# Objective
#10105 changed the ssao input color from the material base color to
white. i can't actually see a difference in the example but there should
be one in some cases.
## Solution
change it back.
# Objective
cleanup some pbr shader code. improve shader stage io consistency and
make pbr.wgsl (probably many people's first foray into bevy shader code)
a little more human-readable. also fix a couple of small issues with
deferred rendering.
## Solution
mesh_vertex_output:
- rename to forward_io (to align with prepass_io)
- rename `MeshVertexOutput` to `VertexOutput` (to align with prepass_io)
- move `Vertex` from mesh.wgsl into here (to align with prepass_io)
prepass_io:
- remove `FragmentInput`, use `VertexOutput` directly (to align with
forward_io)
- rename `VertexOutput::clip_position` to `position` (to align with
forward_io)
pbr.wgsl:
- restructure so we don't need `#ifdefs` on the actual entrypoint, use
VertexOutput and FragmentOutput in all cases and use #ifdefs to import
the right struct definitions.
- rearrange to make the flow clearer
- move alpha_discard up from `pbr_functions::pbr` to avoid needing to
call it on some branches and not others
- add a bunch of comments
deferred_lighting:
- move ssao into the `!unlit` block to reflect forward behaviour
correctly
- fix compile error with deferred + premultiply_alpha
## Migration Guide
in custom material shaders:
- `pbr_functions::pbr` no longer calls to
`pbr_functions::alpha_discard`. if you were using the `pbr` function in
a custom shader with alpha mask mode you now also need to call
alpha_discard manually
- rename imports of `bevy_pbr::mesh_vertex_output` to
`bevy_pbr::forward_io`
- rename instances of `MeshVertexOutput` to `VertexOutput`
in custom material prepass shaders:
- rename instances of `VertexOutput::clip_position` to
`VertexOutput::position`
# Objective
Fixes [#10061]
## Solution
Renamed `RenderInstance` to `ExtractInstance`, `RenderInstances` to
`ExtractedInstances` and `RenderInstancePlugin` to
`ExtractInstancesPlugin`
# Objective
- Add a [Deferred
Renderer](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Deferred_shading) to Bevy.
- This allows subsequent passes to access per pixel material information
before/during shading.
- Accessing this per pixel material information is needed for some
features, like GI. It also makes other features (ex. Decals) simpler to
implement and/or improves their capability. There are multiple
approaches to accomplishing this. The deferred shading approach works
well given the limitations of WebGPU and WebGL2.
Motivation: [I'm working on a GI solution for
Bevy](https://youtu.be/eH1AkL-mwhI)
# Solution
- The deferred renderer is implemented with a prepass and a deferred
lighting pass.
- The prepass renders opaque objects into the Gbuffer attachment
(`Rgba32Uint`). The PBR shader generates a `PbrInput` in mostly the same
way as the forward implementation and then [packs it into the
Gbuffer](ec1465559f/crates/bevy_pbr/src/render/pbr.wgsl (L168)).
- The deferred lighting pass unpacks the `PbrInput` and [feeds it into
the pbr()
function](ec1465559f/crates/bevy_pbr/src/deferred/deferred_lighting.wgsl (L65)),
then outputs the shaded color data.
- There is now a resource
[DefaultOpaqueRendererMethod](ec1465559f/crates/bevy_pbr/src/material.rs (L599))
that can be used to set the default render method for opaque materials.
If materials return `None` from
[opaque_render_method()](ec1465559f/crates/bevy_pbr/src/material.rs (L131))
the `DefaultOpaqueRendererMethod` will be used. Otherwise, custom
materials can also explicitly choose to only support Deferred or Forward
by returning the respective
[OpaqueRendererMethod](ec1465559f/crates/bevy_pbr/src/material.rs (L603))
- Deferred materials can be used seamlessly along with both opaque and
transparent forward rendered materials in the same scene. The [deferred
rendering
example](https://github.com/DGriffin91/bevy/blob/deferred/examples/3d/deferred_rendering.rs)
does this.
- The deferred renderer does not support MSAA. If any deferred materials
are used, MSAA must be disabled. Both TAA and FXAA are supported.
- Deferred rendering supports WebGL2/WebGPU.
## Custom deferred materials
- Custom materials can support both deferred and forward at the same
time. The
[StandardMaterial](ec1465559f/crates/bevy_pbr/src/render/pbr.wgsl (L166))
does this. So does [this
example](https://github.com/DGriffin91/bevy_glowy_orb_tutorial/blob/deferred/assets/shaders/glowy.wgsl#L56).
- Custom deferred materials that require PBR lighting can create a
`PbrInput`, write it to the deferred GBuffer and let it be rendered by
the `PBRDeferredLightingPlugin`.
- Custom deferred materials that require custom lighting have two
options:
1. Use the base_color channel of the `PbrInput` combined with the
`STANDARD_MATERIAL_FLAGS_UNLIT_BIT` flag.
[Example.](https://github.com/DGriffin91/bevy_glowy_orb_tutorial/blob/deferred/assets/shaders/glowy.wgsl#L56)
(If the unlit bit is set, the base_color is stored as RGB9E5 for extra
precision)
2. A Custom Deferred Lighting pass can be created, either overriding the
default, or running in addition. The a depth buffer is used to limit
rendering to only the required fragments for each deferred lighting
pass. Materials can set their respective depth id via the
[deferred_lighting_pass_id](b79182d2a3/crates/bevy_pbr/src/prepass/prepass_io.wgsl (L95))
attachment. The custom deferred lighting pass plugin can then set [its
corresponding
depth](ec1465559f/crates/bevy_pbr/src/deferred/deferred_lighting.wgsl (L37)).
Then with the lighting pass using
[CompareFunction::Equal](ec1465559f/crates/bevy_pbr/src/deferred/mod.rs (L335)),
only the fragments with a depth that equal the corresponding depth
written in the material will be rendered.
Custom deferred lighting plugins can also be created to render the
StandardMaterial. The default deferred lighting plugin can be bypassed
with `DefaultPlugins.set(PBRDeferredLightingPlugin { bypass: true })`
---------
Co-authored-by: nickrart <nickolas.g.russell@gmail.com>
# Objective
- The filter type on the `apply_global_wireframe_material` system had
duplicate filter code and the `clippy::type_complexity` attribute.
## Solution
- Extract the common part of the filter into a type alias
# Objective
- Use the `Material` abstraction for the Wireframes
- Right now this doesn't have many benefits other than simplifying some
of the rendering code
- We can reuse the default vertex shader and avoid rendering
inconsistencies
- The goal is to have a material with a color on each mesh so this
approach will make it easier to implement
- Originally done in https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/5303 but I
decided to split the Material part to it's own PR and then adding
per-entity colors and globally configurable colors will be a much
simpler diff.
## Solution
- Use the new `Material` abstraction for the Wireframes
## Notes
It's possible this isn't ideal since this adds a
`Handle<WireframeMaterial>` to all the meshes compared to the original
approach that didn't need anything. I didn't notice any performance
impact on my machine.
This might be a surprising usage of `Material` at first, because
intuitively you only have one material per mesh, but the way it's
implemented you can have as many different types of materials as you
want on a mesh.
## Migration Guide
`WireframePipeline` was removed. If you were using it directly, please
create an issue explaining your use case.
---------
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
~~Currently blocked on an upstream bug that causes crashes when
minimizing/resizing on dx12 https://github.com/gfx-rs/wgpu/issues/3967~~
wgpu 0.17.1 is out which fixes it
# Objective
Keep wgpu up to date.
## Solution
Update wgpu and naga_oil.
Currently this depends on an unreleased (and unmerged) branch of
naga_oil, and hasn't been properly tested yet.
The wgpu side of this seems to have been an extremely trivial upgrade
(all the upgrade work seems to be in naga_oil). This also lets us remove
the workarounds for pack/unpack4x8unorm in the SSAO shaders.
Lets us close the dx12 part of
https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/8888
related: https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/9304
---
## Changelog
Update to wgpu 0.17 and naga_oil 0.9
# Objective
- This PR aims to make creating meshes a little bit more ergonomic,
specifically by removing the need for intermediate mutable variables.
## Solution
- We add methods that consume the `Mesh` and return a mesh with the
specified changes, so that meshes can be entirely constructed via
builder-style calls, without intermediate variables;
- Methods are flagged with `#[must_use]` to ensure proper use;
- Examples are updated to use the new methods where applicable. Some
examples are kept with the mutating methods so that users can still
easily discover them, and also where the new methods wouldn't really be
an improvement.
## Examples
Before:
```rust
let mut mesh = Mesh::new(PrimitiveTopology::TriangleList);
mesh.insert_attribute(Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_POSITION, vs);
mesh.insert_attribute(Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_NORMAL, vns);
mesh.insert_attribute(Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_UV_0, vts);
mesh.set_indices(Some(Indices::U32(tris)));
mesh
```
After:
```rust
Mesh::new(PrimitiveTopology::TriangleList)
.with_inserted_attribute(Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_POSITION, vs)
.with_inserted_attribute(Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_NORMAL, vns)
.with_inserted_attribute(Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_UV_0, vts)
.with_indices(Some(Indices::U32(tris)))
```
Before:
```rust
let mut cube = Mesh::from(shape::Cube { size: 1.0 });
cube.generate_tangents().unwrap();
PbrBundle {
mesh: meshes.add(cube),
..default()
}
```
After:
```rust
PbrBundle {
mesh: meshes.add(
Mesh::from(shape::Cube { size: 1.0 })
.with_generated_tangents()
.unwrap(),
),
..default()
}
```
---
## Changelog
- Added consuming builder methods for more ergonomic `Mesh` creation:
`with_inserted_attribute()`, `with_removed_attribute()`,
`with_indices()`, `with_duplicated_vertices()`,
`with_computed_flat_normals()`, `with_generated_tangents()`,
`with_morph_targets()`, `with_morph_target_names()`.
# Objective
fix#9605
spotlight culling uses an incorrect cluster aabb for orthographic
projections: it does not take into account the near and far cluster
bounds at all.
## Solution
use z_near and z_far to determine cluster aabb in orthographic mode.
i'm not 100% sure this is the only change that's needed, but i am sure
this change is needed, and the example seems to work well now
(CLUSTERED_FORWARD_DEBUG_CLUSTER_LIGHT_COMPLEXITY shows good bounds
around the cone for a variety of orthographic setups).
# Objective
Webgl2 broke when pcf was merged.
Fixes#10048
## Solution
Change the `textureSampleCompareLevel` in shadow_sampling.wgsl to
`textureSampleCompare` to make it work again.
# Objective
Currently, the only way for custom components that participate in
rendering to opt into the higher-performance extraction method in #9903
is to implement the `RenderInstances` data structure and the extraction
logic manually. This is inconvenient compared to the `ExtractComponent`
API.
## Solution
This commit creates a new `RenderInstance` trait that mirrors the
existing `ExtractComponent` method but uses the higher-performance
approach that #9903 uses. Additionally, `RenderInstance` is more
flexible than `ExtractComponent`, because it can extract multiple
components at once. This makes high-performance rendering components
essentially as easy to write as the existing ones based on component
extraction.
---
## Changelog
### Added
A new `RenderInstance` trait is available mirroring `ExtractComponent`,
but using a higher-performance method to extract one or more components
to the render world. If you have custom components that rendering takes
into account, you may consider migration from `ExtractComponent` to
`RenderInstance` for higher performance.
# Objective
- Improve antialiasing for non-point light shadow edges.
- Very partially addresses
https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/3628.
## Solution
- Implements "The Witness"'s shadow map sampling technique.
- Ported from @superdump's old branch, all credit to them :)
- Implements "Call of Duty: Advanced Warfare"'s stochastic shadow map
sampling technique when the velocity prepass is enabled, for use with
TAA.
- Uses interleaved gradient noise to generate a random angle, and then
averages 8 samples in a spiral pattern, rotated by the random angle.
- I also tried spatiotemporal blue noise, but it was far too noisy to be
filtered by TAA alone. In the future, we should try spatiotemporal blue
noise + a specialized shadow denoiser such as
https://gpuopen.com/fidelityfx-denoiser/#shadow. This approach would
also be useful for hybrid rasterized applications with raytraced
shadows.
- The COD presentation has an interesting temporal dithering of the
noise for use with temporal supersampling that we should revisit when we
get DLSS/FSR/other TSR.
---
## Changelog
* Added `ShadowFilteringMethod`. Improved directional light and
spotlight shadow edges to be less aliased.
## Migration Guide
* Shadows cast by directional lights or spotlights now have smoother
edges. To revert to the old behavior, add
`ShadowFilteringMethod::Hardware2x2` to your cameras.
---------
Co-authored-by: IceSentry <c.giguere42@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Daniel Chia <danstryder@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: robtfm <50659922+robtfm@users.noreply.github.com>
Co-authored-by: Brandon Dyer <brandondyer64@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Edgar Geier <geieredgar@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Robert Swain <robert.swain@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Elabajaba <Elabajaba@users.noreply.github.com>
Co-authored-by: IceSentry <IceSentry@users.noreply.github.com>
# Objective
https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/7328 introduced an API to
override the global wireframe config. I believe it is flawed for a few
reasons.
This PR uses a non-breaking API. Instead of making the `Wireframe` an
enum I introduced the `NeverRenderWireframe` component. Here's the
reason why I think this is better:
- Easier to migrate since it doesn't change the old behaviour.
Essentially nothing to migrate. Right now this PR is a breaking change
but I don't think it has to be.
- It's similar to other "per mesh" rendering features like
NotShadowCaster/NotShadowReceiver
- It doesn't force new users to also think about global vs not global if
all they want is to render a wireframe
- This would also let you filter at the query definition level instead
of filtering when running the query
## Solution
- Introduce a `NeverRenderWireframe` component that ignores the global
config
---
## Changelog
- Added a `NeverRenderWireframe` component that ignores the global
`WireframeConfig`
# Objective
Allow the user to choose between "Add wireframes to these specific
entities" or "Add wireframes to everything _except_ these specific
entities".
Fixes#7309
# Solution
Make the `Wireframe` component act like an override to the global
configuration.
Having `global` set to `false`, and adding a `Wireframe` with `enable:
true` acts exactly as before.
But now the opposite is also possible: Set `global` to `true` and add a
`Wireframe` with `enable: false` will draw wireframes for everything
_except_ that entity.
Updated the example to show how overriding the global config works.
Conventionally, the second UV map (`TEXCOORD1`, `UV1`) is used for
lightmap UVs. This commit allows Bevy to import them, so that a custom
shader that applies lightmaps can use those UVs if desired.
Note that this doesn't actually apply lightmaps to Bevy meshes; that
will be a followup. It does, however, open the door to future Bevy
plugins that implement baked global illumination.
## Changelog
### Added
The Bevy glTF loader now imports a second UV channel (`TEXCOORD1`,
`UV1`) from meshes if present. This can be used by custom shaders to
implement lightmapping.
# Objective
`Has<T>` was added to bevy_ecs, but we're still using the
`Option<With<T>>` pattern in multiple locations.
## Solution
Replace them with `Has<T>`.
# Objective
`extract_meshes` can easily be one of the most expensive operations in
the blocking extract schedule for 3D apps. It also has no fundamentally
serialized parts and can easily be run across multiple threads. Let's
speed it up by parallelizing it!
## Solution
Use the `ThreadLocal<Cell<Vec<T>>>` approach utilized by #7348 in
conjunction with `Query::par_iter` to build a set of thread-local
queues, and collect them after going wide.
## Performance
Using `cargo run --profile stress-test --features trace_tracy --example
many_cubes`. Yellow is this PR. Red is main.
`extract_meshes`:
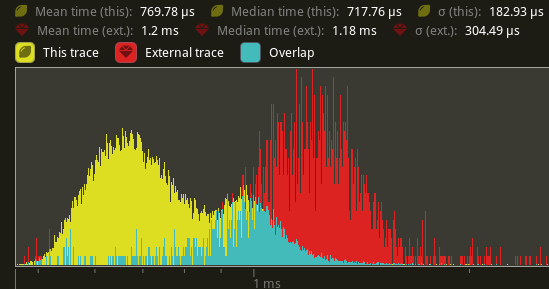
An average reduction from 1.2ms to 770us is seen, a 41.6% improvement.
Note: this is still not including #9950's changes, so this may actually
result in even faster speedups once that's merged in.
# Objective
- Improve rendering performance, particularly by avoiding the large
system commands costs of using the ECS in the way that the render world
does.
## Solution
- Define `EntityHasher` that calculates a hash from the
`Entity.to_bits()` by `i | (i.wrapping_mul(0x517cc1b727220a95) << 32)`.
`0x517cc1b727220a95` is something like `u64::MAX / N` for N that gives a
value close to π and that works well for hashing. Thanks for @SkiFire13
for the suggestion and to @nicopap for alternative suggestions and
discussion. This approach comes from `rustc-hash` (a.k.a. `FxHasher`)
with some tweaks for the case of hashing an `Entity`. `FxHasher` and
`SeaHasher` were also tested but were significantly slower.
- Define `EntityHashMap` type that uses the `EntityHashser`
- Use `EntityHashMap<Entity, T>` for render world entity storage,
including:
- `RenderMaterialInstances` - contains the `AssetId<M>` of the material
associated with the entity. Also for 2D.
- `RenderMeshInstances` - contains mesh transforms, flags and properties
about mesh entities. Also for 2D.
- `SkinIndices` and `MorphIndices` - contains the skin and morph index
for an entity, respectively
- `ExtractedSprites`
- `ExtractedUiNodes`
## Benchmarks
All benchmarks have been conducted on an M1 Max connected to AC power.
The tests are run for 1500 frames. The 1000th frame is captured for
comparison to check for visual regressions. There were none.
### 2D Meshes
`bevymark --benchmark --waves 160 --per-wave 1000 --mode mesh2d`
#### `--ordered-z`
This test spawns the 2D meshes with z incrementing back to front, which
is the ideal arrangement allocation order as it matches the sorted
render order which means lookups have a high cache hit rate.
<img width="1112" alt="Screenshot 2023-09-27 at 07 50 45"
src="https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/assets/302146/e140bc98-7091-4a3b-8ae1-ab75d16d2ccb">
-39.1% median frame time.
#### Random
This test spawns the 2D meshes with random z. This not only makes the
batching and transparent 2D pass lookups get a lot of cache misses, it
also currently means that the meshes are almost certain to not be
batchable.
<img width="1108" alt="Screenshot 2023-09-27 at 07 51 28"
src="https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/assets/302146/29c2e813-645a-43ce-982a-55df4bf7d8c4">
-7.2% median frame time.
### 3D Meshes
`many_cubes --benchmark`
<img width="1112" alt="Screenshot 2023-09-27 at 07 51 57"
src="https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/assets/302146/1a729673-3254-4e2a-9072-55e27c69f0fc">
-7.7% median frame time.
### Sprites
**NOTE: On `main` sprites are using `SparseSet<Entity, T>`!**
`bevymark --benchmark --waves 160 --per-wave 1000 --mode sprite`
#### `--ordered-z`
This test spawns the sprites with z incrementing back to front, which is
the ideal arrangement allocation order as it matches the sorted render
order which means lookups have a high cache hit rate.
<img width="1116" alt="Screenshot 2023-09-27 at 07 52 31"
src="https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/assets/302146/bc8eab90-e375-4d31-b5cd-f55f6f59ab67">
+13.0% median frame time.
#### Random
This test spawns the sprites with random z. This makes the batching and
transparent 2D pass lookups get a lot of cache misses.
<img width="1109" alt="Screenshot 2023-09-27 at 07 53 01"
src="https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/assets/302146/22073f5d-99a7-49b0-9584-d3ac3eac3033">
+0.6% median frame time.
### UI
**NOTE: On `main` UI is using `SparseSet<Entity, T>`!**
`many_buttons`
<img width="1111" alt="Screenshot 2023-09-27 at 07 53 26"
src="https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/assets/302146/66afd56d-cbe4-49e7-8b64-2f28f6043d85">
+15.1% median frame time.
## Alternatives
- Cart originally suggested trying out `SparseSet<Entity, T>` and indeed
that is slightly faster under ideal conditions. However,
`PassHashMap<Entity, T>` has better worst case performance when data is
randomly distributed, rather than in sorted render order, and does not
have the worst case memory usage that `SparseSet`'s dense `Vec<usize>`
that maps from the `Entity` index to sparse index into `Vec<T>`. This
dense `Vec` has to be as large as the largest Entity index used with the
`SparseSet`.
- I also tested `PassHashMap<u32, T>`, intending to use `Entity.index()`
as the key, but this proved to sometimes be slower and mostly no
different.
- The only outstanding approach that has not been implemented and tested
is to _not_ clear the render world of its entities each frame. That has
its own problems, though they could perhaps be solved.
- Performance-wise, if the entities and their component data were not
cleared, then they would incur table moves on spawn, and should not
thereafter, rather just their component data would be overwritten.
Ideally we would have a neat way of either updating data in-place via
`&mut T` queries, or inserting components if not present. This would
likely be quite cumbersome to have to remember to do everywhere, but
perhaps it only needs to be done in the more performance-sensitive
systems.
- The main problem to solve however is that we want to both maintain a
mapping between main world entities and render world entities, be able
to run the render app and world in parallel with the main app and world
for pipelined rendering, and at the same time be able to spawn entities
in the render world in such a way that those Entity ids do not collide
with those spawned in the main world. This is potentially quite
solvable, but could well be a lot of ECS work to do it in a way that
makes sense.
---
## Changelog
- Changed: Component data for entities to be drawn are no longer stored
on entities in the render world. Instead, data is stored in a
`EntityHashMap<Entity, T>` in various resources. This brings significant
performance benefits due to the way the render app clears entities every
frame. Resources of most interest are `RenderMeshInstances` and
`RenderMaterialInstances`, and their 2D counterparts.
## Migration Guide
Previously the render app extracted mesh entities and their component
data from the main world and stored them as entities and components in
the render world. Now they are extracted into essentially
`EntityHashMap<Entity, T>` where `T` are structs containing an
appropriate group of data. This means that while extract set systems
will continue to run extract queries against the main world they will
store their data in hash maps. Also, systems in later sets will either
need to look up entities in the available resources such as
`RenderMeshInstances`, or maintain their own `EntityHashMap<Entity, T>`
for their own data.
Before:
```rust
fn queue_custom(
material_meshes: Query<(Entity, &MeshTransforms, &Handle<Mesh>), With<InstanceMaterialData>>,
) {
...
for (entity, mesh_transforms, mesh_handle) in &material_meshes {
...
}
}
```
After:
```rust
fn queue_custom(
render_mesh_instances: Res<RenderMeshInstances>,
instance_entities: Query<Entity, With<InstanceMaterialData>>,
) {
...
for entity in &instance_entities {
let Some(mesh_instance) = render_mesh_instances.get(&entity) else { continue; };
// The mesh handle in `AssetId<Mesh>` form, and the `MeshTransforms` can now
// be found in `mesh_instance` which is a `RenderMeshInstance`
...
}
}
```
---------
Co-authored-by: robtfm <50659922+robtfm@users.noreply.github.com>
# Objective
This is a minimally disruptive version of #8340. I attempted to update
it, but failed due to the scope of the changes added in #8204.
Fixes#8307. Partially addresses #4642. As seen in
https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/8284, we're actually copying
data twice in Prepare stage systems. Once into a CPU-side intermediate
scratch buffer, and once again into a mapped buffer. This is inefficient
and effectively doubles the time spent and memory allocated to run these
systems.
## Solution
Skip the scratch buffer entirely and use
`wgpu::Queue::write_buffer_with` to directly write data into mapped
buffers.
Separately, this also directly uses
`wgpu::Limits::min_uniform_buffer_offset_alignment` to set up the
alignment when writing to the buffers. Partially addressing the issue
raised in #4642.
Storage buffers and the abstractions built on top of
`DynamicUniformBuffer` will need to come in followup PRs.
This may not have a noticeable performance difference in this PR, as the
only first-party systems affected by this are view related, and likely
are not going to be particularly heavy.
---
## Changelog
Added: `DynamicUniformBuffer::get_writer`.
Added: `DynamicUniformBufferWriter`.
# Objective
mesh.rs is infamously large. We could split off unrelated code.
## Solution
Morph targets are very similar to skinning and have their own module. We
move skinned meshes to an independent module like morph targets and give
the systems similar names.
### Open questions
Should the skinning systems and structs stay public?
---
## Migration Guide
Renamed skinning systems, resources and components:
- extract_skinned_meshes -> extract_skins
- prepare_skinned_meshes -> prepare_skins
- SkinnedMeshUniform -> SkinUniform
- SkinnedMeshJoints -> SkinIndex
---------
Co-authored-by: François <mockersf@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: vero <email@atlasdostal.com>