Didn't remove WgpuWrapper. Not sure if it's needed or not still.
## Testing
- Did you test these changes? If so, how? Example runner
- Are there any parts that need more testing? Web (portable atomics
thingy?), DXC.
## Migration Guide
- Bevy has upgraded to [wgpu
v24](https://github.com/gfx-rs/wgpu/blob/trunk/CHANGELOG.md#v2400-2025-01-15).
- When using the DirectX 12 rendering backend, the new priority system
for choosing a shader compiler is as follows:
- If the `WGPU_DX12_COMPILER` environment variable is set at runtime, it
is used
- Else if the new `statically-linked-dxc` feature is enabled, a custom
version of DXC will be statically linked into your app at compile time.
- Else Bevy will look in the app's working directory for
`dxcompiler.dll` and `dxil.dll` at runtime.
- Else if they are missing, Bevy will fall back to FXC (not recommended)
---------
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: IceSentry <c.giguere42@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: François Mockers <francois.mockers@vleue.com>
# Objective
The entity disabling / default query filter work added in #17514 and
#13120 is neat, but we don't teach users how it works!
We should fix that before 0.16.
## Solution
Write a simple example to teach the basics of entity disabling!
## Testing
`cargo run --example entity_disabling`
## Showcase

---------
Co-authored-by: Zachary Harrold <zac@harrold.com.au>
PR #17684 broke occlusion culling because it neglected to set the
indirect parameter offsets for the late mesh preprocessing stage if the
work item buffers were already set. This PR moves the update of those
values to a new function, `init_work_item_buffers`, which is
unconditionally called for every phase every frame.
Note that there's some complexity in order to handle the case in which
occlusion culling was enabled on one frame and disabled on the next, or
vice versa. This was necessary in order to make the occlusion culling
toggle in the `occlusion_culling` example work again.
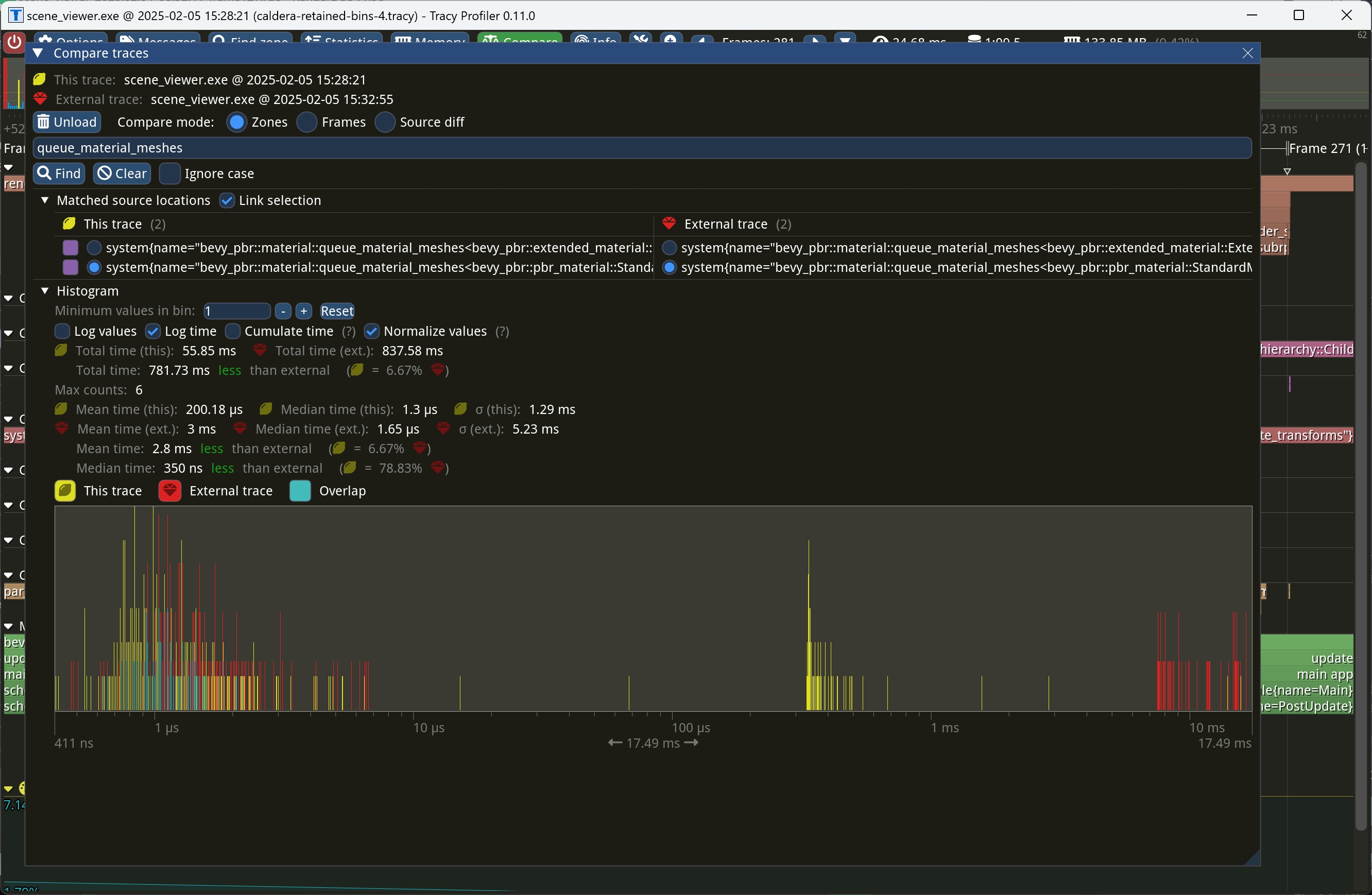
This PR makes Bevy keep entities in bins from frame to frame if they
haven't changed. This reduces the time spent in `queue_material_meshes`
and related functions to near zero for static geometry. This patch uses
the same change tick technique that #17567 uses to detect when meshes
have changed in such a way as to require re-binning.
In order to quickly find the relevant bin for an entity when that entity
has changed, we introduce a new type of cache, the *bin key cache*. This
cache stores a mapping from main world entity ID to cached bin key, as
well as the tick of the most recent change to the entity. As we iterate
through the visible entities in `queue_material_meshes`, we check the
cache to see whether the entity needs to be re-binned. If it doesn't,
then we mark it as clean in the `valid_cached_entity_bin_keys` bit set.
If it does, then we insert it into the correct bin, and then mark the
entity as clean. At the end, all entities not marked as clean are
removed from the bins.
This patch has a dramatic effect on the rendering performance of most
benchmarks, as it effectively eliminates `queue_material_meshes` from
the profile. Note, however, that it generally simultaneously regresses
`batch_and_prepare_binned_render_phase` by a bit (not by enough to
outweigh the win, however). I believe that's because, before this patch,
`queue_material_meshes` put the bins in the CPU cache for
`batch_and_prepare_binned_render_phase` to use, while with this patch,
`batch_and_prepare_binned_render_phase` must load the bins into the CPU
cache itself.
On Caldera, this reduces the time spent in `queue_material_meshes` from
5+ ms to 0.2ms-0.3ms. Note that benchmarking on that scene is very noisy
right now because of https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/17535.
# Objective
After #17461, the ease function labels in this example are a bit
cramped, especially in the bottom row.
This adjusts the spacing slightly and centers the labels.
## Solution
- The label is now a child of the plot and they are drawn around the
center of the transform
- Plot size and extents are now constants, and this thing has been
banished:
```rust
i as f32 * 95.0 - 1280.0 / 2.0 + 25.0,
-100.0 - ((j as f32 * 250.0) - 300.0),
0.0,
```
- There's room for expansion in another row, so make that easier by
doing the chunking by row
- Other misc tidying of variable names, sprinkled in a few comments,
etc.
## Before
<img width="1280" alt="Screenshot 2025-02-08 at 7 33 14 AM"
src="https://github.com/user-attachments/assets/0b79c619-d295-4ab1-8cd1-d23c862d06c5"
/>
## After
<img width="1280" alt="Screenshot 2025-02-08 at 7 32 45 AM"
src="https://github.com/user-attachments/assets/656ef695-9aa8-42e9-b867-1718294316bd"
/>
# Objective
The docs of `EaseFunction` don't visualize the different functions,
requiring you to check out the Bevy repo and running the
`easing_function` example.
## Solution
- Add tool to generate suitable svg graphs. This only needs to be re-run
when adding new ease functions.
- works with all themes
- also add missing easing functions to example.
---
## Showcase

---------
Co-authored-by: François Mockers <mockersf@gmail.com>
Fixes#17535
Bevy's approach to handling "entity mapping" during spawning and cloning
needs some work. The addition of
[Relations](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/17398) both
[introduced a new "duplicate entities" bug when spawning scenes in the
scene system](#17535) and made the weaknesses of the current mapping
system exceedingly clear:
1. Entity mapping requires _a ton_ of boilerplate (implement or derive
VisitEntities and VisitEntitesMut, then register / reflect MapEntities).
Knowing the incantation is challenging and if you forget to do it in
part or in whole, spawning subtly breaks.
2. Entity mapping a spawned component in scenes incurs unnecessary
overhead: look up ReflectMapEntities, create a _brand new temporary
instance_ of the component using FromReflect, map the entities in that
instance, and then apply that on top of the actual component using
reflection. We can do much better.
Additionally, while our new [Entity cloning
system](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/16132) is already pretty
great, it has some areas we can make better:
* It doesn't expose semantic info about the clone (ex: ignore or "clone
empty"), meaning we can't key off of that in places where it would be
useful, such as scene spawning. Rather than duplicating this info across
contexts, I think it makes more sense to add that info to the clone
system, especially given that we'd like to use cloning code in some of
our spawning scenarios.
* EntityCloner is currently built in a way that prioritizes a single
entity clone
* EntityCloner's recursive cloning is built to be done "inside out" in a
parallel context (queue commands that each have a clone of
EntityCloner). By making EntityCloner the orchestrator of the clone we
can remove internal arcs, improve the clarity of the code, make
EntityCloner mutable again, and simplify the builder code.
* EntityCloner does not currently take into account entity mapping. This
is necessary to do true "bullet proof" cloning, would allow us to unify
the per-component scene spawning and cloning UX, and ultimately would
allow us to use EntityCloner in place of raw reflection for scenes like
`Scene(World)` (which would give us a nice performance boost: fewer
archetype moves, less reflection overhead).
## Solution
### Improved Entity Mapping
First, components now have first-class "entity visiting and mapping"
behavior:
```rust
#[derive(Component, Reflect)]
#[reflect(Component)]
struct Inventory {
size: usize,
#[entities]
items: Vec<Entity>,
}
```
Any field with the `#[entities]` annotation will be viewable and
mappable when cloning and spawning scenes.
Compare that to what was required before!
```rust
#[derive(Component, Reflect, VisitEntities, VisitEntitiesMut)]
#[reflect(Component, MapEntities)]
struct Inventory {
#[visit_entities(ignore)]
size: usize,
items: Vec<Entity>,
}
```
Additionally, for relationships `#[entities]` is implied, meaning this
"just works" in scenes and cloning:
```rust
#[derive(Component, Reflect)]
#[relationship(relationship_target = Children)]
#[reflect(Component)]
struct ChildOf(pub Entity);
```
Note that Component _does not_ implement `VisitEntities` directly.
Instead, it has `Component::visit_entities` and
`Component::visit_entities_mut` methods. This is for a few reasons:
1. We cannot implement `VisitEntities for C: Component` because that
would conflict with our impl of VisitEntities for anything that
implements `IntoIterator<Item=Entity>`. Preserving that impl is more
important from a UX perspective.
2. We should not implement `Component: VisitEntities` VisitEntities in
the Component derive, as that would increase the burden of manual
Component trait implementors.
3. Making VisitEntitiesMut directly callable for components would make
it easy to invalidate invariants defined by a component author. By
putting it in the `Component` impl, we can make it harder to call
naturally / unavailable to autocomplete using `fn
visit_entities_mut(this: &mut Self, ...)`.
`ReflectComponent::apply_or_insert` is now
`ReflectComponent::apply_or_insert_mapped`. By moving mapping inside
this impl, we remove the need to go through the reflection system to do
entity mapping, meaning we no longer need to create a clone of the
target component, map the entities in that component, and patch those
values on top. This will make spawning mapped entities _much_ faster
(The default `Component::visit_entities_mut` impl is an inlined empty
function, so it will incur no overhead for unmapped entities).
### The Bug Fix
To solve #17535, spawning code now skips entities with the new
`ComponentCloneBehavior::Ignore` and
`ComponentCloneBehavior::RelationshipTarget` variants (note
RelationshipTarget is a temporary "workaround" variant that allows
scenes to skip these components. This is a temporary workaround that can
be removed as these cases should _really_ be using EntityCloner logic,
which should be done in a followup PR. When that is done,
`ComponentCloneBehavior::RelationshipTarget` can be merged into the
normal `ComponentCloneBehavior::Custom`).
### Improved Cloning
* `Option<ComponentCloneHandler>` has been replaced by
`ComponentCloneBehavior`, which encodes additional intent and context
(ex: `Default`, `Ignore`, `Custom`, `RelationshipTarget` (this last one
is temporary)).
* Global per-world entity cloning configuration has been removed. This
felt overly complicated, increased our API surface, and felt too
generic. Each clone context can have different requirements (ex: what a
user wants in a specific system, what a scene spawner wants, etc). I'd
prefer to see how far context-specific EntityCloners get us first.
* EntityCloner's internals have been reworked to remove Arcs and make it
mutable.
* EntityCloner is now directly stored on EntityClonerBuilder,
simplifying the code somewhat
* EntityCloner's "bundle scratch" pattern has been moved into the new
BundleScratch type, improving its usability and making it usable in
other contexts (such as future cross-world cloning code). Currently this
is still private, but with some higher level safe APIs it could be used
externally for making dynamic bundles
* EntityCloner's recursive cloning behavior has been "externalized". It
is now responsible for orchestrating recursive clones, meaning it no
longer needs to be sharable/clone-able across threads / read-only.
* EntityCloner now does entity mapping during clones, like scenes do.
This gives behavior parity and also makes it more generically useful.
* `RelatonshipTarget::RECURSIVE_SPAWN` is now
`RelationshipTarget::LINKED_SPAWN`, and this field is used when cloning
relationship targets to determine if cloning should happen recursively.
The new `LINKED_SPAWN` term was picked to make it more generically
applicable across spawning and cloning scenarios.
## Next Steps
* I think we should adapt EntityCloner to support cross world cloning. I
think this PR helps set the stage for that by making the internals
slightly more generalized. We could have a CrossWorldEntityCloner that
reuses a lot of this infrastructure.
* Once we support cross world cloning, we should use EntityCloner to
spawn `Scene(World)` scenes. This would yield significant performance
benefits (no archetype moves, less reflection overhead).
---------
Co-authored-by: eugineerd <70062110+eugineerd@users.noreply.github.com>
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
# Objective
- Make use of the new `weak_handle!` macro added in
https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/17384
## Solution
- Migrate bevy from `Handle::weak_from_u128` to the new `weak_handle!`
macro that takes a random UUID
- Deprecate `Handle::weak_from_u128`, since there are no remaining use
cases that can't also be addressed by constructing the type manually
## Testing
- `cargo run -p ci -- test`
---
## Migration Guide
Replace `Handle::weak_from_u128` with `weak_handle!` and a random UUID.
# Objective
- Fixes#17411
## Solution
- Deprecated `Component::register_component_hooks`
- Added individual methods for each hook which return `None` if the hook
is unused.
## Testing
- CI
---
## Migration Guide
`Component::register_component_hooks` is now deprecated and will be
removed in a future release. When implementing `Component` manually,
also implement the respective hook methods on `Component`.
```rust
// Before
impl Component for Foo {
// snip
fn register_component_hooks(hooks: &mut ComponentHooks) {
hooks.on_add(foo_on_add);
}
}
// After
impl Component for Foo {
// snip
fn on_add() -> Option<ComponentHook> {
Some(foo_on_add)
}
}
```
## Notes
I've chosen to deprecate `Component::register_component_hooks` rather
than outright remove it to ease the migration guide. While it is in a
state of deprecation, it must be used by
`Components::register_component_internal` to ensure users who haven't
migrated to the new hook definition scheme aren't left behind. For users
of the new scheme, a default implementation of
`Component::register_component_hooks` is provided which forwards the new
individual hook implementations.
Personally, I think this is a cleaner API to work with, and would allow
the documentation for hooks to exist on the respective `Component`
methods (e.g., documentation for `OnAdd` can exist on
`Component::on_add`). Ideally, `Component::on_add` would be the hook
itself rather than a getter for the hook, but it is the only way to
early-out for a no-op hook, which is important for performance.
## Migration Guide
`Component::register_component_hooks` has been deprecated. If you are
manually implementing the `Component` trait and registering hooks there,
use the individual methods such as `on_add` instead for increased
clarity.
# Objective
Basic `TextShadow` support.
## Solution
New `TextShadow` component with `offset` and `color` fields. Just insert
it on a `Text` node to add a shadow.
New system `extract_text_shadows` handles rendering.
It's not "real" shadows just the text redrawn with an offset and a
different colour. Blur-radius support will need changes to the shaders
and be a lot more complicated, whereas this still looks okay and took a
couple of minutes to implement.
I added the `TextShadow` component to `bevy_ui` rather than `bevy_text`
because it only supports the UI atm.
We can add a `Text2d` version in a followup but getting the same effect
in `Text2d` is trivial even without official support.
---
## Showcase
<img width="122" alt="text_shadow"
src="https://github.com/user-attachments/assets/0333d167-c507-4262-b93b-b6d39e2cf3a4"
/>
<img width="136" alt="g"
src="https://github.com/user-attachments/assets/9b01d5d9-55c9-4af7-9360-a7b04f55944d"
/>
# Objective
The feature gates for the `UiChildren` and `UiRootNodes` system params
make the unconstructable `GhostNode` `PhantomData` trick redundant.
## Solution
Remove the `GhostNode::new` method and change `GhostNode` into a unit
struct.
## Testing
```cargo run --example ghost_nodes```
still works
We were calling `clear()` on the work item buffer table, which caused us
to deallocate all the CPU side buffers. This patch changes the logic to
instead just clear the buffers individually, but leave their backing
stores. This has two consequences:
1. To effectively retain work item buffers from frame to frame, we need
to key them off `RetainedViewEntity` values and not the render world
`Entity`, which is transient. This PR changes those buffers accordingly.
2. We need to clean up work item buffers that belong to views that went
away. Amusingly enough, we actually have a system,
`delete_old_work_item_buffers`, that tries to do this already, but it
wasn't doing anything because the `clear_batched_gpu_instance_buffers`
system already handled that. This patch actually makes the
`delete_old_work_item_buffers` system useful, by removing the clearing
behavior from `clear_batched_gpu_instance_buffers` and instead making
`delete_old_work_item_buffers` delete buffers corresponding to
nonexistent views.
On Bistro, this PR improves the performance of
`batch_and_prepare_binned_render_phase` from 61.2 us to 47.8 us, a 28%
speedup.

# Objective
- Improve CI when testing rendering by having smarter testbeds
## Solution
- CI testing no longer need a config file and will run with a default
config if not found
- It is now possible to give a name to a screenshot instead of just a
frame number
- 2d and 3d testbeds are now driven from code
- a new system in testbed will watch for state changed
- on state changed, trigger a screenshot 100 frames after (so that the
scene has time to render) with the name of the scene
- when the screenshot is taken (`Captured` component has been removed),
switch scene
- this means less setup to run a testbed (no need for a config file),
screenshots have better names, and it's faster as we don't wait 100
frames for the screenshot to be taken
## Testing
- `cargo run --example testbed_2d --features bevy_ci_testing`
# Objective
The bounding_2d example was originally placed in 2d_rendering because
there was no folder for bounding or math, but now that this folder exist
it makes no sense for it to be here.
## Solution
Move the example
## Testing
I ran the example
## Objective
Bevy 0.15 introduced new method in `Material2d` trait- `alpha_mode`.
Before that when new material was created it had alpha blending, now it
does not.
## Solution
While I am okay with it, it could be useful to add the new trait method
implementation to one of the samples so users are more aware of it.
---------
Co-authored-by: IceSentry <IceSentry@users.noreply.github.com>
# Objective
The `ArgList::push` family of methods consume `self` and return a new
`ArgList` which means they can't be used with `&mut ArgList` references.
```rust
fn foo(args: &mut ArgList) {
args.push_owned(47_i32); // doesn't work :(
}
```
It's typical for `push` methods on other existing types to take `&mut
self`.
## Solution
Renamed the existing push methods to `with_arg`, `with_ref` etc and
added new `push` methods which take `&mut self`.
## Migration Guide
Uses of the `ArgList::push` methods should be replaced with the `with`
counterpart.
<details>
| old | new |
| --- | --- |
| push_arg | with_arg |
| push_ref | with_ref |
| push_mut | with_mut |
| push_owned | with_owned |
| push_boxed | with_boxed |
</details>
# Objective
I wrote a box shadow UI material naively thinking I could use the border
widths attribute to hold the border radius but it
doesn't work as the border widths are automatically set in the
extraction function. Need to send border radius to the shader seperately
for it to be viable.
## Solution
Add a `border_radius` vertex attribute to the ui material.
This PR also removes the normalization of border widths for custom UI
materials. The regular UI shader doesn't do this so it's a bit confusing
and means you can't use the logic from `ui.wgsl` in your custom UI
materials.
## Testing / Showcase
Made a change to the `ui_material` example to display border radius:
```cargo run --example ui_material```
<img width="569" alt="corners" src="https://github.com/user-attachments/assets/36412736-a9ee-4042-aadd-68b9cafb17cb" />
Unfortunately, Apple platforms don't have enough texture bindings to
properly support clustered decals. This should be fixed once `wgpu` has
first-class bindless texture support. In the meantime, we disable them.
Closes#17553.
---------
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
*Occlusion culling* allows the GPU to skip the vertex and fragment
shading overhead for objects that can be quickly proved to be invisible
because they're behind other geometry. A depth prepass already
eliminates most fragment shading overhead for occluded objects, but the
vertex shading overhead, as well as the cost of testing and rejecting
fragments against the Z-buffer, is presently unavoidable for standard
meshes. We currently perform occlusion culling only for meshlets. But
other meshes, such as skinned meshes, can benefit from occlusion culling
too in order to avoid the transform and skinning overhead for unseen
meshes.
This commit adapts the same [*two-phase occlusion culling*] technique
that meshlets use to Bevy's standard 3D mesh pipeline when the new
`OcclusionCulling` component, as well as the `DepthPrepass` component,
are present on the camera. It has these steps:
1. *Early depth prepass*: We use the hierarchical Z-buffer from the
previous frame to cull meshes for the initial depth prepass, effectively
rendering only the meshes that were visible in the last frame.
2. *Early depth downsample*: We downsample the depth buffer to create
another hierarchical Z-buffer, this time with the current view
transform.
3. *Late depth prepass*: We use the new hierarchical Z-buffer to test
all meshes that weren't rendered in the early depth prepass. Any meshes
that pass this check are rendered.
4. *Late depth downsample*: Again, we downsample the depth buffer to
create a hierarchical Z-buffer in preparation for the early depth
prepass of the next frame. This step is done after all the rendering, in
order to account for custom phase items that might write to the depth
buffer.
Note that this patch has no effect on the per-mesh CPU overhead for
occluded objects, which remains high for a GPU-driven renderer due to
the lack of `cold-specialization` and retained bins. If
`cold-specialization` and retained bins weren't on the horizon, then a
more traditional approach like potentially visible sets (PVS) or low-res
CPU rendering would probably be more efficient than the GPU-driven
approach that this patch implements for most scenes. However, at this
point the amount of effort required to implement a PVS baking tool or a
low-res CPU renderer would probably be greater than landing
`cold-specialization` and retained bins, and the GPU driven approach is
the more modern one anyway. It does mean that the performance
improvements from occlusion culling as implemented in this patch *today*
are likely to be limited, because of the high CPU overhead for occluded
meshes.
Note also that this patch currently doesn't implement occlusion culling
for 2D objects or shadow maps. Those can be addressed in a follow-up.
Additionally, note that the techniques in this patch require compute
shaders, which excludes support for WebGL 2.
This PR is marked experimental because of known precision issues with
the downsampling approach when applied to non-power-of-two framebuffer
sizes (i.e. most of them). These precision issues can, in rare cases,
cause objects to be judged occluded that in fact are not. (I've never
seen this in practice, but I know it's possible; it tends to be likelier
to happen with small meshes.) As a follow-up to this patch, we desire to
switch to the [SPD-based hi-Z buffer shader from the Granite engine],
which doesn't suffer from these problems, at which point we should be
able to graduate this feature from experimental status. I opted not to
include that rewrite in this patch for two reasons: (1) @JMS55 is
planning on doing the rewrite to coincide with the new availability of
image atomic operations in Naga; (2) to reduce the scope of this patch.
A new example, `occlusion_culling`, has been added. It demonstrates
objects becoming quickly occluded and disoccluded by dynamic geometry
and shows the number of objects that are actually being rendered. Also,
a new `--occlusion-culling` switch has been added to `scene_viewer`, in
order to make it easy to test this patch with large scenes like Bistro.
[*two-phase occlusion culling*]:
https://medium.com/@mil_kru/two-pass-occlusion-culling-4100edcad501
[Aaltonen SIGGRAPH 2015]:
https://www.advances.realtimerendering.com/s2015/aaltonenhaar_siggraph2015_combined_final_footer_220dpi.pdf
[Some literature]:
https://gist.github.com/reduz/c5769d0e705d8ab7ac187d63be0099b5?permalink_comment_id=5040452#gistcomment-5040452
[SPD-based hi-Z buffer shader from the Granite engine]:
https://github.com/Themaister/Granite/blob/master/assets/shaders/post/hiz.comp
## Migration guide
* When enqueuing a custom mesh pipeline, work item buffers are now
created with
`bevy::render::batching::gpu_preprocessing::get_or_create_work_item_buffer`,
not `PreprocessWorkItemBuffers::new`. See the
`specialized_mesh_pipeline` example.
## Showcase
Occlusion culling example:

Bistro zoomed out, before occlusion culling:

Bistro zoomed out, after occlusion culling:

In this scene, occlusion culling reduces the number of meshes Bevy has
to render from 1591 to 585.
This commit allows specular highlights to be tinted with a color and for
the reflectance and color tint values to vary across a model via a pair
of maps. The implementation follows the [`KHR_materials_specular`] glTF
extension. In order to reduce the number of samplers and textures in the
default `StandardMaterial` configuration, the maps are gated behind the
`pbr_specular_textures` Cargo feature.
Specular tinting is currently unsupported in the deferred renderer,
because I didn't want to bloat the deferred G-buffers. A possible fix
for this in the future would be to make the G-buffer layout more
configurable, so that specular tints could be supported on an opt-in
basis. As an alternative, Bevy could force meshes with specular tints to
render in forward mode. Both of these solutions require some more
design, so I consider them out of scope for now.
Note that the map is a *specular* map, not a *reflectance* map. In Bevy
and Filament terms, the reflectance values in the specular map range
from [0.0, 0.5], rather than [0.0, 1.0]. This is an unfortunate
[`KHR_materials_specular`] specification requirement that stems from the
fact that glTF is specified in terms of a specular strength model, not
the reflectance model that Filament and Bevy use. A workaround, which is
noted in the `StandardMaterial` documentation, is to set the
`reflectance` value to 2.0, which spreads the specular map range from
[0.0, 1.0] as normal.
The glTF loader has been updated to parse the [`KHR_materials_specular`]
extension. Note that, unless the non-default `pbr_specular_textures` is
supplied, the maps are ignored. The `specularFactor` value is applied as
usual. Note that, as with the specular map, the glTF `specularFactor` is
twice Bevy's `reflectance` value.
This PR adds a new example, `specular_tint`, which demonstrates the
specular tint and map features. Note that this example requires the
[`KHR_materials_specular`] Cargo feature.
[`KHR_materials_specular`]:
https://github.com/KhronosGroup/glTF/tree/main/extensions/2.0/Khronos/KHR_materials_specular
## Changelog
### Added
* Specular highlights can now be tinted with the `specular_tint` field
in `StandardMaterial`.
* Specular maps are now available in `StandardMaterial`, gated behind
the `pbr_specular_textures` Cargo feature.
* The `KHR_materials_specular` glTF extension is now supported, allowing
for customization of specular reflectance and specular maps. Note that
the latter are gated behind the `pbr_specular_textures` Cargo feature.
This commit adds support for *decal projectors* to Bevy, allowing for
textures to be projected on top of geometry. Decal projectors are
clusterable objects, just as punctual lights and light probes are. This
means that decals are only evaluated for objects within the conservative
bounds of the projector, and they don't require a second pass.
These clustered decals require support for bindless textures and as such
currently don't work on WebGL 2, WebGPU, macOS, or iOS. For an
alternative that doesn't require bindless, see PR #16600. I believe that
both contact projective decals in #16600 and clustered decals are
desirable to have in Bevy. Contact projective decals offer broader
hardware and driver support, while clustered decals don't require the
creation of bounding geometry.
A new example, `decal_projectors`, has been added, which demonstrates
multiple decals on a rotating object. The decal projectors can be scaled
and rotated with the mouse.
There are several limitations of this initial patch that can be
addressed in follow-ups:
1. There's no way to specify the Z-index of decals. That is, the order
in which multiple decals are blended on top of one another is arbitrary.
A follow-up could introduce some sort of Z-index field so that artists
can specify that some decals should be blended on top of others.
2. Decals don't take the normal of the surface they're projected onto
into account. Most decal implementations in other engines have a feature
whereby the angle between the decal projector and the normal of the
surface must be within some threshold for the decal to appear. Often,
artists can specify a fade-off range for a smooth transition between
oblique surfaces and aligned surfaces.
3. There's no distance-based fadeoff toward the end of the projector
range. Many decal implementations have this.
This addresses #2401.
## Showcase

# Objective
Bevy sprite image mode lacks proportional scaling for the underlying
texture. In many cases, it's required. For example, if it is desired to
support a wide variety of screens with a single texture, it's okay to
cut off some portion of the original texture.
## Solution
I added scaling of the texture during the preparation step. To fill the
sprite with the original texture, I scaled UV coordinates accordingly to
the sprite size aspect ratio and texture size aspect ratio. To fit
texture in a sprite the original `quad` is scaled and then the
additional translation is applied to place the scaled quad properly.
## Testing
For testing purposes could be used `2d/sprite_scale.rs`. Also, I am
thinking that it would be nice to have some tests for a
`crates/bevy_sprite/src/render/mod.rs:sprite_scale`.
---
## Showcase
<img width="1392" alt="image"
src="https://github.com/user-attachments/assets/c2c37b96-2493-4717-825f-7810d921b4bc"
/>
# Objective
Fixes#17487
- Adds a new field `refresh_interval` to `FpsOverlayConfig` to allow the
user setting a minimum time before each refresh of the FPS display
## Solution
- Add `refresh_interval` to `FpsOverlayConfig`
- When updating the on screen text, check a duration of
`refresh_interval` has passed, if not, don't update the FPS counter
## Testing
- Created a new bevy project
- Included the `FpsOverlayPlugin` with the default `refresh_interval`
(100 ms)
- Included the `FpsOverlayPlugin` with an obnoxious `refresh_interval`
(2 seconds)
---
---------
Co-authored-by: Benjamin Brienen <benjamin.brienen@outlook.com>
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
# Objective
- This PR adds a new stress test called `many_materials` to benchmark
the rendering performance of many animated materials.
- Fixes#11588
- This PR continues the work started in the previous PR #11592, which
was closed due to inactivity.
## Solution
- Created a new example (`examples/stress_tests/many_materials.rs`) that
renders a grid of cubes with animated materials.
- The size of the grid can be configured using the `-n` command-line
argument (or `--grid-size`). The default grid size is 10x10.
- The materials animate by cycling through colors in the HSL color
space.
## Testing
- I have tested these changes locally on my Linux machine.
- Reviewers can test the changes by running the example with different
grid sizes and observing the performance (FPS, frame time).
- I have not tested on other platforms (macOS, Windows, wasm), but I
expect it to work as the code uses standard Bevy features.
---
## Showcase
<details>
<summary>Click to view showcase</summary>

</details>
# Objective
- Make `CustomCursor::Image` easier to work with by splitting the enum
variants off into `CustomCursorImage` and `CustomCursorUrl` structs and
deriving `Default` on those structs.
- Refs #17276.
## Testing
- Ran two examples: `cargo run --example custom_cursor_image
--features=custom_cursor` and `cargo run --example window_settings
--features=custom_cursor`
- CI.
---
## Migration Guide
The `CustomCursor` enum's variants now hold instances of
`CustomCursorImage` or `CustomCursorUrl`. Update your uses of
`CustomCursor` accordingly.
Implement procedural atmospheric scattering from [Sebastien Hillaire's
2020 paper](https://sebh.github.io/publications/egsr2020.pdf). This
approach should scale well even down to mobile hardware, and is
physically accurate.
## Co-author: @mate-h
He helped massively with getting this over the finish line, ensuring
everything was physically correct, correcting several places where I had
misunderstood or misapplied the paper, and improving the performance in
several places as well. Thanks!
## Credits
@aevyrie: helped find numerous bugs and improve the example to best show
off this feature :)
Built off of @mtsr's original branch, which handled the transmittance
lut (arguably the most important part)
## Showcase:


## For followup
- Integrate with pcwalton's volumetrics code
- refactor/reorganize for better integration with other effects
- have atmosphere transmittance affect directional lights
- add support for generating skybox/environment map
---------
Co-authored-by: Emerson Coskey <56370779+EmersonCoskey@users.noreply.github.com>
Co-authored-by: atlv <email@atlasdostal.com>
Co-authored-by: JMS55 <47158642+JMS55@users.noreply.github.com>
Co-authored-by: Emerson Coskey <coskey@emerlabs.net>
Co-authored-by: Máté Homolya <mate.homolya@gmail.com>
# Objective
Make the examples look more uniform and more polished.
following the issue #17167
## Solution
- [x] Added a minimal UI explaining how to interact with the examples
only when needed.
- [x] Used the same notation for interactions ex : "Up Arrow: Move
Forward \nLeft / Right Arrow: Turn"
- [x] Set the color to
[GRAY](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/17237#discussion_r1907560092)
when it's not visible enough
- [x] Changed some colors to be easy on the eyes
- [x] removed the //camera comment
- [x] Unified the use of capital letters in the examples.
- [x] Simplified the mesh2d_arc offset calculations.
...
---------
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Rob Parrett <robparrett@gmail.com>
# Objective
- Contributes to #16877
## Solution
- Moved `hashbrown`, `foldhash`, and related types out of `bevy_utils`
and into `bevy_platform_support`
- Refactored the above to match the layout of these types in `std`.
- Updated crates as required.
## Testing
- CI
---
## Migration Guide
- The following items were moved out of `bevy_utils` and into
`bevy_platform_support::hash`:
- `FixedState`
- `DefaultHasher`
- `RandomState`
- `FixedHasher`
- `Hashed`
- `PassHash`
- `PassHasher`
- `NoOpHash`
- The following items were moved out of `bevy_utils` and into
`bevy_platform_support::collections`:
- `HashMap`
- `HashSet`
- `bevy_utils::hashbrown` has been removed. Instead, import from
`bevy_platform_support::collections` _or_ take a dependency on
`hashbrown` directly.
- `bevy_utils::Entry` has been removed. Instead, import from
`bevy_platform_support::collections::hash_map` or
`bevy_platform_support::collections::hash_set` as appropriate.
- All of the above equally apply to `bevy::utils` and
`bevy::platform_support`.
## Notes
- I left `PreHashMap`, `PreHashMapExt`, and `TypeIdMap` in `bevy_utils`
as they might be candidates for micro-crating. They can always be moved
into `bevy_platform_support` at a later date if desired.
# Objective
- Make the function signature for `ComponentHook` less verbose
## Solution
- Refactored `Entity`, `ComponentId`, and `Option<&Location>` into a new
`HookContext` struct.
## Testing
- CI
---
## Migration Guide
Update the function signatures for your component hooks to only take 2
arguments, `world` and `context`. Note that because `HookContext` is
plain data with all members public, you can use de-structuring to
simplify migration.
```rust
// Before
fn my_hook(
mut world: DeferredWorld,
entity: Entity,
component_id: ComponentId,
) { ... }
// After
fn my_hook(
mut world: DeferredWorld,
HookContext { entity, component_id, caller }: HookContext,
) { ... }
```
Likewise, if you were discarding certain parameters, you can use `..` in
the de-structuring:
```rust
// Before
fn my_hook(
mut world: DeferredWorld,
entity: Entity,
_: ComponentId,
) { ... }
// After
fn my_hook(
mut world: DeferredWorld,
HookContext { entity, .. }: HookContext,
) { ... }
```
# Objective
Fixes#14708
Also fixes some commands not updating tracked location.
## Solution
`ObserverTrigger` has a new `caller` field with the
`track_change_detection` feature;
hooks take an additional caller parameter (which is `Some(…)` or `None`
depending on the feature).
## Testing
See the new tests in `src/observer/mod.rs`
---
## Showcase
Observers now know from where they were triggered (if
`track_change_detection` is enabled):
```rust
world.observe(move |trigger: Trigger<OnAdd, Foo>| {
println!("Added Foo from {}", trigger.caller());
});
```
## Migration
- hooks now take an additional `Option<&'static Location>` argument
---------
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
# Objective
After #17398, Bevy now has relations! We don't teach users how to make /
work with these in the examples yet though, but we definitely should.
## Solution
- Add a simple abstract example that goes over defining, spawning,
traversing and removing a custom relations.
- ~~Add `Relationship` and `RelationshipTarget` to the prelude: the
trait methods are really helpful here.~~
- this causes subtle ambiguities with method names and weird compiler
errors. Not doing it here!
- Clean up related documentation that I referenced when writing this
example.
## Testing
`cargo run --example relationships`
## Notes to reviewers
1. Yes, I know that the cycle detection code could be more efficient. I
decided to reduce the caching to avoid distracting from the broader
point of "here's how you traverse relationships".
2. Instead of using an `App`, I've decide to use
`World::run_system_once` + system functions defined inside of `main` to
do something closer to literate programming.
---------
Co-authored-by: Joona Aalto <jondolf.dev@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: MinerSebas <66798382+MinerSebas@users.noreply.github.com>
Co-authored-by: Kristoffer Søholm <k.soeholm@gmail.com>
Fixes#17412
## Objective
`Parent` uses the "has a X" naming convention. There is increasing
sentiment that we should use the "is a X" naming convention for
relationships (following #17398). This leaves `Children` as-is because
there is prevailing sentiment that `Children` is clearer than `ParentOf`
in many cases (especially when treating it like a collection).
This renames `Parent` to `ChildOf`.
This is just the implementation PR. To discuss the path forward, do so
in #17412.
## Migration Guide
- The `Parent` component has been renamed to `ChildOf`.
# Objective
The existing `RelationshipSourceCollection` uses `Vec` as the only
possible backing for our relationships. While a reasonable choice,
benchmarking use cases might reveal that a different data type is better
or faster.
For example:
- Not all relationships require a stable ordering between the
relationship sources (i.e. children). In cases where we a) have many
such relations and b) don't care about the ordering between them, a hash
set is likely a better datastructure than a `Vec`.
- The number of children-like entities may be small on average, and a
`smallvec` may be faster
## Solution
- Implement `RelationshipSourceCollection` for `EntityHashSet`, our
custom entity-optimized `HashSet`.
-~~Implement `DoubleEndedIterator` for `EntityHashSet` to make things
compile.~~
- This implementation was cursed and very surprising.
- Instead, by moving the iterator type on `RelationshipSourceCollection`
from an erased RPTIT to an explicit associated type we can add a trait
bound on the offending methods!
- Implement `RelationshipSourceCollection` for `SmallVec`
## Testing
I've added a pair of new tests to make sure this pattern compiles
successfully in practice!
## Migration Guide
`EntityHashSet` and `EntityHashMap` are no longer re-exported in
`bevy_ecs::entity` directly. If you were not using `bevy_ecs` / `bevy`'s
`prelude`, you can access them through their now-public modules,
`hash_set` and `hash_map` instead.
## Notes to reviewers
The `EntityHashSet::Iter` type needs to be public for this impl to be
allowed. I initially renamed it to something that wasn't ambiguous and
re-exported it, but as @Victoronz pointed out, that was somewhat
unidiomatic.
In
1a8564898f,
I instead made the `entity_hash_set` public (and its `entity_hash_set`)
sister public, and removed the re-export. I prefer this design (give me
module docs please), but it leads to a lot of churn in this PR.
Let me know which you'd prefer, and if you'd like me to split that
change out into its own micro PR.
# Objective
The gltf-json crate seems like it strips/adds an `_` when doing the name
comparison for custom vertex attributes.
* gltf-json
[add](88e719d5de/gltf-json/src/mesh.rs (L341))
* gltf-json
[strip](88e719d5de/gltf-json/src/mesh.rs (L298C12-L298C42))
* [bevy's
handling](b66c3ceb0e/crates/bevy_gltf/src/vertex_attributes.rs (L273-L276))
seems like it uses the non-underscore'd version.
The bevy example gltf:
[barycentric.gltf](b66c3ceb0e/assets/models/barycentric/barycentric.gltf),
includes two underscores: `__BARYCENTRIC` in the gltf file, resulting in
needing `_BARYCENTRIC` (one underscore) as the attribute name in Bevy.
This extra underscore is redundant and does not appear if exporting from
blender, which only requires a single underscore to trigger the
attribute export.
I'm not sure if we want to change the example itself (maybe there's a
reason it has two underscores, I couldn't find a reason), but a docs
comment would help.
## Solution
add docs detailing the behavior
# Objective
Make the `animated_mesh` example more intuitive and easier for the user
to extend.
# Solution
The `animated_mesh` example shows how to spawn a single mesh and play a
single animation. The original code is roughly:
1. In `setup_mesh_and_animation`, spawn an entity with a SceneRoot that
will load and spawn the mesh. Also record the animation to play as a
resource.
2. Use `play_animation_once_loaded` to detect when any animation players
are spawned, then play the animation from the resource.
When I used this example as a starting point for my own app, I hit a
wall when trying to spawn multiple meshes with different animations.
`play_animation_once_loaded` tells me an animation player spawned
somewhere, but how do I get from there to the right animation? The
entity it runs on is spawned by the scene so I can't attach any data to
it?
The new code takes a different approach. Instead of a global resource,
the animation is recorded as a component on the entity with the
SceneRoot. Instead of detecting animation players spawning wherever, an
observer is attached to that specific entity.
This feels more intuitive and localised, and I think most users will
work out how to get from there to different animations and meshes. The
downside is more lines of code, and the "find the animation players"
part still feels a bit magical and inefficient.
# Side Notes
- The solution was mostly stolen from
https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/14852#issuecomment-2481401769.
- The example still feels too complicated.
- "Why do I have to make this graph to play one animation?"
- "Why can't I choose and play the animation in one step and avoid this
temporary component?"
- I think this requires engine changes.
- I originally started on a separate example of multiple meshes
([branch](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/compare/main...greeble-dev:bevy:animated-mesh-multiple)).
- I decided that the user could probably work this out themselves from
the single animation example.
- But maybe still worth following through.
# Testing
`cargo run --example animated_mesh`
---------
Co-authored-by: Rob Parrett <robparrett@gmail.com>
# Objective
`Text2d` ignores `TextBounds` when calculating the offset for text
aligment.
On main a text entity positioned in the center of the window with center
justification and 600px horizontal text bounds isn't centered like it
should be but shifted off to the right:
<img width="305" alt="hellox"
src="https://github.com/user-attachments/assets/8896c6f0-1b9f-4633-9c12-1de6eff5f3e1"
/>
(second example in the testing section below)
Fixes#14266
I already had a PR in review for this (#14270) but it used post layout
adjustment (which we want to avoid) and ignored `TextBounds`.
## Solution
* If `TextBounds` are present for an axis, use them instead of the size
of the computed text layout size to calculate the offset.
* Adjust the vertical offset of text so it's top is aligned with the top
of the texts bounding rect (when present).
## Testing
```
use bevy::prelude::*;
use bevy::color::palettes;
use bevy::sprite::Anchor;
use bevy::text::TextBounds;
fn main() {
App::new()
.add_plugins(DefaultPlugins)
.add_systems(Startup, setup)
.run();
}
fn example(commands: &mut Commands, dest: Vec3, justify: JustifyText) {
commands.spawn((
Sprite {
color: palettes::css::YELLOW.into(),
custom_size: Some(10. * Vec2::ONE),
anchor: Anchor::Center,
..Default::default()
},
Transform::from_translation(dest),
));
for a in [
Anchor::TopLeft,
Anchor::TopRight,
Anchor::BottomRight,
Anchor::BottomLeft,
] {
commands.spawn((
Text2d(format!("L R\n{:?}\n{:?}", a, justify)),
TextFont {
font_size: 14.0,
..default()
},
TextLayout {
justify,
..Default::default()
},
TextBounds::new(300., 75.),
Transform::from_translation(dest + Vec3::Z),
a,
));
}
}
fn setup(mut commands: Commands) {
commands.spawn(Camera2d::default());
for (i, j) in [
JustifyText::Left,
JustifyText::Right,
JustifyText::Center,
JustifyText::Justified,
]
.into_iter()
.enumerate()
{
example(&mut commands, (300. - 150. * i as f32) * Vec3::Y, j);
}
commands.spawn(Sprite {
color: palettes::css::YELLOW.into(),
custom_size: Some(10. * Vec2::ONE),
anchor: Anchor::Center,
..Default::default()
});
}
```
<img width="566" alt="cap"
src="https://github.com/user-attachments/assets/e6a98fa5-80b2-4380-a9b7-155bb49635b8"
/>
This probably looks really confusing but it should make sense if you
imagine each block of text surrounded by a 300x75 rectangle that is
anchored to the center of the yellow square.
#
```
use bevy::prelude::*;
use bevy::sprite::Anchor;
use bevy::text::TextBounds;
fn main() {
App::new()
.add_plugins(DefaultPlugins)
.add_systems(Startup, setup)
.run();
}
fn setup(mut commands: Commands) {
commands.spawn(Camera2d::default());
commands.spawn((
Text2d::new("hello"),
TextFont {
font_size: 60.0,
..default()
},
TextLayout::new_with_justify(JustifyText::Center),
TextBounds::new(600., 200.),
Anchor::Center,
));
}
```
<img width="338" alt="hello"
src="https://github.com/user-attachments/assets/e5e89364-afda-4baa-aca8-df4cdacbb4ed"
/>
The text being above the center is intended. When `TextBounds` are
present, the text block's offset is calculated using its `TextBounds`
not the layout size returned by cosmic-text.
#
Probably we should add a vertical alignment setting for Text2d. Didn't
do it here as this is intended for a 0.15.2 release.
This commit overhauls the documentation in the Bevy scene loading
example. It adds thorough explanatory comments to guide new Rust and
Bevy developers. The rewritten docs clarify how to:
- Register types for reflection, enabling serialization and dynamic
property access
- Skip serializing certain fields with `#[reflect(skip_serializing)]`
- Use `FromWorld` for components that require runtime initialization
- Store and serialize `Resources` in scene files
- Load scenes using a `DynamicSceneRoot` and handle updates in a system
- Serialize a brand-new scene to a separate file asynchronously using
`IoTaskPool`
These additions aim to provide a clear, step-by-step reference that
demonstrates how to implement a scene-based workflow, making it easier
for beginners and experienced developers alike to use Bevy’s scene
system effectively.
---------
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
# Objective
It's not immediately obvious that `TargetCamera` only works with UI node
entities. It's natural to assume from looking at something like the
`multiple_windows` example that it will work with everything.
## Solution
Rename `TargetCamera` to `UiTargetCamera`.
## Migration Guide
`TargetCamera` has been renamed to `UiTargetCamera`.
# Objective
Segment2d and Segment3d are currently hard to work with because unlike
many other primary shapes, they are bound to the origin.
The objective of this PR is to allow these segments to exist anywhere in
cartesian space, making them much more useful in a variety of contexts.
## Solution
Reworking the existing segment type's internal fields and methods to
allow them to exist anywhere in cartesian space.
I have done both reworks for 2d and 3d segments but I was unsure if I
should just have it all here or not so feel free to tell me how I should
proceed, for now I have only pushed Segment2d changes.
As I am not a very seasoned contributor, this first implementation is
very likely sloppy and will need some additional work from my end, I am
open to all criticisms and willing to work to get this to bevy's
standards.
## Testing
I am not very familiar with the standards of testing. Of course my
changes had to pass the thorough existing tests for primitive shapes.
I also checked the gizmo 2d shapes intersection example and everything
looked fine.
I did add a few utility methods to the types that have no tests yet. I
am willing to implement some if it is deemed necessary
## Migration Guide
The segment type constructors changed so if someone previously created a
Segment2d with a direction and length they would now need to use the
`from_direction` constructor
---------
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Joona Aalto <jondolf.dev@gmail.com>
This adds support for one-to-many non-fragmenting relationships (with
planned paths for fragmenting and non-fragmenting many-to-many
relationships). "Non-fragmenting" means that entities with the same
relationship type, but different relationship targets, are not forced
into separate tables (which would cause "table fragmentation").
Functionally, this fills a similar niche as the current Parent/Children
system. The biggest differences are:
1. Relationships have simpler internals and significantly improved
performance and UX. Commands and specialized APIs are no longer
necessary to keep everything in sync. Just spawn entities with the
relationship components you want and everything "just works".
2. Relationships are generalized. Bevy can provide additional built in
relationships, and users can define their own.
**REQUEST TO REVIEWERS**: _please don't leave top level comments and
instead comment on specific lines of code. That way we can take
advantage of threaded discussions. Also dont leave comments simply
pointing out CI failures as I can read those just fine._
## Built on top of what we have
Relationships are implemented on top of the Bevy ECS features we already
have: components, immutability, and hooks. This makes them immediately
compatible with all of our existing (and future) APIs for querying,
spawning, removing, scenes, reflection, etc. The fewer specialized APIs
we need to build, maintain, and teach, the better.
## Why focus on one-to-many non-fragmenting first?
1. This allows us to improve Parent/Children relationships immediately,
in a way that is reasonably uncontroversial. Switching our hierarchy to
fragmenting relationships would have significant performance
implications. ~~Flecs is heavily considering a switch to non-fragmenting
relations after careful considerations of the performance tradeoffs.~~
_(Correction from @SanderMertens: Flecs is implementing non-fragmenting
storage specialized for asset hierarchies, where asset hierarchies are
many instances of small trees that have a well defined structure)_
2. Adding generalized one-to-many relationships is currently a priority
for the [Next Generation Scene / UI
effort](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/discussions/14437).
Specifically, we're interested in building reactions and observers on
top.
## The changes
This PR does the following:
1. Adds a generic one-to-many Relationship system
3. Ports the existing Parent/Children system to Relationships, which now
lives in `bevy_ecs::hierarchy`. The old `bevy_hierarchy` crate has been
removed.
4. Adds on_despawn component hooks
5. Relationships can opt-in to "despawn descendants" behavior, meaning
that the entire relationship hierarchy is despawned when
`entity.despawn()` is called. The built in Parent/Children hierarchies
enable this behavior, and `entity.despawn_recursive()` has been removed.
6. `world.spawn` now applies commands after spawning. This ensures that
relationship bookkeeping happens immediately and removes the need to
manually flush. This is in line with the equivalent behaviors recently
added to the other APIs (ex: insert).
7. Removes the ValidParentCheckPlugin (system-driven / poll based) in
favor of a `validate_parent_has_component` hook.
## Using Relationships
The `Relationship` trait looks like this:
```rust
pub trait Relationship: Component + Sized {
type RelationshipSources: RelationshipSources<Relationship = Self>;
fn get(&self) -> Entity;
fn from(entity: Entity) -> Self;
}
```
A relationship is a component that:
1. Is a simple wrapper over a "target" Entity.
2. Has a corresponding `RelationshipSources` component, which is a
simple wrapper over a collection of entities. Every "target entity"
targeted by a "source entity" with a `Relationship` has a
`RelationshipSources` component, which contains every "source entity"
that targets it.
For example, the `Parent` component (as it currently exists in Bevy) is
the `Relationship` component and the entity containing the Parent is the
"source entity". The entity _inside_ the `Parent(Entity)` component is
the "target entity". And that target entity has a `Children` component
(which implements `RelationshipSources`).
In practice, the Parent/Children relationship looks like this:
```rust
#[derive(Relationship)]
#[relationship(relationship_sources = Children)]
pub struct Parent(pub Entity);
#[derive(RelationshipSources)]
#[relationship_sources(relationship = Parent)]
pub struct Children(Vec<Entity>);
```
The Relationship and RelationshipSources derives automatically implement
Component with the relevant configuration (namely, the hooks necessary
to keep everything in sync).
The most direct way to add relationships is to spawn entities with
relationship components:
```rust
let a = world.spawn_empty().id();
let b = world.spawn(Parent(a)).id();
assert_eq!(world.entity(a).get::<Children>().unwrap(), &[b]);
```
There are also convenience APIs for spawning more than one entity with
the same relationship:
```rust
world.spawn_empty().with_related::<Children>(|s| {
s.spawn_empty();
s.spawn_empty();
})
```
The existing `with_children` API is now a simpler wrapper over
`with_related`. This makes this change largely non-breaking for existing
spawn patterns.
```rust
world.spawn_empty().with_children(|s| {
s.spawn_empty();
s.spawn_empty();
})
```
There are also other relationship APIs, such as `add_related` and
`despawn_related`.
## Automatic recursive despawn via the new on_despawn hook
`RelationshipSources` can opt-in to "despawn descendants" behavior,
which will despawn all related entities in the relationship hierarchy:
```rust
#[derive(RelationshipSources)]
#[relationship_sources(relationship = Parent, despawn_descendants)]
pub struct Children(Vec<Entity>);
```
This means that `entity.despawn_recursive()` is no longer required.
Instead, just use `entity.despawn()` and the relevant related entities
will also be despawned.
To despawn an entity _without_ despawning its parent/child descendants,
you should remove the `Children` component first, which will also remove
the related `Parent` components:
```rust
entity
.remove::<Children>()
.despawn()
```
This builds on the on_despawn hook introduced in this PR, which is fired
when an entity is despawned (before other hooks).
## Relationships are the source of truth
`Relationship` is the _single_ source of truth component.
`RelationshipSources` is merely a reflection of what all the
`Relationship` components say. By embracing this, we are able to
significantly improve the performance of the system as a whole. We can
rely on component lifecycles to protect us against duplicates, rather
than needing to scan at runtime to ensure entities don't already exist
(which results in quadratic runtime). A single source of truth gives us
constant-time inserts. This does mean that we cannot directly spawn
populated `Children` components (or directly add or remove entities from
those components). I personally think this is a worthwhile tradeoff,
both because it makes the performance much better _and_ because it means
theres exactly one way to do things (which is a philosophy we try to
employ for Bevy APIs).
As an aside: treating both sides of the relationship as "equivalent
source of truth relations" does enable building simple and flexible
many-to-many relationships. But this introduces an _inherent_ need to
scan (or hash) to protect against duplicates.
[`evergreen_relations`](https://github.com/EvergreenNest/evergreen_relations)
has a very nice implementation of the "symmetrical many-to-many"
approach. Unfortunately I think the performance issues inherent to that
approach make it a poor choice for Bevy's default relationship system.
## Followup Work
* Discuss renaming `Parent` to `ChildOf`. I refrained from doing that in
this PR to keep the diff reasonable, but I'm personally biased toward
this change (and using that naming pattern generally for relationships).
* [Improved spawning
ergonomics](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/discussions/16920)
* Consider adding relationship observers/triggers for "relationship
targets" whenever a source is added or removed. This would replace the
current "hierarchy events" system, which is unused upstream but may have
existing users downstream. I think triggers are the better fit for this
than a buffered event queue, and would prefer not to add that back.
* Fragmenting relations: My current idea hinges on the introduction of
"value components" (aka: components whose type _and_ value determines
their ComponentId, via something like Hashing / PartialEq). By labeling
a Relationship component such as `ChildOf(Entity)` as a "value
component", `ChildOf(e1)` and `ChildOf(e2)` would be considered
"different components". This makes the transition between fragmenting
and non-fragmenting a single flag, and everything else continues to work
as expected.
* Many-to-many support
* Non-fragmenting: We can expand Relationship to be a list of entities
instead of a single entity. I have largely already written the code for
this.
* Fragmenting: With the "value component" impl mentioned above, we get
many-to-many support "for free", as it would allow inserting multiple
copies of a Relationship component with different target entities.
Fixes#3742 (If this PR is merged, I think we should open more targeted
followup issues for the work above, with a fresh tracking issue free of
the large amount of less-directed historical context)
Fixes#17301Fixes#12235Fixes#15299Fixes#15308
## Migration Guide
* Replace `ChildBuilder` with `ChildSpawnerCommands`.
* Replace calls to `.set_parent(parent_id)` with
`.insert(Parent(parent_id))`.
* Replace calls to `.replace_children()` with `.remove::<Children>()`
followed by `.add_children()`. Note that you'll need to manually despawn
any children that are not carried over.
* Replace calls to `.despawn_recursive()` with `.despawn()`.
* Replace calls to `.despawn_descendants()` with
`.despawn_related::<Children>()`.
* If you have any calls to `.despawn()` which depend on the children
being preserved, you'll need to remove the `Children` component first.
---------
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
Added an external assets section to .gitignore. This prevents
contributors from accidentally adding or committing them.
I believe currently the only externel asset is the meshlet bunny.
# Objective
While working on more complex directional navigation work, I noticed a
few small things.
## Solution
Rather than stick them in a bigger PR, split them out now.
- Include more useful information when responding to
`DirectionalNavigationError`.
- Use the less controversial `Click` events (rather than `Pressed`) in
the example
- Implement add_looping_edges in terms of `add_edges`. Thanks @rparrett
for the idea.
## Testing
Ran the `directional_navigation` example and things still work.
# Objective
While `add_looping_edges` is a helpful method for manually defining
directional navigation maps, we don't always want to loop around!
## Solution
Add a non-looping variant.
These commits are cherrypicked from the more complex #17247.
## Testing
I've updated the `directional_navigation` example to use these changes,
and verified that it works.
---------
Co-authored-by: Rob Parrett <robparrett@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Benjamin Brienen <benjamin.brienen@outlook.com>