (Some((viewport_origin, _)), Some(viewport_size), Some(target_size)) = (
|
|
camera.physical_viewport_rect(),
|
|
camera.physical_viewport_size(),
|
|
camera.physical_target_size(),
|
|
) {
|
|
if target_size.x == 0 || target_size.y == 0 {
|
|
continue;
|
|
}
|
|
commands.get_or_spawn(entity).insert((
|
|
ExtractedCamera {
|
|
target: camera.target.clone(),
|
|
viewport: camera.viewport.clone(),
|
|
physical_viewport_size: Some(viewport_size),
|
|
physical_target_size: Some(target_size),
|
|
render_graph: camera_render_graph.0.clone(),
|
|
priority: camera.priority,
|
|
},
|
|
ExtractedView {
|
|
projection: camera.projection_matrix(),
|
|
transform: *transform,
|
|
hdr: camera.hdr,
|
|
viewport: UVec4::new(
|
|
viewport_origin.x,
|
|
viewport_origin.y,
|
|
viewport_size.x,
|
|
viewport_size.y,
|
|
),
|
|
},
|
|
visible_entities.clone(),
|
|
));
|
|
}
|
|
}
|
|
}
|