# Objective
- Some crates don't compile or have clippy warnings when building for
wasm32
## Solution
- bevy_asset: unused lifetime
- bevy_gltf: the error is not too large in wasm32
- bevy_remote: fails to compile as feature http is also gated on wasm32
- bevy_winit: unused import `error`
# Objective
`cargo clippy -p bevy_asset` warns on a pair of lints on my Windows 10
development machine (return from let binding).
## Solution
Addressed them!
## Testing
- CI
# Objective
Bevy 0.15 used to have methods on `Children` for sorting and reordering
them. This is very important, because in certain situations, the order
of children matters. For example, in the context of UI nodes.
These methods are missing/omitted/forgotten in the current version,
after the Relationships rework.
Without them, it is impossible for me to upgrade `iyes_perf_ui` to Bevy
0.16.
## Solution
Reintroduce the methods. This PR simply copy-pastes them from Bevy 0.15.
# Objective
Create new `NonSendMarker` that does not depend on `NonSend`.
Required, in order to accomplish #17682. In that issue, we are trying to
replace `!Send` resources with `thread_local!` in order to unblock the
resources-as-components effort. However, when we remove all the `!Send`
resources from a system, that allows the system to run on a thread other
than the main thread, which is against the design of the system. So this
marker gives us the control to require a system to run on the main
thread without depending on `!Send` resources.
## Solution
Create a new `NonSendMarker` to replace the existing one that does not
depend on `NonSend`.
## Testing
Other than running tests, I ran a few examples:
- `window_resizing`
- `wireframe`
- `volumetric_fog` (looks so cool)
- `rotation`
- `button`
There is a Mac/iOS-specific change and I do not have a Mac or iOS device
to test it. I am doubtful that it would cause any problems for 2
reasons:
1. The change is the same as the non-wasm change which I did test
2. The Pixel Eagle tests run Mac tests
But it wouldn't hurt if someone wanted to spin up an example that
utilizes the `bevy_render` crate, which is where the Mac/iSO change was.
## Migration Guide
If `NonSendMarker` is being used from `bevy_app::prelude::*`, replace it
with `bevy_ecs::system::NonSendMarker` or use it from
`bevy_ecs::prelude::*`. In addition to that, `NonSendMarker` does not
need to be wrapped like so:
```rust
fn my_system(_non_send_marker: Option<NonSend<NonSendMarker>>) {
...
}
```
Instead, it can be used without any wrappers:
```rust
fn my_system(_non_send_marker: NonSendMarker) {
...
}
```
---------
Co-authored-by: Chris Russell <8494645+chescock@users.noreply.github.com>
# Objective
`queue_uinodes` looks up the `ExtractedView` for every extracted UI
node, but there's no need to look it up again if consecutive nodes have
the same `extracted_camera_entity`.
## Solution
In queue uinodes reuse the previously looked up extracted view if the
`extracted_camera_entity` doesn't change
## Showcase
```
cargo run --example many_buttons --release --features "trace_tracy"
```
<img width="521" alt="queue-ui-improvement"
src="https://github.com/user-attachments/assets/2f111837-8c2e-4a6d-94cd-3c3462c58bc9"
/>
yellow is this PR, red is main
# Objective
- `bevy_ecs` has lint errors without some features
## Solution
- Fix `clippy::allow-attributes-without-reason` when `bevy_reflect` is
disabled by adding a reason
- Fix `clippy::needless_return` when `std` is disabled by adding a gated
`expect` attribute and a comment to remove it when the `no_std` stuff is
addressed
## Testing
- `cargo clippy -p bevy_ecs --no-default-features --no-deps -- --D
warnings`
- CI
# Objective
- Compiling `bevy_time` without the `std`-feature results in a
`clippy::unnecessary-literal-unwrap`.
## Solution
- Fix lint error
## Testing
- CI
---
# Objective
- Compiling `bevy_a11y` without default features fails because you need
to select a floating point backed. But you actually don't need it, this
requirement is from an unused linkage to `bevy_input_focus`
## Solution
- Remove link
## Testing
- CI
---------
Co-authored-by: François Mockers <mockersf@gmail.com>
# Objective
- Compile failure with `bevy_anti_aliasing` due to `dds` feature not
enabling `bevy_core_pipeline/dds`, causing a public API desync.
## Solution
- Ensured feature is enabled
## Testing
- CI
# Objective
Noticed that `bevy_remote` fails to compile without default features.
## Solution
Adjusted offending method to avoid reliance on `http` module when it is
disabled.
## Testing
- CI
- `cargo clippy -p bevy_remote --no-default-features`
# Objective
Every time I run `cargo clippy -p bevy_ecs` it pops up and it's
distracting.
## Solution
Removed unnecessary returns. The blocks themselves are necessary or the
`#[cfg(...)]` doesn't apply properly
## Testing
`cargo clippy -p bevy_ecs` + ci build tests
# Objective
The `Anchor` component doesn't need to be a enum. The variants are just
mapped to `Vec2`s so it could be changed to a newtype with associated
const values, saving the space needed for the discriminator by the enum.
Also there was no benefit I think in hiding the underlying `Vec2`
representation of `Anchor`s.
Suggested by @atlv24.
Fixes#18459Fixes#18460
## Solution
Change `Anchor` to a struct newtyping a `Vec2`, and its variants into
associated constants.
## Migration Guide
The anchor component has been changed from an enum to a struct newtyping
a `Vec2`. The `Custom` variant has been removed, instead to construct a
custom `Anchor` use its tuple constructor:
```rust
Sprite {
anchor: Anchor(Vec2::new(0.25, 0.4)),
..default()
}
```
The other enum variants have been replaced with corresponding constants:
* `Anchor::BottomLeft` to `Anchor::BOTTOM_LEFT`
* `Anchor::Center` to `Anchor::CENTER`
* `Anchor::TopRight` to `Anchor::TOP_RIGHT`
* .. and so on for the remaining variants
# Objective
There are currently too many disparate ways to handle entity mapping,
especially after #17687. We now have MapEntities, VisitEntities,
VisitEntitiesMut, Component::visit_entities,
Component::visit_entities_mut.
Our only known use case at the moment for these is entity mapping. This
means we have significant consolidation potential.
Additionally, VisitEntitiesMut cannot be implemented for map-style
collections like HashSets, as you cant "just" mutate a `&mut Entity`.
Our current approach to Component mapping requires VisitEntitiesMut,
meaning this category of entity collection isn't mappable. `MapEntities`
is more generally applicable. Additionally, the _existence_ of the
blanket From impl on VisitEntitiesMut blocks us from implementing
MapEntities for HashSets (or any types we don't own), because the owner
could always add a conflicting impl in the future.
## Solution
Use `MapEntities` everywhere and remove all "visit entities" usages.
* Add `Component::map_entities`
* Remove `Component::visit_entities`, `Component::visit_entities_mut`,
`VisitEntities`, and `VisitEntitiesMut`
* Support deriving `Component::map_entities` in `#[derive(Coomponent)]`
* Add `#[derive(MapEntities)]`, and share logic with the
`Component::map_entities` derive.
* Add `ComponentCloneCtx::queue_deferred`, which is command-like logic
that runs immediately after normal clones. Reframe `FromWorld` fallback
logic in the "reflect clone" impl to use it. This cuts out a lot of
unnecessary work and I think justifies the existence of a pseudo-command
interface (given how niche, yet performance sensitive this is).
Note that we no longer auto-impl entity mapping for ` IntoIterator<Item
= &'a Entity>` types, as this would block our ability to implement cases
like `HashMap`. This means the onus is on us (or type authors) to add
explicit support for types that should be mappable.
Also note that the Component-related changes do not require a migration
guide as there hasn't been a release with them yet.
## Migration Guide
If you were previously implementing `VisitEntities` or
`VisitEntitiesMut` (likely via a derive), instead use `MapEntities`.
Those were almost certainly used in the context of Bevy Scenes or
reflection via `ReflectMapEntities`. If you have a case that uses
`VisitEntities` or `VisitEntitiesMut` directly, where `MapEntities` is
not a viable replacement, please let us know!
```rust
// before
#[derive(VisitEntities, VisitEntitiesMut)]
struct Inventory {
items: Vec<Entity>,
#[visit_entities(ignore)]
label: String,
}
// after
#[derive(MapEntities)]
struct Inventory {
#[entities]
items: Vec<Entity>,
label: String,
}
```
# Objective
Const values should be more ergonomic to insert, since this is too
verbose
``` rust
#[derive(Component)]
#[require(
LockedAxes(||LockedAxes::ROTATION_LOCKED),
)]
pub struct CharacterController;
```
instead, users can now abbreviate that nonsense like this
``` rust
#[derive(Component)]
#[require(
LockedAxes = ROTATION_LOCKED),
)]
pub struct CharacterController;
```
it also works for enum labels.
I chose to omit the type, since were trying to reduce typing here. The
alternative would have been this:
```rust
#[require(
LockedAxes = LockedAxes::ROTATION_LOCKED),
)]
```
This of course has its disadvantages, since the const has to be
associated, but the old closure method is still possible, so I dont
think its a problem.
- Fixes#16720
## Testing
I added one new test in the docs, which also explain the new change. I
also saw that the docs for the required components on line 165 was
missing an assertion, so I added it back in
---------
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
# Objective
While working on #18058 I realized I could use
`RelationshipTargetCollection::new`, so I added it.
## Solution
- Add `RelationshipTargetCollection::new`
- Add `RelationshipTargetCollection::reserve`. Could generally be useful
when doing micro-optimizations.
- Add `RelationshipTargetCollection::shrink_to_fit`. Rust collections
generally don't shrink when removing elements. Might be a good idea to
call this once in a while.
## Testing
`cargo clippy`
---
## Showcase
`RelationshipSourceCollection` now implements `new`, `reserve` and
`shrink_to_fit` to give greater control over how much memory it
consumes.
## Migration Guide
Any type implementing `RelationshipSourceCollection` now needs to also
implement `new`, `reserve` and `shrink_to_fit`. `reserve` and
`shrink_to_fit` can be made no-ops if they conceptually mean nothing to
a collection.
---------
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Chris Russell <8494645+chescock@users.noreply.github.com>
# Objective
correctly load gltfs without explicit bindposes
## Solution
use identity matrices if bindposes are not found.
note: currently does nothing, as gltfs without explicit bindposes fail
to load, see <https://github.com/gltf-rs/gltf/pull/449>
---------
Co-authored-by: François Mockers <francois.mockers@vleue.com>
# Objective
Add a way to efficiently replace a set of specifically related entities
with a new set.
Closes#18041
## Solution
Add new `replace_(related/children)` to `EntityWorldMut` and friends.
## Testing
Added a new test to `hierarchy.rs` that specifically check if
`replace_children` actually correctly replaces the children on a entity
while keeping the original one.
---
## Showcase
`EntityWorldMut` and `EntityCommands` can now be used to efficiently
replace the entities a entity is related to.
```rust
/// `parent` has 2 children. `entity_a` and `entity_b`.
assert_eq!([entity_a, entity_b], world.entity(parent).get::<Children>());
/// Replace `parent`s children with `entity_a` and `entity_c`
world.entity_mut(parent).replace_related(&[entity_a, entity_c]);
/// `parent` now has 2 children. `entity_a` and `entity_c`.
///
/// `replace_children` has saved time by not removing and reading
/// the relationship between `entity_a` and `parent`
assert_eq!([entity_a, entity_c], world.entity(parent).get::<Children>());
---------
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
## Objective
Fix `bevy_ecs` doc tests failing when used with `--all-features`.
```
---- crates\bevy_ecs\src\error\handler.rs - error::handler::GLOBAL_ERROR_HANDLER (line 87) stdout ----
error[E0425]: cannot find function `default_error_handler` in this scope
--> crates\bevy_ecs\src\error\handler.rs:92:24
|
8 | let error_handler = default_error_handler();
| ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^ not found in this scope
```
I happened to come across this while testing #12207. I'm not sure it
actually needs fixing but seemed worth a go
## Testing
```
cargo test --doc -p bevy_ecs --all-features
```
## Side Notes
The CI misses this error as it doesn't use `--all-features`. Perhaps it
should?
I tried adding `--all-features` to `ci/src/commands/doc_tests.rs` but
this triggered a linker error:
```
Compiling bevy_dylib v0.16.0-dev (C:\Projects\bevy\crates\bevy_dylib)
error: linking with `link.exe` failed: exit code: 1189
= note: LINK : fatal error LNK1189: library limit of 65535 objects exceeded␍
```
# Objective
- bevy_core_pipeline is getting really big and it's a big bottleneck for
compilation time. A lot of parts of it can be broken up
## Solution
- Add a new bevy_anti_aliasing crate that contains all the anti_aliasing
implementations
- I didn't move any MSAA related code to this new crate because that's a
lot more invasive
## Testing
- Tested the anti_aliasing example to make sure all methods still worked
---
## Showcase
before:

after:

Notice that now bevy_core_pipeline is 1s shorter and bevy_anti_aliasing
now compiles in parallel with bevy_pbr.
## Migration Guide
When using anti aliasing features, you now need to import them from
`bevy::anti_aliasing` instead of `bevy::core_pipeline`
# Objective
- Fixes https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/18332
## Solution
- Move specialize_shadows to ManageViews so that it can run after
prepare_lights, so that shadow views exist for specialization.
- Unfortunately this means that specialize_shadows is no longer in
PrepareMeshes like the rest of the specialization systems.
## Testing
- Ran anti_aliasing example, switched between the different AA options,
observed no glitches.
# Objective
For materials that aren't being used or a visible entity doesn't have an
instance of, we were unnecessarily constantly checking whether they
needed specialization, saying yes (because the material had never been
specialized for that entity), and failing to look up the material
instance.
## Solution
If an entity doesn't have an instance of the material, it can't possibly
need specialization, so exit early before spending time doing the check.
Fixes#18388.
# Objective
- bevy_dylib fails to build:
```
Compiling bevy_dylib v0.16.0-rc.1 (/bevy/crates/bevy_dylib)
error: linking with `cc` failed: exit status: 1
|
= note: some arguments are omitted. use `--verbose` to show all linker arguments
= note: Undefined symbols for architecture arm64:
"__critical_section_1_0_acquire", referenced from:
critical_section::with::h00cfbe529dea9dc9 in libbevy_tasks-53c9db6a3865f250.rlib[58](bevy_tasks-53c9db6a3865f250.evom2xwveqp508omiiqb25xig.rcgu.o)
"__critical_section_1_0_release", referenced from:
core::ptr::drop_in_place$LT$critical_section..with..Guard$GT$::hfa034e0208e1a49d in libbevy_tasks-53c9db6a3865f250.rlib[48](bevy_tasks-53c9db6a3865f250.d9dwgpd0156zfn2h5z5ff94zn.rcgu.o)
ld: symbol(s) not found for architecture arm64
clang: error: linker command failed with exit code 1 (use -v to see invocation)
```
## Solution
- enable `std` when building bevy_dylib
---------
Co-authored-by: Zachary Harrold <zac@harrold.com.au>
# Objective
- `collect_path` is only declared when feature `bevy_animation` is
enabled
- it is imported without checking for the feature, not compiling when
not enabled
## Solution
- Gate the import
# Objective
I was looking over a PR yesterday, and got confused by the docs on
deferred world. I thought I would add a little more detail to the struct
in order to clarify it a little.
## Solution
Document some more about deferred worlds.
# Objective
@cart noticed some issues with my work in
https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/17348#discussion_r2001815637,
which I somehow missed before merging the PR.
## Solution
- feature gate the UiPickingPlugin correctly
- don't manually add the picking plugins
## Testing
Ran the debug_picking and sprite_picking examples (for UI and sprites
respectively): both seem to work fine.
# Objective
The resources were converted via `clone_reflect_value` and the cloned
value was mapped. But the value that is inserted is the source of the
clone, which was not mapped.
I ran into this issue while working on #18380. Having non consecutive
entity allocations has caught a lot of bugs.
## Solution
Use the cloned value for insertion if it exists.
# Objective
- ECS error handling is a lovely flagship feature for Bevy 0.16, all in
the name of reducing panics and encouraging better error handling
(#14275).
- Currently though, command and system error handling are completely
disjoint and use different mechanisms.
- Additionally, there's a number of distinct ways to set the
default/fallback/global error handler that have limited value. As far as
I can tell, this will be cfg flagged to toggle between dev and
production builds in 99.9% of cases, with no real value in more granular
settings or helpers.
- Fixes#17272
## Solution
- Standardize error handling on the OnceLock global error mechanisms
ironed out in https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/17215
- As discussed there, there are serious performance concerns there,
especially for commands
- I also think this is a better fit for the use cases, as it's truly
global
- Move from `SystemErrorContext` to a more general purpose
`ErrorContext`, which can handle observers and commands more clearly
- Cut the superfluous setter methods on `App` and `SubApp`
- Rename the limited (and unhelpful) `fallible_systems` example to
`error_handling`, and add an example of command error handling
## Testing
Ran the `error_handling` example.
## Notes for reviewers
- Do you see a clear way to allow commands to retain &mut World access
in the per-command custom error handlers? IMO that's a key feature here
(allowing the ad-hoc creation of custom commands), but I'm not sure how
to get there without exploding complexity.
- I've removed the feature gate on the default_error_handler: contrary
to @cart's opinion in #17215 I think that virtually all apps will want
to use this. Can you think of a category of app that a) is extremely
performance sensitive b) is fine with shipping to production with the
panic error handler? If so, I can try to gather performance numbers
and/or reintroduce the feature flag. UPDATE: see benches at the end of
this message.
- ~~`OnceLock` is in `std`: @bushrat011899 what should we do here?~~
- Do you have ideas for more automated tests for this collection of
features?
## Benchmarks
I checked the impact of the feature flag introduced: benchmarks might
show regressions. This bears more investigation. I'm still skeptical
that there are users who are well-served by a fast always panicking
approach, but I'm going to re-add the feature flag here to avoid
stalling this out.

---------
Co-authored-by: Zachary Harrold <zac@harrold.com.au>
# Objective
Currently, our picking backends are inconsistent:
- Mesh picking and sprite picking both have configurable opt in/out
behavior. UI picking does not.
- Sprite picking uses `SpritePickingCamera` and `Pickable` for control,
but mesh picking uses `RayCastPickable`.
- `MeshPickingPlugin` is not a part of `DefaultPlugins`.
`SpritePickingPlugin` and `UiPickingPlugin` are.
## Solution
- Add configurable opt in/out behavior to UI picking (defaults to opt
out).
- Replace `RayCastPickable` with `MeshPickingCamera` and `Pickable`.
- Remove `SpritePickingPlugin` and `UiPickingPlugin` from
`DefaultPlugins`.
## Testing
Ran some examples.
## Migration Guide
`UiPickingPlugin` and `SpritePickingPlugin` are no longer included in
`DefaultPlugins`. They must be explicitly added.
`RayCastPickable` has been replaced in favor of the `MeshPickingCamera`
and `Pickable` components. You should add them to cameras and entities,
respectively, if you have `MeshPickingSettings::require_markers` set to
`true`.
---------
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
# Objective
Fixes https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/18366 which seems to
have a similar underlying cause than the already closed (but not fixed)
https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/16185.
## Solution
For Windows with the AMD vulkan driver, there was already a hack to
force serial command encoding, which prevented these issues. The Linux
version of the AMD vulkan driver seems to have similar issues than its
Windows counterpart, so I extended the hack to also cover AMD on Linux.
I also removed the mention of `wgpu` since it was already outdated, and
doesn't seem to be relevant to the core issue (the AMD driver being
buggy).
## Testing
- Did you test these changes? If so, how?
- I ran the `3d_scene` example, which on `main` produced the flickering
shadows on Linux with the amdvlk driver, while it no longer does with
the workaround applied.
- Are there any parts that need more testing?
- Not sure.
- How can other people (reviewers) test your changes? Is there anything
specific they need to know?
- Requires a Linux system with an AMD card and the AMDVLK driver.
- If relevant, what platforms did you test these changes on, and are
there any important ones you can't test?
- My change should only affect Linux, where I did test it.
# Objective
- #17219 introduced a circular dependency between bevy_image and
bevy_sprite for documentation
## Solution
- Remove the circular dependency
- Simplify the doc example
# Objective
Fixes#18357
## Solution
Generalize `RelationshipInsertHookMode` to `RelationshipHookMode`, wire
it up to on_replace execution, and use it in the
`Relationship::on_replace` hook.
# Objective
- https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/17887 introduced a circular
dependency between bevy_image and bevy_core_pipeline
- This makes it impossible to publish Bevy
## Solution
- Remove the circular dependency, reintroduce the compilation failure
- This failure shouldn't be an issue for users of Bevy, only for users
of subcrates, and can be workaround
- Proper fix should be done with
https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/17891
- Limited compilation failure is better than publish failure
# Objective
Extract sprites into a `Vec` instead of a `HashMap`.
## Solution
Extract UI nodes into a `Vec` instead of an `EntityHashMap`.
Add an index into the `Vec` to `Transparent2d`.
Compare both the index and render entity in prepare so there aren't any
collisions.
## Showcase
yellow this PR, red main
```
cargo run --example many_sprites --release --features "trace_tracy"
```
`extract_sprites`
<img width="452" alt="extract_sprites"
src="https://github.com/user-attachments/assets/66c60406-7c2b-4367-907d-4a71d3630296"
/>
`queue_sprites`
<img width="463" alt="queue_sprites"
src="https://github.com/user-attachments/assets/54b903bd-4137-4772-9f87-e10e1e050d69"
/>
---------
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
# Objective
- Fixes#17506
- Fixes#16258
## Solution
- Added a new folder of examples, `no_std`, similar to the `mobile`
folder.
- Added a single example, `no_std_library`, which demonstrates how to
make a `no_std` compatible Bevy library.
- Added a new CI task, `check-compiles-no-std-examples`, which checks
that `no_std` examples compile on `no_std` targets.
- Added `bevy_platform_support::prelude` to `bevy::prelude`.
## Testing
- CI
---
## Notes
- I've structured the folders here to permit further `no_std` examples
(e.g., GameBoy Games, ESP32 firmware, etc.), but I am starting with the
simplest and least controversial example.
- I've tried to be as clear as possible with the documentation for this
example, catering to an audience who may not have even heard of `no_std`
before.
---------
Co-authored-by: Greeble <166992735+greeble-dev@users.noreply.github.com>
# Objective
I experienced an issue where `HashMap::new` was not returning a value
typed appropriately for a `HashMap<K,V>` declaration that omitted the
Hasher- e.g. the Default Hasher for the type is different than what the
`new` method produces.
After discussion on discord, this appears to be an issue in `hashbrown`,
and working around it would be very nontrivial, requiring a newtype on
top of the `hashbrown` implementation. Rather than doing that, it was
suggested that we add docs to make the issue more visible and provide a
clear workaround.
## Solution
Updated the docs for `bevy_platform_support::collections`. I couldn't
update Struct docs because they're re-exports, so I had to settle for
the module.
Note that the `[HashMap::new]` link wasn't generating properly- I'm not
sure why. I see the method in the docs.rs site,
https://docs.rs/hashbrown/0.15.1/hashbrown/struct.HashMap.html#method.new,
but not on the generated internal documentation. I wonder if `hashbrown`
isn't actually implementing the new or something?
## Testing
n/a although I did generate and open the docs on my Ubuntu machine.
---
## Showcase
before:

after:

---------
Co-authored-by: Zachary Harrold <zac@harrold.com.au>
# Objective
WESL was broken on windows.
## Solution
- Upgrade to `wesl_rs` 1.2.
- Fix path handling on windows.
- Improve example for khronos demo this week.
# Objective
- #17581 broke gizmos
- Fixes#18325
## Solution
- Revert #17581
- Add gizmos to testbed
## Testing
- Run any example with gizmos, it renders correctly
# Objective
On iOS:
- Allow `std` to do its runtime initialization.
- Avoid requiring the user to specify linked libraries and framework in
Xcode.
- Reduce the amount of work that `#[bevy_main]` does
- In the future we may also be able to eliminate the need for it on
Android, cc @daxpedda.
## Solution
We previously:
- Exposed an `extern "C" fn main_rs` entry point.
- Ran Cargo in a separate Xcode target as an external build system.
- Imported that as a dependency of `bevy_mobile_example.app`.
- Compiled a trampoline C file with Xcode that called `main_rs`.
- Linked that via. Xcode.
All of this is unnecessary; `rustc` is well capable of creating iOS
executables, the trick is just to place it at the correct location for
Xcode to understand it, namely `$TARGET_BUILD_DIR/$EXECUTABLE_PATH`
(places it in `bevy_mobile_example.app/bevy_mobile_example`).
Note: We might want to wait with the changes to `#[bevy_main]` until the
problem is resolved on Android too, to make the migration easier.
## Testing
Open the Xcode project, and build for an iOS target.
---
## Migration Guide
**If you have been building your application for iOS:**
Previously, the `#[bevy_main]` attribute created a `main_rs` entry point
that most Xcode templates were using to run your Rust code from C. This
was found to be unnecessary, as you can simply let Rust build your
application as a binary, and run that directly.
You have two options for dealing with this:
If you've added further C code and Xcode customizations, or it makes
sense for your use-case to continue link with Xcode, you can revert to
the old behaviour by adding `#[no_mangle] extern "C" main_rs() { main()
}` to your `main.rs`. Note that the old approach of linking a static
library prevents the Rust standard library from doing runtime
initialization, so certain functionality provided by `std` might be
unavailable (stack overflow handlers, stdout/stderr flushing and other
such functionality provided by the initialization routines).
The other, preferred option is to remove your "compile" and "link" build
phases, and instead replace it with a "run script" phase that invokes
`cargo build --bin ...`, and moves the built binary to the Xcode path
`$TARGET_BUILD_DIR/$EXECUTABLE_PATH`. An example of how to do this can
be viewed at [INSERT LINK TO UPDATED EXAMPLE PROJECT].
To make the debugging experience in Xcode nicer after this, you might
also want to consider either enabling `panic = "abort"` or to set a
breakpoint on the `rust_panic` symbol.
---------
Co-authored-by: François Mockers <mockersf@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: François Mockers <francois.mockers@vleue.com>
# Objective
As pointed out by @cart on
[Discord](https://discord.com/channels/691052431525675048/1002362493634629796/1351279139872571462),
we should be careful when using tuple shorthand to register types. Doing
so incurs some unnecessary penalties such as memory/compile/performance
cost to generate registrations for a tuple type that will never be used.
A better solution would be to create a custom lint for this, but for now
we can at least remove the existing usages of this pattern.
> [!note]
> This pattern of using tuples to register multiple types at once isn't
inherently bad. Users should feel free to use this pattern, knowing the
side effects it may have. What this problem really is about is using
this in _library_ code, where users of Bevy have no choice in whether a
tuple is unnecessarily registered in an internal plugin or not.
## Solution
Replace tuple registrations with single-type registrations.
Note that I left the tuple registrations in test code since I feel like
brevity is more important in those cases. But let me know if I should
change them or leave a comment above them!
## Testing
You can test locally by running:
```
cargo check --workspace --all-features
```
# Objective
FilteredResource::get should return a Result instead of Option
Fixes#17480
---
## Migration Guide
Users will need to handle the different return type on
FilteredResource::get, FilteredResource::get_id,
FilteredResource::get_mut as it is now a Result not an Option.
# Objective
Continuation of #17449.
#17449 implemented the wrapper types around `IndexMap`/`Set` and co.,
however punted on the slice types.
They are needed to support creating `EntitySetIterator`s from their
slices, not just the base maps and sets.
## Solution
Add the wrappers, in the same vein as #17449 and #17589 before.
The `Index`/`IndexMut` implementations take up a lot of space, however
they cannot be merged because we'd then get overlaps.
They are simply named `Slice` to match the `indexmap` naming scheme, but
this means they cannot be differentiated properly until their modules
are made public, which is already a follow-up mentioned in #17954.
# Objective
Now that #13432 has been merged, it's important we update our reflected
types to properly opt into this feature. If we do not, then this could
cause issues for users downstream who want to make use of
reflection-based cloning.
## Solution
This PR is broken into 4 commits:
1. Add `#[reflect(Clone)]` on all types marked `#[reflect(opaque)]` that
are also `Clone`. This is mandatory as these types would otherwise cause
the cloning operation to fail for any type that contains it at any
depth.
2. Update the reflection example to suggest adding `#[reflect(Clone)]`
on opaque types.
3. Add `#[reflect(clone)]` attributes on all fields marked
`#[reflect(ignore)]` that are also `Clone`. This prevents the ignored
field from causing the cloning operation to fail.
Note that some of the types that contain these fields are also `Clone`,
and thus can be marked `#[reflect(Clone)]`. This makes the
`#[reflect(clone)]` attribute redundant. However, I think it's safer to
keep it marked in the case that the `Clone` impl/derive is ever removed.
I'm open to removing them, though, if people disagree.
4. Finally, I added `#[reflect(Clone)]` on all types that are also
`Clone`. While not strictly necessary, it enables us to reduce the
generated output since we can just call `Clone::clone` directly instead
of calling `PartialReflect::reflect_clone` on each variant/field. It
also means we benefit from any optimizations or customizations made in
the `Clone` impl, including directly dereferencing `Copy` values and
increasing reference counters.
Along with that change I also took the liberty of adding any missing
registrations that I saw could be applied to the type as well, such as
`Default`, `PartialEq`, and `Hash`. There were hundreds of these to
edit, though, so it's possible I missed quite a few.
That last commit is **_massive_**. There were nearly 700 types to
update. So it's recommended to review the first three before moving onto
that last one.
Additionally, I can break the last commit off into its own PR or into
smaller PRs, but I figured this would be the easiest way of doing it
(and in a timely manner since I unfortunately don't have as much time as
I used to for code contributions).
## Testing
You can test locally with a `cargo check`:
```
cargo check --workspace --all-features
```
# Objective
Add a `UiRect::AUTO` const which is a `UiRect` with all its edge values
set to `Val::Auto`.
IIRC `UiRect`'s default for its fields a few versions ago was
`Val::Auto` because positions were represented using a `UiRect` and they
required `Val::Auto` as a default. Then when position was split up and
the `UiRect` default was changed, we forgot add a `UiRect::AUTO` const.
Extracted from my DLSS branch.
## Changelog
* Added `source_texture` and `destination_texture` to
`PostProcessWrite`, in addition to the existing texture views.
obtaining a reference to an empty enum is not possible in Rust, so I
just replaced any match on self with an `unreachable!()`
I checked if an enum is empty by checking if the `variant_patterns` vec
of the `EnumVariantOutputData` struct is empty
Fixes#18277
## Testing
I added one new unit test.
``` rust
#[test]
fn should_allow_empty_enums() {
#[derive(Reflect)]
enum Empty {}
assert_impl_all!(Empty: Reflect);
}
```
# Objective
In its existing form, the clamping that's done in `camera_system`
doesn't work well when the `physical_position` of the associated
viewport is nonzero. In such cases, it may produce invalid viewport
rectangles (i.e. not lying inside the render target), which may result
in crashes during the render pass.
The goal of this PR is to eliminate this possibility by making the
clamping behavior always result in a valid viewport rectangle when
possible.
## Solution
Incorporate the `physical_position` information into the clamping
behavior. In particular, always cut off enough so that it's contained in
the render target rather than clamping it to the same dimensions as the
target itself. In weirder situations, still try to produce a valid
viewport rectangle to avoid crashes.
## Testing
Tested these changes on my work branch where I encountered the crash.
# Objective
Currently experimenting with manually implementing
`Relationship`/`RelationshipTarget` to support associated edge data,
which means I need to replace the default hook implementations provided
by those traits. However, copying them over for editing revealed that
`UnsafeWorldCell::get_raw_command_queue` is `pub(crate)`, and I would
like to not have to clone the source collection, like the default impl.
So instead, I've taken to providing a safe abstraction for being able to
access entities and queue commands simultaneously.
## Solution
Added `World::entities_and_commands` and
`DeferredWorld::entities_and_commands`, which can be used like so:
```rust
let eid: Entity = /* ... */;
let (mut fetcher, mut commands) = world.entities_and_commands();
let emut = fetcher.get_mut(eid).unwrap();
commands.entity(eid).despawn();
```
## Testing
- Added a new test for each of the added functions.
---------
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
# Objective
Continuation to #16547 and #17954.
The `get_many` family are the last methods on `Query`/`QueryState` for
which we're still missing a `unique` version.
## Solution
Offer `get_many_unique`/`get_many_unique_mut` and
`get_many_unique_inner`!
Their implementation is the same as `get_many`, the difference lies in
their guaranteed-to-be unique inputs, meaning we never do any aliasing
checks.
To reduce confusion, we also rename `get_many_readonly` into
`get_many_inner` and the current `get_many_inner` into
`get_many_mut_inner` to clarify their purposes.
## Testing
Doc examples.
## Migration Guide
`get_many_inner` is now called `get_many_mut_inner`.
`get_many_readonly` is now called `get_many_inner`.
# Objective
- Fixes#18342.
## Solution
- Canonicalize the root path so that when we try to strip the prefix, it
matches the canonicalized asset path.
- This is basically just a followup to #18023.
## Testing
- Ran the hot_asset_reloading example and it no longer panics.
# Objective
The `ViewportConversionError` error type does not implement `Error`,
making it incompatible with `BevyError`.
## Solution
Derive `Error` for `ViewportConversionError`.
I chose to use `thiserror` since it's already a dependency, but do let
me know if we should be preferring `derive_more`.
## Testing
You can test this by trying to compile the following:
```rust
let error: BevyError = ViewportConversionError::InvalidData.into();
```
Registering dynamic bundles was not possible for the user yet.
It is alone not very useful though as there are no methods to clone,
move or remove components via a `BundleId`. This could be a follow-up
work if this PR is approved and such a third (besides `T: Bundle` and
`ComponentId`(s)) API for structural operation is desired. I certainly
would use a hypothetical `EntityClonerBuilder::allow_by_bundle_id`.
I personally still would like this register method because I have a
`Bundles`-like custom data structure and I would like to not reinvent
the wheel. Then instead of having boxed `ComponentId` slices in my
collection I could look up explicit and required components there.
For reference scroll up to the typed version right above the new one.
# Objective
I was setting up an asset loader that passes settings through to
`ImageLoader`, and i have to clone the settings to achieve this.
## Solution
Derive `Clone` for `ImageLoaderSettings` and `ImageFormatSetting`.
## Testing
Full CI passed.
I mistakenly thought that with the wgpu upgrade we'd have
`PARTIALLY_BOUND_BINDING_ARRAY` everywhere. Unfortunately this is not
the case. This PR adds a workaround back in.
Closes#18098.
Fix https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/17763.
Attachment info needs to be created outside of the command encoding
task, as it needs to be part of the serial node runners in order to get
the ordering correct.
Less data accessed and compared gives better batching performance.
# Objective
- Use a smaller id to represent the lightmap in batch data to enable a
faster implementation of draw streams.
- Improve batching performance for 3D sorted render phases.
## Solution
- 3D batching can use `LightmapSlabIndex` (a `NonMaxU32` which is 4
bytes) instead of the lightmap `AssetId<Image>` (an enum where the
largest variant is a 16-byte UUID) to discern the ability to batch.
## Testing
Tested main (yellow) vs this PR (red) on an M4 Max using the
`many_cubes` example with `WGPU_SETTINGS_PRIO=webgl2` to avoid
GPU-preprocessing, and modifying the materials in `many_cubes` to have
`AlphaMode::Blend` so that they would rely on the less efficient sorted
render phase batching.
<img width="1500" alt="Screenshot_2025-03-15_at_12 17 21"
src="https://github.com/user-attachments/assets/14709bd3-6d06-40fb-aa51-e1d2d606ebe3"
/>
A 44.75us or 7.5% reduction in median execution time of the batch and
prepare sorted render phase system for the `Transparent3d` phase
(handling 160k cubes).
---
## Migration Guide
- Changed: `RenderLightmap::new()` no longer takes an `AssetId<Image>`
argument for the asset id of the lightmap image.
# Objective
Installment of the #16547 series.
The vast majority of uses for these types will be the `Entity` case, so
it makes sense for it to be the default.
## Solution
`UniqueEntityVec`, `UniqueEntitySlice`, `UniqueEntityArray` and their
helper iterator aliases now have `Entity` as a default.
Unfortunately, this means the the `T` parameter for `UniqueEntityArray`
now has to be ordered after the `N` constant, which breaks the
consistency to `[T; N]`.
Same with about a dozen iterator aliases that take some `P`/`F`
predicate/function parameter.
This should however be an ergonomic improvement in most cases, so we'll
just have to live with this inconsistency.
## Migration Guide
Switch type parameter order for the relevant wrapper types/aliases.
# Objective
#13432 added proper reflection-based cloning. This is a better method
than cloning via `clone_value` for reasons detailed in the description
of that PR. However, it may not be immediately apparent to users why one
should be used over the other, and what the gotchas of `clone_value`
are.
## Solution
This PR marks `PartialReflect::clone_value` as deprecated, with the
deprecation notice pointing users to `PartialReflect::reflect_clone`.
However, it also suggests using a new method introduced in this PR:
`PartialReflect::to_dynamic`.
`PartialReflect::to_dynamic` is essentially a renaming of
`PartialReflect::clone_value`. By naming it `to_dynamic`, we make it
very obvious that what's returned is a dynamic type. The one caveat to
this is that opaque types still use `reflect_clone` as they have no
corresponding dynamic type.
Along with changing the name, the method is now optional, and comes with
a default implementation that calls out to the respective reflection
subtrait method. This was done because there was really no reason to
require manual implementors provide a method that almost always calls
out to a known set of methods.
Lastly, to make this default implementation work, this PR also did a
similar thing with the `clone_dynamic ` methods on the reflection
subtraits. For example, `Struct::clone_dynamic` has been marked
deprecated and is superseded by `Struct::to_dynamic_struct`. This was
necessary to avoid the "multiple names in scope" issue.
### Open Questions
This PR maintains the original signature of `clone_value` on
`to_dynamic`. That is, it takes `&self` and returns `Box<dyn
PartialReflect>`.
However, in order for this to work, it introduces a panic if the value
is opaque and doesn't override the default `reflect_clone`
implementation.
One thing we could do to avoid the panic would be to make the conversion
fallible, either returning `Option<Box<dyn PartialReflect>>` or
`Result<Box<dyn PartialReflect>, ReflectCloneError>`.
This makes using the method a little more involved (i.e. users have to
either unwrap or handle the rare possibility of an error), but it would
set us up for a world where opaque types don't strictly need to be
`Clone`. Right now this bound is sort of implied by the fact that
`clone_value` is a required trait method, and the default behavior of
the macro is to use `Clone` for opaque types.
Alternatively, we could keep the signature but make the method required.
This maintains that implied bound where manual implementors must provide
some way of cloning the value (or YOLO it and just panic), but also
makes the API simpler to use.
Finally, we could just leave it with the panic. It's unlikely this would
occur in practice since our macro still requires `Clone` for opaque
types, and thus this would only ever be an issue if someone were to
manually implement `PartialReflect` without a valid `to_dynamic` or
`reflect_clone` method.
## Testing
You can test locally using the following command:
```
cargo test --package bevy_reflect --all-features
```
---
## Migration Guide
`PartialReflect::clone_value` is being deprecated. Instead, use
`PartialReflect::to_dynamic` if wanting to create a new dynamic instance
of the reflected value. Alternatively, use
`PartialReflect::reflect_clone` to attempt to create a true clone of the
underlying value.
Similarly, the following methods have been deprecated and should be
replaced with these alternatives:
- `Array::clone_dynamic` → `Array::to_dynamic_array`
- `Enum::clone_dynamic` → `Enum::to_dynamic_enum`
- `List::clone_dynamic` → `List::to_dynamic_list`
- `Map::clone_dynamic` → `Map::to_dynamic_map`
- `Set::clone_dynamic` → `Set::to_dynamic_set`
- `Struct::clone_dynamic` → `Struct::to_dynamic_struct`
- `Tuple::clone_dynamic` → `Tuple::to_dynamic_tuple`
- `TupleStruct::clone_dynamic` → `TupleStruct::to_dynamic_tuple_struct`
# Objective
- Prevents #18291.
- Previously, attempting to direct-nested-load a subasset would return
the root of the nested-loaded asset. This is most problematic when doing
direct-nested-**untyped**-loads of subassets, where you may not even
realize you're dealing with the entirely wrong asset (at least with
typed loads, *most of the time* the root asset has a different type from
the subasset, and so at least you'd get an error that the types don't
match).
## Solution
- We now return an error when doing these kinds of loads.
Note an alternative would be to "solve" this problem, by just looking up
the appropriate subasset after doing the nested load. However there's
two problems: 1) we don't know which subassets of the root asset are
necessary for the subasset we are looking up (so any handles in that
subasset may never get registered), 2) a solution will likely hamper
attempts to resolve#18010. AFAICT, no one has complained about this
issue, so it doesn't seem critical to fix this for now.
## Testing
- Added a test to ensure this returns an error. I also checked that the
error before this was just a mismatched type error, meaning it was
trying to pass off the root asset type `CoolText` as the subasset type
`SubText` (which would have worked had I not been using typed loads).
# Objective
While poking at https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/17272, I
noticed a few small things to clean up.
## Solution
- Improve the docs
- ~~move `SystemErrorContext` out of the `handler.rs` module: it's not
an error handler~~
# Objective
Probably just because of an oversight, bounding primitives like `Aabb3d`
did not implement `Serialize`/`Deserialize` with the `serialize` feature
enabled, so the goal of this PR is to fill the gap.
## Solution
Derive it conditionally, just like we do for everything else. Also added
in `PartialEq`, just because I touched the files.
## Testing
Compiled with different feature combinations.
# Objective
When reviewing #18263, I noticed that `BevyManifest` internally stores a
`DocumentMut`, a mutable TOML document, instead of an `ImDocument`, an
immutable one. The process of creating a `DocumentMut` first involves
creating a `ImDocument` and then cloning all the referenced spans of
text into their own allocations (internally referred to as `despan` in
`toml_edit`). As such, using a `DocumentMut` without mutation is
strictly additional overhead.
In addition, I noticed that the filesystem operations associated with
reading a manifest and parsing it were written to be completed _while_ a
write-lock was held on `MANIFESTS`. This likely doesn't translate into a
performance or deadlock issue as the manifest files are generally small
and can be read quickly, but it is generally considered a bad practice.
## Solution
- Switched to `ImDocument<Box<str>>` instead of `DocumentMut`
- Re-ordered operations in `BevyManifest::shared` to minimise time spent
holding open the write-lock on `MANIFESTS`
## Testing
- CI
---
## Notes
I wasn't able to measure a meaningful performance difference with this
PR, so this is purely a code quality change and not one for performance.
---------
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
# Objective
Upgrade to `cosmic-text` 0.13
https://github.com/pop-os/cosmic-text/releases
This should include some performance improvements for layout and system
font loading.
## Solution
Bump version, fix the one changed API.
## Testing
Tested some examples locally, will invoke the example runner.
## Layout Perf
||main fps|cosmic-13 fps|
|-|-|-|
|many_buttons --recompute-text --no-borders|6.79|9.42 🟩 +38.7%|
|many_text2d --no-frustum-culling --recompute|3.19|4.28 🟩 +34.0%|
|many_glyphs --recompute-text|7.09|11.17 🟩 +57.6%|
|text_pipeline |140.15|139.90 ⬜ -0.2%|
## System Font Loading Perf
I tested on macOS somewhat lazily by adding the following system to the
`system_fonts` example from #16365.
<details>
<summary>Expand code</summary>
```rust
fn exit_on_load(
mut reader: EventReader<bevy::text::SystemFontsAvailable>,
mut writer: EventWriter<AppExit>,
) {
for _evt in reader.read() {
writer.write(AppExit::Success);
}
}
```
</details>
And running `hyperfine 'cargo run --release --example system_fonts
--features=system_font'`.
The results were nearly identical with and without this PR cherry-picked
there.
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
# Objective
The sort key for the transparent UI phase is a (float32, u32) pair
consisting of the stack index and the render entity's index.
I guess the render entity index was intended to break ties but it's not
needed as the sort is stable. It also assumes the indices of the render
entities are generated sequentially, which isn't guaranteed.
Fixes the issues with the text wrap example seen in #18266
## Solution
Change the sort key to just use the stack index alone.
# Objective
Fixes#18103#17330 introduced a significant compile time performance regression
(affects normal builds, clippy, and Rust Analyzer). While it did fix the
type-resolution bug (and the general approach there is still our best
known solution to the problem that doesn't involve [significant
maintenance
overhead](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/18103#issuecomment-2702724676)),
the changes had a couple of issues:
1. It used a Mutex, which poses a significant threat to parallelization.
2. It externalized existing, relatively simple, performance critical
Bevy code to a crate outside of our control. I am not comfortable doing
that for cases like this. Going forward @bevyengine/maintainer-team
should be much stricter about this.
3. There were a number of other areas that introduced complexity and
overhead that I consider unnecessary for our use case. On a case by case
basis, if we encounter a need for more capabilities we can add them (and
weigh them against the cost of doing so).
## Solution
1. I moved us back to our original code as a baseline
2. I selectively ported over the minimal changes required to fix the
type resolution bug
3. I swapped `Mutex<BTreeMap<PathBuf, &'static Mutex<CargoManifest>>>`
for `RwLock<BTreeMap<PathBuf, CargoManifest>>`. Note that I used the
`parking_lot` RwLock because it has a mapping API that enables us to
return mapped guards.
# Objective
Prevents duplicate implementation between IntoSystemConfigs and
IntoSystemSetConfigs using a generic, adds a NodeType trait for more
config flexibility (opening the door to implement
https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/14195?).
## Solution
Followed writeup by @ItsDoot:
https://hackmd.io/@doot/rJeefFHc1x
Removes IntoSystemConfigs and IntoSystemSetConfigs, instead using
IntoNodeConfigs with generics.
## Testing
Pending
---
## Showcase
N/A
## Migration Guide
SystemSetConfigs -> NodeConfigs<InternedSystemSet>
SystemConfigs -> NodeConfigs<ScheduleSystem>
IntoSystemSetConfigs -> IntoNodeConfigs<InternedSystemSet, M>
IntoSystemConfigs -> IntoNodeConfigs<ScheduleSystem, M>
---------
Co-authored-by: Christian Hughes <9044780+ItsDoot@users.noreply.github.com>
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
# Objective
In updating examples to use the Improved Spawning API I got tripped up
on being able to spawn children with a Vec. I eventually figured out
that I could use `Children::spawn(SpawnIter(my_vec.into_iter()))` but
thought there might be a more ergonomic way to approach it. After
tinkering with it for a while I came up with the implementation here. It
allows authors to use `Children::spawn(my_vec)` as an equivalent
implementation.
## Solution
- Implements `<R: Relationship, B: Bundle SpawnableList<R> for Vec<B>`
- uses `alloc::vec::Vec` for compatibility with `no_std` (`std::Vec`
also inherits implementations against the `alloc::vec::Vec` because std
is a re-export of the alloc struct, thanks @bushrat011899 for the info
on this!)
## Testing
- Did you test these changes? If so, how?
- Opened the examples before and after and verified the same behavior
was observed. I did this on Ubuntu 24.04.2 LTS using `--features
wayland`.
- Are there any parts that need more testing?
- Other OS's and features can't hurt, but this is such a small change it
shouldn't be a problem.
- How can other people (reviewers) test your changes? Is there anything
specific they need to know?
- Run the examples yourself with and without these changes.
- If relevant, what platforms did you test these changes on, and are
there any important ones you can't test?
- see above
## Showcase
n/a
## Migration Guide
- Optional: you may use the new API to spawn `Vec`s of `Bundle` instead
of using the `SpawnIter` approach.
# Objective
Add `#[derive(Clone, PartialEq, Debug, Reflect)]` to DragEntry so it
matches the other picking events.
## Solution
Copy/paste (RIP Larry Tesler)
## Testing
Just ran cargo check. I don't believe this should break anything because
I did not remove any derives it had before.
---
# Objective
- Prevent usage of `println!`, `eprintln!` and the like because they
require `std`
- Fixes#17446
## Solution
- Enable the `print_stdout` and `print_stderr` clippy lints
- Replace all `println!` and `eprintln!` occurrences with `log::*` where
applicable or alternatively ignore the warnings
## Testing
- Run `cargo clippy --workspace` to ensure that there are no warnings
relating to printing to `stdout` or `stderr`
# Objective
Using `Reflect::clone_value` can be somewhat confusing to those
unfamiliar with how Bevy's reflection crate works. For example take the
following code:
```rust
let value: usize = 123;
let clone: Box<dyn Reflect> = value.clone_value();
```
What can we expect to be the underlying type of `clone`? If you guessed
`usize`, then you're correct! Let's try another:
```rust
#[derive(Reflect, Clone)]
struct Foo(usize);
let value: Foo = Foo(123);
let clone: Box<dyn Reflect> = value.clone_value();
```
What about this code? What is the underlying type of `clone`? If you
guessed `Foo`, unfortunately you'd be wrong. It's actually
`DynamicStruct`.
It's not obvious that the generated `Reflect` impl actually calls
`Struct::clone_dynamic` under the hood, which always returns
`DynamicStruct`.
There are already some efforts to make this a bit more apparent to the
end-user: #7207 changes the signature of `Reflect::clone_value` to
instead return `Box<dyn PartialReflect>`, signaling that we're
potentially returning a dynamic type.
But why _can't_ we return `Foo`?
`Foo` can obviously be cloned— in fact, we already derived `Clone` on
it. But even without the derive, this seems like something `Reflect`
should be able to handle. Almost all types that implement `Reflect`
either contain no data (trivially clonable), they contain a
`#[reflect_value]` type (which, by definition, must implement `Clone`),
or they contain another `Reflect` type (which recursively fall into one
of these three categories).
This PR aims to enable true reflection-based cloning where you get back
exactly the type that you think you do.
## Solution
Add a `Reflect::reflect_clone` method which returns `Result<Box<dyn
Reflect>, ReflectCloneError>`, where the `Box<dyn Reflect>` is
guaranteed to be the same type as `Self`.
```rust
#[derive(Reflect)]
struct Foo(usize);
let value: Foo = Foo(123);
let clone: Box<dyn Reflect> = value.reflect_clone().unwrap();
assert!(clone.is::<Foo>());
```
Notice that we didn't even need to derive `Clone` for this to work: it's
entirely powered via reflection!
Under the hood, the macro generates something like this:
```rust
fn reflect_clone(&self) -> Result<Box<dyn Reflect>, ReflectCloneError> {
Ok(Box::new(Self {
// The `reflect_clone` impl for `usize` just makes use of its `Clone` impl
0: Reflect::reflect_clone(&self.0)?.take().map_err(/* ... */)?,
}))
}
```
If we did derive `Clone`, we can tell `Reflect` to rely on that instead:
```rust
#[derive(Reflect, Clone)]
#[reflect(Clone)]
struct Foo(usize);
```
<details>
<summary>Generated Code</summary>
```rust
fn reflect_clone(&self) -> Result<Box<dyn Reflect>, ReflectCloneError> {
Ok(Box::new(Clone::clone(self)))
}
```
</details>
Or, we can specify our own cloning function:
```rust
#[derive(Reflect)]
#[reflect(Clone(incremental_clone))]
struct Foo(usize);
fn incremental_clone(value: &usize) -> usize {
*value + 1
}
```
<details>
<summary>Generated Code</summary>
```rust
fn reflect_clone(&self) -> Result<Box<dyn Reflect>, ReflectCloneError> {
Ok(Box::new(incremental_clone(self)))
}
```
</details>
Similarly, we can specify how fields should be cloned. This is important
for fields that are `#[reflect(ignore)]`'d as we otherwise have no way
to know how they should be cloned.
```rust
#[derive(Reflect)]
struct Foo {
#[reflect(ignore, clone)]
bar: usize,
#[reflect(ignore, clone = "incremental_clone")]
baz: usize,
}
fn incremental_clone(value: &usize) -> usize {
*value + 1
}
```
<details>
<summary>Generated Code</summary>
```rust
fn reflect_clone(&self) -> Result<Box<dyn Reflect>, ReflectCloneError> {
Ok(Box::new(Self {
bar: Clone::clone(&self.bar),
baz: incremental_clone(&self.baz),
}))
}
```
</details>
If we don't supply a `clone` attribute for an ignored field, then the
method will automatically return
`Err(ReflectCloneError::FieldNotClonable {/* ... */})`.
`Err` values "bubble up" to the caller. So if `Foo` contains `Bar` and
the `reflect_clone` method for `Bar` returns `Err`, then the
`reflect_clone` method for `Foo` also returns `Err`.
### Attribute Syntax
You might have noticed the differing syntax between the container
attribute and the field attribute.
This was purely done for consistency with the current attributes. There
are PRs aimed at improving this. #7317 aims at making the
"special-cased" attributes more in line with the field attributes
syntactically. And #9323 aims at moving away from the stringified paths
in favor of just raw function paths.
### Compatibility with Unique Reflect
This PR was designed with Unique Reflect (#7207) in mind. This method
actually wouldn't change that much (if at all) under Unique Reflect. It
would still exist on `Reflect` and it would still `Option<Box<dyn
Reflect>>`. In fact, Unique Reflect would only _improve_ the user's
understanding of what this method returns.
We may consider moving what's currently `Reflect::clone_value` to
`PartialReflect` and possibly renaming it to `partial_reflect_clone` or
`clone_dynamic` to better indicate how it differs from `reflect_clone`.
## Testing
You can test locally by running the following command:
```
cargo test --package bevy_reflect
```
---
## Changelog
- Added `Reflect::reflect_clone` method
- Added `ReflectCloneError` error enum
- Added `#[reflect(Clone)]` container attribute
- Added `#[reflect(clone)]` field attribute
# Objective
Part of the #16547 series.
The entity wrapper types often have some associated types an aliases
with them that cannot be re-exported into an outer module together.
Some helper types are best used with part of their path:
`bevy::ecs::entity::index_set::Slice` as `index_set::Slice`.
This has already been done for `entity::hash_set` and
`entity::hash_map`.
## Solution
Publicize the `index_set`, `index_map`, `unique_vec`, `unique_slice`,
and `unique_array` modules.
## Migration Guide
Any mention or import of types in the affected modules have to add the
respective module name to the import path.
F.e.:
`bevy::ecs::entity::EntityIndexSet` ->
`bevy::ecs::entity::index_set::EntityIndexSet`
# Objective
- #16883
- Improve the default behaviour of the exclusive fullscreen API.
## Solution
This PR changes the exclusive fullscreen window mode to require the type
`WindowMode::Fullscreen(MonitorSelection, VideoModeSelection)` and
removes `WindowMode::SizedFullscreen`. This API somewhat intentionally
more closely resembles Winit 0.31's upcoming fullscreen and video mode
API.
The new VideoModeSelection enum is specified as follows:
```rust
pub enum VideoModeSelection {
/// Uses the video mode that the monitor is already in.
Current,
/// Uses a given [`crate::monitor::VideoMode`]. A list of video modes supported by the monitor
/// is supplied by [`crate::monitor::Monitor::video_modes`].
Specific(VideoMode),
}
```
### Changing default behaviour
This might be contentious because it removes the previous behaviour of
`WindowMode::Fullscreen` which selected the highest resolution possible.
While the previous behaviour would be quite easy to re-implement as
additional options, or as an impl method on Monitor, I would argue that
this isn't an implementation that should be encouraged.
From the perspective of a Windows user, I prefer what the majority of
modern games do when entering fullscreen which is to preserve the OS's
current resolution settings, which allows exclusive fullscreen to be
entered faster, and to only have it change if I manually select it in
either the options of the game or the OS. The highest resolution
available is not necessarily what the user prefers.
I am open to changing this if I have just missed a good use case for it.
Likewise, the only functionality that `WindowMode::SizedFullscreen`
provided was that it selected the resolution closest to the current size
of the window so it was removed since this behaviour can be replicated
via the new `VideoModeSelection::Specific` if necessary.
## Out of scope
WindowResolution and scale factor act strangely in exclusive fullscreen,
this PR doesn't address it or regress it.
## Testing
- Tested on Windows 11 and macOS 12.7
- Linux untested
## Migration Guide
`WindowMode::SizedFullscreen(MonitorSelection)` and
`WindowMode::Fullscreen(MonitorSelection)` has become
`WindowMode::Fullscreen(MonitorSelection, VideoModeSelection)`.
Previously, the VideoMode was selected based on the closest resolution
to the current window size for SizedFullscreen and the largest
resolution for Fullscreen. It is possible to replicate that behaviour by
searching `Monitor::video_modes` and selecting it with
`VideoModeSelection::Specific(VideoMode)` but it is recommended to use
`VideoModeSelection::Current` as the default video mode when entering
fullscreen.
# Objective
While redoing #18058 I needed `RelationshipSourceCollection` (henceforth
referred to as the **Trait**) to implement `clear` so I added it.
## Solution
Add the `clear` method to the **Trait**.
Also make `add` and `remove` report if they succeeded.
## Testing
Eyeballs
---
## Showcase
The `RelationshipSourceCollection` trait now reports if adding or
removing an entity from it was successful.
It also not contains the `clear` method so you can easily clear the
collection in generic contexts.
## Changes
EDITED by Alice: We should get this into 0.16, so no migration guide
needed.
The `RelationshipSourceCollection` methods `add` and `remove` now need
to return a boolean indicating if they were successful (adding a entity
to a set that already contains it counts as failure). Additionally the
`clear` method has been added to support clearing the collection in
generic contexts.
_Note from BD103: this PR was adopted from #16148. The majority of this
PR's description is copied from the original._
# Objective
Adds tests to cover various mesh picking cases and removes sources of
panics.
It should prevent users being able to trigger panics in `bevy_picking`
code via bad mesh data such as #15891, and is a follow up to my comments
in [#15800
(review)](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/15800#pullrequestreview-2361694213).
This is motivated by #15979
## Testing
Adds 8 new tests to cover `ray_mesh_intersection` code.
## Changes from original PR
I reverted the changes to the benchmarks, since that was the largest
factor blocking it merging. I'll open a follow-up issue so that those
benchmark changes can be implemented.
---------
Co-authored-by: Trent <2771466+tbillington@users.noreply.github.com>
# Objective
- Allow for convenient access and mutation of color saturation providing
following the `Hue`, `Luminance` traits.
- `with_saturation()` builder method
- `saturation()` to get the saturation of a `Color`
- `set_saturation()` to set the saturation of a mutable `Color`
## Solution
- Defined `Saturation` trait in `color_ops.rs`
- Implemented `Saturation` on `Hsla` and `Hsva`
- Implemented `Saturation` on `Color` which proxies to other color space
impls.
- In the case of colorspaces which don't have native saturation
components
the color is converted to 'Hsla` internally
## Testing
- Empirically tested
---
## Showcase
```rust
fn next_golden(&mut self) -> Color {
self.current
.rotate_hue((1.0 / GOLDEN_RATIO) * 360.0)
.with_saturation(self.rand_saturation())
.with_luminance(self.rand_luminance())
.into()
}
```
---------
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
# Objective
I was recently exploreing `Entities` and stumbled on something strange.
`Entities::len` (the field) has the comment `Stores the number of free
entities for [`len`](Entities::len)`, refering to the method. But that
method says `The count of currently allocated entities.` Looking at the
code, the field's comment is wrong, and the public `len()` is correct.
Phew!
## Solution
So, I was just going to fix the comment, so it didn't confuse anyone
else, but as it turns out, we can just remove the field entirely. As a
bonus, this saves some book keeping work too. We can just calculate it
on the fly.
Also, add additional length methods and documentation for completeness.
These new length methods might be useful debug tools in the future.
---------
Co-authored-by: Chris Russell <8494645+chescock@users.noreply.github.com>
# Objective
Make component registration faster. This is a tinny, almost petty PR,
but it led to roughly 10% faster registration, according to my
benchmarks in #17871.
Up to y'all if we do this or not. It is completely unnecessary, but its
such low hanging fruit that I wanted to put it out there.
## Solution
Instead of cloning a `HashSet`, collect it into a `SmallVec`. Since this
is empty for many components, this saves a lot of allocation and hashing
work.
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
# Objective
This is an alternative to #17871 and #17701 for tracking issue #18155.
This thanks to @maniwani for help with this design.
The goal is to enable component ids to be reserved from multiple threads
concurrently and with only `&World`. This contributes to assets as
entities, read-only query and system parameter initialization, etc.
## What's wrong with #17871 ?
In #17871, I used my proposed staging utilities to allow *fully*
registering components from any thread concurrently with only
`&Components`. However, if we want to pursue components as entities
(which is desirable for a great many reasons. See
[here](https://discord.com/channels/691052431525675048/692572690833473578/1346499196655505534)
on discord), this staging isn't going to work. After all, if registering
a component requires spawning an entity, and spawning an entity requires
`&mut World`, it is impossible to register a component fully with only
`&World`.
## Solution
But what if we don't have to register it all the way? What if it's
enough to just know the `ComponentId` it will have once it is registered
and to queue it to be registered at a later time? Spoiler alert: That is
all we need for these features.
Here's the basic design:
Queue a registration:
1. Check if it has already been registered.
2. Check if it has already been queued.
3. Reserve a `ComponentId`.
4. Queue the registration at that id.
Direct (normal) registration:
1. Check if this registration has been queued.
2. If it has, use the queued registration instead.
3. Otherwise, proceed like normal.
Appllying the queue:
1. Pop queued items off one by one.
2. Register them directly.
One other change:
The whole point of this design over #17871 is to facilitate coupling
component registration with the World. To ensure that this would fully
work with that, I went ahead and moved the `ComponentId` generator onto
the world itself. That stemmed a couple of minor organizational changes
(see migration guide). As we do components as entities, we will replace
this generator with `Entities`, which lives on `World` too. Doing this
move early let me verify the design and will reduce migration headaches
in the future. If components as entities is as close as I think it is, I
don't think splitting this up into different PRs is worth it. If it is
not as close as it is, it might make sense to still do #17871 in the
meantime (see the risks section). I'll leave it up to y'all what we end
up doing though.
## Risks and Testing
The biggest downside of this compared to #17871 is that now we have to
deal with correct but invalid `ComponentId`s. They are invalid because
the component still isn't registered, but they are correct because, once
registered, the component will have exactly that id.
However, the only time this becomes a problem is if some code violates
safety rules by queuing a registration and using the returned id as if
it was valid. As this is a new feature though, nothing in Bevy does
this, so no new tests were added for it. When we do use it, I left
detailed docs to help mitigate issues here, and we can test those
usages. Ex: we will want some tests on using queries initialized from
queued registrations.
## Migration Guide
Component registration can now be queued with only `&World`. To
facilitate this, a few APIs needed to be moved around.
The following functions have moved from `Components` to
`ComponentsRegistrator`:
- `register_component`
- `register_component_with_descriptor`
- `register_resource_with_descriptor`
- `register_non_send`
- `register_resource`
- `register_required_components_manual`
Accordingly, functions in `Bundle` and `Component` now take
`ComponentsRegistrator` instead of `Components`.
You can obtain `ComponentsRegistrator` from the new
`World::components_registrator`.
You can obtain `ComponentsQueuedRegistrator` from the new
`World::components_queue`, and use it to stage component registration if
desired.
# Open Question
Can we verify that it is enough to queue registration with `&World`? I
don't think it would be too difficult to package this up into a
`Arc<MyComponentsManager>` type thing if we need to, but keeping this on
`&World` certainly simplifies things. If we do need the `Arc`, we'll
need to look into partitioning `Entities` for components as entities, so
we can keep most of the allocation fast on `World` and only keep a
smaller partition in the `Arc`. I'd love an SME on assets as entities to
shed some light on this.
---------
Co-authored-by: andriyDev <andriydzikh@gmail.com>
PR #17965 mistakenly made the `AsBindGroup` macro no longer emit a bind
group layout entry and a resource descriptor for buffers. This commit
adds that functionality back, fixing the `shader_material_bindless`
example.
Closes#18124.
# Objective
Fixes#18030
## Solution
When running a one-shot system, requeue the system's command queue onto
the world's command queue, then execute the later.
If running the entire command queue of the world is undesired, I could
add a new method to `RawCommandQueue` to only apply part of it.
## Testing
See the new test.
---
## Showcase
```rust
#[derive(Resource)]
pub struct Test {
id: SystemId,
counter: u32,
}
let mut world = World::new();
let id = world.register_system(|mut commands: Commands, mut test: ResMut<Test>| {
print!("{:?} ", test.counter);
test.counter -= 1;
if test.counter > 0 {
commands.run_system(test.id);
}
});
world.insert_resource(Test { id, counter: 5 });
world.run_system(id).unwrap();
```
```
5 4 3 2 1
```
# Objective
I found a bug while working on #17871. When required components are
registered, ones that are more specific (smaller inheritance depth) are
preferred to others. So, if a ComponentA is already required, but it is
registered as required again, it will be updated if and only if the new
requirement has a smaller inheritance depth (is more specific). However,
this logic was not reflected in merging `RequriedComponents`s together.
Hence, for complicated requirement trees, the wrong initializer could be
used.
## Solution
Re-write merging to work by extending the collection via
`require_dynamic` instead of blindly combining the inner storage.
## Testing
I created this test to ensure this bug doesn't creep back in. This test
fails on main, but passes on this branch.
```rs
#[test]
fn required_components_inheritance_depth_bias() {
#[derive(Component, PartialEq, Eq, Clone, Copy, Debug)]
struct MyRequired(bool);
#[derive(Component, Default)]
#[require(MyRequired(|| MyRequired(false)))]
struct MiddleMan;
#[derive(Component, Default)]
#[require(MiddleMan)]
struct ConflictingRequire;
#[derive(Component, Default)]
#[require(MyRequired(|| MyRequired(true)))]
struct MyComponent;
let mut world = World::new();
let order_a = world
.spawn((ConflictingRequire, MyComponent))
.get::<MyRequired>()
.cloned();
let order_b = world
.spawn((MyComponent, ConflictingRequire))
.get::<MyRequired>()
.cloned();
assert_eq!(order_a, Some(MyRequired(true)));
assert_eq!(order_b, Some(MyRequired(true)));
}
```
Note that when the inheritance depth is 0 (Like if there were no middle
man above), the order of the components in the bundle still matters.
## Migration Guide
`RequiredComponents::register_dynamic` has been changed to
`RequiredComponents::register_dynamic_with`.
Old:
```rust
required_components.register_dynamic(
component_id,
component_constructor.clone(),
requirement_inheritance_depth,
);
```
New:
```rust
required_components.register_dynamic_with(
component_id,
requirement_inheritance_depth,
|| component_constructor.clone(),
);
```
This can prevent unnecessary cloning.
---------
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Joona Aalto <jondolf.dev@gmail.com>
# Objective
Fix unsound lifetimes in `Query::join` and `Query::join_filtered`.
The joined query allowed access from either input query, but it only
took the `'world` lifetime from `self`, not from `other`. This meant
that after the borrow of `other` ended, the joined query would unsoundly
alias `other`.
## Solution
Change the lifetimes on `join` and `join_filtered` to require mutable
borrows of the *same* lifetime for the input queries. This ensures both
input queries are borrowed for the full lifetime of the joined query.
Change `join_inner` to take `other` by value instead of reference so
that the returned query is still usable without needing to borrow from a
local variable.
## Testing
Added a compile-fail test.
# Objective
`extract_text_shadows` was still using `UiTargetCamera` and
`DefaultUiCamera` for UI camera resolution, which no longer always
selects the right camera.
To see this modify the last lines of the `multiple_windows` example
from:
```rust
commands.spawn((
Text::new("First window"),
node.clone(),
// Since we are using multiple cameras, we need to specify which camera UI should be rendered to
UiTargetCamera(first_window_camera),
));
commands.spawn((
Text::new("Second window"),
node,
UiTargetCamera(second_window_camera),
));
```
to:
```rust
commands
.spawn((
node.clone(),
// Since we are using multiple cameras, we need to specify which camera UI should be rendered to
UiTargetCamera(first_window_camera),
))
.with_child((Text::new("First window"), TextShadow::default()));
commands
.spawn((node, UiTargetCamera(second_window_camera)))
.with_child((Text::new("Second window"), TextShadow::default()));
```
which results in the shadow that is meant to be displayed for the
"Second Window" label instead being written over the first:
<img width="800" alt="first_window_label"
src="https://github.com/user-attachments/assets/2eebccba-5749-4064-bb1c-e4f25ff0baf7">
## Solution
Remove the `UiTargetCamera` query and the `default_camera` parameter
from `extract_text_shadows` and use `UiCameraMap` with
`ComputedNodeTarget` instead.
## Testing
The `multiple_windows` example for this PR has been updated to add text
shadow to the window labels. You should see that it displays the "Second
Window" label's shadow correctly now.
# Objective
- In `Camera::viewport_to_world_2d`, `Camera::viewport_to_world`,
`Camera::world_to_viewport` and `Camera::world_to_viewport_with_depth`,
the results were incorrect when the `Camera::viewport` field was
configured with a viewport position that was non-zero. This PR attempts
to correct that.
- Fixes#16200
## Solution
- This PR now takes the viewport position into account in the functions
mentioned above.
- Extended `2d_viewport_to_world` example to test the functions with a
dynamic viewport position and size, camera positions and zoom levels. It
is probably worth discussing whether to change the example, add a new
one or just completely skip touching the examples.
## Testing
Used the modified example to test the functions with dynamic camera
transform as well as dynamic viewport size and position.
# Objective
This PR enables `bevy_gizmos` to be used without `bevy_pbr`, for user
who want to create their custom mesh rendering logic.
It can also be useful for user who just want to use bevy for drawing
lines (why not).
This work is part of a bigger effort to make the bevy rendering pipeline
more modular. I would like to contribute an exemple to render custom
meshes without `bevy_pbr`. Something like
[this](https://github.com/rambip/plant-mesh/blob/main/src/shader/mod.rs)
## Solution
Now, `bevy_pbr` is an optional dependency, and used only to debug
lights.
I query the `ViewUniforms` manually, instead of using `bevy_pbr` to get
the heavy `MeshViewLayout`
## Testing
I'm not used to testing with bevy at all, but I was able to use
successfully in my project.
It might break for some different mesh pipelines, but I don't think so.
---
## Showcase

So nice ...
## Migration Guide
I don't think there is any breaking change
# Remaining work
Before merging it, it would be useful to:
- rewrite the `pipeline_2d.rs` logic to remove the `bevy_sprite`
depedency too
- move `view.rs` to `bevy_render`, so that it can be used in a more
modular way.
~~- include the most recent changes from 0.16~~
---------
Co-authored-by: IceSentry <IceSentry@users.noreply.github.com>
# Objective
Make `bevy_error_panic_hook` threadsafe. As it relies on a global
variable, it fails when multiple threads panic.
## Solution
Switch from a global variable for storing whether an error message was
printed to a thread-local one.
`thread_local` is in `std`; the `backtrace` already relies on `std`
APIs. It didn't depend on the `std` feature though, so I've added that.
I've also put `bevy_error_panic_hook` behind the `backtrace` feature,
since it relies on the thread local variable, which fixes#18231.
## Testing
The following now loops instead of crashing:
```rust
std:🧵:scope(|s| {
use bevy_ecs::error::*;
#[derive(Debug)]
struct E;
impl std::fmt::Display for E {
fn fmt(&self, _: &mut std::fmt::Formatter<'_>) -> std::fmt::Result {
todo!()
}
}
impl std::error::Error for E {}
std::panic::set_hook(Box::new(bevy_error_panic_hook(|_| {
unreachable!();
})));
for _ in 0..2 {
s.spawn(|| {
loop {
let _ = std::panic::catch_unwind(|| {
panic!("{:?}", BevyError::from(E));
});
}
});
}
});
```
# Objective
Defocusing a window while a key is held (such as when Alt+tabbing), will
currently send a key release on X11 and Windows. This is likely the
behavior that most people expect.
However it's synthetic events from winit are unimplemented for WASM and
some other platforms. (See
https://github.com/rust-windowing/winit/issues/1272).
While we can implement it upstream, there is also some doubt about the
synthetic events API as a whole
(https://github.com/rust-windowing/winit/issues/3543), so I propose to
do it in bevy directly for now.
## Solution
This PR implements key tracking in bevy directly so we can synthesize
our own key release events across all platforms.
Note regarding X11 specifically:
- On `main`, pressing a keyboard shortcut to unfocus the window (`Ctrl +
Super + ArrowRight` in my case) will yield the following events:
```
Pressed Control
Pressed Super
Released Control
Released ArrowRight
Released Super
```
- On this branch, it will yield the following sequence:
```
Pressed Control
Pressed Super
Released Control
Released Super
```
To me the behavior of this branch is more expected than `main`, because
`main` produces an `ArrowRight` release without producing a press first.
## Testing
Tested in WASM and X11 with
```rust
App::new()
.add_plugins(DefaultPlugins)
.add_systems(Update, |mut keys: EventReader<KeyboardInput>| {
for ev in keys.read() {
error!("received {ev:?}");
}
})
.run();
```
# Objective
Because `prepare_assets::<T>` had a mutable reference to the
`RenderAssetBytesPerFrame` resource, no render asset preparation could
happen in parallel. This PR fixes this by using an `AtomicUsize` to
count bytes written (if there's a limit in place), so that the system
doesn't need mutable access.
- Related: https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/12622
**Before**
<img width="1049" alt="Screenshot 2025-02-17 at 11 40 53 AM"
src="https://github.com/user-attachments/assets/040e6184-1192-4368-9597-5ceda4b8251b"
/>
**After**
<img width="836" alt="Screenshot 2025-02-17 at 1 38 37 PM"
src="https://github.com/user-attachments/assets/95488796-3323-425c-b0a6-4cf17753512e"
/>
## Testing
- Tested on a local project (with and without limiting enabled)
- Someone with more knowledge of wgpu/underlying driver guts should
confirm that this doesn't actually bite us by introducing contention
(i.e. if buffer writing really *should be* serial).
# Objective
As pointed out in #18177 this line in the doc comment for
`UiTargetCamera`:
```
/// Optional if there is only one camera in the world. Required otherwise.
```
Is incorrect, `UiTargetCamera` component is only needed when you want to
display UI nodes using a camera other than the default camera.
## Solution
Change it to:
```
/// Root node's without an explicit [`UiTargetCamera`] will be rendered to the default UI camera,
/// which is either a single camera with the [`IsDefaultUiCamera`] marker component or the highest
/// order camera targeting the primary window.
```
# Objective
- Allow bevy and wgpu developers to test newer versions of wgpu without
having to update naga_oil.
## Solution
- Currently bevy feeds wgsl through naga_oil to get a naga::Module that
it passes to wgpu.
- Added a way to pass wgsl through naga_oil, and then serialize the
naga::Module back into a wgsl string to feed to wgpu, allowing wgpu to
parse it using it's internal version of naga (and not the version of
naga bevy_render/naga_oil is using).
## Testing
1. Run 3d_scene (it works)
2. Run 3d_scene with `--features bevy_render/decoupled_naga` (it still
works)
3. Add the following patch to bevy/Cargo.toml, run cargo update, and
compile again (it will fail)
```toml
[patch.crates-io]
wgpu = { git = "https://github.com/gfx-rs/wgpu", rev = "2764e7a39920e23928d300e8856a672f1952da63" }
wgpu-core = { git = "https://github.com/gfx-rs/wgpu", rev = "2764e7a39920e23928d300e8856a672f1952da63" }
wgpu-hal = { git = "https://github.com/gfx-rs/wgpu", rev = "2764e7a39920e23928d300e8856a672f1952da63" }
wgpu-types = { git = "https://github.com/gfx-rs/wgpu", rev = "2764e7a39920e23928d300e8856a672f1952da63" }
```
4. Fix errors and compile again (it will work, and you didn't have to
touch naga_oil)
# Objective
#17404 reworked the `Segment2d` and `Segment3d` types to be defined by
two endpoints rather than a direction and half-length. However, the API
is still very minimal and limited, and documentation is inconsistent and
outdated.
## Solution
Add the following helper methods for `Segment2d` and `Segment3d`:
- `from_scaled_direction`
- `from_ray_and_length`
- `length_squared`
- `direction`
- `try_direction`
- `scaled_direction`
- `transformed`
- `reversed`
`Segment2d` has a few 2D-specific methods:
- `left_normal`
- `try_left_normal`
- `scaled_left_normal`
- `right_normal`
- `try_right_normal`
- `scaled_right_normal`
There are now also `From` implementations for converting `[Vec2; 2]` and
`(Vec2, Vec2)` to a `Segment2d`, and similarly for 3D.
I have also updated documentation to be more accurate and consistent,
and simplified a few methods.
---
## Prior Art
Parry's
[`Segment`](https://docs.rs/parry2d/latest/parry2d/shape/struct.Segment.html)
type has a lot of similar methods, though my implementation is a bit
more comprehensive. A lot of these methods can be useful for various
geometry algorithms.
---------
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Greeble <166992735+greeble-dev@users.noreply.github.com>
# Overview
Fixes https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/17869.
# Summary
`WGPU_SETTINGS_PRIO` changes various limits on `RenderDevice`. This is
useful to simulate platforms with lower limits.
However, some plugins only check the limits on `RenderAdapter` (the
actual GPU) - these limits are not affected by `WGPU_SETTINGS_PRIO`. So
the plugins try to use features that are unavailable and wgpu says "oh
no". See https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/17869 for details.
The PR adds various checks on `RenderDevice` limits. This is enough to
get most examples working, but some are not fixed (see below).
# Testing
- Tested native, with and without "WGPU_SETTINGS=webgl2".
Win10/Vulkan/Nvidia".
- Also WebGL. Win10/Chrome/Nvidia.
```
$env:WGPU_SETTINGS_PRIO = "webgl2"
cargo run --example testbed_3d
cargo run --example testbed_2d
cargo run --example testbed_ui
cargo run --example deferred_rendering
cargo run --example many_lights
cargo run --example order_independent_transparency # Still broken, see below.
cargo run --example occlusion_culling # Still broken, see below.
```
# Not Fixed
While testing I found a few other cases of limits being broken.
"Compatibility" settings (WebGPU minimums) breaks native in various
examples.
```
$env:WGPU_SETTINGS_PRIO = "compatibility"
cargo run --example testbed_3d
In Device::create_bind_group_layout, label = 'build mesh uniforms GPU early occlusion culling bind group layout'
Too many bindings of type StorageBuffers in Stage ShaderStages(COMPUTE), limit is 8, count was 9. Check the limit `max_storage_buffers_per_shader_stage` passed to `Adapter::request_device`
```
`occlusion_culling` breaks fake webgl.
```
$env:WGPU_SETTINGS_PRIO = "webgl2"
cargo run --example occlusion_culling
thread '<unnamed>' panicked at C:\Projects\bevy\crates\bevy_render\src\render_resource\pipeline_cache.rs:555:28:
index out of bounds: the len is 0 but the index is 2
Encountered a panic in system `bevy_render::renderer::render_system`!
```
`occlusion_culling` breaks real webgl.
```
cargo run --example occlusion_culling --target wasm32-unknown-unknown
ERROR app: panicked at C:\Users\T\.cargo\registry\src\index.crates.io-1949cf8c6b5b557f\glow-0.16.0\src\web_sys.rs:4223:9:
Tex storage 2D multisample is not supported
```
OIT breaks fake webgl.
```
$env:WGPU_SETTINGS_PRIO = "webgl2"
cargo run --example order_independent_transparency
In Device::create_bind_group, label = 'mesh_view_bind_group'
Number of bindings in bind group descriptor (28) does not match the number of bindings defined in the bind group layout (25)
```
OIT breaks real webgl
```
cargo run --example order_independent_transparency --target wasm32-unknown-unknown
In Device::create_render_pipeline, label = 'pbr_oit_mesh_pipeline'
Error matching ShaderStages(FRAGMENT) shader requirements against the pipeline
Shader global ResourceBinding { group: 0, binding: 34 } is not available in the pipeline layout
Binding is missing from the pipeline layout
```
# Objective
- Allow `Query` methods such as `Query::get` to have their error
short-circuited using `?` in systems using Bevy's `Error` type
## Solution
- Removed `UnsafeWorldCell<'w>` from `QueryEntityError` and instead
store `ArchetypeId` (the information the error formatter was extracting
anyway).
- Replaced trait implementations with derives now that the type is
plain-old-data.
## Testing
- CI
---
## Migration Guide
- `QueryEntityError::QueryDoesNotMatch.1` is of type `ArchetypeId`
instead of `UnsafeWorldCell`. It is up to the caller to obtain an
`UnsafeWorldCell` now.
- `QueryEntityError` no longer has a lifetime parameter, remove it from
type signatures where required.
## Notes
This was discussed on Discord and accepted by Cart as the desirable path
forward in [this
message](https://discord.com/channels/691052431525675048/749335865876021248/1346611950527713310).
Scroll up from this point for context.
---------
Co-authored-by: SpecificProtagonist <30270112+SpecificProtagonist@users.noreply.github.com>
# Objective
- Optimize static scene performance by marking unchanged subtrees.
## Solution
- Mark hierarchy subtrees with dirty bits to avoid transform propagation
where not needed
- This causes a performance regression when spawning many entities, or
when the scene is entirely dynamic.
- This results in massive speedups for largely static scenes.
- In the future we could allow the user to change this behavior, or add
some threshold based on how dynamic the scene is?
## Testing
- Caldera Hotel scene
# Objective
WESL's pre-MVP `0.1.0` has been
[released](https://docs.rs/wesl/latest/wesl/)!
Add support for WESL shader source so that we can begin playing and
testing WESL, as well as aiding in their development.
## Solution
Adds a `ShaderSource::WESL` that can be used to load `.wesl` shaders.
Right now, we don't support mixing `naga-oil`. Additionally, WESL
shaders currently need to pass through the naga frontend, which the WESL
team is aware isn't great for performance (they're working on compiling
into naga modules). Also, since our shaders are managed using the asset
system, we don't currently support using file based imports like `super`
or package scoped imports. Further work will be needed to asses how we
want to support this.
---
## Showcase
See the `shader_material_wesl` example. Be sure to press space to
activate party mode (trigger conditional compilation)!
https://github.com/user-attachments/assets/ec6ad19f-b6e4-4e9d-a00f-6f09336b08a4
# Objective
- Fixes#18200
## Solution
- Ensure `bevy_utils` is included with `bevy_transform/std`
## Testing
- `cargo build --no-default-features --features std`
## Notes
Compilation failure was caused by `bevy_transform`'s new parallel
propagation system requiring `bevy_utils/std` when `bevy_transform/std`
was active, but it was left optional. Additionally,
`bevy_transform/async_executor` wasn't being enabled by
`bevy/async_executor`.
# Objective
Adds information about the byte length and index of a glyph to
`PositionedGlyph`. Useful for text picking, allows for picking with
multi-byte characters. Also adds a `line` field that helps with
converting back and forth from cosmic's `Cursor`.
## Solution
Retrieve the relevant data from cosmic and add it to the glyph in the
text pipeline.
## Testing
`cargo r -p ci`
---
## Migration Guide
`PositionedGlyph::new()` has been removed as there is no longer an
unused field. Create new `PositionedGlyph`s directly.
also updates Relationship docs terminology
# Objective
- Contributes to #18111
## Solution
Updates Component docs with a new section linking to Relationship. Also
updates some Relationship terminology as I understand it.
## Testing
- Did you test these changes? If so, how?
- opened Docs, verified link
- Are there any parts that need more testing?
- I don't think so
- How can other people (reviewers) test your changes? Is there anything
specific they need to know?
- run `cargo doc --open` and check out Component and Relationship docs,
verify their correctness
- If relevant, what platforms did you test these changes on, and are
there any important ones you can't test?
- I think this is n/a but I ran the doc command on Ubuntu 24.04.2 LTS
---
## Showcase

## Migration Guide
n/a
# Objective
- Contributes to #15460
- Supersedes #8520
- Fixes#4906
## Solution
- Added a new `web` feature to `bevy`, and several of its crates.
- Enabled new `web` feature automatically within crates without `no_std`
support.
## Testing
- `cargo build --no-default-features --target wasm32v1-none`
---
## Migration Guide
When using Bevy crates which _don't_ automatically enable the `web`
feature, please enable it when building for the browser.
## Notes
- I added [`cfg_if`](https://crates.io/crates/cfg-if) to help manage
some of the feature gate gore that this extra feature introduces. It's
still pretty ugly, but I think much easier to read.
- Certain `wasm` targets (e.g.,
[wasm32-wasip1](https://doc.rust-lang.org/nightly/rustc/platform-support/wasm32-wasip1.html#wasm32-wasip1))
provide an incomplete implementation for `std`. I have not tested these
platforms, but I suspect Bevy's liberal use of usually unsupported
features (e.g., threading) will cause these targets to fail. As such,
consider `wasm32-unknown-unknown` as the only `wasm` platform with
support from Bevy for `std`. All others likely will need to be treated
as `no_std` platforms.
Fixes#17170
# Objective
Tangents are not currently transformed as described in #17170. I came
across this while working on #17989 and it seemed like low hanging
fruit.
# Objective
- Fixes#15460 (will open new issues for further `no_std` efforts)
- Supersedes #17715
## Solution
- Threaded in new features as required
- Made certain crates optional but default enabled
- Removed `compile-check-no-std` from internal `ci` tool since GitHub CI
can now simply check `bevy` itself now
- Added CI task to check `bevy` on `thumbv6m-none-eabi` to ensure
`portable-atomic` support is still valid [^1]
[^1]: This may be controversial, since it could be interpreted as
implying Bevy will maintain support for `thumbv6m-none-eabi` going
forward. In reality, just like `x86_64-unknown-none`, this is a
[canary](https://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/canary_in_a_coal_mine) target to
make it clear when `portable-atomic` no longer works as intended (fixing
atomic support on atomically challenged platforms). If a PR comes
through and makes supporting this class of platforms impossible, then
this CI task can be removed. I however wager this won't be a problem.
## Testing
- CI
---
## Release Notes
Bevy now has support for `no_std` directly from the `bevy` crate.
Users can disable default features and enable a new `default_no_std`
feature instead, allowing `bevy` to be used in `no_std` applications and
libraries.
```toml
# Bevy for `no_std` platforms
bevy = { version = "0.16", default-features = false, features = ["default_no_std"] }
```
`default_no_std` enables certain required features, such as `libm` and
`critical-section`, and as many optional crates as possible (currently
just `bevy_state`). For atomically-challenged platforms such as the
Raspberry Pi Pico, `portable-atomic` will be used automatically.
For library authors, we recommend depending on `bevy` with
`default-features = false` to allow `std` and `no_std` users to both
depend on your crate. Here are some recommended features a library crate
may want to expose:
```toml
[features]
# Most users will be on a platform which has `std` and can use the more-powerful `async_executor`.
default = ["std", "async_executor"]
# Features for typical platforms.
std = ["bevy/std"]
async_executor = ["bevy/async_executor"]
# Features for `no_std` platforms.
libm = ["bevy/libm"]
critical-section = ["bevy/critical-section"]
[dependencies]
# We disable default features to ensure we don't accidentally enable `std` on `no_std` targets, for example.
bevy = { version = "0.16", default-features = false }
```
While this is verbose, it gives the maximum control to end-users to
decide how they wish to use Bevy on their platform.
We encourage library authors to experiment with `no_std` support. For
libraries relying exclusively on `bevy` and no other dependencies, it
may be as simple as adding `#![no_std]` to your `lib.rs` and exposing
features as above! Bevy can also provide many `std` types, such as
`HashMap`, `Mutex`, and `Instant` on all platforms. See
`bevy::platform_support` for details on what's available out of the box!
## Migration Guide
- If you were previously relying on `bevy` with default features
disabled, you may need to enable the `std` and `async_executor`
features.
- `bevy_reflect` has had its `bevy` feature removed. If you were relying
on this feature, simply enable `smallvec` and `smol_str` instead.
---------
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
# Objective
Alternative to and closes#18120.
Sibling to #18082, see that PR for broader reasoning.
Folks weren't sold on the name `many` (get_many is clearer, and this is
rare), and that PR is much more complex.
## Solution
- Simply deprecate `Query::many` and `Query::many_mut`
- Clean up internal usages
Mentions of this in the docs can wait until it's fully removed in the
0.17 cycle IMO: it's much easier to catch the problems when doing that.
## Testing
CI!
## Migration Guide
`Query::many` and `Query::many_mut` have been deprecated to reduce
panics and API duplication. Use `Query::get_many` and
`Query::get_many_mut` instead, and handle the `Result`.
---------
Co-authored-by: Chris Russell <8494645+chescock@users.noreply.github.com>
# Objective
simplify some code and improve Event macro
Closes https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/14336,
# Showcase
you can now write derive Events like so
```rust
#[derive(event)]
#[event(auto_propagate, traversal = MyType)]
struct MyEvent;
```
# Objective
I'm building a bloxel game in which I (currently) use a texture atlas to
render the blocks the world is made of. While I was coding it, I was
using the `TextureAtlas...` types to build the terrain's texture atlas
at runtime as shown in the
[example](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/blob/latest/examples/2d/texture_atlas.rs).
But when I was using it to build a 3D mesh out of the blocks, I found
that there was no easy way get the texture rect in UV coordinates, only
in pixels via `texture_rect()`. I had to resort to writing code like
this:
```rs
let size = layout.size.as_vec2();
if let Some(rect) = sources.texture_rect(layout, texture) {
let rect = rect.as_rect();
let uvs = Rect::from_corners(rect.min / size, rect.max / size);
// use the UVs here, such as to build vertex buffer
}
```
That is, until I wrote a helper function that's practically identical to
the one in this PR.
## Solution
Add a `uv_rect` function to `TextureAtlasSources` that will return a
`Rect` with coordinates in the range of 0.0 to 1.0 – that is, UV
coordinates – which can then be used directly to build `Vec2` UV values
to put into a buffer and send to the GPU.
I'm a little unsure about the wording of the `texture_rect`
documentation but I kept it intact and based mine on it. If you think
this could be improved and have some advice, I'd love to include that in
this PR.
## Testing
I've not done any testing with the updated bevy branch, other than
seeing that the original helper function (identical in functionality)
worked in my currently very small project, and making sure `cargo build`
doesn't error, but I'm new to making changes to Bevy so unsure if this
is sufficient.
## Showcase

## Objective
Fixes#18092
Bevy's current error type is a simple type alias for `Box<dyn Error +
Send + Sync + 'static>`. This largely works as a catch-all error, but it
is missing a critical feature: the ability to capture a backtrace at the
point that the error occurs. The best way to do this is `anyhow`-style
error handling: a new error type that takes advantage of the fact that
the `?` `From` conversion happens "inline" to capture the backtrace at
the point of the error.
## Solution
This PR adds a new `BevyError` type (replacing our old
`std::error::Error` type alias), which uses the "from conversion
backtrace capture" approach:
```rust
fn oh_no() -> Result<(), BevyError> {
// this fails with Rust's built in ParseIntError, which
// is converted into the catch-all BevyError type
let number: usize = "hi".parse()?;
println!("parsed {number}");
Ok(())
}
```
This also updates our exported `Result` type alias to default to
`BevyError`, meaning you can write this instead:
```rust
fn oh_no() -> Result {
let number: usize = "hi".parse()?;
println!("parsed {number}");
Ok(())
}
```
When a BevyError is encountered in a system, it will use Bevy's default
system error handler (which panics by default). BevyError does custom
"backtrace filtering" by default, meaning we can cut out the _massive_
amount of "rust internals", "async executor internals", and "bevy system
scheduler internals" that show up in backtraces. It also trims out the
first generally-unnecssary `From` conversion backtrace lines that make
it harder to locate the real error location. The result is a blissfully
simple backtrace by default:

The full backtrace can be shown by setting the `BEVY_BACKTRACE=full`
environment variable. Non-BevyError panics still use the default Rust
backtrace behavior.
One issue that prevented the truly noise-free backtrace during panics
that you see above is that Rust's default panic handler will print the
unfiltered (and largely unhelpful real-panic-point) backtrace by
default, in _addition_ to our filtered BevyError backtrace (with the
helpful backtrace origin) that we capture and print. To resolve this, I
have extended Bevy's existing PanicHandlerPlugin to wrap the default
panic handler. If we panic from the result of a BevyError, we will skip
the default "print full backtrace" panic handler. This behavior can be
enabled and disabled using the new `error_panic_hook` cargo feature in
`bevy_app` (which is enabled by default).
One downside to _not_ using `Box<dyn Error>` directly is that we can no
longer take advantage of the built-in `Into` impl for strings to errors.
To resolve this, I have added the following:
```rust
// Before
Err("some error")?
// After
Err(BevyError::message("some error"))?
```
We can discuss adding shorthand methods or macros for this (similar to
anyhow's `anyhow!("some error")` macro), but I'd prefer to discuss that
later.
I have also added the following extension method:
```rust
// Before
some_option.ok_or("some error")?;
// After
some_option.ok_or_message("some error")?;
```
I've also moved all of our existing error infrastructure from
`bevy_ecs::result` to `bevy_ecs::error`, as I think that is the better
home for it
## Why not anyhow (or eyre)?
The biggest reason is that `anyhow` needs to be a "generically useful
error type", whereas Bevy is a much narrower scope. By using our own
error, we can be significantly more opinionated. For example, anyhow
doesn't do the extensive (and invasive) backtrace filtering that
BevyError does because it can't operate on Bevy-specific context, and
needs to be generically useful.
Bevy also has a lot of operational context (ex: system info) that could
be useful to attach to errors. If we have control over the error type,
we can add whatever context we want to in a structured way. This could
be increasingly useful as we add more visual / interactive error
handling tools and editor integrations.
Additionally, the core approach used is simple and requires almost no
code. anyhow clocks in at ~2500 lines of code, but the impl here uses
160. We are able to boil this down to exactly what we need, and by doing
so we improve our compile times and the understandability of our code.
# Objective
The fix in #18105 includes a check for running headless, but this allows
for an extra world update during shutdown.
This commit checks if the `AppExit` event has been recorded and prevents
the additional world update.
### Before
```
2025-03-06T03:11:59.999679Z INFO bevy_window::system: No windows are open, exiting
2025-03-06T03:12:00.001942Z INFO bevy_winit::system: Closing window 0v1
2025-03-06T03:12:00.012691Z INFO bevy_window::system: No windows are open, exiting
```
### After
```
2025-03-06T03:18:45.552243Z INFO bevy_window::system: No windows are open, exiting
2025-03-06T03:18:45.554119Z INFO bevy_winit::system: Closing window 0v1
```
## Testing
Ran `window` examples
- `monitor_info` continues to run after all windows are closed (it has
`ExitCondition::DontExit`)
- `window_settings` invisible window creation works as expected
- `multiple_windows` exits after both windows are closed with a single
exit message
# Objective
- Today, enabling asset processing can generate many meta files. This
makes it a painful transition for users as they get a "mega commit"
containing tons of meta files.
## Solution
- Stop automatically generating meta files! Users can just leave the
meta files defaulted.
- Add a function `AssetServer::write_default_meta_file_for_path`
## Testing
- Tested this manually on the asset_processing example (by removing the
meta files for the assets that had default meta files).
- I did not add a unit test for the `write_default_meta_file_for_path`
since we don't have an in-memory asset writer. Writing one could be
useful in the future.
---
## Showcase
Asset processing no longer automatically generates meta files! This
makes it much easier to transition to using asset processing since you
don't suddenly get many meta files when turning it on.
You can still manually generate meta files using the new
`AssetServer::write_default_meta_file_for_path` function.
# Objective
Based on #18054, this PR builds on #18035 to deprecate:
- `Commands::insert_or_spawn_batch`
- `Entities::alloc_at_without_replacement`
- `Entities::alloc_at`
- `World::insert_or_spawn_batch`
- `World::insert_or_spawn_batch_with_caller`
## Testing
Just deprecation, so no new tests. Note that as of writing #18035 is
still under testing and review.
## Open Questions
- [x] Should `entity::AllocAtWithoutReplacement` be deprecated? It is
internal and only used in `Entities::alloc_at_without_replacement`.
**EDIT:** Now deprecated.
## Migration Guide
The following functions have been deprecated:
- `Commands::insert_or_spawn_batch`
- `World::insert_or_spawn_batch`
- `World::insert_or_spawn_batch_with_caller`
These functions, when used incorrectly, can cause major performance
problems and are generally viewed as anti-patterns and foot guns. These
are planned to be removed altogether in 0.17.
Instead of these functions consider doing one of the following:
Option A) Instead of despawing entities and re-spawning them at a
particular id, insert the new `Disabled` component without despawning
the entity, and use `try_insert_batch` or `insert_batch` and remove
`Disabled` instead of re-spawning it.
Option B) Instead of giving special meaning to an entity id, simply use
`spawn_batch` and ensure entity references are valid when despawning.
---------
Co-authored-by: JaySpruce <jsprucebruce@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
In 0.11 you could easily access the inverse model matrix inside a WGSL
shader with `transpose(mesh.inverse_transpose_model)`. This was changed
in 0.12 when `inverse_transpose_model` was removed and it's now not as
straightfoward. I wrote a helper function for my own code and thought
I'd submit a pull request in case it would be helpful to others.
# Objective
This PR adds:
- function call hook attributes `#[component(on_add = func(42))]`
- main feature of this commit
- closure hook attributes `#[component(on_add = |w, ctx| { /* ... */
})]`
- maybe too verbose
- but was easy to add
- was suggested on discord
This allows to reuse common functionality without replicating a lot of
boilerplate. A small example is a hook which just adds different default
sprites. The sprite loading code would be the same for every component.
Unfortunately we can't use the required components feature, since we
need at least an `AssetServer` or other `Resource`s or `Component`s to
load the sprite.
```rs
fn load_sprite(path: &str) -> impl Fn(DeferredWorld, HookContext) {
|mut world, ctx| {
// ... use world to load sprite
}
}
#[derive(Component)]
#[component(on_add = load_sprite("knight.png"))]
struct Knight;
#[derive(Component)]
#[component(on_add = load_sprite("monster.png"))]
struct Monster;
```
---
The commit also reorders the logic of the derive macro a bit. It's
probably a bit less lazy now, but the functionality shouldn't be
performance critical and is executed at compile time anyways.
## Solution
- Introduce `HookKind` enum in the component proc macro module
- extend parsing to allow more cases of expressions
## Testing
I have some code laying around. I'm not sure where to put it yet though.
Also is there a way to check compilation failures? Anyways, here it is:
```rs
use bevy::prelude::*;
#[derive(Component)]
#[component(
on_add = fooing_and_baring,
on_insert = fooing_and_baring,
on_replace = fooing_and_baring,
on_despawn = fooing_and_baring,
on_remove = fooing_and_baring
)]
pub struct FooPath;
fn fooing_and_baring(
world: bevy::ecs::world::DeferredWorld,
ctx: bevy::ecs::component::HookContext,
) {
}
#[derive(Component)]
#[component(
on_add = baring_and_bazzing("foo"),
on_insert = baring_and_bazzing("foo"),
on_replace = baring_and_bazzing("foo"),
on_despawn = baring_and_bazzing("foo"),
on_remove = baring_and_bazzing("foo")
)]
pub struct FooCall;
fn baring_and_bazzing(
path: &str,
) -> impl Fn(bevy::ecs::world::DeferredWorld, bevy::ecs::component::HookContext) {
|world, ctx| {}
}
#[derive(Component)]
#[component(
on_add = |w,ctx| {},
on_insert = |w,ctx| {},
on_replace = |w,ctx| {},
on_despawn = |w,ctx| {},
on_remove = |w,ctx| {}
)]
pub struct FooClosure;
#[derive(Component, Debug)]
#[relationship(relationship_target = FooTargets)]
#[component(
on_add = baring_and_bazzing("foo"),
// on_insert = baring_and_bazzing("foo"),
// on_replace = baring_and_bazzing("foo"),
on_despawn = baring_and_bazzing("foo"),
on_remove = baring_and_bazzing("foo")
)]
pub struct FooTargetOf(Entity);
#[derive(Component, Debug)]
#[relationship_target(relationship = FooTargetOf)]
#[component(
on_add = |w,ctx| {},
on_insert = |w,ctx| {},
// on_replace = |w,ctx| {},
// on_despawn = |w,ctx| {},
on_remove = |w,ctx| {}
)]
pub struct FooTargets(Vec<Entity>);
// MSG: mismatched types expected fn pointer `for<'w> fn(bevy::bevy_ecs::world::DeferredWorld<'w>, bevy::bevy_ecs::component::HookContext)` found struct `Bar`
//
// pub struct Bar;
// #[derive(Component)]
// #[component(
// on_add = Bar,
// )]
// pub struct FooWrongPath;
// MSG: this function takes 1 argument but 2 arguements were supplied
//
// #[derive(Component)]
// #[component(
// on_add = wrong_bazzing("foo"),
// )]
// pub struct FooWrongCall;
//
// fn wrong_bazzing(path: &str) -> impl Fn(bevy::ecs::world::DeferredWorld) {
// |world| {}
// }
// MSG: expected 1 argument, found 2
//
// #[derive(Component)]
// #[component(
// on_add = |w| {},
// )]
// pub struct FooWrongCall;
```
---
## Showcase
I'll try to continue to work on this to have a small section in the
release notes.
## Objective
`insert_or_spawn_batch` is due to be deprecated eventually (#15704), and
removing uses internally will make that easier.
## Solution
Replaced internal uses of `insert_or_spawn_batch` with
`try_insert_batch` (non-panicking variant because
`insert_or_spawn_batch` didn't panic).
All of the internal uses are in rendering code. Since retained rendering
was meant to get rid non-opaque entity IDs, I assume the code was just
using `insert_or_spawn_batch` because `insert_batch` didn't exist and
not because it actually wanted to spawn something. However, I am *not*
confident in my ability to judge rendering code.
# Objective
Component `require()` IDE integration is fully broken, as of #16575.
## Solution
This reverts us back to the previous "put the docs on Component trait"
impl. This _does_ reduce the accessibility of the required components in
rust docs, but the complete erasure of "required component IDE
experience" is not worth the price of slightly increased prominence of
requires in docs.
Additionally, Rust Analyzer has recently started including derive
attributes in suggestions, so we aren't losing that benefit of the
proc_macro attribute impl.
This reverts commit 0b5302d96a.
# Objective
- Fixes#18158
- #17482 introduced rendering changes and was merged a bit too fast
## Solution
- Revert #17482 so that it can be redone and rendering changes discussed
before being merged. This will make it easier to compare changes with
main in the known "valid" state
This is not an issue with the work done in #17482 that is still
interesting
Fixes#17720
## Objective
Spawning RelationshipTargets from scenes currently fails to preserve
RelationshipTarget ordering (ex: `Children` has an arbitrary order).
This is because it uses the normal hook flow to set up the collection,
which means we are pushing onto the collection in _spawn order_ (which
is currently in archetype order, which will often produce mismatched
orderings).
We need to preserve the ordering in the original RelationshipTarget
collection. Ideally without expensive checking / fixups.
## Solution
One solution would be to spawn in hierarchy-order. However this gets
complicated as there can be multiple hierarchies, and it also means we
can't spawn in more cache-friendly orders (ex: the current per-archetype
spawning, or future even-smarter per-table spawning). Additionally,
same-world cloning has _slightly_ more nuanced needs (ex: recursively
clone linked relationships, while maintaining _original_ relationships
outside of the tree via normal hooks).
The preferred approach is to directly spawn the remapped
RelationshipTarget collection, as this trivially preserves the ordering.
Unfortunately we can't _just_ do that, as when we spawn the children
with their Relationships (ex: `ChildOf`), that will insert a duplicate.
We could "fixup" the collection retroactively by just removing the back
half of duplicates, but this requires another pass / more lookups /
allocating twice as much space. Additionally, it becomes complicated
because observers could insert additional children, making it harder
(aka more expensive) to determine which children are dupes and which are
not.
The path I chose is to support "opting out" of the relationship target
hook in the contexts that need that, as this allows us to just cheaply
clone the mapped collection. The relationship hook can look for this
configuration when it runs and skip its logic when that happens. A
"simple" / small-amount-of-code way to do this would be to add a "skip
relationship spawn" flag to World. Sadly, any hook / observer that runs
_as the result of an insert_ would also read this flag. We really need a
way to scope this setting to a _specific_ insert.
Therefore I opted to add a new `RelationshipInsertHookMode` enum and an
`entity.insert_with_relationship_insert_hook_mode` variant. Obviously
this is verbose and ugly. And nobody wants _more_ insert variants. But
sadly this was the best I could come up with from a performance and
capability perspective. If you have alternatives let me know!
There are three variants:
1. `RelationshipInsertHookMode::Run`: always run relationship insert
hooks (this is the default)
2. `RelationshipInsertHookMode::Skip`: do not run any relationship
insert hooks for this insert (this is used by spawner code)
3. `RelationshipInsertHookMode::RunIfNotLinked`: only run hooks for
_unlinked_ relationships (this is used in same-world recursive entity
cloning to preserve relationships outside of the deep-cloned tree)
Note that I have intentionally only added "insert with relationship hook
mode" variants to the cases we absolutely need (everything else uses the
default `Run` mode), just to keep the code size in check. I do not think
we should add more without real _very necessary_ use cases.
I also made some other minor tweaks:
1. I split out `SourceComponent` from `ComponentCloneCtx`. Reading the
source component no longer needlessly blocks mutable access to
`ComponentCloneCtx`.
2. Thanks to (1), I've removed the `RefCell` wrapper over the cloned
component queue.
3. (1) also allowed me to write to the EntityMapper while queuing up
clones, meaning we can reserve entities during the component clone and
write them to the mapper _before_ inserting the component, meaning
cloned collections can be mapped on insert.
4. I've removed the closure from `write_target_component_ptr` to
simplify the API / make it compatible with the split `SourceComponent`
approach.
5. I've renamed `EntityCloner::recursive` to
`EntityCloner::linked_cloning` to connect that feature more directly
with `RelationshipTarget::LINKED_SPAWN`
6. I've removed `EntityCloneBehavior::RelationshipTarget`. This was
always intended to be temporary, and this new behavior removes the need
for it.
---------
Co-authored-by: Viktor Gustavsson <villor94@gmail.com>
# Objective
Fix unsound query transmutes on queries obtained from
`Query::as_readonly()`.
The following compiles, and the call to `transmute_lens()` should panic,
but does not:
```rust
fn bad_system(query: Query<&mut A>) {
let mut readonly = query.as_readonly();
let mut lens: QueryLens<&mut A> = readonly.transmute_lens();
let other_readonly: Query<&A> = query.as_readonly();
// `lens` and `other_readonly` alias, and are both alive here!
}
```
To make `Query::as_readonly()` zero-cost, we pointer-cast
`&QueryState<D, F>` to `&QueryState<D::ReadOnly, F>`. This means that
the `component_access` for a read-only query's state may include
accesses for the original mutable version, but the `Query` does not have
exclusive access to those components! `transmute` and `join` use that
access to ensure that a join is valid, and will incorrectly allow a
transmute that includes mutable access.
As a bonus, allow `Query::join`s that output `FilteredEntityRef` or
`FilteredEntityMut` to receive access from the `other` query. Currently
they only receive access from `self`.
## Solution
When transmuting or joining from a read-only query, remove any writes
before performing checking that the transmute is valid. For joins, be
sure to handle the case where one input query was the result of
`as_readonly()` but the other has valid mutable access.
This requires identifying read-only queries, so add a
`QueryData::IS_READ_ONLY` associated constant. Note that we only call
`QueryState::as_transmuted_state()` with `NewD: ReadOnlyQueryData`, so
checking for read-only queries is sufficient to check for
`as_transmuted_state()`.
Removing writes requires allocating a new `FilteredAccess`, so only do
so if the query is read-only and the state has writes. Otherwise, the
existing access is correct and we can continue using a reference to it.
Use the new read-only state to call `NewD::set_access`, so that
transmuting to a `FilteredAccessMut` results in a read-only
`FilteredAccessMut`. Otherwise, it would take the original write access,
and then the transmute would panic because it had too much access.
Note that `join` was previously passing `self.component_access` to
`NewD::set_access`. Switching it to `joined_component_access` also
allows a join that outputs `FilteredEntity(Ref|Mut)` to receive access
from `other`. The fact that it didn't do that before seems like an
oversight, so I didn't try to prevent that change.
## Testing
Added unit tests with the unsound transmute and join.
# Objective
Many systems like `Schedule` rely on the fact that every structural ECS
changes are deferred until an exclusive system flushes the `World`
itself. This gives us the benefits of being able to run systems in
parallel without worrying about dangling references caused by memory
(re)allocations, which will in turn lead to **Undefined Behavior**.
However, this isn't explicitly documented in `SystemParam`; currently it
only vaguely hints that in `init_state`, based on the fact that
structural ECS changes require mutable access to the _whole_ `World`.
## Solution
Document this behavior explicitly in `SystemParam`'s type-level
documentations.
# Objective
- Fixes#16339
## Solution
- Replaced `component_reads_and_writes` and `component_writes` with
`try_iter_component_access`.
## Testing
- Ran `dynamic` example to confirm behaviour is unchanged.
- CI
---
## Migration Guide
The following methods (some removed in previous PRs) are now replaced by
`Access::try_iter_component_access`:
* `Access::component_reads_and_writes`
* `Access::component_reads`
* `Access::component_writes`
As `try_iter_component_access` returns a `Result`, you'll now need to
handle the failing case (e.g., `unwrap()`). There is currently a single
failure mode, `UnboundedAccess`, which occurs when the `Access` is for
all `Components` _except_ certain exclusions. Since this list is
infinite, there is no meaningful way for `Access` to provide an
iterator. Instead, get a list of components (e.g., from the `Components`
structure) and iterate over that instead, filtering using
`Access::has_component_read`, `Access::has_component_write`, etc.
Additionally, you'll need to `filter_map` the accesses based on which
method you're attempting to replace:
* `Access::component_reads_and_writes` -> `Exclusive(_) | Shared(_)`
* `Access::component_reads` -> `Shared(_)`
* `Access::component_writes` -> `Exclusive(_)`
To ease migration, please consider the below extension trait which you
can include in your project:
```rust
pub trait AccessCompatibilityExt {
/// Returns the indices of the components this has access to.
fn component_reads_and_writes(&self) -> impl Iterator<Item = T> + '_;
/// Returns the indices of the components this has non-exclusive access to.
fn component_reads(&self) -> impl Iterator<Item = T> + '_;
/// Returns the indices of the components this has exclusive access to.
fn component_writes(&self) -> impl Iterator<Item = T> + '_;
}
impl<T: SparseSetIndex> AccessCompatibilityExt for Access<T> {
fn component_reads_and_writes(&self) -> impl Iterator<Item = T> + '_ {
self
.try_iter_component_access()
.expect("Access is unbounded. Please refactor the usage of this method to directly use try_iter_component_access")
.filter_map(|component_access| {
let index = component_access.index().sparse_set_index();
match component_access {
ComponentAccessKind::Archetypal(_) => None,
ComponentAccessKind::Shared(_) => Some(index),
ComponentAccessKind::Exclusive(_) => Some(index),
}
})
}
fn component_reads(&self) -> impl Iterator<Item = T> + '_ {
self
.try_iter_component_access()
.expect("Access is unbounded. Please refactor the usage of this method to directly use try_iter_component_access")
.filter_map(|component_access| {
let index = component_access.index().sparse_set_index();
match component_access {
ComponentAccessKind::Archetypal(_) => None,
ComponentAccessKind::Shared(_) => Some(index),
ComponentAccessKind::Exclusive(_) => None,
}
})
}
fn component_writes(&self) -> impl Iterator<Item = T> + '_ {
self
.try_iter_component_access()
.expect("Access is unbounded. Please refactor the usage of this method to directly use try_iter_component_access")
.filter_map(|component_access| {
let index = component_access.index().sparse_set_index();
match component_access {
ComponentAccessKind::Archetypal(_) => None,
ComponentAccessKind::Shared(_) => None,
ComponentAccessKind::Exclusive(_) => Some(index),
}
})
}
}
```
Please take note of the use of `expect(...)` in these methods. You
should consider using these as a starting point for a more appropriate
migration based on your specific needs.
## Notes
- This new method is fallible based on whether the `Access` is bounded
or unbounded (unbounded occurring with inverted component sets). If
bounded, will return an iterator of every item and its access level. I
believe this makes sense without exposing implementation details around
`Access`.
- The access level is defined by an `enum` `ComponentAccessKind<T>`,
either `Archetypical`, `Shared`, or `Exclusive`. As a convenience, this
`enum` has a method `index` to get the inner `T` value without a match
statement. It does add more code, but the API is clearer.
- Within `QueryBuilder` this new method simplifies several pieces of
logic without changing behaviour.
- Within `QueryState` the logic is simplified and the amount of
iteration is reduced, potentially improving performance.
- Within the `dynamic` example it has identical behaviour, with the
inversion footgun explicitly highlighted by an `unwrap`.
---------
Co-authored-by: Chris Russell <8494645+chescock@users.noreply.github.com>
Co-authored-by: Mike <2180432+hymm@users.noreply.github.com>
# Objective
The doc comment for `BorderRadius::resolve_single_corner` returns a
value in physical pixels but the doc comments implies it returns a
logical value.
# Objective
Minimal implementation of directed one-to-one relationships via
implementing `RelationshipSourceCollection` for `Entity`.
Now you can do
```rust
#[derive(Component)]
#[relationship(relationship_target = Below)]
pub struct Above(Entity);
#[derive(Component)]
#[relationship_target(relationship = Above)]
pub struct Below(Entity);
```
## Future Work
It would be nice if the relationships could be fully symmetrical in the
future - in the example above, since `Above` is the source of truth you
can't add `Below` to an entity and have `Above` added automatically.
## Testing
Wrote unit tests for new relationship sources and and verified
adding/removing relationships maintains connection as expected.
# Objective
Work for issue #17682
What's in this PR:
* Removal of some `!Send` resources that Bevy uses internally
* Replaces `!Send` resources with `thread_local!` static
What this PR does not cover:
* The ability to create `!Send` resources still exists
* Tests that test `!Send` resources are present (and should not be
removed until the ability to create `!Send` resources is removed)
* The example `log_layers_ecs` still uses a `!Send` resource. In this
example, removing the `!Send` resource results in the system that uses
it running on a thread other than the main thread, which doesn't work
with lazily initialized `thread_local!` static data. Removing this
`!Send` resource will need to be deferred until the System API is
extended to support configuring which thread the System runs on. Once an
issue for this work is created, it will be mentioned in #17667
Once the System API is extended to allow control of which thread the
System runs on, the rest of the `!Send` resources can be removed in a
different PR.
# Objective
Transparently uses simple `EnvironmentMapLight`s to mimic
`AmbientLight`s. Implements the first part of #17468, but I can
implement hemispherical lights in this PR too if needed.
## Solution
- A function `EnvironmentMapLight::solid_color(&mut Assets<Image>,
Color)` is provided to make an environment light with a solid color.
- A new system is added to `SimulationLightSystems` that maps
`AmbientLight`s on views or the world to a corresponding
`EnvironmentMapLight`.
I have never worked with (or on) Bevy before, so nitpicky comments on
how I did things are appreciated :).
## Testing
Testing was done on a modified version of the `3d/lighting` example,
where I removed all lights except the ambient light. I have not included
the example, but can if required.
## Migration
`bevy_pbr::AmbientLight` has been deprecated, so all usages of it should
be replaced by a `bevy_pbr::EnvironmentMapLight` created with
`EnvironmentMapLight::solid_color` placed on the camera. There is no
alternative to ambient lights as resources.
# Objective
- Fixes the issue described in this comment:
https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/16680#issuecomment-2522764239.
## Solution
- Cache one-shot systems by `S: IntoSystem` (which is const-asserted to
be a ZST) rather than `S::System`.
## Testing
Added a new unit test named `cached_system_into_same_system_type` to
`system_registry.rs`.
---
## Migration Guide
The `CachedSystemId` resource has been changed:
```rust
// Before:
let cached_id = CachedSystemId::<S::System>(id);
assert!(id == cached_id.0);
// After:
let cached_id = CachedSystemId::<S>::new(id);
assert!(id == SystemId::from_entity(cached_id.entity));
```
This commit makes the
`mark_meshes_as_changed_if_their_materials_changed` system use the new
`AssetChanged<MeshMaterial3d>` query filter in addition to
`Changed<MeshMaterial3d>`. This ensures that we update the
`MeshInputUniform`, which contains the bindless material slot. Updating
the `MeshInputUniform` fixes problems that occurred when the
`MeshBindGroupAllocator` reallocated meshes in such a way as to change
their bindless slot.
Closes#18102.
The test case `query_iter_sorts` was doing lots of comparisons to ensure
that various query arrays were sorted, but the arrays were all empty.
This PR spawns some entities so that the entity lists to compare not
empty, and sorting can actually be tested for correctness.
# Objective
Fixes https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/17590.
## Solution
`prepare_volumetric_fog_uniforms` adds a uniform for each combination of
fog volume and view. But it only allocated enough uniforms for one fog
volume per view.
## Testing
Ran the `volumetric_fog` example with 1/2/3/4 fog volumes. Also checked
the `fog_volumes` and `scrolling_fog` examples (without multiple
volumes). Win10/Vulkan/Nvidia.
To test multiple views I tried adding fog volumes to the `split_screen`
example. This doesn't quite work - the fog should be centred on the fox,
but instead it's centred on the window. Same result with and without the
PR, so I'm assuming it's a separate bug.

# Objective
As discussed in #14275, Bevy is currently too prone to panic, and makes
the easy / beginner-friendly way to do a large number of operations just
to panic on failure.
This is seriously frustrating in library code, but also slows down
development, as many of the `Query::single` panics can actually safely
be an early return (these panics are often due to a small ordering issue
or a change in game state.
More critically, in most "finished" products, panics are unacceptable:
any unexpected failures should be handled elsewhere. That's where the
new
With the advent of good system error handling, we can now remove this.
Note: I was instrumental in a) introducing this idea in the first place
and b) pushing to make the panicking variant the default. The
introduction of both `let else` statements in Rust and the fancy system
error handling work in 0.16 have changed my mind on the right balance
here.
## Solution
1. Make `Query::single` and `Query::single_mut` (and other random
related methods) return a `Result`.
2. Handle all of Bevy's internal usage of these APIs.
3. Deprecate `Query::get_single` and friends, since we've moved their
functionality to the nice names.
4. Add detailed advice on how to best handle these errors.
Generally I like the diff here, although `get_single().unwrap()` in
tests is a bit of a downgrade.
## Testing
I've done a global search for `.single` to track down any missed
deprecated usages.
As to whether or not all the migrations were successful, that's what CI
is for :)
## Future work
~~Rename `Query::get_single` and friends to `Query::single`!~~
~~I've opted not to do this in this PR, and smear it across two releases
in order to ease the migration. Successive deprecations are much easier
to manage than the semantics and types shifting under your feet.~~
Cart has convinced me to change my mind on this; see
https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/18082#discussion_r1974536085.
## Migration guide
`Query::single`, `Query::single_mut` and their `QueryState` equivalents
now return a `Result`. Generally, you'll want to:
1. Use Bevy 0.16's system error handling to return a `Result` using the
`?` operator.
2. Use a `let else Ok(data)` block to early return if it's an expected
failure.
3. Use `unwrap()` or `Ok` destructuring inside of tests.
The old `Query::get_single` (etc) methods which did this have been
deprecated.
# Objective
Documentation correction.
# Reasoning
The `GamepadAxis::RightZ` and `LeftZ` do not map to the trigger buttons
on a gamepad. They are in fact for the twisting/yaw of a flight Joystick
and throttle lever respectively. I confirmed this with two gamepads that
has analog triggers (Logitech F710, 8bitdo ultimate BT controller) and a
HOTAS joystick (Saitek X52).
# Objective
Fixes#18022
## Solution
Canonicalize asset paths
## Testing
I ran the examples `sprite`, `desk_toy` and `game_menu` with the feature
`file_watcher` enabled. All correctly updated an asset when the source
file was altered.
Co-authored-by: Threadzless <threadzless@gmail.com>
# Objective
Fixes#18027
## Solution
Run `redraw_requested` logic in `about_to_wait` on Windows during
initial application startup and when in headless mode
## Testing
- Ran `cargo run --example window_settings` to demonstrate invisible
window creation worked again and fixes#18027
- Ran `cargo run --example eased_motion` to demonstrate no regression
with the fix for #17488
Ran all additional `window` examples.
Notes:
- The `transparent_window` was not transparent but this appears to have
been broken prior to #18004. See: #7544
I noticed this while working on #18017 . Some of the `stderr`
compile_fail tests were updated while I generated the output for the new
tests I introduced in the mentioned PR.
I'm on rust 1.85.0
## Objective
`EntityCommands::trigger` internally uses `Commands::trigger_targets`,
which means it gets queued using `Commands::queue` rather
`EntityCommands::queue`. This previously wouldn't have made much
difference, but now entity commands check whether the entity exists, and
that check never happens in this case.
## Solution
- Add `entity_command::trigger`, which calls the same function as before
(`World::trigger_targets_with_caller`) but through the `EntityWorldMut`
passed to entity commands.
- Change `EntityCommands::trigger` to queue the new entity command
normally.
https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/17905 replaced `ChildOf(entity)`
with `ChildOf { parent: entity }`, but some deprecation advice was
overlooked. Also corrected formatting in documentation.
## Testing
Added a `set_parent` to a random example. Confirmed that the deprecation
warning shows and the advice can be pasted in.
# Objective
Fixes#17988
## Solution
Added two Debug impls to the `impl_ptr` macro - one for Aligned and one
for Unaligned.
## Testing
No tests have been added. Would a test guaranteeing debug layout be
appropriate?
---
## Showcase
The debug representation of a `Ptr<'_, Aligned>` follows. `PtrMut` and
`OwningPtr` are similar.
`Ptr<Aligned>(0x0123456789ab)`
# Objective
There are currently three ways to access the parent stored on a ChildOf
relationship:
1. `child_of.parent` (field accessor)
2. `child_of.get()` (get function)
3. `**child_of` (Deref impl)
I will assert that we should only have one (the field accessor), and
that the existence of the other implementations causes confusion and
legibility issues. The deref approach is heinous, and `child_of.get()`
is significantly less clear than `child_of.parent`.
## Solution
Remove `impl Deref for ChildOf` and `ChildOf::get`.
The one "downside" I'm seeing is that:
```rust
entity.get::<ChildOf>().map(ChildOf::get)
```
Becomes this:
```rust
entity.get::<ChildOf>().map(|c| c.parent)
```
I strongly believe that this is worth the increased clarity and
consistency. I'm also not really a huge fan of the "pass function
pointer to map" syntax. I think most people don't think this way about
maps. They think in terms of a function that takes the item in the
Option and returns the result of some action on it.
## Migration Guide
```rust
// Before
**child_of
// After
child_of.parent
// Before
child_of.get()
// After
child_of.parent
// Before
entity.get::<ChildOf>().map(ChildOf::get)
// After
entity.get::<ChildOf>().map(|c| c.parent)
```
## Objective
Alternative to #18001.
- Now that systems can handle the `?` operator, `get_entity` returning
`Result` would be more useful than `Option`.
- With `get_entity` being more flexible, combined with entity commands
now checking the entity's existence automatically, the panic in `entity`
isn't really necessary.
## Solution
- Changed `Commands::get_entity` to return `Result<EntityCommands,
EntityDoesNotExistError>`.
- Removed panic from `Commands::entity`.
# Objective
fixes#17896
## Solution
Change ChildOf ( Entity ) to ChildOf { parent: Entity }
by doing this we also allow users to use named structs for relationship
derives, When you have more than 1 field in a struct with named fields
the macro will look for a field with the attribute #[relationship] and
all of the other fields should implement the Default trait. Unnamed
fields are still supported.
When u have a unnamed struct with more than one field the macro will
fail.
Do we want to support something like this ?
```rust
#[derive(Component)]
#[relationship_target(relationship = ChildOf)]
pub struct Children (#[relationship] Entity, u8);
```
I could add this, it but doesn't seem nice.
## Testing
crates/bevy_ecs - cargo test
## Showcase
```rust
use bevy_ecs::component::Component;
use bevy_ecs::entity::Entity;
#[derive(Component)]
#[relationship(relationship_target = Children)]
pub struct ChildOf {
#[relationship]
pub parent: Entity,
internal: u8,
};
#[derive(Component)]
#[relationship_target(relationship = ChildOf)]
pub struct Children {
children: Vec<Entity>
};
```
---------
Co-authored-by: Tim Overbeek <oorbecktim@Tims-MacBook-Pro.local>
Co-authored-by: Tim Overbeek <oorbecktim@c-001-001-042.client.nl.eduvpn.org>
Co-authored-by: Tim Overbeek <oorbecktim@c-001-001-059.client.nl.eduvpn.org>
Co-authored-by: Tim Overbeek <oorbecktim@c-001-001-054.client.nl.eduvpn.org>
Co-authored-by: Tim Overbeek <oorbecktim@c-001-001-027.client.nl.eduvpn.org>
## Objective
`insert_by_id` is unsafe, but I forgot to add that to the
manually-queueable version in `entity_command`.
It also can only insert using `InsertMode::Replace`, when it could
easily be configurable by threading an `InsertMode` parameter to the
final `BundleInserter::insert` call.
## Solution
- Add `unsafe` and safety comment.
- Add `InsertMode` parameter to `entity_command::insert_by_id`,
`EntityWorldMut::insert_by_id_with_caller`, and
`EntityWorldMut::insert_dynamic_bundle`.
- Add `InsertMode` parameter to `entity_command::insert` and remove
`entity_command::insert_if_new`, for consistency with the other
manually-queued insertion commands.
# Objective
Fixes#17828
This fixes two bugs:
1. Exclusive systems should see the effect of all commands queued to
that point. That does not happen when the system is configured with
`*_ignore_deferred` which may lead to surprising situations. These
configurations should not behave like that.
2. If `*_ignore_deferred` is used, no sync point may be added at all
**after** the config. Currently this can happen if the last nodes in
that config have no deferred parameters themselves. Instead, sync points
should always be added after such a config, so long systems have
deferred parameters.
## Solution
1. When adding sync points on edges, do not consider
`AutoInsertApplyDeferredPass::no_sync_edges` if the target is an
exclusive system.
2. when going through the nodes in a directed way, store the information
that `AutoInsertApplyDeferredPass::no_sync_edges` suppressed adding a
sync point at the target node. Then, when the target node is evaluated
later by the iteration and that prior suppression was the case, the
target node will behave like it has deferred parameters even if the
system itself does not.
## Testing
I added a test for each bug, please let me know if more are wanted and
if yes, which cases you would want to see.
These tests also can be read as examples how the current code would
fail.
# Objective
- Fixes#17642
## Solution
- Implemented method `new_bezier(points: [P; 4]) -> Self` for
`CubicSegment<P>`
- Old implementation of `new_bezier` is now `new_bezier_easing(p1: impl
Into<Vec2>, p2: impl Into<Vec2>) -> Self` (**breaking change**)
- ~~added method `new_bezier_with_anchor`, which can make a bezier curve
between two points with one control anchor~~
- added methods `iter_positions`, `iter_velocities`,
`iter_accelerations`, the same as in `CubicCurve` (**copied code,
potentially can be reduced)**
- bezier creation logic is moved from `CubicCurve` to `CubicSegment`,
removing the unneeded allocation
## Testing
- Did you test these changes? If so, how?
- Run tests inside `crates/bevy_math/`
- Tested the functionality in my project
- Are there any parts that need more testing?
- Did not run `cargo test` on the whole bevy directory because of OOM
- Performance improvements are expected when creating `CubicCurve` with
`new_bezier` and `new_bezier_easing`, but not tested
- How can other people (reviewers) test your changes? Is there anything
specific they need to know?
- Use in any code that works created `CubicCurve::new_bezier`
- If relevant, what platforms did you test these changes on, and are
there any important ones you can't test?
- I don't think relevant
---
## Showcase
```rust
// Imagine a car goes towards a local target
// Create a simple `CubicSegment`, without using heap
let planned_path = CubicSegment::new_bezier([
car_pos,
car_pos + car_dir * turn_radius,
target_point - target_dir * turn_radius,
target_point,
]);
// Check if the planned path itersect other entities
for pos in planned_path.iter_positions(8) {
// do some collision checks
}
```
## Migration Guide
> This section is optional. If there are no breaking changes, you can
delete this section.
- Replace `CubicCurve::new_bezier` with `CubicCurve::new_bezier_easing`
# Objective
`QueryIter::sort_by()` is unsound. It passes the lens items with the
full `'w` lifetime, and a malicious user could smuggle them out of the
closure where they could alias with the query results.
## Solution
Make the sort closures generic in the lifetime parameter of the lens
item. This ensures the lens items cannot outlive the call to the
closure.
## Testing
Added a compile-fail test that demonstrates the unsound pattern.
## Migration Guide
The `sort` family of methods on `QueryIter` unsoundly gave access
`L::Item<'w>` with the full `'w` lifetime. It has been shortened to
`L::Item<'w>` so that items cannot escape the comparer. If you get
lifetime errors using these methods, you will need to make the comparer
generic in the new lifetime. Often this can be done by replacing named
`'w` with `'_`, or by replacing the use of a function item with a
closure.
```rust
// Before: Now fails with "error: implementation of `FnMut` is not general enough"
query.iter().sort_by::<&C>(Ord::cmp);
// After: Wrap in a closure
query.iter().sort_by::<&C>(|l, r| Ord::cmp(l, r));
query.iter().sort_by::<&C>(comparer);
// Before: Uses specific `'w` lifetime from some outer scope
// now fails with "error: implementation of `FnMut` is not general enough"
fn comparer(left: &&'w C, right: &&'w C) -> Ordering { /* ... */ }
// After: Accepts any lifetime using inferred lifetime parameter
fn comparer(left: &&C, right: &&C) -> Ordering { /* ... */ }
# Objective
So far, built-in BRP methods allow users to interact with entities'
components, but global resources have remained beyond its reach. The
goal of this PR is to take the first steps in rectifying this shortfall.
## Solution
Added five new default methods to BRP:
- `bevy/get_resource`: Extracts the value of a given resource from the
world.
- `bevy/insert_resource`: Serializes an input value to a given resource
type and inserts it into the world.
- `bevy/remove_resource`: Removes the given resource from the world.
- `bevy/mutate_resource`: Replaces the value of a field in a given
resource with the result of serializing a given input value.
- `bevy/list_resources`: Lists all resources in the type registry with
an available `ReflectResource`.
## Testing
Added a test resource to the `server` example scene that you can use to
mess around with the new BRP methods.
## Showcase
Resources can now be retrieved and manipulated remotely using a handful
of new BRP methods. For example, a resource that looks like this:
```rust
#[derive(Resource, Reflect, Serialize, Deserialize)]
#[reflect(Resource, Serialize, Deserialize)]
pub struct PlayerSpawnSettings {
pub location: Vec2,
pub lives: u8,
}
```
can be manipulated remotely as follows.
Retrieving the value of the resource:
```json
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 1,
"method": "bevy/get_resource",
"params": {
"resource": "path::to::my::module::PlayerSpawnSettings"
}
}
```
Inserting a resource value into the world:
```json
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 2,
"method": "bevy/insert_resource",
"params": {
"resource": "path::to::my::module::PlayerSpawnSettings",
"value": {
"location": [
2.5,
2.5
],
"lives": 25
}
}
}
```
Removing the resource from the world:
```json
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 3,
"method": "bevy/remove_resource",
"params": {
"resource": "path::to::my::module::PlayerSpawnSettings"
}
}
```
Mutating a field of the resource specified by a path:
```json
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 4,
"method": "bevy/mutate_resource",
"params": {
"resource": "path::to::my::module::PlayerSpawnSettings",
"path": ".location.x",
"value": -3.0
}
}
```
Listing all manipulable resources in the type registry:
```json
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 5,
"method": "bevy/list_resources"
}
```
# Objective
Refactor `bevy_gltf`, the criteria for the split is kind of arbitrary
but at least it is not a 2.6k line file.
## Solution
Move methods and structs found in `bevy_gltf/loader.rs` into multiple
new modules.
## Testing
`cargo run -p ci`
# Objective
- Systems that use the task pool, either explicitly or implicitly using
parallel queries, will often end up executing tasks from different
systems.
- This can cause random tasks to block the main or render schedule at
random, adding frame variance and increasing frame times when CPU bound.
- This profile is a common occurrence on `main`.
`propagate_parent_transforms` takes more than twice as long as it
should, blocking the main schedule for that time, because it uses `task
pool.scope`, which has decided to execute tasks from the render schedule
on the main schedule.

## Solution
- In task pool scope execution, prefer to check if the current task is
complete instead of ticking the executor to find new work.
## Testing
- Ran the scene viewer with tracy to look for images like the one in the
objective section.
- Things look much, much better, and I could not find any occurrences:


# Objective
- Fixes#16416
## Solution
- Add a intermediate temporary mutable `RequiredComponents` to get avoid
of the borrowing issues.
## Testing
- I have run `cargo test --package bevy_ecs -- --exact --show-output`
and past all the tests.
## Objective
The closure argument for
`EntityClonerBuilder::without_required_components` has `Send + Sync +
'static` bounds, but the closure immediately gets called and never needs
to be sent anywhere. (This was my fault :P )
## Solution
Remove the bounds so that users aren't unnecessarily restricted.
I also took the opportunity to expand the tests a little.
# Objective
This prevents overflowing the `last_trigger_id` property that leads to a
panic in debug mode.
```bash
panicked at C:\XXX\.cargo\registry\src\index.crates.io-6f17d22bba15001f\bevy_ecs-0.15.2\src\world\unsafe_world_cell.rs:630:18:
attempt to add with overflow
Encountered a panic when applying buffers for system `bevy_sprite::calculate_bounds_2d`!
Encountered a panic in system `bevy_ecs::schedule::executor::apply_deferred`!
```
## Solution
As this value is only used for detecting a change, we can wrap when it
reaches max value.
## Testing
This can be verified by running `cargo run --example observers`
# Objective
Closes#17572
## Solution
Add the `add_one_related` methods to `EntityCommands` and
`EntityWorldMut`.
## Testing
Clippy
---
## Showcase
The `EntityWorldMut` and `FilteredResourcesMut` now include the
`add_one_related` method if you just want to relate 2 entities.
Currently, we reload a glTF skin each time we encounter a node that
references it. By checking for duplicates, PR #18013 turned this into a
fatal error. But this was always wasteful. This commit fixes the issue
by caching each skin by its index as we load it.
The Maya babylon.js export plugin likes to emit glTFs with multiple
nodes that reference the same skin, so this effectively unbreaks Maya
rigs.
# Objective
* Fixes https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/14074
* Applies CI fixes for #16326
It is currently not possible to issues a trigger that targets a specific
list of components AND a specific list of entities
## Solution
We can now use `((A, B), (entity_1, entity_2))` as a trigger target, as
well as the reverse
## Testing
Added a unit test.
The triggering rules for observers are quite confusing:
Triggers once per entity target
For each entity target, an observer system triggers if any of its
components matches the trigger target components (but it triggers at
most once, since we use an internal counter to make sure that an
observer can run at most once per entity target)
(copied from #14563)
(copied from #16326)
## Notes
All credit to @BenjaminBrienen and @cBournhonesque! Just applying a
small fix to this PR so it can be merged.
---------
Co-authored-by: Benjamin Brienen <Benjamin.Brienen@outlook.com>
Co-authored-by: Christian Hughes <xdotdash@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
# Objective
- Makes #18010 more easily debuggable. This doesn't solve that issue,
but protects us from it in the future.
## Solution
- Make `LoadContext::add_labeled_asset` and friends return an error if
it finds a duplicate asset.
## Testing
- Added a test - it fails before the fix.
---
## Migration Guide
- `AssetLoader`s must now handle the case of a duplicate subasset label
when using `LoadContext::add_labeled_asset` and its variants. If you
know your subasset labels are unique by construction (e.g., they include
an index number), you can simply unwrap this result.
Even though opaque deferred entities aren't placed into the `Opaque3d`
bin, we still want to cache them as though they were, so that we don't
have to re-queue them every frame. This commit implements that logic,
reducing the time of `queue_material_meshes` to near-zero on Caldera.
Currently, the structure-level `#[uniform]` attribute of `AsBindGroup`
creates a binding array of individual buffers, each of which contains
data for a single material. A more efficient approach would be to
provide a single buffer with an array containing all of the data for all
materials in the bind group. Because `StandardMaterial` uses
`#[uniform]`, this can be notably inefficient with large numbers of
materials.
This patch introduces a new attribute on `AsBindGroup`, `#[data]`, which
works identically to `#[uniform]` except that it concatenates all the
data into a single buffer that the material bind group allocator itself
manages. It also converts `StandardMaterial` to use this new
functionality. This effectively provides the "material data in arrays"
feature.
# Objective
Continuation of #17589 and #16547.
`get_many` is last of the `many` methods with a missing `unique`
counterpart.
It both takes and returns arrays, thus necessitates a matching
`UniqueEntityArray` type!
Plus, some slice methods involve returning arrays, which are currently
missing from `UniqueEntitySlice`.
## Solution
Add the type, the related methods and trait impls.
Note that for this PR, we abstain from some methods/trait impls that
create `&mut UniqueEntityArray`, because it can be successfully
mem-swapped. This can potentially invalidate a larger slice, which is
the same reason we punted on some mutable slice methods in #17589. We
can follow-up on all of these together in a following PR.
The new `unique_array` module is not glob-exported, because the trait
alias `unique_array::IntoIter` would conflict with
`unique_vec::IntoIter`.
The solution for this is to make the various `unique_*` modules public,
which I intend to do in yet another PR.
# Objective
Fixes#17945
## Solution
Check if the view being extracted has OIT enabled and incorporate the
associated bit into the mesh pipeline key.
I basically have no idea what's going on in the renderer, so let me know
if I missed something, which is extraordinarily possible.
## Testing
I modified the `order_independent_transparency` example to put
everything on the default render layer and render a gizmo at the origin.
Previously, this would cause the application to panic.
# Objective
- Fixes#17897.
## Solution
- When removing components, we filter the list of components in the
removed bundle based on whether they are actually in the archetype.
## Testing
- Added a test.
# Objective
Allow prepass to run without ATTRIBUTE_NORMAL.
This is needed for custom materials with non-standard vertex attributes.
For example a voxel material with manually packed vertex data.
Fixes#13054.
This PR covers the first part of the **stale** PR #13569 to only focus
on fixing #13054.
## Solution
- Only push normals `vertex_attributes` when the layout contains
`Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_NORMAL`
## Testing
- Did you test these changes? If so, how?
**Tested the fix on my own project with a mesh without normal
attribute.**
- Are there any parts that need more testing?
**I don't think so.**
- How can other people (reviewers) test your changes? Is there anything
specific they need to know?
**Prepass should not be blocked on a mesh without normal attributes
(with or without custom material).**
- If relevant, what platforms did you test these changes on, and are
there any important ones you can't test?
**Probably irrelevant, but Windows/Vulkan.**
# Objective
Implements and closes#17515
## Solution
Add `uv_transform` to `ColorMaterial`
## Testing
Create a example similar to `repeated_texture` but for `Mesh2d` and
`MeshMaterial2d<ColorMaterial>`
## Showcase

## Migration Guide
Add `uv_transform` field to constructors of `ColorMaterial`
# Objective
Fix https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/17108
See
https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/17108#issuecomment-2653020889
## Solution
- Make the query match `&Pickable` instead `Option<&Pickable>`
## Testing
- Run the `sprite_picking` example and everything still work
## Migration Guide
- Sprite picking are now opt-in, make sure you insert `Pickable`
component when using sprite picking.
```diff
-commands.spawn(Sprite { .. } );
+commands.spawn((Sprite { .. }, Pickable::default());
```
# Objective
Fixes#17761
## Solution
- Added core error to InvalidDirectionError
## Testing
- Did you test these changes? If so, how?
- An added test that pulls in anyhow as a dev dependency to ensure the
conversion is accounted for in creation via From
- Are there any parts that need more testing?
- I'm unsure but probably not due to being a trivial change
- How can other people (reviewers) test your changes? Is there anything
specific they need to know?
- I did not try a fully built version of Bevy. Relied purely on tests.
- If relevant, what platforms did you test these changes on, and are
there any important ones you can't test?
- Only windows
---------
Co-authored-by: Chanceler Shaffer <cshaffer2@lululemon.com>
Co-authored-by: Chanceler Shaffer <chancelershaffer@lululemon.com>
# Objective
A `TransparentUI` phase's items all target the same camera so there is
no need to store the current camera entity in `UiBatch` and ending the
current `UiBatch` on camera changes is pointless as the camera doesn't
change.
## Solution
Remove the `camera` fields from `UiBatch`, `UiShadowsBatch` and
`UiTextureSliceBatch`.
Remove the camera changed check from `prepare_uinodes`.
## Testing
The `multiple_windows` and `split_screen` examples both render UI
elements to multiple cameras and can be used to test these changes.
The UI material plugin already didn't store the camera entity per batch
and worked fine without it.
# Objective
- Contributes to #15460
- Reduce quantity and complexity of feature gates across Bevy
## Solution
- Used `target_has_atomic` configuration variable to automatically
detect impartial atomic support and automatically switch to
`portable-atomic` over the standard library on an as-required basis.
## Testing
- CI
## Notes
To explain the technique employed here, consider getting `Arc` either
from `alloc::sync` _or_ `portable-atomic-util`. First, we can inspect
the `alloc` crate to see that you only have access to `Arc` _if_
`target_has_atomic = "ptr"`. We add a target dependency for this
particular configuration _inverted_:
```toml
[target.'cfg(not(target_has_atomic = "ptr"))'.dependencies]
portable-atomic-util = { version = "0.2.4", default-features = false }
```
This ensures we only have the dependency when it is needed, and it is
entirely excluded from the dependency graph when it is not. Next, we
adjust our configuration flags to instead of checking for `feature =
"portable-atomic"` to instead check for `target_has_atomic = "ptr"`:
```rust
// `alloc` feature flag hidden for brevity
#[cfg(not(target_has_atomic = "ptr"))]
use portable_atomic_util as arc;
#[cfg(target_has_atomic = "ptr")]
use alloc::sync as arc;
pub use arc::{Arc, Weak};
```
The benefits of this technique are three-fold:
1. For platforms without full atomic support, the functionality is
enabled automatically.
2. For platforms with atomic support, the dependency is never included,
even if a feature was enabled using `--all-features` (for example)
3. The `portable-atomic` feature no longer needs to virally spread to
all user-facing crates, it's instead something handled within
`bevy_platform_support` (with some extras where other dependencies also
need their features enabled).
# Objective
- The previous implementation of automatically inserting sync points did
not consider explicitly added sync points. This created additional sync
points. For example:
```
A-B
C-D-E
```
If `A` and `B` needed a sync point, and `D` was an `ApplyDeferred`, an
additional sync point would be generated between `A` and `B`.
```
A-D2-B
C-D -E
```
This can result in the following system ordering:
```
A-D2-(B-C)-D-E
```
Where only `B` and `C` run in parallel. If we could reuse `D` as the
sync point, we would get the following ordering:
```
(A-C)-D-(B-E)
```
Now we have two more opportunities for parallelism!
## Solution
- In the first pass, we:
- Compute the number of sync points before each node
- This was already happening but now we consider `ApplyDeferred` nodes
as creating a sync point.
- Pick an arbitrary explicit `ApplyDeferred` node for each "sync point
index" that we can (some required sync points may be missing!)
- In the second pass, we:
- For each edge, if two nodes have a different number of sync points
before them then there must be a sync point between them.
- Look for an explicit `ApplyDeferred`. If one exists, use it as the
sync point.
- Otherwise, generate a new sync point.
I believe this should also gracefully handle changes to the
`ScheduleGraph`. Since automatically inserted sync points are inserted
as systems, they won't look any different to explicit sync points, so
they are also candidates for "reusing" sync points.
One thing this solution does not handle is "deduping" sync points. If
you add 10 sync points explicitly, there will be at least 10 sync
points. You could keep track of all the sync points at the same
"distance" and then hack apart the graph to dedup those, but that could
be a follow-up step (and it's more complicated since you have to worry
about transferring edges between nodes).
## Testing
- Added a test to test the feature.
- The existing tests from all our crates still pass.
## Showcase
- Automatically inserted sync points can now reuse explicitly inserted
`ApplyDeferred` systems! Previously, Bevy would add new sync points
between systems, ignoring the explicitly added sync points. This would
reduce parallelism of systems in some situations. Now, the parallelism
has been improved!
# Objective
- Closes#12944.
## Solution
- Load `R8G8B8` textures by transcoding to an rgba format since `wgpu`
does not support texture formats with 3 channels.
- Switch to erroring out instead of panicking on an invalid dds file.
---
## Changelog
### Added
- DDS Textures with the `R8G8B8` format are now supported. They require
an additional conversion step, so using `R8G8B8A8` or a similar format
is preferable for texture loading performance.
# Objective
- Fixes#17960
## Solution
- Followed the [edition upgrade
guide](https://doc.rust-lang.org/edition-guide/editions/transitioning-an-existing-project-to-a-new-edition.html)
## Testing
- CI
---
## Summary of Changes
### Documentation Indentation
When using lists in documentation, proper indentation is now linted for.
This means subsequent lines within the same list item must start at the
same indentation level as the item.
```rust
/* Valid */
/// - Item 1
/// Run-on sentence.
/// - Item 2
struct Foo;
/* Invalid */
/// - Item 1
/// Run-on sentence.
/// - Item 2
struct Foo;
```
### Implicit `!` to `()` Conversion
`!` (the never return type, returned by `panic!`, etc.) no longer
implicitly converts to `()`. This is particularly painful for systems
with `todo!` or `panic!` statements, as they will no longer be functions
returning `()` (or `Result<()>`), making them invalid systems for
functions like `add_systems`. The ideal fix would be to accept functions
returning `!` (or rather, _not_ returning), but this is blocked on the
[stabilisation of the `!` type
itself](https://doc.rust-lang.org/std/primitive.never.html), which is
not done.
The "simple" fix would be to add an explicit `-> ()` to system
signatures (e.g., `|| { todo!() }` becomes `|| -> () { todo!() }`).
However, this is _also_ banned, as there is an existing lint which (IMO,
incorrectly) marks this as an unnecessary annotation.
So, the "fix" (read: workaround) is to put these kinds of `|| -> ! { ...
}` closuers into variables and give the variable an explicit type (e.g.,
`fn()`).
```rust
// Valid
let system: fn() = || todo!("Not implemented yet!");
app.add_systems(..., system);
// Invalid
app.add_systems(..., || todo!("Not implemented yet!"));
```
### Temporary Variable Lifetimes
The order in which temporary variables are dropped has changed. The
simple fix here is _usually_ to just assign temporaries to a named
variable before use.
### `gen` is a keyword
We can no longer use the name `gen` as it is reserved for a future
generator syntax. This involved replacing uses of the name `gen` with
`r#gen` (the raw-identifier syntax).
### Formatting has changed
Use statements have had the order of imports changed, causing a
substantial +/-3,000 diff when applied. For now, I have opted-out of
this change by amending `rustfmt.toml`
```toml
style_edition = "2021"
```
This preserves the original formatting for now, reducing the size of
this PR. It would be a simple followup to update this to 2024 and run
`cargo fmt`.
### New `use<>` Opt-Out Syntax
Lifetimes are now implicitly included in RPIT types. There was a handful
of instances where it needed to be added to satisfy the borrow checker,
but there may be more cases where it _should_ be added to avoid
breakages in user code.
### `MyUnitStruct { .. }` is an invalid pattern
Previously, you could match against unit structs (and unit enum
variants) with a `{ .. }` destructuring. This is no longer valid.
### Pretty much every use of `ref` and `mut` are gone
Pattern binding has changed to the point where these terms are largely
unused now. They still serve a purpose, but it is far more niche now.
### `iter::repeat(...).take(...)` is bad
New lint recommends using the more explicit `iter::repeat_n(..., ...)`
instead.
## Migration Guide
The lifetimes of functions using return-position impl-trait (RPIT) are
likely _more_ conservative than they had been previously. If you
encounter lifetime issues with such a function, please create an issue
to investigate the addition of `+ use<...>`.
## Notes
- Check the individual commits for a clearer breakdown for what
_actually_ changed.
---------
Co-authored-by: François Mockers <francois.mockers@vleue.com>
# Objective
`Eq`/`PartialEq` are currently implemented for `MeshMaterial{2|3}d` only
through the derive macro. Since we don't have perfect derive yet, the
impls are only present for `M: Eq` and `M: PartialEq`. On the other
hand, I want to be able to compare material components for my toy
reactivity project.
## Solution
Switch to manual `Eq`/`PartialEq` impl.
## Testing
Boy I hope this didn't break anything!
# Objective
Fixes#17488
## Solution
The world update logic happened in the the `about_to_wait` winit window
callback, but this is is not correct as (1) the winit documentation
states that the callback should not be used for that purpose and (2) the
callback is not fired when the window is resized or being dragged.
However, that callback was used in #11245 to fix an iOS bug (which
caused the regression). The solution presented here is a workaround
until the event loop code can be re-written.
## Testing
I confirmed that the `eased_motion` example continued to be animated
when dragging or resizing the window.
https://github.com/user-attachments/assets/ffaf0abf-4cd7-479b-83e9-e1850aaf3513
- Remove references to the short-lived `CommandError` type.
- Add a sentence to the explanation of error handlers.
- Clean up spacing/linebreaks.
- Use `where` notation for command-related trait `impl`s to make the big
ones easier to parse.
Fixes#17856.
## Migration Guide
- `EventWriter::send` has been renamed to `EventWriter::write`.
- `EventWriter::send_batch` has been renamed to
`EventWriter::write_batch`.
- `EventWriter::send_default` has been renamed to
`EventWriter::write_default`.
---------
Co-authored-by: François Mockers <mockersf@gmail.com>
# Objective
- Make transform propagation faster.
## Solution
- Work sharing worker threads
- Parallel tree traversal excluding leaves
- Second cache friendly wide pass over all leaves
- 3-10x faster than main
## Testing
- Tracy
- Caldera hotel is showing 3-7x faster on my M4 Max. Timing for bevy's
existing transform system shifts wildly run to run, so I don't know that
I would advertise a particular number. But this implementation is faster
in a... statistically significant way.

---------
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: François Mockers <mockersf@gmail.com>
PR #17898 regressed this, causing much of #17970. This commit fixes the
issue by freeing and reallocating materials in the
`MaterialBindGroupAllocator` on change. Note that more efficiency is
possible, but I opted for the simple approach because (1) we should fix
this bug ASAP; (2) I'd like #17965 to land first, because that unlocks
the biggest potential optimization, which is not recreating the bind
group if it isn't necessary to do so.
We might not be able to prepare a material on the first frame we
encounter a mesh using it for various reasons, including that the
material hasn't been loaded yet or that preparing the material is
exceeding the per-frame cap on number of bytes to load. When this
happens, we currently try to find the material in the
`MaterialBindGroupAllocator`, fail, and then fall back to group 0, slot
0, the default `MaterialBindGroupId`, which is obviously incorrect.
Worse, we then fail to dirty the mesh and reextract it when we *do*
finish preparing the material, so the mesh will continue to be rendered
with an incorrect material.
This patch fixes both problems. In `collect_meshes_for_gpu_building`, if
we fail to find a mesh's material in the `MeshBindGroupAllocator`, then
we detect that case, bail out, and add it to a list,
`MeshesToReextractNextFrame`. On subsequent frames, we process all the
meshes in `MeshesToReextractNextFrame` as though they were changed. This
ensures both that we don't render a mesh if its material hasn't been
loaded and that we start rendering the mesh once its material does load.
This was first noticed in the intermittent Pixel Eagle failures in the
`testbed_3d` patch in #17898, although the problem has actually existed
for some time. I believe it just so happened that the changes to the
allocator in that PR caused the problem to appear more commonly than it
did before.
This patch fixes two bugs in the new non-bindless material allocator
that landed in PR #17898:
1. A debug assertion to prevent double frees had been flipped: we
checked to see whether the slot was empty before freeing, while we
should have checked to see whether the slot was full.
2. The non-bindless allocator returned `None` when querying a slab that
hadn't been prepared yet instead of returning a handle to that slab.
This resulted in a 1-frame delay when modifying materials. In the
`animated_material` example, this resulted in the meshes never showing
up at all, because that example changes every material every frame.
Together with #17979, this patch locally fixes the problems with
`animated_material` on macOS that were reported in #17970.
# Objective
Fixes#8615
## Solution
Bevy currently interprets 1x1 dds textures as 1-dimensional. I think it
might be more common for game engines to assume two dimensions in this
ambiguous case. [citation needed]
I reworked the dimension choosing logic to only use 1d if there's a
dimension > 1, and assume 2d otherwise. I kept the assumption that
compressed textures are probably 2d.
## Testing
Modified `sprite.rs` to use `Tex_0012_0.dds` from the linked issue.
---------
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
# Objective
Fix#17924
## Solution
Use fully qualified syntax (`usize::from` rather than `.into()`).
## Testing
Ran a build for the platform specified in the issue.
---------
Co-authored-by: Gino Valente <49806985+MrGVSV@users.noreply.github.com>
Fixes#17883
# Objective + Solution
When doing normal scene root entity despawns (which are notably now
recursive), do not despawn instanced entities that are no longer in the
hierarchy.
(I would not classify this as a bug, but rather a behavior change)
## Migration Guide
If you previously relied on scene entities no longer in the hierarchy
being despawned when the scene root is despawned , use
`SceneSpawner::despawn_instance()` instead.
# Objective
Calling `define_label!` in a `no_std` 3rd party crate currently requires
the user to import `Box` themselves due to a non-fully-specified
reference to `Box`.
## Solution
Add a fully specified path for `Box` in the one location necessary, to
match all of the other cases.
Two-phase occlusion culling can be helpful for shadow maps just as it
can for a prepass, in order to reduce vertex and alpha mask fragment
shading overhead. This patch implements occlusion culling for shadow
maps from directional lights, when the `OcclusionCulling` component is
present on the entities containing the lights. Shadow maps from point
lights are deferred to a follow-up patch. Much of this patch involves
expanding the hierarchical Z-buffer to cover shadow maps in addition to
standard view depth buffers.
The `scene_viewer` example has been updated to add `OcclusionCulling` to
the directional light that it creates.
This improved the performance of the rend3 sci-fi test scene when
enabling shadows.
Currently, Bevy's implementation of bindless resources is rather
unusual: every binding in an object that implements `AsBindGroup` (most
commonly, a material) becomes its own separate binding array in the
shader. This is inefficient for two reasons:
1. If multiple materials reference the same texture or other resource,
the reference to that resource will be duplicated many times. This
increases `wgpu` validation overhead.
2. It creates many unused binding array slots. This increases `wgpu` and
driver overhead and makes it easier to hit limits on APIs that `wgpu`
currently imposes tight resource limits on, like Metal.
This PR fixes these issues by switching Bevy to use the standard
approach in GPU-driven renderers, in which resources are de-duplicated
and passed as global arrays, one for each type of resource.
Along the way, this patch introduces per-platform resource limits and
bumps them from 16 resources per binding array to 64 resources per bind
group on Metal and 2048 resources per bind group on other platforms.
(Note that the number of resources per *binding array* isn't the same as
the number of resources per *bind group*; as it currently stands, if all
the PBR features are turned on, Bevy could pack as many as 496 resources
into a single slab.) The limits have been increased because `wgpu` now
has universal support for partially-bound binding arrays, which mean
that we no longer need to fill the binding arrays with fallback
resources on Direct3D 12. The `#[bindless(LIMIT)]` declaration when
deriving `AsBindGroup` can now simply be written `#[bindless]` in order
to have Bevy choose a default limit size for the current platform.
Custom limits are still available with the new
`#[bindless(limit(LIMIT))]` syntax: e.g. `#[bindless(limit(8))]`.
The material bind group allocator has been completely rewritten. Now
there are two allocators: one for bindless materials and one for
non-bindless materials. The new non-bindless material allocator simply
maintains a 1:1 mapping from material to bind group. The new bindless
material allocator maintains a list of slabs and allocates materials
into slabs on a first-fit basis. This unfortunately makes its
performance O(number of resources per object * number of slabs), but the
number of slabs is likely to be low, and it's planned to become even
lower in the future with `wgpu` improvements. Resources are
de-duplicated with in a slab and reference counted. So, for instance, if
multiple materials refer to the same texture, that texture will exist
only once in the appropriate binding array.
To support these new features, this patch adds the concept of a
*bindless descriptor* to the `AsBindGroup` trait. The bindless
descriptor allows the material bind group allocator to probe the layout
of the material, now that an array of `BindGroupLayoutEntry` records is
insufficient to describe the group. The `#[derive(AsBindGroup)]` has
been heavily modified to support the new features. The most important
user-facing change to that macro is that the struct-level `uniform`
attribute, `#[uniform(BINDING_NUMBER, StandardMaterial)]`, now reads
`#[uniform(BINDLESS_INDEX, MATERIAL_UNIFORM_TYPE,
binding_array(BINDING_NUMBER)]`, allowing the material to specify the
binding number for the binding array that holds the uniform data.
To make this patch simpler, I removed support for bindless
`ExtendedMaterial`s, as well as field-level bindless uniform and storage
buffers. I intend to add back support for these as a follow-up. Because
they aren't in any released Bevy version yet, I figured this was OK.
Finally, this patch updates `StandardMaterial` for the new bindless
changes. Generally, code throughout the PBR shaders that looked like
`base_color_texture[slot]` now looks like
`bindless_2d_textures[material_indices[slot].base_color_texture]`.
This patch fixes a system hang that I experienced on the [Caldera test]
when running with `caldera --random-materials --texture-count 100`. The
time per frame is around 19.75 ms, down from 154.2 ms in Bevy 0.14: a
7.8× speedup.
[Caldera test]: https://github.com/DGriffin91/bevy_caldera_scene
Deferred rendering currently doesn't support occlusion culling. This PR
implements it in a straightforward way, mirroring what we already do for
the non-deferred pipeline.
On the rend3 sci-fi base test scene, this resulted in roughly a 2×
speedup when applied on top of my other patches. For that scene, it was
useful to add another option, `--add-light`, which forces the addition
of a shadow-casting light, to the scene viewer, which I included in this
patch.
This commit restructures the multidrawable batch set builder for better
performance in various ways:
* The bin traversal is optimized to make the best use of the CPU cache.
* The inner loop that iterates over the bins, which is the hottest part
of `batch_and_prepare_binned_render_phase`, has been shrunk as small as
possible.
* Where possible, multiple elements are added to or reserved from GPU
buffers as a batch instead of one at a time.
* Methods that LLVM wasn't inlining have been marked `#[inline]` where
doing so would unlock optimizations.
This code has also been refactored to avoid duplication between the
logic for indexed and non-indexed meshes via the introduction of a
`MultidrawableBatchSetPreparer` object.
Together, this improved the `batch_and_prepare_binned_render_phase` time
on Caldera by approximately 2×.
Eventually, we should optimize the batchable-but-not-multidrawable and
unbatchable logic as well, but these meshes are much rarer, so in the
interests of keeping this patch relatively small I opted to leave those
to a follow-up.
# Objective
Fix incorrect mesh culling where objects (particularly directional
shadows) were being incorrectly culled during the early preprocessing
phase. The issue manifested specifically on Apple M1 GPUs but not on
newer devices like the M4. The bug was in the
`view_frustum_intersects_obb` function, where including the w component
(plane distance) in the dot product calculations led to false positive
culling results. This caused objects to be incorrectly culled before
shadow casting could begin.
## Issue Details
The problem of missing shadows is reproducible on Apple M1 GPUs as of
this commit (bisected):
```
00722b8d0 Make indirect drawing opt-out instead of opt-in, enabling multidraw by default. (#16757)
```
and as recent as this commit:
```
c818c9214 Add option to animate materials in many_cubes (#17927)
```
- The frustum culling calculation incorrectly included the w component
(plane distance) when transforming basis vectors
- The relative radius calculation should only consider directional
transformation (xyz), not positional information (w)
- This caused false positive culling specifically on M1 devices likely
due to different device-specific floating-point behavior
- When objects were incorrectly culled, `early_instance_count` never
incremented, leading to missing geometry in the shadow pass
## Testing
- Tested on M1 and M4 devices to verify the fix
- Verified shadows and geometry render correctly on both platforms
- Confirmed the solution matches the existing Rust implementation's
behavior for calculating the relative radius:
c818c92143/crates/bevy_render/src/primitives/mod.rs (L77-L87)
- The fix resolves a mathematical error in the frustum culling
calculation while maintaining correct culling behavior across all
platforms.
---
## Showcase
`c818c9214`
<img width="1284" alt="c818c9214"
src="https://github.com/user-attachments/assets/fe1c7ea9-b13d-422e-b12d-f1cd74475213"
/>
`mate-h/frustum-cull-fix`
<img width="1283" alt="frustum-cull-fix"
src="https://github.com/user-attachments/assets/8a9ccb2a-64b6-4d5e-a17d-ac4798da5b51"
/>
# Objective
Make checked vs unchecked shaders configurable
Fixes#17786
## Solution
Added `ValidateShaders` enum to `Shader` and added
`create_and_validate_shader_module` to `RenderDevice`
## Testing
I tested the shader examples locally and they all worked. I'd like to
write a few tests to verify but am unsure how to start.
---------
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
The `check_visibility` system currently follows this algorithm:
1. Store all meshes that were visible last frame in the
`PreviousVisibleMeshes` set.
2. Determine which meshes are visible. For each such visible mesh,
remove it from `PreviousVisibleMeshes`.
3. Mark all meshes that remain in `PreviousVisibleMeshes` as invisible.
This algorithm would be correct if the `check_visibility` were the only
system that marked meshes visible. However, it's not: the shadow-related
systems `check_dir_light_mesh_visibility` and
`check_point_light_mesh_visibility` can as well. This results in the
following sequence of events for meshes that are in a shadow map but
*not* visible from a camera:
A. `check_visibility` runs, finds that no camera contains these meshes,
and marks them hidden, which sets the changed flag.
B. `check_dir_light_mesh_visibility` and/or
`check_point_light_mesh_visibility` run, discover that these meshes
are visible in the shadow map, and marks them as visible, again
setting the `ViewVisibility` changed flag.
C. During the extraction phase, the mesh extraction system sees that
`ViewVisibility` is changed and re-extracts the mesh.
This is inefficient and results in needless work during rendering.
This patch fixes the issue in two ways:
* The `check_dir_light_mesh_visibility` and
`check_point_light_mesh_visibility` systems now remove meshes that they
discover from `PreviousVisibleMeshes`.
* Step (3) above has been moved from `check_visibility` to a separate
system, `mark_newly_hidden_entities_invisible`. This system runs after
all visibility-determining systems, ensuring that
`PreviousVisibleMeshes` contains only those meshes that truly became
invisible on this frame.
This fix dramatically improves the performance of [the Caldera
benchmark], when combined with several other patches I've submitted.
[the Caldera benchmark]:
https://github.com/DGriffin91/bevy_caldera_scene
PR #17688 broke motion vector computation, and therefore motion blur,
because it enabled retention of `MeshInputUniform`s, and
`MeshInputUniform`s contain the indices of the previous frame's
transform and the previous frame's skinned mesh joint matrices. On frame
N, if a `MeshInputUniform` is retained on GPU from the previous frame,
the `previous_input_index` and `previous_skin_index` would refer to the
indices for frame N - 2, not the index for frame N - 1.
This patch fixes the problems. It solves these issues in two different
ways, one for transforms and one for skins:
1. To fix transforms, this patch supplies the *frame index* to the
shader as part of the view uniforms, and specifies which frame index
each mesh's previous transform refers to. So, in the situation described
above, the frame index would be N, the previous frame index would be N -
1, and the `previous_input_frame_number` would be N - 2. The shader can
now detect this situation and infer that the mesh has been retained, and
can therefore conclude that the mesh's transform hasn't changed.
2. To fix skins, this patch replaces the explicit `previous_skin_index`
with an invariant that the index of the joints for the current frame and
the index of the joints for the previous frame are the same. This means
that the `MeshInputUniform` never has to be updated even if the skin is
animated. The downside is that we have to copy joint matrices from the
previous frame's buffer to the current frame's buffer in
`extract_skins`.
The rationale behind (2) is that we currently have no mechanism to
detect when joints that affect a skin have been updated, short of
comparing all the transforms and setting a flag for
`extract_meshes_for_gpu_building` to consume, which would regress
performance as we want `extract_skins` and
`extract_meshes_for_gpu_building` to be able to run in parallel.
To test this change, use `cargo run --example motion_blur`.
Currently, the specialized pipeline cache maps a (view entity, mesh
entity) tuple to the retained pipeline for that entity. This causes two
problems:
1. Using the view entity is incorrect, because the view entity isn't
stable from frame to frame.
2. Switching the view entity to a `RetainedViewEntity`, which is
necessary for correctness, significantly regresses performance of
`specialize_material_meshes` and `specialize_shadows` because of the
loss of the fast `EntityHash`.
This patch fixes both problems by switching to a *two-level* hash table.
The outer level of the table maps each `RetainedViewEntity` to an inner
table, which maps each `MainEntity` to its pipeline ID and change tick.
Because we loop over views first and, within that loop, loop over
entities visible from that view, we hoist the slow lookup of the view
entity out of the inner entity loop.
Additionally, this patch fixes a bug whereby pipeline IDs were leaked
when removing the view. We still have a problem with leaking pipeline
IDs for deleted entities, but that won't be fixed until the specialized
pipeline cache is retained.
This patch improves performance of the [Caldera benchmark] from 7.8×
faster than 0.14 to 9.0× faster than 0.14, when applied on top of the
global binding arrays PR, #17898.
[Caldera benchmark]: https://github.com/DGriffin91/bevy_caldera_scene
Currently, Bevy rebuilds the buffer containing all the transforms for
joints every frame, during the extraction phase. This is inefficient in
cases in which many skins are present in the scene and their joints
don't move, such as the Caldera test scene.
To address this problem, this commit switches skin extraction to use a
set of retained GPU buffers with allocations managed by the offset
allocator. I use fine-grained change detection in order to determine
which skins need updating. Note that the granularity is on the level of
an entire skin, not individual joints. Using the change detection at
that level would yield poor performance in common cases in which an
entire skin is animated at once. Also, this patch yields additional
performance from the fact that changing joint transforms no longer
requires the skinned mesh to be re-extracted.
Note that this optimization can be a double-edged sword. In
`many_foxes`, fine-grained change detection regressed the performance of
`extract_skins` by 3.4x. This is because every joint is updated every
frame in that example, so change detection is pointless and is pure
overhead. Because the `many_foxes` workload is actually representative
of animated scenes, this patch includes a heuristic that disables
fine-grained change detection if the number of transformed entities in
the frame exceeds a certain fraction of the total number of joints.
Currently, this threshold is set to 25%. Note that this is a crude
heuristic, because it doesn't distinguish between the number of
transformed *joints* and the number of transformed *entities*; however,
it should be good enough to yield the optimum code path most of the
time.
Finally, this patch fixes a bug whereby skinned meshes are actually
being incorrectly retained if the buffer offsets of the joints of those
skinned meshes changes from frame to frame. To fix this without
retaining skins, we would have to re-extract every skinned mesh every
frame. Doing this was a significant regression on Caldera. With this PR,
by contrast, mesh joints stay at the same buffer offset, so we don't
have to update the `MeshInputUniform` containing the buffer offset every
frame. This also makes PR #17717 easier to implement, because that PR
uses the buffer offset from the previous frame, and the logic for
calculating that is simplified if the previous frame's buffer offset is
guaranteed to be identical to that of the current frame.
On Caldera, this patch reduces the time spent in `extract_skins` from
1.79 ms to near zero. On `many_foxes`, this patch regresses the
performance of `extract_skins` by approximately 10%-25%, depending on
the number of foxes. This has only a small impact on frame rate.
The GPU can fill out many of the fields in `IndirectParametersMetadata`
using information it already has:
* `early_instance_count` and `late_instance_count` are always
initialized to zero.
* `mesh_index` is already present in the work item buffer as the
`input_index` of the first work item in each batch.
This patch moves these fields to a separate buffer, the *GPU indirect
parameters metadata* buffer. That way, it avoids having to write them on
CPU during `batch_and_prepare_binned_render_phase`. This effectively
reduces the number of bits that that function must write per mesh from
160 to 64 (in addition to the 64 bits per mesh *instance*).
Additionally, this PR refactors `UntypedPhaseIndirectParametersBuffers`
to add another layer, `MeshClassIndirectParametersBuffers`, which allows
abstracting over the buffers corresponding indexed and non-indexed
meshes. This patch doesn't make much use of this abstraction, but
forthcoming patches will, and it's overall a cleaner approach.
This didn't seem to have much of an effect by itself on
`batch_and_prepare_binned_render_phase` time, but subsequent PRs
dependent on this PR yield roughly a 2× speedup.
# Objective
- #17787 removed sweeping of binned render phases from 2D by accident
due to them not using the `BinnedRenderPhasePlugin`.
- Fixes#17885
## Solution
- Schedule `sweep_old_entities` in `QueueSweep` like
`BinnedRenderPhasePlugin` does, but for 2D where that plugin is not
used.
## Testing
Tested with the modified `shader_defs` example in #17885 .
Fixes#17290.
<details>
<summary>Compilation errors before fix</summary>
`cargo clippy --tests --all-features --package bevy_image`:
```rust
error[E0061]: this function takes 7 arguments but 6 arguments were supplied
--> crates/bevy_core_pipeline/src/tonemapping/mod.rs:451:5
|
451 | Image::from_buffer(
| ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
...
454 | bytes,
| ----- argument #1 of type `std::string::String` is missing
|
note: associated function defined here
--> /Users/josiahnelson/Desktop/Programming/Rust/bevy/crates/bevy_image/src/image.rs:930:12
|
930 | pub fn from_buffer(
| ^^^^^^^^^^^
help: provide the argument
|
451 | Image::from_buffer(/* std::string::String */, bytes, image_type, CompressedImageFormats::NONE, false, image_sampler, RenderAssetUsages::RENDER_WORLD)
| ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
```
`cargo clippy --tests --all-features --package bevy_gltf`:
```rust
error[E0560]: struct `bevy_pbr::StandardMaterial` has no field named `specular_channel`
--> crates/bevy_gltf/src/loader.rs:1343:13
|
1343 | specular_channel: specular.specular_channel,
| ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^ `bevy_pbr::StandardMaterial` does not have this field
|
= note: available fields are: `emissive_exposure_weight`, `diffuse_transmission`, `diffuse_transmission_channel`, `diffuse_transmission_texture`, `flip_normal_map_y` ... and 9 others
error[E0560]: struct `bevy_pbr::StandardMaterial` has no field named `specular_texture`
--> crates/bevy_gltf/src/loader.rs:1345:13
|
1345 | specular_texture: specular.specular_texture,
| ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^ `bevy_pbr::StandardMaterial` does not have this field
|
= note: available fields are: `emissive_exposure_weight`, `diffuse_transmission`, `diffuse_transmission_channel`, `diffuse_transmission_texture`, `flip_normal_map_y` ... and 9 others
error[E0560]: struct `bevy_pbr::StandardMaterial` has no field named `specular_tint_channel`
--> crates/bevy_gltf/src/loader.rs:1351:13
|
1351 | specular_tint_channel: specular.specular_color_channel,
| ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^ `bevy_pbr::StandardMaterial` does not have this field
|
= note: available fields are: `emissive_exposure_weight`, `diffuse_transmission`, `diffuse_transmission_channel`, `diffuse_transmission_texture`, `flip_normal_map_y` ... and 9 others
error[E0560]: struct `bevy_pbr::StandardMaterial` has no field named `specular_tint_texture`
--> crates/bevy_gltf/src/loader.rs:1353:13
|
1353 | specular_tint_texture: specular.specular_color_texture,
| ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^ `bevy_pbr::StandardMaterial` does not have this field
|
= note: available fields are: `emissive_exposure_weight`, `diffuse_transmission`, `diffuse_transmission_channel`, `diffuse_transmission_texture`, `flip_normal_map_y` ... and 9 others
```
</details>
# Objective
Fixes#17022
## Solution
Only enable `bevy_gltf/dds` if `bevy_gltf` is already enabled.
## Testing
Tested with empty project
```toml
[dependencies]
bevy = { version = "0.16.0-dev", path = "../bevy", default-features = false, features = [
"dds",
] }
```
### Before
```
cargo tree --depth 1 -i bevy_gltf
bevy_gltf v0.16.0-dev (/Users/robparrett/src/bevy/crates/bevy_gltf)
└── bevy_internal v0.16.0-dev (/Users/robparrett/src/bevy/crates/bevy_internal)
```
### After
```
cargo tree --depth 1 -i bevy_gltf
warning: nothing to print.
To find dependencies that require specific target platforms, try to use option `--target all` first, and then narrow your search scope accordingly.
```
# Context
Renaming `Parent` to `ChildOf` in #17247 has been contentious. While
those users concerns are valid (especially around legibility of code
IMO!), @cart [has
decided](https://discord.com/channels/691052431525675048/749335865876021248/1340434322833932430)
to stick with the new name.
> In general this conversation is unsurprising to me, as it played out
essentially the same way when I asked for opinions in my PR. There are
strong opinions on both sides. Everyone is right in their own way.
>
> I chose ChildOf for the following reasons:
>
> 1. I think it derives naturally from the system we have built, the
concepts we have chosen, and how we generally name the types that
implement a trait in Rust. This is the name of the type implementing
Relationship. We are adding that Relationship component to a given
entity (whether it "is" the relationship or "has" the relationship is
kind of immaterial ... we are naming the relationship that it "is" or
"has"). What is the name of the relationship that a child has to its
parent? It is a "child" of the parent of course!
> 2. In general the non-parent/child relationships I've seen in the wild
generally benefit from (or need to) use the naming convention in (1)
(aka calling the Relationship the name of the relationship the entity
has). Many relationships don't have an equivalent to the Parent/Child
name concept.
> 3. I do think we could get away with using (1) for pretty much
everything else and special casing Parent/Children. But by embracing the
naming convention, we help establish that this is in fact a pattern, and
we help prime people to think about these things in a consistent way.
Consistency and predictability is a generally desirable property. And
for something as divisive and polarizing as relationship naming, I think
drawing a hard line in the sand is to the benefit of the community as a
whole.
> 4. I believe the fact that we dont see as much of the XOf naming style
elsewhere is to our benefit. When people see things in that style, they
are primed to think of them as relationships (after some exposure to
Bevy and the ecosystem). I consider this a useful hint.
> 5. Most of the practical confusion from using ChildOf seems to be from
calling the value of the target field we read from the relationship
child_of. The name of the target field should be parent (we could even
consider renaming child_of.0 to child_of.parent for clarity). I suspect
that existing Bevy users renaming their existing code will feel the most
friction here, as this requires a reframing. Imo it is natural and
expected to receive pushback from these users hitting this case.
## Objective
The new documentation doesn't do a particularly good job at quickly
explaining the meaning of each component or how to work with them;
making a tricky migration more painful and slowing down new users as
they learn about some of the most fundamental types in Bevy.
## Solution
1. Clearly explain what each component does in the very first line,
assuming no background knowledge. This is the first relationships that
99% of users will encounter, so explaining that they are relationships
is unhelpful as an introduction.
2. Add doc aliases for the rejected `IsParent`/`IsChild`/`Parent` names,
to improve autocomplete and doc searching.
3. Do some assorted docs cleanup while we're here.
---------
Co-authored-by: Eagster <79881080+ElliottjPierce@users.noreply.github.com>
## Objective
There's no general error for when an entity doesn't exist, and some
methods are going to need one when they get Resultified. The closest
thing is `EntityFetchError`, but that error has a slightly more specific
purpose.
## Solution
- Added `EntityDoesNotExistError`.
- Contains `Entity` and `EntityDoesNotExistDetails`.
- Changed `EntityFetchError` and `QueryEntityError`:
- Changed `NoSuchEntity` variant to wrap `EntityDoesNotExistError` and
renamed the variant to `EntityDoesNotExist`.
- Renamed `EntityFetchError` to `EntityMutableFetchError` to make its
purpose clearer.
- Renamed `TryDespawnError` to `EntityDespawnError` to make it more
general.
- Changed `World::inspect_entity` to return `Result<[ok],
EntityDoesNotExistError>` instead of panicking.
- Changed `World::get_entity` and `WorldEntityFetch::fetch_ref` to
return `Result<[ok], EntityDoesNotExistError>` instead of `Result<[ok],
Entity>`.
- Changed `UnsafeWorldCell::get_entity` to return
`Result<UnsafeEntityCell, EntityDoesNotExistError>` instead of
`Option<UnsafeEntityCell>`.
## Migration Guide
- `World::inspect_entity` now returns `Result<impl Iterator<Item =
&ComponentInfo>, EntityDoesNotExistError>` instead of `impl
Iterator<Item = &ComponentInfo>`.
- `World::get_entity` now returns `EntityDoesNotExistError` as an error
instead of `Entity`. You can still access the entity's ID through the
error's `entity` field.
- `UnsafeWorldCell::get_entity` now returns `Result<UnsafeEntityCell,
EntityDoesNotExistError>` instead of `Option<UnsafeEntityCell>`.
Appending to these vectors is performance-critical in
`batch_and_prepare_binned_render_phase`, so `RawBufferVec`, which
doesn't have the overhead of `encase`, is more appropriate.
The `collect_buffers_for_phase` system tries to reuse these buffers, but
its efforts are stymied by the fact that
`clear_batched_gpu_instance_buffers` clears the containing hash table
and therefore frees the buffers. This patch makes
`clear_batched_gpu_instance_buffers` stop doing that so that the
allocations can be reused.
# Objective
Simplify the API surface by removing duplicated functionality between
`Query` and `QueryState`.
Reduce the amount of `unsafe` code required in `QueryState`.
This is a follow-up to #15858.
## Solution
Move implementations of `Query` methods from `QueryState` to `Query`.
Instead of the original methods being on `QueryState`, with `Query`
methods calling them by passing the individual parameters, the original
methods are now on `Query`, with `QueryState` methods calling them by
constructing a `Query`.
This also adds two `_inner` methods that were missed in #15858:
`iter_many_unique_inner` and `single_inner`.
One goal here is to be able to deprecate and eventually remove many of
the methods on `QueryState`, reducing the overall API surface. (I
expected to do that in this PR, but this change was large enough on its
own!) Now that the `QueryState` methods each consist of a simple
expression like `self.query(world).get_inner(entity)`, a future PR can
deprecate some or all of them with simple migration instructions.
The other goal is to reduce the amount of `unsafe` code. The current
implementation of a read-only method like `QueryState::get` directly
calls the `unsafe fn get_unchecked_manual` and needs to repeat the proof
that `&World` has enough access. With this change, `QueryState::get` is
entirely safe code, with the proof that `&World` has enough access done
by the `query()` method and shared across all read-only operations.
## Future Work
The next step will be to mark the `QueryState` methods as
`#[deprecated]` and migrate callers to the methods on `Query`.
# Objective
Support accessing resources using reflection when using
`FilteredResources` in a dynamic system. This is similar to how
components can be queried using reflection when using
`FilteredEntityRef|Mut`.
## Solution
Change `ReflectResource` from taking `&World` and `&mut World` to taking
`impl Into<FilteredResources>` and `impl Into<FilteredResourcesMut>`,
similar to how `ReflectComponent` takes `impl Into<FilteredEntityRef>`
and `impl Into<FilteredEntityMut>`. There are `From` impls that ensure
code passing `&World` and `&mut World` continues to work as before.
## Migration Guide
If you are manually creating a `ReflectComponentFns` struct, the
`reflect` function now takes `FilteredResources` instead `&World`, and
there is a new `reflect_mut` function that takes `FilteredResourcesMut`.
# Objective
Add reference to reported position space in picking backend docs.
Fixes#17844
## Solution
Add explanatory docs to the implementation notes of each picking
backend.
## Testing
`cargo r -p ci -- doc-check` & `cargo r -p ci -- lints`
# Objective
It is impossible to register a type with `TypeRegistry::register` if the
type is unnameable (in the current scope).
## Solution
Add `TypeRegistry::register_by_val` which mirrors std's `size_of_val`
and friends.
## Testing
There's a doc test (unrelated but there seem to be some pre-existing
broken doc links in `bevy_reflect`).
There was nonsense code in `batch_and_prepare_sorted_render_phase` that
created temporary buffers to add objects to instead of using the correct
ones. I think this was debug code. This commit removes that code in
favor of writing to the actual buffers.
Closes#17846.
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
# Objective
`bevy_assets` has long been unapproachable for contributors and users.
More and better documentation would help that.
We're gradually moving towards globally denying missing docs (#3492)!
However, writing all of the hundreds of missing doc strings in a single
go will be miserable to review.
## Solution
Remove the allow for missing docs temporarily, and then pick some easy
missing doc warnings largely at random to tackle.
Stop when the change set is starting to feel intimidating.
The `output_index` field is only used in direct mode, and the
`indirect_parameters_index` field is only used in indirect mode.
Consequently, we can combine them into a single field, reducing the size
of `PreprocessWorkItem`, which
`batch_and_prepare_{binned,sorted}_render_phase` must construct every
frame for every mesh instance, from 96 bits to 64 bits.
# Objective
Continuation of #16547.
We do not yet have parallel versions of `par_iter_many` and
`par_iter_many_unique`. It is currently very painful to try and use
parallel iteration over entity lists. Even if a list is not long, each
operation might still be very expensive, and worth parallelizing.
Plus, it has been requested several times!
## Solution
Once again, we implement what we lack!
These parallel iterators collect their input entity list into a
`Vec`/`UniqueEntityVec`, then chunk that over the available threads,
inspired by the original `par_iter`.
Since no order guarantee is given to the caller, we could sort the input
list according to `EntityLocation`, but that would likely only be worth
it for very large entity lists.
There is some duplication which could likely be improved, but I'd like
to leave that for a follow-up.
## Testing
The doc tests on `for_each_init` of `QueryParManyIter` and
`QueryParManyUniqueIter`.
# Objective
While surveying the state of documentation for bevy_assets, I noticed a
few minor issues.
## Solution
Revise the docs to focus on clear explanations of core ideas and
cross-linking related objects.
# Objective
Update typos, fix new typos.
1.29.6 was just released to fix an
[issue](https://github.com/crate-ci/typos/issues/1228) where January's
corrections were not included in the binaries for the last release.
Reminder: typos can be tossed in the monthly [non-critical corrections
issue](https://github.com/crate-ci/typos/issues/1221).
## Solution
I chose to allow `implementors`, because a good argument seems to be
being made [here](https://github.com/crate-ci/typos/issues/1226) and
there is now a PR to address that.
## Discussion
Should I exclude `bevy_mikktspace`?
At one point I think we had an informal policy of "don't mess with
mikktspace until https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/9050 is merged"
but it doesn't seem like that is likely to be merged any time soon.
I think these particular corrections in mikktspace are fine because
- The same typo mistake seems to have been fixed in that PR
- The entire file containing these corrections was deleted in that PR
## Typo of the Month
correspindong -> corresponding
# Objective
Updates the now inaccurate position docs
Fixes#17832
## Solution
From
`The position of the intersection in the world, if the data is available
from the backend.`
To
`The position reported by the backend, if the data is available.
Position data may be in any space (e.g. World space, Screen space, Local
space), specified by the backend providing it.`
## Testing
uhh reading :)
Currently, invocations of `batch_and_prepare_binned_render_phase` and
`batch_and_prepare_sorted_render_phase` can't run in parallel because
they write to scene-global GPU buffers. After PR #17698,
`batch_and_prepare_binned_render_phase` started accounting for the
lion's share of the CPU time, causing us to be strongly CPU bound on
scenes like Caldera when occlusion culling was on (because of the
overhead of batching for the Z-prepass). Although I eventually plan to
optimize `batch_and_prepare_binned_render_phase`, we can obtain
significant wins now by parallelizing that system across phases.
This commit splits all GPU buffers that
`batch_and_prepare_binned_render_phase` and
`batch_and_prepare_sorted_render_phase` touches into separate buffers
for each phase so that the scheduler will run those phases in parallel.
At the end of batch preparation, we gather the render phases up into a
single resource with a new *collection* phase. Because we already run
mesh preprocessing separately for each phase in order to make occlusion
culling work, this is actually a cleaner separation. For example, mesh
output indices (the unique ID that identifies each mesh instance on GPU)
are now guaranteed to be sequential starting from 0, which will simplify
the forthcoming work to remove them in favor of the compute dispatch ID.
On Caldera, this brings the frame time down to approximately 9.1 ms with
occlusion culling on.

# Objective
Fix unsoundness introduced by #15858. `QueryLens::query()` would hand
out a `Query` with the full `'w` lifetime, and the new `_inner` methods
would let the results outlive the `Query`. This could be used to create
aliasing mutable references, like
```rust
fn bad<'w>(mut lens: QueryLens<'w, EntityMut>, entity: Entity) {
let one: EntityMut<'w> = lens.query().get_inner(entity).unwrap();
let two: EntityMut<'w> = lens.query().get_inner(entity).unwrap();
assert!(one.entity() == two.entity());
}
```
Fixes#17693
## Solution
Restrict the `'world` lifetime in the `Query` returned by
`QueryLens::query()` to `'_`, the lifetime of the borrow of the
`QueryLens`.
The model here is that `Query<'w, 's, D, F>` and `QueryLens<'w, D, F>`
have permission to access their components for the lifetime `'w`. So
going from `&'a mut QueryLens<'w>` to `Query<'w, 'a>` would borrow the
permission only for the `'a` lifetime, but incorrectly give it out for
the full `'w` lifetime.
To handle any cases where users were calling `get_inner()` or
`iter_inner()` on the `Query` and expecting the full `'w` lifetime, we
introduce a new `QueryLens::query_inner()` method. This is only valid
for `ReadOnlyQueryData`, so it may safely hand out a copy of the
permission for the full `'w` lifetime. Since `get_inner()` and
`iter_inner()` were only valid on `ReadOnlyQueryData` prior to #15858,
that should cover any uses that relied on the longer lifetime.
## Migration Guide
Users of `QueryLens::query()` who were calling `get_inner()` or
`iter_inner()` will need to replace the call with
`QueryLens::query_inner()`.
Conceptually, bins are ordered hash maps. We currently implement these
as a list of keys with an associated hash map. But we already have a
data type that implements ordered hash maps directly: `IndexMap`. This
patch switches Bevy to use `IndexMap`s for bins. Because we're memory
bound, this doesn't affect performance much, but it is cleaner.
# Objective
Related to #17784. The ticket is actually about just getting rid of
`Entity{Ref,Mut}Except` in favor of `FilteredEntity{Ref,Mut}`, but I got
told the unification of Entity types is a bigger endeavor that has been
going on for a while now (as the "Pointing Fingers" working group) and I
should just add the functions I actually need in the meantime.
## Solution
This PR adds all of the functions necessary to access components by
TypeId or ComponentId instead of static types.
## Testing
> Did you test these changes? If so, how?
Haven't tested it yet, but the changes are mostly copy/paste from other
implementations in the same file, since there is a lot of duplicated
functionality there.
## Not a Migration Guide
There shouldn't be any breaking changes, it's just a few new functions
on existing types.
I had to shuffle around the lifetimes in `From<&EntityMutExcept<'a, B>>
for EntityRefExcept<'a, B>` (originally it was `From<&'a
EntityMutExcept<'_, B>> for EntityRefExcept<'_, B>`) to make the borrow
checker happy, but I don't think that this should have an impact on user
code (correct me if I'm wrong).
* Use texture atomics rather than buffer atomics for the visbuffer
(haven't tested perf on a raster-heavy scene yet)
* Unfortunately to clear the visbuffer we now need a compute pass to
clear it. Using wgpu's clear_texture function internally uses a buffer
-> image copy that's insanely expensive. Ideally it should be using
vkCmdClearColorImage, which I've opened an issue for
https://github.com/gfx-rs/wgpu/issues/7090. For now we'll have to stick
with a custom compute pass and all the extra code that brings.
* Faster resolve depth pass by discarding 0 depth pixels instead of
redundantly writing zero (2x faster for big depth textures like shadow
views)
# Objective
- Wgpu has some expensive code it injects into shaders to avoid the
possibility of things like infinite loops. Generally our shaders are
written by users who won't do this, so it just makes our shaders perform
worse.
## Solution
- Turn off the checks.
- We could try to conditionally keep them, but that complicates the code
and 99.9% of users won't want this.
## Migration Guide
- Bevy no longer turns on wgpu's runtime safety checks
https://docs.rs/wgpu/latest/wgpu/struct.ShaderRuntimeChecks.html. If you
were using Bevy with untrusted shaders, please file an issue.
---------
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
# Objective
Continuation of #17589 and #16547.
Slices have several methods that return iterators which themselves yield
slices, which we have not yet implemented.
An example use is `par_iter_many` style logic.
## Solution
Their implementation is rather straightforward, we simply delegate all
impls to `[T]`.
The resulting iterator types need their own wrappers in the form of
`UniqueEntitySliceIter` and `UniqueEntitySliceIterMut`.
We also add three free functions that cast slices of entity slices to
slices of `UniqueEntitySlice`.
These three should be sufficient, though infinite nesting is achievable
with a trait (like `TrustedEntityBorrow` works over infinite reference
nesting), should the need ever arise.
## Objective
Get rid of a redundant Cargo feature flag.
## Solution
Use the built-in `target_abi = "sim"` instead of a custom Cargo feature
flag, which is set for the iOS (and visionOS and tvOS) simulator. This
has been stable since Rust 1.78.
In the future, some of this may become redundant if Wgpu implements
proper supper for the iOS Simulator:
https://github.com/gfx-rs/wgpu/issues/7057
CC @mockersf who implemented [the original
fix](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/10178).
## Testing
- Open mobile example in Xcode.
- Launch the simulator.
- See that no errors are emitted.
- Remove the code cfg-guarded behind `target_abi = "sim"`.
- See that an error now happens.
(I haven't actually performed these steps on the latest `main`, because
I'm hitting an unrelated error (EDIT: It was
https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/17637). But tested it on
0.15.0).
---
## Migration Guide
> If you're using a project that builds upon the mobile example, remove
the `ios_simulator` feature from your `Cargo.toml` (Bevy now handles
this internally).
Currently, we look up each `MeshInputUniform` index in a hash table that
maps the main entity ID to the index every frame. This is inefficient,
cache unfriendly, and unnecessary, as the `MeshInputUniform` index for
an entity remains the same from frame to frame (even if the input
uniform changes). This commit changes the `IndexSet` in the `RenderBin`
to an `IndexMap` that maps the `MainEntity` to `MeshInputUniformIndex`
(a new type that this patch adds for more type safety).
On Caldera with parallel `batch_and_prepare_binned_render_phase`, this
patch improves that function from 3.18 ms to 2.42 ms, a 31% speedup.
Currently, when a mesh slab overflows, we recreate the allocator and
reinsert all the meshes that were in it in an arbitrary order. This can
result in the meshes moving around. Before `MeshInputUniform`s were
retained, this was slow but harmless, because the `MeshInputUniform`
that contained the positions of the vertex and index data in the slab
would be recreated every frame. However, with mesh retention, there's no
guarantee that the `MeshInputUniform`, which could be cached from the
previous frame, will reflect the new position of the mesh data within
the buffer if that buffer happened to grow. This manifested itself as
seeming mesh data corruption when adding many meshes dynamically to the
scene.
There are three possible ways that I could have fixed this that I can
see:
1. Invalidate and rebuild all the `MeshInputUniform`s belonging to all
meshes in a slab when that mesh grows.
2. Introduce a second layer of indirection so that the
`MeshInputUniform` points to a *mesh allocation table* that contains the
current locations of the data of each mesh.
3. Avoid moving meshes when reallocating the buffer.
To be efficient, option (1) would require scanning meshes to see if
their positions changed, a la
`mark_meshes_as_changed_if_their_materials_changed`. Option (2) would
add more runtime indirection and would require additional bookkeeping on
the part of the allocator.
Therefore, this PR chooses option (3), which was remarkably simple to
implement. The key is that the offset allocator happens to allocate
addresses from low addresses to high addresses. So all we have to do is
to *conceptually* allocate the full 512 MiB mesh slab as far as the
offset allocator is concerned, and grow the underlying backing store
from 1 MiB to 512 MiB as needed. In other words, the allocator now
allocates *virtual* GPU memory, and the actual backing slab resizes to
fit the virtual memory. This ensures that the location of mesh data
remains constant for the lifetime of the mesh asset, and we can remove
the code that reinserts meshes one by one when the slab grows in favor
of a single buffer copy.
Closes#17766.
# Objective
- Fixes#17797
## Solution
- `mesh` in `bevy_pbr::mesh_bindings` is behind a `ifndef
MESHLET_MESH_MATERIAL_PASS`. also gate `get_tag` which uses this `mesh`
## Testing
- Run the meshlet example
# Objective
- In #17743, attention was raised to the fact that we supported an
unusual kind of step easing function. The author of the fix kindly
provided some links to standards used in CSS. It would be desirable to
support generally agreed upon standards so this PR here tries to
implement an extra configuration option of the step easing function
- Resolve#17744
## Solution
- Introduce `StepConfig`
- `StepConfig` can configure both the number of steps and the jumping
behavior of the function
- `StepConfig` replaces the raw `usize` parameter of the
`EasingFunction::Steps(usize)` construct.
- `StepConfig`s default jumping behavior is `end`, so in that way it
follows #17743
## Testing
- I added a new test per `JumpAt` jumping behavior. These tests
replicate the visuals that can be found at
https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/CSS/easing-function/steps#description
## Migration Guide
- `EasingFunction::Steps` now uses a `StepConfig` instead of a raw
`usize`. You can replicate the previous behavior by replaceing
`EasingFunction::Steps(10)` with
`EasingFunction::Steps(StepConfig::new(10))`.
---------
Co-authored-by: François Mockers <francois.mockers@vleue.com>
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
## Objective
There's no need for the `span_index` and `color` variables in
`extract_text_shadows` and `extract_text_sections` and we can remove one
of the span index comparisons since text colors are only set per
section.
## Testing
<img width="454" alt="trace"
src="https://github.com/user-attachments/assets/3109d1df-0817-46c2-9889-0459ac93a42c"
/>
This commit builds on top of the work done in #16589 and #17051, by
adding support for fallible observer systems.
As with the previous work, the actual results of the observer system are
suppressed for now, but the intention is to provide a way to handle
errors in a global way.
Until then, you can use a `PipeSystem` to manually handle results.
---------
Signed-off-by: Jean Mertz <git@jeanmertz.com>
## What problem does this solve or what need does it fill?
There are some situations
(https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/13735) where the ticks that
are present inside `Ref` are incorrect, for example if `Ref` is created
outside of a `SystemParam`.
I still want to use `Ref` because it has convenient `is_added` and
`is_changed` methods.
My current solution is to build my own `Ref` by copy-pasting most the
bevy code to do that via something like
```rust
/// This method is necessary because there is no easy way to
pub(crate) fn get_ref<C: Component>(
world: &World,
entity: Entity,
last_run: Tick,
this_run: Tick,
) -> Ref<C> {
unsafe {
let component_id = world
.components()
.get_id(TypeId::of::<C>())
.unwrap_unchecked();
let world = world.as_unsafe_world_cell_readonly();
let entity_cell = world.get_entity(entity).unwrap_unchecked();
get_component_and_ticks(
world,
component_id,
C::STORAGE_TYPE,
entity,
entity_cell.location(),
)
.map(|(value, cells, _caller)| {
Ref::new(
value.deref::<C>(),
cells.added.deref(),
cells.changed.deref(),
last_run,
this_run,
#[cfg(feature = "track_location")]
_caller.deref(),
)
})
.unwrap_unchecked()
}
}
// Utility function to return
#[inline]
unsafe fn get_component_and_ticks(
world: UnsafeWorldCell<'_>,
component_id: ComponentId,
storage_type: StorageType,
entity: Entity,
location: EntityLocation,
) -> Option<(Ptr<'_>, TickCells<'_>, MaybeUnsafeCellLocation<'_>)> {
match storage_type {
StorageType::Table => {
let table = unsafe { world.storages().tables.get(location.table_id) }?;
// SAFETY: archetypes only store valid table_rows and caller ensure aliasing rules
Some((
table.get_component(component_id, location.table_row)?,
TickCells {
added: table
.get_added_tick(component_id, location.table_row)
.unwrap_unchecked(),
changed: table
.get_changed_tick(component_id, location.table_row)
.unwrap_unchecked(),
},
#[cfg(feature = "track_location")]
table
.get_changed_by(component_id, location.table_row)
.unwrap_unchecked(),
#[cfg(not(feature = "track_location"))]
(),
))
}
StorageType::SparseSet => {
let storage = unsafe { world.storages() }.sparse_sets.get(component_id)?;
storage.get_with_ticks(entity)
}
}
}
```
It would be very convenient if instead bevy exposed a way to create a
`Ref` object with custom `last_run` and `this_run` ticks.
This PR does this by exposing a function to overwrite the `last_run` and
`this_run` ticks.
(Same with `Mut`)
I am ok with marking the method unsafe or risky if it's deemed to risky
for end-users.
# Objective
Add position reporting to `HitData` sent from the UI picking backend.
## Solution
Add the computed normalized relative cursor position to `hit_data`
alongside the `Entity`.
The position reported in `HitData` is normalized relative to the node,
with `(0.,0.,0.)` at the top left and `(1., 1., 0.)` in the bottom
right. Coordinates are relative to the entire node, not just the visible
region.
`HitData` needs a `Vec3` so I just extended with 0.0. I considered
inserting the `depth` here but thought it would be redundant.
I also considered putting the screen space position in the `normal`
field of `HitData`, but that would require renaming of the field or a
separate data structure.
## Testing
Tested with mouse on X11 with entities that have `Node` components.
---
## Showcase
```rs
// Get click position relative to node
fn hit_position(trigger: Trigger<Pointer<Click>>) {
let hit_pos = trigger.event.hit.position.expect("no position");
info!("{}", hit_pos);
}
```
---------
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
You can now configure error handlers for fallible systems. These can be
configured on several levels:
- Globally via `App::set_systems_error_handler`
- Per-schedule via `Schedule::set_error_handler`
- Per-system via a piped system (this is existing functionality)
The default handler of panicking on error keeps the same behavior as
before this commit.
The "fallible_systems" example demonstrates the new functionality.
This builds on top of #17731, #16589, #17051.
---------
Signed-off-by: Jean Mertz <git@jeanmertz.com>
This is a follow up fix for #17330 and fixes#17780.
There was a logic error in the ambiguity detection of
`cargo-manifest-proc-macros`.
`cargo-manifest-proc-macros` now has a test for this case to prevent the
issue in the future.
I also opted to hard fail if the `cargo-manifest-proc-macros` crate
fails. That way the error is more obvious and easier to fix and
diagnose.
## Testing
- The reproducer:
https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy_editor_prototypes/pull/178 works for
me using these fixes.
# Objective
Currently, default query filters, as added in #13120 / #17514 are
hardcoded to only use a single query filter.
This is limiting, as multiple distinct disabling components can serve
important distinct roles. I ran into this limitation when experimenting
with a workflow for prefabs, which don't represent the same state as "an
entity which is temporarily nonfunctional".
## Solution
1. Change `DefaultQueryFilters` to store a SmallVec of ComponentId,
rather than an Option.
2. Expose methods on `DefaultQueryFilters`, `World` and `App` to
actually configure this.
3. While we're here, improve the docs, write some tests, make use of
FromWorld and make some method names more descriptive.
## Follow-up
I'm not convinced that supporting sparse set disabling components is
useful, given the hit to iteration performance and runtime checks
incurred. That's disjoint from this PR though, so I'm not doing it here.
The existing warnings are fine for now.
## Testing
I've added both a doc test and an mid-level unit test to verify that
this works!
# Objective
Allow quick jump to definition of types of GlTFs labeled assets.
## Solution
Add links to the types refered on the docs of `GltfAssetLabel`
## Testing
Ran `cargo run -p ci`
# Objective
Since previously we only had the alpha channel available, we stored the
mean of the transmittance in the aerial view lut, resulting in a grayer
fog than should be expected.
## Solution
- Calculate transmittance to scene in `render_sky` with two samples from
the transmittance lut
- use dual-source blending to effectively have per-component alpha
blending
Currently, we *sweep*, or remove entities from bins when those entities
became invisible or changed phases, during `queue_material_meshes` and
similar phases. This, however, is wrong, because `queue_material_meshes`
executes once per material type, not once per phase. This could result
in sweeping bins multiple times per phase, which can corrupt the bins.
This commit fixes the issue by moving sweeping to a separate system that
runs after queuing.
This manifested itself as entities appearing and disappearing seemingly
at random.
Closes#17759.
---------
Co-authored-by: Robert Swain <robert.swain@gmail.com>
# Objective
Because of mesh preprocessing, users cannot rely on
`@builtin(instance_index)` in order to reference external data, as the
instance index is not stable, either from frame to frame or relative to
the total spawn order of mesh instances.
## Solution
Add a user supplied mesh index that can be used for referencing external
data when drawing instanced meshes.
Closes#13373
## Testing
Benchmarked `many_cubes` showing no difference in total frame time.
## Showcase
https://github.com/user-attachments/assets/80620147-aafc-4d9d-a8ee-e2149f7c8f3b
---------
Co-authored-by: IceSentry <IceSentry@users.noreply.github.com>
# Objective
- Expand the documentation for `EasingCurve`.
- I suspect this might have avoided the confusion in
https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/17711.
- Also add a shortcut for simple cases.
## Solution
- Added various examples and extra context.
- Implemented `Curve<T>` for `EaseFunction`.
- This means `EasingCurve::new(0.0, 1.0, EaseFunction::X)` can be
shortened to `EaseFunction::X`.
- In some cases this will be a minor performance improvement.
- Added test to confirm they're the same.
- ~~Added some benchmarks for bonus points.~~
## Side Notes
- I would have liked to rename `EaseFunction` to `EaseFn` for brevity,
but that would be a breaking change and maybe controversial.
- Also suspect `EasingCurve` should be `EaseCurve`, but say la vee.
- Benchmarks show that calling `EaseFunction::Smoothstep` is still
slower than calling `smoothstep` directly.
- I think this is because the compiler refuses to inline
`EaseFunction::eval`.
- I don't see any good solution - might need a whole different
interface.
## Testing
```sh
cargo test --package bevy_math
cargo doc --package bevy_math
./target/doc/bevy_math/curve/easing/struct.EasingCurve.html
cargo bench --package benches --bench math -- easing
```
# Objective
https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/17746
## Solution
- Change `Image.data` from being a `Vec<u8>` to a `Option<Vec<u8>>`
- Added functions to help with creating images
## Testing
- Did you test these changes? If so, how?
All current tests pass
Tested a variety of existing examples to make sure they don't crash
(they don't)
- If relevant, what platforms did you test these changes on, and are
there any important ones you can't test?
Linux x86 64-bit NixOS
---
## Migration Guide
Code that directly access `Image` data will now need to use unwrap or
handle the case where no data is provided.
Behaviour of new_fill slightly changed, but not in a way that is likely
to affect anything. It no longer panics and will fill the whole texture
instead of leaving black pixels if the data provided is not a nice
factor of the size of the image.
---------
Co-authored-by: IceSentry <IceSentry@users.noreply.github.com>
# Objective
Currently
[CosmicBuffer](https://docs.rs/bevy/latest/bevy/text/struct.CosmicBuffer.html)
is a public type with a public field that is not used or accessible in
any public API. Since it is prominently shown in the docs it is the
obvious place to start when trying to access `cosmic_string` features
such as for mapping between screen coordinates and positions in the
displayed text.
The only place `CosmicBuffer` is currently used is as a field of
`ComputedTextBlock`, where a comment explains why the field is private:
/// Buffer for managing text layout and creating [`TextLayoutInfo`].
///
/// This is private because buffer contents are always refreshed from
ECS state when writing glyphs to
/// `TextLayoutInfo`. If you want to control the buffer contents
manually or use the `cosmic-text`
/// editor, then you need to not use `TextLayout` and instead manually
implement the conversion to
/// `TextLayoutInfo`.
#[reflect(ignore)]
pub(crate) buffer: CosmicBuffer,
Unfortunately this comment does not appear in the docs, so a user
looking for a way to access `CosmicBuffer` will not find it unless they
check the source code.
Also there does not seem to be any alternative way to map between screen
coordinates and positions in the displayed text, which would be highly
useful for things like text edit widgets or tool tips. The reasons given
for making the field private only apply for mutable access, so
non-mutable access would presumably be fine.
## Solution
I added a getter to `ComputedTextBlock`, and added the explanation for
why there is no mutable access in the comment:
/// Accesses the underling buffer which can be used for `cosmic-text`
APIs such as accessing layout information
/// or calculating a cursor position.
///
/// Mutable access not offered because changes would be overwritten
during the automated layout calculation.
/// If you want to control the buffer contents manually or use the
`cosmic-text`
/// editor, then you need to not use `TextLayout` and instead manually
implement the conversion to
/// `TextLayoutInfo`.
pub fn get_buffer(&self) -> &CosmicBuffer {
&self.buffer
}
## Testing
I tested that the getter could be used to map from screen coordinates to
string positions by creating a rudimentary text edit widget and trying
it out.
## Alternatives
An alternative to making `CosmicBuffer` accessible would be to make the
type private so that no one wastes time looking for a way of accessing
it, and adding additional methods to `ComputedTextBlock` that make use
of the buffer as implementation detail and offer access to currently
inaccessible functionality.
---------
Co-authored-by: Rob Parrett <robparrett@gmail.com>
# Objective
- bevy_math fails to publish because of the self dev-dependency
- it's used to enable the `approx` feature in tests
## Solution
- Don't specify a version in the dev-dependency. dependencies without a
version are ignored by cargo when publishing
- Gate all the tests that depend on the `approx` feature so that it
doesn't fail to compile when not enabled
- Also gate an import that wasn't used without `bevy_reflect`
## Testing
- with at least cargo 1.84: `cargo package -p bevy_math`
- `cd target/package/bevy_math_* && cargo test`
# Objective
Restore the behavior of `Query::get_many` prior to #15858.
When passed duplicate `Entity`s, `get_many` is supposed to return
results for all of them, since read-only queries don't alias. However,
#15858 merged the implementation with `get_many_mut` and caused it to
return `QueryEntityError::AliasedMutability`.
## Solution
Introduce a new `Query::get_many_readonly` method that consumes the
`Query` like `get_many_inner`, but that is constrained to `D:
ReadOnlyQueryData` so that it can skip the aliasing check. Implement
`Query::get_many` in terms of that new method. Add a test, and a comment
explaining why it doesn't match the pattern of the other `&self`
methods.
This method returns `None` if `meta.location.archetype_id` is
`ArchetypeId::INVALID`.
`EntityLocation::INVALID.archetype_id` is `ArchetypeId::INVALID`.
Therefore this method cannot return `Some(EntityLocation::INVALID)`.
Linking to it in the docs is futile anyway as that constant is not
public.
# Objective
`bevy_picking` currently does not support scroll events.
## Solution
This pr adds a new event type for scroll, and updates the default input
system for mouse pointers to read and emit this event.
## Testing
- Did you test these changes? If so, how?
- Are there any parts that need more testing?
- How can other people (reviewers) test your changes? Is there anything
specific they need to know?
- If relevant, what platforms did you test these changes on, and are
there any important ones you can't test?
I haven't tested these changes, if the reviewers can advise me how to do
so I'd appreciate it!
# Objective
- Allow users to configure volume using decibels by changing the
`Volume` type from newtyping an `f32` to an enum with `Linear` and
`Decibels` variants.
- Fixes#9507.
- Alternative reworked version of closed#9582.
## Solution
Compared to https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/9582, this PR has
the following main differences:
1. It uses the term "linear scale" instead of "amplitude" per
https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/9582/files#r1513529491.
2. Supports `ops` for doing `Volume` arithmetic. Can add two volumes,
e.g. to increase/decrease the current volume. Can multiply two volumes,
e.g. to get the “effective” volume of an audio source considering global
volume.
[requested and blessed on Discord]:
https://discord.com/channels/691052431525675048/749430447326625812/1318272597003341867
## Testing
- Ran `cargo run --example soundtrack`.
- Ran `cargo run --example audio_control`.
- Ran `cargo run --example spatial_audio_2d`.
- Ran `cargo run --example spatial_audio_3d`.
- Ran `cargo run --example pitch`.
- Ran `cargo run --example decodable`.
- Ran `cargo run --example audio`.
---
## Migration Guide
Audio volume can now be configured using decibel values, as well as
using linear scale values. To enable this, some types and functions in
`bevy_audio` have changed.
- `Volume` is now an enum with `Linear` and `Decibels` variants.
Before:
```rust
let v = Volume(1.0);
```
After:
```rust
let volume = Volume::Linear(1.0);
let volume = Volume::Decibels(0.0); // or now you can deal with decibels if you prefer
```
- `Volume::ZERO` has been renamed to the more semantically correct
`Volume::SILENT` because `Volume` now supports decibels and "zero
volume" in decibels actually means "normal volume".
- The `AudioSinkPlayback` trait's volume-related methods now deal with
`Volume` types rather than `f32`s. `AudioSinkPlayback::volume()` now
returns a `Volume` rather than an `f32`. `AudioSinkPlayback::set_volume`
now receives a `Volume` rather than an `f32`. This affects the
`AudioSink` and `SpatialAudioSink` implementations of the trait. The
previous `f32` values are equivalent to the volume converted to linear
scale so the `Volume:: Linear` variant should be used to migrate between
`f32`s and `Volume`.
- The `GlobalVolume::new` function now receives a `Volume` instead of an
`f32`.
---------
Co-authored-by: Zachary Harrold <zac@harrold.com.au>
# Objective
Eliminate the need to write `cfg(feature = "track_location")` every time
one uses an API that may use location tracking. It's verbose, and a
little intimidating. And it requires code outside of `bevy_ecs` that
wants to use location tracking needs to either unconditionally enable
the feature, or include conditional compilation of its own. It would be
good for users to be able to log locations when they are available
without needing to add feature flags to their own crates.
Reduce the number of cases where code compiles with the `track_location`
feature enabled, but not with it disabled, or vice versa. It can be hard
to remember to test it both ways!
Remove the need to store a `None` in `HookContext` when the
`track_location` feature is disabled.
## Solution
Create an `MaybeLocation<T>` type that contains a `T` if the
`track_location` feature is enabled, and is a ZST if it is not. The
overall API is similar to `Option`, but whether the value is `Some` or
`None` is set at compile time and is the same for all values.
Default `T` to `&'static Location<'static>`, since that is the most
common case.
Remove all `cfg(feature = "track_location")` blocks outside of the
implementation of that type, and instead call methods on it.
When `track_location` is disabled, `MaybeLocation` is a ZST and all
methods are `#[inline]` and empty, so they should be entirely removed by
the compiler. But the code will still be visible to the compiler and
checked, so if it compiles with the feature disabled then it should also
compile with it enabled, and vice versa.
## Open Questions
Where should these types live? I put them in `change_detection` because
that's where the existing `MaybeLocation` types were, but we now use
these outside of change detection.
While I believe that the compiler should be able to remove all of these
calls, I have not actually tested anything. If we want to take this
approach, what testing is required to ensure it doesn't impact
performance?
## Migration Guide
Methods like `Ref::changed_by()` that return a `&'static
Location<'static>` will now be available even when the `track_location`
feature is disabled, but they will return a new `MaybeLocation` type.
`MaybeLocation` wraps a `&'static Location<'static>` when the feature is
enabled, and is a ZST when the feature is disabled.
Existing code that needs a `&Location` can call `into_option().unwrap()`
to recover it. Many trait impls are forwarded, so if you only need
`Display` then no changes will be necessary.
If that code was conditionally compiled, you may instead want to use the
methods on `MaybeLocation` to remove the need for conditional
compilation.
Code that constructs a `Ref`, `Mut`, `Res`, or `ResMut` will now need to
provide location information unconditionally. If you are creating them
from existing Bevy types, you can obtain a `MaybeLocation` from methods
like `Table::get_changed_by_slice_for()` or
`ComponentSparseSet::get_with_ticks`. Otherwise, you will need to store
a `MaybeLocation` next to your data and use methods like `as_ref()` or
`as_mut()` to obtain wrapped references.
# Objective
Fixes#15417.
## Solution
- Remove the `labeled_assets` fields from `LoadedAsset` and
`ErasedLoadedAsset`.
- Created new structs `CompleteLoadedAsset` and
`CompleteErasedLoadedAsset` to hold the `labeled_subassets`.
- When a subasset is `LoadContext::finish`ed, it produces a
`CompleteLoadedAsset`.
- When a `CompleteLoadedAsset` is added to a `LoadContext` (as a
subasset), their `labeled_assets` are merged, reporting any overlaps.
One important detail to note: nested subassets with overlapping names
could in theory have been used in the past for the purposes of asset
preprocessing. Even though there was no way to access these "shadowed"
nested subassets, asset preprocessing does get access to these nested
subassets. This does not seem like a case we should support though. It
is confusing at best.
## Testing
- This is just a refactor.
---
## Migration Guide
- Most uses of `LoadedAsset` and `ErasedLoadedAsset` should be replaced
with `CompleteLoadedAsset` and `CompleteErasedLoadedAsset` respectively.
# Objective
https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/16966 tried to fix a bug where
`slot` wasn't passed to `parallaxed_uv` when not running under bindless,
but failed to account for meshlets. This surfaces on macOS where
bindless is disabled.
## Solution
Lift the slot variable out of the bindless condition so it's always
available.
# Objective
It's difficult to understand or make changes to the UI systems because
of how each system needs to individually track changes to scale factor,
windows and camera targets in local hashmaps, particularly for new
contributors. Any major change inevitably introduces new scale factor
bugs.
Instead of per-system resolution we can resolve the camera target info
for all UI nodes in a system at the start of `PostUpdate` and then store
it per-node in components that can be queried with change detection.
Fixes#17578Fixes#15143
## Solution
Store the UI render target's data locally per node in a component that
is updated in `PostUpdate` before any other UI systems run.
This component can be then be queried with change detection so that UI
systems no longer need to have knowledge of cameras and windows and
don't require fragile custom change detection solutions using local
hashmaps.
## Showcase
Compare `measure_text_system` from main (which has a bug the causes it
to use the wrong scale factor when a node's camera target changes):
```
pub fn measure_text_system(
mut scale_factors_buffer: Local<EntityHashMap<f32>>,
mut last_scale_factors: Local<EntityHashMap<f32>>,
fonts: Res<Assets<Font>>,
camera_query: Query<(Entity, &Camera)>,
default_ui_camera: DefaultUiCamera,
ui_scale: Res<UiScale>,
mut text_query: Query<
(
Entity,
Ref<TextLayout>,
&mut ContentSize,
&mut TextNodeFlags,
&mut ComputedTextBlock,
Option<&UiTargetCamera>,
),
With<Node>,
>,
mut text_reader: TextUiReader,
mut text_pipeline: ResMut<TextPipeline>,
mut font_system: ResMut<CosmicFontSystem>,
) {
scale_factors_buffer.clear();
let default_camera_entity = default_ui_camera.get();
for (entity, block, content_size, text_flags, computed, maybe_camera) in &mut text_query {
let Some(camera_entity) = maybe_camera
.map(UiTargetCamera::entity)
.or(default_camera_entity)
else {
continue;
};
let scale_factor = match scale_factors_buffer.entry(camera_entity) {
Entry::Occupied(entry) => *entry.get(),
Entry::Vacant(entry) => *entry.insert(
camera_query
.get(camera_entity)
.ok()
.and_then(|(_, c)| c.target_scaling_factor())
.unwrap_or(1.0)
* ui_scale.0,
),
};
if last_scale_factors.get(&camera_entity) != Some(&scale_factor)
|| computed.needs_rerender()
|| text_flags.needs_measure_fn
|| content_size.is_added()
{
create_text_measure(
entity,
&fonts,
scale_factor.into(),
text_reader.iter(entity),
block,
&mut text_pipeline,
content_size,
text_flags,
computed,
&mut font_system,
);
}
}
core::mem::swap(&mut *last_scale_factors, &mut *scale_factors_buffer);
}
```
with `measure_text_system` from this PR (which always uses the correct
scale factor):
```
pub fn measure_text_system(
fonts: Res<Assets<Font>>,
mut text_query: Query<
(
Entity,
Ref<TextLayout>,
&mut ContentSize,
&mut TextNodeFlags,
&mut ComputedTextBlock,
Ref<ComputedNodeTarget>,
),
With<Node>,
>,
mut text_reader: TextUiReader,
mut text_pipeline: ResMut<TextPipeline>,
mut font_system: ResMut<CosmicFontSystem>,
) {
for (entity, block, content_size, text_flags, computed, computed_target) in &mut text_query {
// Note: the ComputedTextBlock::needs_rerender bool is cleared in create_text_measure().
if computed_target.is_changed()
|| computed.needs_rerender()
|| text_flags.needs_measure_fn
|| content_size.is_added()
{
create_text_measure(
entity,
&fonts,
computed_target.scale_factor.into(),
text_reader.iter(entity),
block,
&mut text_pipeline,
content_size,
text_flags,
computed,
&mut font_system,
);
}
}
}
```
## Testing
I removed an alarming number of tests from the `layout` module but they
were mostly to do with the deleted camera synchronisation logic. The
remaining tests should all pass now.
The most relevant examples are `multiple_windows` and `split_screen`,
the behaviour of both should be unchanged from main.
---------
Co-authored-by: UkoeHB <37489173+UkoeHB@users.noreply.github.com>
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
## Objective
A major critique of Bevy at the moment is how boilerplatey it is to
compose (and read) entity hierarchies:
```rust
commands
.spawn(Foo)
.with_children(|p| {
p.spawn(Bar).with_children(|p| {
p.spawn(Baz);
});
p.spawn(Bar).with_children(|p| {
p.spawn(Baz);
});
});
```
There is also currently no good way to statically define and return an
entity hierarchy from a function. Instead, people often do this
"internally" with a Commands function that returns nothing, making it
impossible to spawn the hierarchy in other cases (direct World spawns,
ChildSpawner, etc).
Additionally, because this style of API results in creating the
hierarchy bits _after_ the initial spawn of a bundle, it causes ECS
archetype changes (and often expensive table moves).
Because children are initialized after the fact, we also can't count
them to pre-allocate space. This means each time a child inserts itself,
it has a high chance of overflowing the currently allocated capacity in
the `RelationshipTarget` collection, causing literal worst-case
reallocations.
We can do better!
## Solution
The Bundle trait has been extended to support an optional
`BundleEffect`. This is applied directly to World immediately _after_
the Bundle has fully inserted. Note that this is
[intentionally](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/discussions/16920)
_not done via a deferred Command_, which would require repeatedly
copying each remaining subtree of the hierarchy to a new command as we
walk down the tree (_not_ good performance).
This allows us to implement the new `SpawnRelated` trait for all
`RelationshipTarget` impls, which looks like this in practice:
```rust
world.spawn((
Foo,
Children::spawn((
Spawn((
Bar,
Children::spawn(Spawn(Baz)),
)),
Spawn((
Bar,
Children::spawn(Spawn(Baz)),
)),
))
))
```
`Children::spawn` returns `SpawnRelatedBundle<Children, L:
SpawnableList>`, which is a `Bundle` that inserts `Children`
(preallocated to the size of the `SpawnableList::size_hint()`).
`Spawn<B: Bundle>(pub B)` implements `SpawnableList` with a size of 1.
`SpawnableList` is also implemented for tuples of `SpawnableList` (same
general pattern as the Bundle impl).
There are currently three built-in `SpawnableList` implementations:
```rust
world.spawn((
Foo,
Children::spawn((
Spawn(Name::new("Child1")),
SpawnIter(["Child2", "Child3"].into_iter().map(Name::new),
SpawnWith(|parent: &mut ChildSpawner| {
parent.spawn(Name::new("Child4"));
parent.spawn(Name::new("Child5"));
})
)),
))
```
We get the benefits of "structured init", but we have nice flexibility
where it is required!
Some readers' first instinct might be to try to remove the need for the
`Spawn` wrapper. This is impossible in the Rust type system, as a tuple
of "child Bundles to be spawned" and a "tuple of Components to be added
via a single Bundle" is ambiguous in the Rust type system. There are two
ways to resolve that ambiguity:
1. By adding support for variadics to the Rust type system (removing the
need for nested bundles). This is out of scope for this PR :)
2. Using wrapper types to resolve the ambiguity (this is what I did in
this PR).
For the single-entity spawn cases, `Children::spawn_one` does also
exist, which removes the need for the wrapper:
```rust
world.spawn((
Foo,
Children::spawn_one(Bar),
))
```
## This works for all Relationships
This API isn't just for `Children` / `ChildOf` relationships. It works
for any relationship type, and they can be mixed and matched!
```rust
world.spawn((
Foo,
Observers::spawn((
Spawn(Observer::new(|trigger: Trigger<FuseLit>| {})),
Spawn(Observer::new(|trigger: Trigger<Exploded>| {})),
)),
OwnerOf::spawn(Spawn(Bar))
Children::spawn(Spawn(Baz))
))
```
## Macros
While `Spawn` is necessary to satisfy the type system, we _can_ remove
the need to express it via macros. The example above can be expressed
more succinctly using the new `children![X]` macro, which internally
produces `Children::spawn(Spawn(X))`:
```rust
world.spawn((
Foo,
children![
(
Bar,
children![Baz],
),
(
Bar,
children![Baz],
),
]
))
```
There is also a `related!` macro, which is a generic version of the
`children!` macro that supports any relationship type:
```rust
world.spawn((
Foo,
related!(Children[
(
Bar,
related!(Children[Baz]),
),
(
Bar,
related!(Children[Baz]),
),
])
))
```
## Returning Hierarchies from Functions
Thanks to these changes, the following pattern is now possible:
```rust
fn button(text: &str, color: Color) -> impl Bundle {
(
Node {
width: Val::Px(300.),
height: Val::Px(100.),
..default()
},
BackgroundColor(color),
children![
Text::new(text),
]
)
}
fn ui() -> impl Bundle {
(
Node {
width: Val::Percent(100.0),
height: Val::Percent(100.0),
..default(),
},
children![
button("hello", BLUE),
button("world", RED),
]
)
}
// spawn from a system
fn system(mut commands: Commands) {
commands.spawn(ui());
}
// spawn directly on World
world.spawn(ui());
```
## Additional Changes and Notes
* `Bundle::from_components` has been split out into
`BundleFromComponents::from_components`, enabling us to implement
`Bundle` for types that cannot be "taken" from the ECS (such as the new
`SpawnRelatedBundle`).
* The `NoBundleEffect` trait (which implements `BundleEffect`) is
implemented for empty tuples (and tuples of empty tuples), which allows
us to constrain APIs to only accept bundles that do not have effects.
This is critical because the current batch spawn APIs cannot efficiently
apply BundleEffects in their current form (as doing so in-place could
invalidate the cached raw pointers). We could consider allocating a
buffer of the effects to be applied later, but that does have
performance implications that could offset the balance and value of the
batched APIs (and would likely require some refactors to the underlying
code). I've decided to be conservative here. We can consider relaxing
that requirement on those APIs later, but that should be done in a
followup imo.
* I've ported a few examples to illustrate real-world usage. I think in
a followup we should port all examples to the `children!` form whenever
possible (and for cases that require things like SpawnIter, use the raw
APIs).
* Some may ask "why not use the `Relationship` to spawn (ex:
`ChildOf::spawn(Foo)`) instead of the `RelationshipTarget` (ex:
`Children::spawn(Spawn(Foo))`)?". That _would_ allow us to remove the
`Spawn` wrapper. I've explicitly chosen to disallow this pattern.
`Bundle::Effect` has the ability to create _significant_ weirdness.
Things in `Bundle` position look like components. For example
`world.spawn((Foo, ChildOf::spawn(Bar)))` _looks and reads_ like Foo is
a child of Bar. `ChildOf` is in Foo's "component position" but it is not
a component on Foo. This is a huge problem. Now that `Bundle::Effect`
exists, we should be _very_ principled about keeping the "weird and
unintuitive behavior" to a minimum. Things that read like components
_should be the components they appear to be".
## Remaining Work
* The macros are currently trivially implemented using macro_rules and
are currently limited to the max tuple length. They will require a
proc_macro implementation to work around the tuple length limit.
## Next Steps
* Port the remaining examples to use `children!` where possible and raw
`Spawn` / `SpawnIter` / `SpawnWith` where the flexibility of the raw API
is required.
## Migration Guide
Existing spawn patterns will continue to work as expected.
Manual Bundle implementations now require a `BundleEffect` associated
type. Exisiting bundles would have no bundle effect, so use `()`.
Additionally `Bundle::from_components` has been moved to the new
`BundleFromComponents` trait.
```rust
// Before
unsafe impl Bundle for X {
unsafe fn from_components<T, F>(ctx: &mut T, func: &mut F) -> Self {
}
/* remaining bundle impl here */
}
// After
unsafe impl Bundle for X {
type Effect = ();
/* remaining bundle impl here */
}
unsafe impl BundleFromComponents for X {
unsafe fn from_components<T, F>(ctx: &mut T, func: &mut F) -> Self {
}
}
```
---------
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Gino Valente <49806985+MrGVSV@users.noreply.github.com>
Co-authored-by: Emerson Coskey <emerson@coskey.dev>
# Objective
Solves https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/17747.
## Solution
- Adds an example for creating a default value for Local.
## Testing
- Example code compiles and passes assertions.
This pr uses the `extern crate self as` trick to make proc macros behave
the same way inside and outside bevy.
# Objective
- Removes noise introduced by `crate as` in the whole bevy repo.
- Fixes#17004.
- Hardens proc macro path resolution.
## TODO
- [x] `BevyManifest` needs cleanup.
- [x] Cleanup remaining `crate as`.
- [x] Add proper integration tests to the ci.
## Notes
- `cargo-manifest-proc-macros` is written by me and based/inspired by
the old `BevyManifest` implementation and
[`bkchr/proc-macro-crate`](https://github.com/bkchr/proc-macro-crate).
- What do you think about the new integration test machinery I added to
the `ci`?
More and better integration tests can be added at a later stage.
The goal of these integration tests is to simulate an actual separate
crate that uses bevy. Ideally they would lightly touch all bevy crates.
## Testing
- Needs RA test
- Needs testing from other users
- Others need to run at least `cargo run -p ci integration-test` and
verify that they work.
---------
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
Didn't remove WgpuWrapper. Not sure if it's needed or not still.
## Testing
- Did you test these changes? If so, how? Example runner
- Are there any parts that need more testing? Web (portable atomics
thingy?), DXC.
## Migration Guide
- Bevy has upgraded to [wgpu
v24](https://github.com/gfx-rs/wgpu/blob/trunk/CHANGELOG.md#v2400-2025-01-15).
- When using the DirectX 12 rendering backend, the new priority system
for choosing a shader compiler is as follows:
- If the `WGPU_DX12_COMPILER` environment variable is set at runtime, it
is used
- Else if the new `statically-linked-dxc` feature is enabled, a custom
version of DXC will be statically linked into your app at compile time.
- Else Bevy will look in the app's working directory for
`dxcompiler.dll` and `dxil.dll` at runtime.
- Else if they are missing, Bevy will fall back to FXC (not recommended)
---------
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: IceSentry <c.giguere42@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: François Mockers <francois.mockers@vleue.com>
# Objective
Fix#16477.
## Solution
- Remove temporary silence introduced in #16763
- bump version of `notify-debouncer-full` to remove transitive
dependency on `instant` crate.
# Objective
- publish script copy the license files to all subcrates, meaning that
all publish are dirty. this breaks git verification of crates
- the order and list of crates to publish is manually maintained,
leading to error. cargo 1.84 is more strict and the list is currently
wrong
## Solution
- duplicate all the licenses to all crates and remove the
`--allow-dirty` flag
- instead of a manual list of crates, get it from `cargo package
--workspace`
- remove the `--no-verify` flag to... verify more things?
# Objective
Things were breaking post-cs.
## Solution
`specialize_mesh_materials` must run after
`collect_meshes_for_gpu_building`. Therefore, its placement in the
`PrepareAssets` set didn't make sense (also more generally). To fix, we
put this class of system in ~`PrepareResources`~ `QueueMeshes`, although
it potentially could use a more descriptive location. We may want to
review the placement of `check_views_need_specialization` which is also
currently in `PrepareAssets`.
PR #17684 broke occlusion culling because it neglected to set the
indirect parameter offsets for the late mesh preprocessing stage if the
work item buffers were already set. This PR moves the update of those
values to a new function, `init_work_item_buffers`, which is
unconditionally called for every phase every frame.
Note that there's some complexity in order to handle the case in which
occlusion culling was enabled on one frame and disabled on the next, or
vice versa. This was necessary in order to make the occlusion culling
toggle in the `occlusion_culling` example work again.
Right now, we key the cached light change ticks off the `LightEntity`.
This uses the render world entity, which isn't stable between frames.
Thus in practice few shadows are retained from frame to frame. This PR
fixes the issue by keying off the `RetainedViewEntity` instead, which is
designed to be stable from frame to frame.
This PR makes Bevy keep entities in bins from frame to frame if they
haven't changed. This reduces the time spent in `queue_material_meshes`
and related functions to near zero for static geometry. This patch uses
the same change tick technique that #17567 uses to detect when meshes
have changed in such a way as to require re-binning.
In order to quickly find the relevant bin for an entity when that entity
has changed, we introduce a new type of cache, the *bin key cache*. This
cache stores a mapping from main world entity ID to cached bin key, as
well as the tick of the most recent change to the entity. As we iterate
through the visible entities in `queue_material_meshes`, we check the
cache to see whether the entity needs to be re-binned. If it doesn't,
then we mark it as clean in the `valid_cached_entity_bin_keys` bit set.
If it does, then we insert it into the correct bin, and then mark the
entity as clean. At the end, all entities not marked as clean are
removed from the bins.
This patch has a dramatic effect on the rendering performance of most
benchmarks, as it effectively eliminates `queue_material_meshes` from
the profile. Note, however, that it generally simultaneously regresses
`batch_and_prepare_binned_render_phase` by a bit (not by enough to
outweigh the win, however). I believe that's because, before this patch,
`queue_material_meshes` put the bins in the CPU cache for
`batch_and_prepare_binned_render_phase` to use, while with this patch,
`batch_and_prepare_binned_render_phase` must load the bins into the CPU
cache itself.
On Caldera, this reduces the time spent in `queue_material_meshes` from
5+ ms to 0.2ms-0.3ms. Note that benchmarking on that scene is very noisy
right now because of https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/17535.
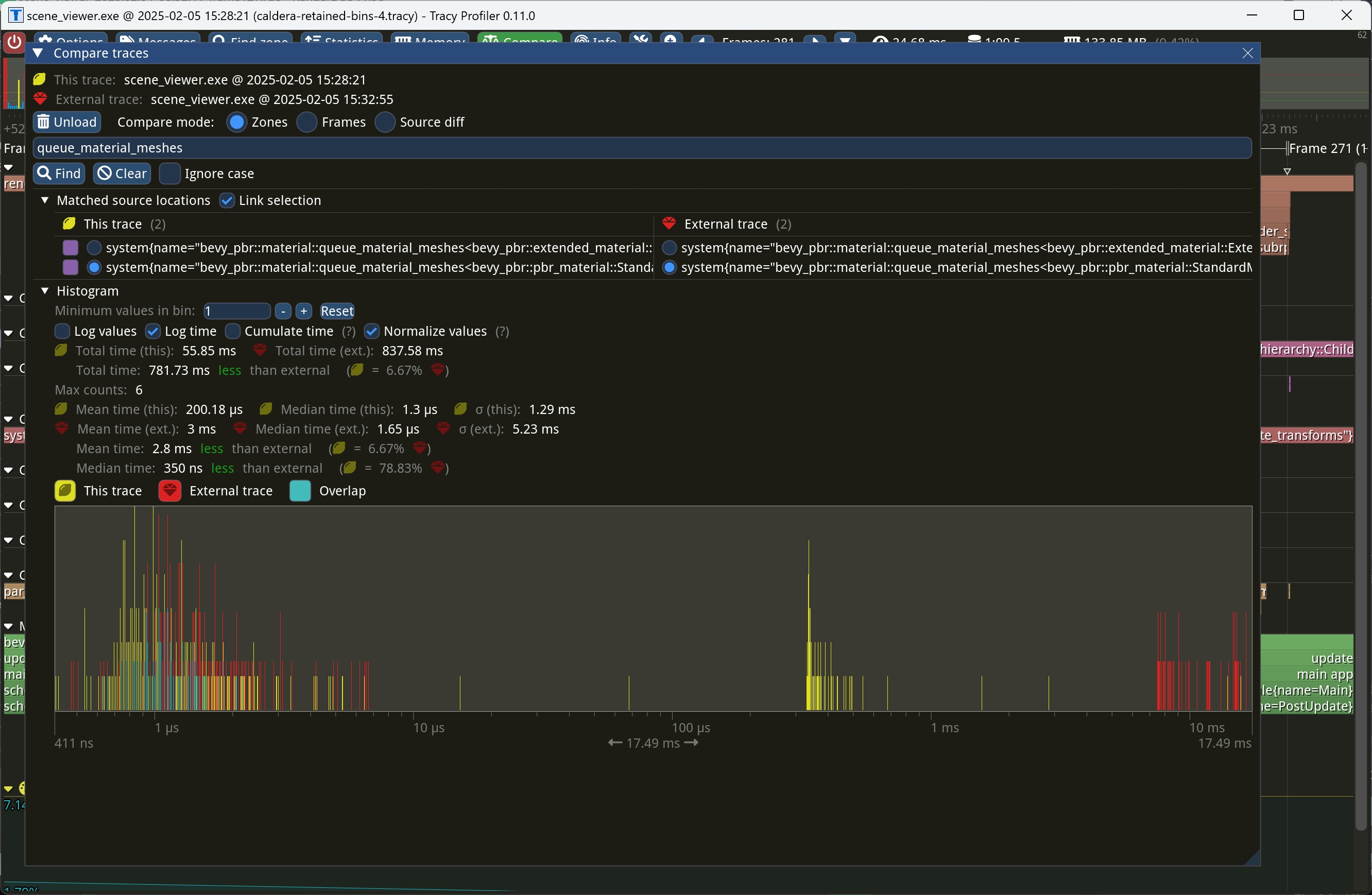
# Objective
The docs of `EaseFunction` don't visualize the different functions,
requiring you to check out the Bevy repo and running the
`easing_function` example.
## Solution
- Add tool to generate suitable svg graphs. This only needs to be re-run
when adding new ease functions.
- works with all themes
- also add missing easing functions to example.
---
## Showcase

---------
Co-authored-by: François Mockers <mockersf@gmail.com>
Right now, meshes aren't grouped together based on the bindless texture
slab when drawing shadows. This manifests itself as flickering in
Bistro. I believe that there are two causes of this:
1. Alpha masked shadows may try to sample from the wrong texture,
causing the alpha mask to appear and disappear.
2. Objects may try to sample from the blank textures that we pad out the
bindless slabs with, causing them to vanish intermittently.
This commit fixes the issue by including the material bind group ID as
part of the shadow batch set key, just as we do for the prepass and main
pass.
# Objective
Fixes#17718
## Solution
Schedule `text_system` before `AssetEvents`.
I guess what was happening here is that glyphs weren't shown because
`text_system` was running before `AssetEevents` and so `prepare_uinodes`
never recieves the the asset modified event about the glyph texture
atlas image.
Fixes#17535
Bevy's approach to handling "entity mapping" during spawning and cloning
needs some work. The addition of
[Relations](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/17398) both
[introduced a new "duplicate entities" bug when spawning scenes in the
scene system](#17535) and made the weaknesses of the current mapping
system exceedingly clear:
1. Entity mapping requires _a ton_ of boilerplate (implement or derive
VisitEntities and VisitEntitesMut, then register / reflect MapEntities).
Knowing the incantation is challenging and if you forget to do it in
part or in whole, spawning subtly breaks.
2. Entity mapping a spawned component in scenes incurs unnecessary
overhead: look up ReflectMapEntities, create a _brand new temporary
instance_ of the component using FromReflect, map the entities in that
instance, and then apply that on top of the actual component using
reflection. We can do much better.
Additionally, while our new [Entity cloning
system](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/16132) is already pretty
great, it has some areas we can make better:
* It doesn't expose semantic info about the clone (ex: ignore or "clone
empty"), meaning we can't key off of that in places where it would be
useful, such as scene spawning. Rather than duplicating this info across
contexts, I think it makes more sense to add that info to the clone
system, especially given that we'd like to use cloning code in some of
our spawning scenarios.
* EntityCloner is currently built in a way that prioritizes a single
entity clone
* EntityCloner's recursive cloning is built to be done "inside out" in a
parallel context (queue commands that each have a clone of
EntityCloner). By making EntityCloner the orchestrator of the clone we
can remove internal arcs, improve the clarity of the code, make
EntityCloner mutable again, and simplify the builder code.
* EntityCloner does not currently take into account entity mapping. This
is necessary to do true "bullet proof" cloning, would allow us to unify
the per-component scene spawning and cloning UX, and ultimately would
allow us to use EntityCloner in place of raw reflection for scenes like
`Scene(World)` (which would give us a nice performance boost: fewer
archetype moves, less reflection overhead).
## Solution
### Improved Entity Mapping
First, components now have first-class "entity visiting and mapping"
behavior:
```rust
#[derive(Component, Reflect)]
#[reflect(Component)]
struct Inventory {
size: usize,
#[entities]
items: Vec<Entity>,
}
```
Any field with the `#[entities]` annotation will be viewable and
mappable when cloning and spawning scenes.
Compare that to what was required before!
```rust
#[derive(Component, Reflect, VisitEntities, VisitEntitiesMut)]
#[reflect(Component, MapEntities)]
struct Inventory {
#[visit_entities(ignore)]
size: usize,
items: Vec<Entity>,
}
```
Additionally, for relationships `#[entities]` is implied, meaning this
"just works" in scenes and cloning:
```rust
#[derive(Component, Reflect)]
#[relationship(relationship_target = Children)]
#[reflect(Component)]
struct ChildOf(pub Entity);
```
Note that Component _does not_ implement `VisitEntities` directly.
Instead, it has `Component::visit_entities` and
`Component::visit_entities_mut` methods. This is for a few reasons:
1. We cannot implement `VisitEntities for C: Component` because that
would conflict with our impl of VisitEntities for anything that
implements `IntoIterator<Item=Entity>`. Preserving that impl is more
important from a UX perspective.
2. We should not implement `Component: VisitEntities` VisitEntities in
the Component derive, as that would increase the burden of manual
Component trait implementors.
3. Making VisitEntitiesMut directly callable for components would make
it easy to invalidate invariants defined by a component author. By
putting it in the `Component` impl, we can make it harder to call
naturally / unavailable to autocomplete using `fn
visit_entities_mut(this: &mut Self, ...)`.
`ReflectComponent::apply_or_insert` is now
`ReflectComponent::apply_or_insert_mapped`. By moving mapping inside
this impl, we remove the need to go through the reflection system to do
entity mapping, meaning we no longer need to create a clone of the
target component, map the entities in that component, and patch those
values on top. This will make spawning mapped entities _much_ faster
(The default `Component::visit_entities_mut` impl is an inlined empty
function, so it will incur no overhead for unmapped entities).
### The Bug Fix
To solve #17535, spawning code now skips entities with the new
`ComponentCloneBehavior::Ignore` and
`ComponentCloneBehavior::RelationshipTarget` variants (note
RelationshipTarget is a temporary "workaround" variant that allows
scenes to skip these components. This is a temporary workaround that can
be removed as these cases should _really_ be using EntityCloner logic,
which should be done in a followup PR. When that is done,
`ComponentCloneBehavior::RelationshipTarget` can be merged into the
normal `ComponentCloneBehavior::Custom`).
### Improved Cloning
* `Option<ComponentCloneHandler>` has been replaced by
`ComponentCloneBehavior`, which encodes additional intent and context
(ex: `Default`, `Ignore`, `Custom`, `RelationshipTarget` (this last one
is temporary)).
* Global per-world entity cloning configuration has been removed. This
felt overly complicated, increased our API surface, and felt too
generic. Each clone context can have different requirements (ex: what a
user wants in a specific system, what a scene spawner wants, etc). I'd
prefer to see how far context-specific EntityCloners get us first.
* EntityCloner's internals have been reworked to remove Arcs and make it
mutable.
* EntityCloner is now directly stored on EntityClonerBuilder,
simplifying the code somewhat
* EntityCloner's "bundle scratch" pattern has been moved into the new
BundleScratch type, improving its usability and making it usable in
other contexts (such as future cross-world cloning code). Currently this
is still private, but with some higher level safe APIs it could be used
externally for making dynamic bundles
* EntityCloner's recursive cloning behavior has been "externalized". It
is now responsible for orchestrating recursive clones, meaning it no
longer needs to be sharable/clone-able across threads / read-only.
* EntityCloner now does entity mapping during clones, like scenes do.
This gives behavior parity and also makes it more generically useful.
* `RelatonshipTarget::RECURSIVE_SPAWN` is now
`RelationshipTarget::LINKED_SPAWN`, and this field is used when cloning
relationship targets to determine if cloning should happen recursively.
The new `LINKED_SPAWN` term was picked to make it more generically
applicable across spawning and cloning scenarios.
## Next Steps
* I think we should adapt EntityCloner to support cross world cloning. I
think this PR helps set the stage for that by making the internals
slightly more generalized. We could have a CrossWorldEntityCloner that
reuses a lot of this infrastructure.
* Once we support cross world cloning, we should use EntityCloner to
spawn `Scene(World)` scenes. This would yield significant performance
benefits (no archetype moves, less reflection overhead).
---------
Co-authored-by: eugineerd <70062110+eugineerd@users.noreply.github.com>
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
# Objective
This is a follow up to #9822, which automatically adds sync points
during the Schedule build process.
However, the implementation in #9822 feels very "special case" to me. As
the number of things we want to do with the `Schedule` grows, we need a
modularized way to manage those behaviors. For example, in one of my
current experiments I want to automatically add systems to apply GPU
pipeline barriers between systems accessing GPU resources.
For dynamic modifications of the schedule, we mostly need these
capabilities:
- Storing custom data on schedule edges
- Storing custom data on schedule nodes
- Modify the schedule graph whenever it builds
These should be enough to allows us to add "hooks" to the schedule build
process for various reasons.
cc @hymm
## Solution
This PR abstracts the process of schedule modification and created a new
trait, `ScheduleBuildPass`. Most of the logics in #9822 were moved to an
implementation of `ScheduleBuildPass`, `AutoInsertApplyDeferredPass`.
Whether a dependency edge should "ignore deferred" is now indicated by
the presence of a marker struct, `IgnoreDeferred`.
This PR has no externally visible effects. However, in a future PR I
propose to change the `before_ignore_deferred` and
`after_ignore_deferred` API into a more general form,
`before_with_options` and `after_with_options`.
```rs
schedule.add_systems(
system.before_with_options(another_system, IgnoreDeferred)
);
schedule.add_systems(
system.before_with_options(another_system, (
IgnoreDeferred,
AnyOtherOption {
key: value
}
))
);
schedule.add_systems(
system.before_with_options(another_system, ())
);
```
# Objective
- Make use of the new `weak_handle!` macro added in
https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/17384
## Solution
- Migrate bevy from `Handle::weak_from_u128` to the new `weak_handle!`
macro that takes a random UUID
- Deprecate `Handle::weak_from_u128`, since there are no remaining use
cases that can't also be addressed by constructing the type manually
## Testing
- `cargo run -p ci -- test`
---
## Migration Guide
Replace `Handle::weak_from_u128` with `weak_handle!` and a random UUID.
# Objective
There was a bug in the default `Relationship::on_insert` implementation
that caused it to not properly handle entities targeting themselves in
relationships. The relationship component was properly removed, but it
would go on to add itself to its own target component.
## Solution
Added a missing `return` and a couple of tests
(`self_relationship_fails` failed on its second assert prior to this
PR).
## Testing
See above.
# Objective
Progresses #17569. The end goal here is to synchronize component
registration. See the other PR for details for the motivation behind
that.
For this PR specifically, the objective is to decouple `Components` from
`Storages`. What components are registered etc should have nothing to do
with what Storages looks like. Storages should only care about what
entity archetypes have been spawned.
## Solution
Previously, this was used to create sparse sets for relevant components
when those components were registered. Now, we do that when the
component is inserted/spawned.
This PR proposes doing that in `BundleInfo::new`, but there may be a
better place.
## Testing
In theory, this shouldn't have changed any functionality, so no new
tests were created. I'm not aware of any examples that make heavy use of
sparse set components either.
## Migration Guide
- Remove storages from functions where it is no longer needed.
- Note that SparseSets are no longer present for all registered sparse
set components, only those that have been spawned.
---------
Co-authored-by: SpecificProtagonist <vincentjunge@posteo.net>
Co-authored-by: Chris Russell <8494645+chescock@users.noreply.github.com>
# Objective
- Fixes#17411
## Solution
- Deprecated `Component::register_component_hooks`
- Added individual methods for each hook which return `None` if the hook
is unused.
## Testing
- CI
---
## Migration Guide
`Component::register_component_hooks` is now deprecated and will be
removed in a future release. When implementing `Component` manually,
also implement the respective hook methods on `Component`.
```rust
// Before
impl Component for Foo {
// snip
fn register_component_hooks(hooks: &mut ComponentHooks) {
hooks.on_add(foo_on_add);
}
}
// After
impl Component for Foo {
// snip
fn on_add() -> Option<ComponentHook> {
Some(foo_on_add)
}
}
```
## Notes
I've chosen to deprecate `Component::register_component_hooks` rather
than outright remove it to ease the migration guide. While it is in a
state of deprecation, it must be used by
`Components::register_component_internal` to ensure users who haven't
migrated to the new hook definition scheme aren't left behind. For users
of the new scheme, a default implementation of
`Component::register_component_hooks` is provided which forwards the new
individual hook implementations.
Personally, I think this is a cleaner API to work with, and would allow
the documentation for hooks to exist on the respective `Component`
methods (e.g., documentation for `OnAdd` can exist on
`Component::on_add`). Ideally, `Component::on_add` would be the hook
itself rather than a getter for the hook, but it is the only way to
early-out for a no-op hook, which is important for performance.
## Migration Guide
`Component::register_component_hooks` has been deprecated. If you are
manually implementing the `Component` trait and registering hooks there,
use the individual methods such as `on_add` instead for increased
clarity.
# Objective
- A common bevy pattern is to pre-allocate a weak `Handle` with a
static, random ID and fill it during `Plugin::build` via
`load_internal_asset!`
- This requires generating a random 128-bit number that is interpreted
as a UUID. This is much less convenient than generating a UUID directly,
and also, strictly speaking, error prone, since it often results in an
invalid UUIDv4 – they have to follow the pattern
`xxxxxxxx-xxxx-4xxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx`, where `x` is a random nibble (in
practice this doesn't matter, since the UUID is just interpreted as a
bag of bytes).
## Solution
- Add a `weak_handle!` macro that internally calls
[`uuid::uuid!`](https://docs.rs/uuid/1.12.0/uuid/macro.uuid.html) to
parse a UUID from a string literal.
- Now any random UUID generation tool can be used to generate an asset
ID, such as `uuidgen` or entering "uuid" in DuckDuckGo.
Previously:
```rust
const SHADER: Handle<Shader> = Handle::weak_from_u128(314685653797097581405914117016993910609);
```
After this PR:
```rust
const SHADER: Handle<Shader> = weak_handle!("1347c9b7-c46a-48e7-b7b8-023a354b7cac");
```
Note that I did not yet migrate any of the existing uses. I can do that
if desired, but want to have some feedback first to avoid wasted effort.
## Testing
Tested via the included doctest.
# Objective
Basic `TextShadow` support.
## Solution
New `TextShadow` component with `offset` and `color` fields. Just insert
it on a `Text` node to add a shadow.
New system `extract_text_shadows` handles rendering.
It's not "real" shadows just the text redrawn with an offset and a
different colour. Blur-radius support will need changes to the shaders
and be a lot more complicated, whereas this still looks okay and took a
couple of minutes to implement.
I added the `TextShadow` component to `bevy_ui` rather than `bevy_text`
because it only supports the UI atm.
We can add a `Text2d` version in a followup but getting the same effect
in `Text2d` is trivial even without official support.
---
## Showcase
<img width="122" alt="text_shadow"
src="https://github.com/user-attachments/assets/0333d167-c507-4262-b93b-b6d39e2cf3a4"
/>
<img width="136" alt="g"
src="https://github.com/user-attachments/assets/9b01d5d9-55c9-4af7-9360-a7b04f55944d"
/>
# Objective
Fixes#17662
## Solution
Moved `Item` and `fetch` from `WorldQuery` to `QueryData`, and adjusted
their implementations accordingly.
Currently, documentation related to `fetch` is written under
`WorldQuery`. It would be more appropriate to move it to the `QueryData`
documentation for clarity.
I am not very experienced with making contributions. If there are any
mistakes or areas for improvement, I would appreciate any suggestions
you may have.
## Migration Guide
The `WorldQuery::Item` type and `WorldQuery::fetch` method have been
moved to `QueryData`, as they were not useful for `QueryFilter` types.
---------
Co-authored-by: Chris Russell <8494645+chescock@users.noreply.github.com>
# Objective
The feature gates for the `UiChildren` and `UiRootNodes` system params
make the unconstructable `GhostNode` `PhantomData` trick redundant.
## Solution
Remove the `GhostNode::new` method and change `GhostNode` into a unit
struct.
## Testing
```cargo run --example ghost_nodes```
still works
# Objective
Simplify and expand the API for `QueryState`.
`QueryState` has a lot of methods that mirror those on `Query`. These
are then multiplied by variants that take `&World`, `&mut World`, and
`UnsafeWorldCell`. In addition, many of them have `_manual` variants
that take `&QueryState` and avoid calling `update_archetypes()`. Not all
of the combinations exist, however, so some operations are not possible.
## Solution
Introduce methods to get a `Query` from a `QueryState`. That will reduce
duplication between the types, and ensure that the full `Query` API is
always available for `QueryState`.
Introduce methods on `Query` that consume the query to return types with
the full `'w` lifetime. This avoids issues with borrowing where things
like `query_state.query(&world).get(entity)` don't work because they
borrow from the temporary `Query`.
Finally, implement `Copy` for read-only `Query`s. `get_inner` and
`iter_inner` currently take `&self`, so changing them to consume `self`
would be a breaking change. By making `Query: Copy`, they can consume a
copy of `self` and continue to work.
The consuming methods also let us simplify the implementation of methods
on `Query`, by doing `fn foo(&self) { self.as_readonly().foo_inner() }`
and `fn foo_mut(&mut self) { self.reborrow().foo_inner() }`. That
structure makes it more difficult to accidentally extend lifetimes,
since the safe `as_readonly()` and `reborrow()` methods shrink them
appropriately. The optimizer is able to see that they are both identity
functions and inline them, so there should be no performance cost.
Note that this change would conflict with #15848. If `QueryState` is
stored as a `Cow`, then the consuming methods cannot be implemented, and
`Copy` cannot be implemented.
## Future Work
The next step is to mark the methods on `QueryState` as `#[deprecated]`,
and move the implementations into `Query`.
## Migration Guide
`Query::to_readonly` has been renamed to `Query::as_readonly`.
# Cold Specialization
## Objective
An ongoing part of our quest to retain everything in the render world,
cold-specialization aims to cache pipeline specialization so that
pipeline IDs can be recomputed only when necessary, rather than every
frame. This approach reduces redundant work in stable scenes, while
still accommodating scenarios in which materials, views, or visibility
might change, as well as unlocking future optimization work like
retaining render bins.
## Solution
Queue systems are split into a specialization system and queue system,
the former of which only runs when necessary to compute a new pipeline
id. Pipelines are invalidated using a combination of change detection
and ECS ticks.
### The difficulty with change detection
Detecting “what changed” can be tricky because pipeline specialization
depends not only on the entity’s components (e.g., mesh, material, etc.)
but also on which view (camera) it is rendering in. In other words, the
cache key for a given pipeline id is a view entity/render entity pair.
As such, it's not sufficient simply to react to change detection in
order to specialize -- an entity could currently be out of view or could
be rendered in the future in camera that is currently disabled or hasn't
spawned yet.
### Why ticks?
Ticks allow us to ensure correctness by allowing us to compare the last
time a view or entity was updated compared to the cached pipeline id.
This ensures that even if an entity was out of view or has never been
seen in a given camera before we can still correctly determine whether
it needs to be re-specialized or not.
## Testing
TODO: Tested a bunch of different examples, need to test more.
## Migration Guide
TODO
- `AssetEvents` has been moved into the `PostUpdate` schedule.
---------
Co-authored-by: Patrick Walton <pcwalton@mimiga.net>
# Objective
Follow-up to #17549 and #16547.
A large part of `Vec`s usefulness is behind its ability to be sliced,
like sorting f.e., so we want the same to be possible for
`UniqueEntityVec`.
## Solution
Add a `UniqueEntitySlice` type. It is a wrapper around `[T]`, and itself
a DST.
Because `mem::swap` has a `Sized` bound, DSTs cannot be swapped, and we
can freely hand out mutable subslices without worrying about the
uniqueness invariant of the backing collection!
`UniqueEntityVec` and the relevant `UniqueEntityIter`s now have methods
and trait impls that return `UniqueEntitySlice`s.
`UniqueEntitySlice` itself can deref into normal slices, which means we
can avoid implementing the vast majority of immutable slice methods.
Most of the remaining methods:
- split a slice/collection in further unique subsections/slices
- reorder the slice: `sort`, `rotate_*`, `swap`
- construct/deconstruct/convert pointer-like types: `Box`, `Arc`, `Rc`,
`Cow`
- are comparison trait impls
As this PR is already larger than I'd like, we leave several things to
follow-ups:
- `UniqueEntityArray` and the related slice methods that would return it
- denoted by "chunk", "array_*" for iterators
- Methods that return iterators with `UniqueEntitySlice` as their item
- `windows`, `chunks` and `split` families
- All methods that are capable of actively mutating individual elements.
While they could be offered unsafely, subslicing makes their safety
contract weird enough to warrant its own discussion.
- `fill_with`, `swap_with_slice`, `iter_mut`, `split_first/last_mut`,
`select_nth_unstable_*`
Note that `Arc`, `Rc` and `Cow` are not fundamental types, so even if
they contain `UniqueEntitySlice`, we cannot write direct trait impls for
them.
On top of that, `Cow` is not a receiver (like `self: Arc<Self>` is) so
we cannot write inherent methods for it either.
We were calling `clear()` on the work item buffer table, which caused us
to deallocate all the CPU side buffers. This patch changes the logic to
instead just clear the buffers individually, but leave their backing
stores. This has two consequences:
1. To effectively retain work item buffers from frame to frame, we need
to key them off `RetainedViewEntity` values and not the render world
`Entity`, which is transient. This PR changes those buffers accordingly.
2. We need to clean up work item buffers that belong to views that went
away. Amusingly enough, we actually have a system,
`delete_old_work_item_buffers`, that tries to do this already, but it
wasn't doing anything because the `clear_batched_gpu_instance_buffers`
system already handled that. This patch actually makes the
`delete_old_work_item_buffers` system useful, by removing the clearing
behavior from `clear_batched_gpu_instance_buffers` and instead making
`delete_old_work_item_buffers` delete buffers corresponding to
nonexistent views.
On Bistro, this PR improves the performance of
`batch_and_prepare_binned_render_phase` from 61.2 us to 47.8 us, a 28%
speedup.

This patch fixes a bug whereby we're re-extracting every mesh every
frame. It's a regression from PR #17413. The code in question has
actually been in the tree with this bug for quite a while; it's that
just the code didn't actually run unless the renderer considered the
previous view transforms necessary. Occlusion culling expanded the set
of circumstances under which Bevy computes the previous view transforms,
causing this bug to appear more often.
This patch fixes the issue by checking to see if the previous transform
of a mesh actually differs from the current transform before copying the
current transform to the previous transform.
# Objective
- Fixes CI failure due to `uuid` 1.13 using the new version of
`getrandom` which requires using a new API to work on Wasm.
## Solution
- Based on [`uuid` 1.13 release
notes](https://github.com/uuid-rs/uuid/releases/tag/1.13.0) I've enabled
the `js` feature on `wasm32`. This will need to be revisited once #17499
is up for review
- Updated minimum `uuid` version to 1.13.1, which fixes a separate issue
with `target_feature = atomics` on `wasm`.
## Testing
- `cargo check --target wasm32-unknown-unknown`
# Objective
Fix text 2d. Fixes https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/17670
## Solution
Evidently there's a 1:N extraction going on here that requires using the
render entity rather than main entity.
## Testing
Text 2d example
Data for the other batches is only accessed by the GPU, not the CPU, so
it's a waste of time and memory to store information relating to those
other batches.
On Bistro, this reduces time spent in
`batch_and_prepare_binned_render_phase` from 85.9 us to 61.2 us, a 40%
speedup.

# Objective
While working on #17649, I found the docs for `WorldQuery` and the
related traits frustratingly vague.
## Solution
Clarify them and add some more tangible advice.
Also fix a copy-pasted typo in related comments.
---------
Co-authored-by: James O'Brien <james.obrien@drafly.net>
# Objective
Allow mapping `Mut` to another value while returning a custom error on
failure.
## Solution
Added `try_map_unchanged` to `Mut` which returns a `Result` instead of
`Option` .
# Objective
- When obtaining an axis from the transform and putting that into
`Transform::rotate_axis` or `Transform::rotate_axis_local`, floating
point errors could accumulate exponentially, resulting in denormalized
rotation.
- This is an alternative to and closes#17604, due to lack of consent
around this in the [discord
discussion](https://discord.com/channels/691052431525675048/1203087353850364004/1334232710658392227)
- Closes#16480
## Solution
- Add a warning of this issue and a recommendation to normalize to the
API docs.
- Add a runtime warning that checks for denormalized axis in debug mode,
with a reference to the API docs.
# Objective
Prevent unsound uses of `DeferredWorld` as a `SystemParam`. It is
currently unsound because it does not check for existing access, and
because it incorrectly registers filtered access.
## Solution
Have `DeferredWorld` panic if a previous parameter has conflicting
access.
Have `DeferredWorld` update `archetype_component_access` so that the
multi-threaded executor sees the access.
Fix `FilteredAccessSet::read_all()` and `write_all()` to correctly add a
`FilteredAccess` with no filter so that `Query` is able to detect the
conflicts.
Remove redundant `read_all()` call, since `write_all()` already declares
read access.
Remove unnecessary `set_has_deferred()` call, since `<DeferredWorld as
SystemParam>::apply_deferred()` does nothing. Previously we were
inserting unnecessary `apply_deferred` systems in the schedule.
## Testing
Added unit tests for systems where `DeferredWorld` conflicts with a
`Query` in the same system.
# Objective
- Most of the `*MeshBuilder` classes are not implementing `Reflect`
## Solution
- Implementing `Reflect` for all `*MeshBuilder` were is possible.
- Make sure all `*MeshBuilder` implements `Default`.
- Adding new `MeshBuildersPlugin` that registers all `*MeshBuilder`
types.
## Testing
- `cargo run -p ci`
- Tested some examples like `3d_scene` just in case something was
broken.
# Objective
- Fix the atmosphere LUT parameterization in the aerial -view and
sky-view LUTs
- Correct the light accumulation according to a ray-marched reference
- Avoid negative values of the sun disk illuminance when the sun disk is
below the horizon
## Solution
- Adding a Newton's method iteration to `fast_sqrt` function
- Switched to using `fast_acos_4` for better precision of the sun angle
towards the horizon (view mu angle = 0)
- Simplified the function for mapping to and from the Sky View UV
coordinates by removing an if statement and correctly apply the method
proposed by the [Hillarie
paper](https://sebh.github.io/publications/egsr2020.pdf) detailed in
section 5.3 and 5.4.
- Replaced the `ray_dir_ws.y` term with a shadow factor in the
`sample_sun_illuminance` function that correctly approximates the sun
disk occluded by the earth from any view point
## Testing
- Ran the atmosphere and SSAO examples to make sure the shaders still
compile and run as expected.
---
## Showcase
<img width="1151" alt="showcase-img"
src="https://github.com/user-attachments/assets/de875533-42bd-41f9-9fd0-d7cc57d6e51c"
/>
---------
Co-authored-by: Emerson Coskey <emerson@coskey.dev>
# Objective
The method `World::as_unsafe_world_cell_readonly` is used to create an
`UnsafeWorldCell` which is only allowed to access world data immutably.
This can be tricky to use, as the data that an `UnsafeWorldCell` is
allowed to access exists only in documentation (you could think of it as
a "doc-time abstraction" rather than a "compile-time" abstraction). It's
quite easy to forget where a particular instance came from and attempt
to use it for mutable access, leading to instant, silent undefined
behavior.
## Solution
Add a debug-mode only flag to `UnsafeWorldCell` which tracks whether or
not the instance can be used to access world data mutably. This should
catch basic improper usages of `as_unsafe_world_cell_readonly`.
## Future work
There are a few ways that you can bypass the runtime checks introduced
by this PR:
* Any world accesses done via `UnsafeWorldCell::storages` are completely
invisible to these runtime checks. Unfortunately, `storages` constitutes
most of the world accesses used in the engine itself, so this PR will
mostly benefit downstream users of bevy.
* It's possible to call `get_resource_by_id`, and then convert the
returned `Ptr` to a `PtrMut` by calling `assert_unique`. In the future
we'll probably want to add a debug-mode only flag to `Ptr` which tracks
whether or not it can be upgraded to a `PtrMut`. I didn't include this
change in this PR as those types are currently defined using macros
which makes it a bit tricky to modify their definitions.
* Any data accesses done through a mutable `UnsafeWorldCell` are
completely unchecked, meaning it's possible to unsoundly create multiple
mutable references to a single component, for example. In the future we
may want to store an `Access<>` set inside of the world's `Storages` to
add granular debug-mode runtime checks.
That said, I'd consider this PR to be a good first step towards adding
full runtime checks to `UnsafeWorldCell`.
## Testing
Added a few tests that basic invalid mutable world access result in a
panic.
---------
Co-authored-by: Joseph <21144246+JoJoJet@users.noreply.github.com>
Co-authored-by: Alice I Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
# Objective
Our
[`TextSpan`](https://docs.rs/bevy/latest/bevy/prelude/struct.TextSpan.html)
docs include a code example that does not actually "work." The code
silently does not render anything, and the `Text*Writer` helpers fail.
This seems to be by design, because we can't use `Text` or `Text2d` from
`bevy_ui` or `bevy_sprite` within docs in `bevy_text`. (Correct me if I
am wrong)
I have seen multiple users confused by these docs.
Also fixes#16794
## Solution
Remove the code example from `TextSpan`, and instead encourage users to
seek docs on `Text` or `Text2d`.
Add examples with nested `TextSpan`s in those areas.
# Objective
```
cargo test --package bevy_ecs --lib --all-features
```
fails to compile, with output like
> error[E0433]: failed to resolve: could not find `Serialize` in `serde`
> --> crates/bevy_ecs/src/entity/index_set.rs:14:69
> |
> 14 | #[cfg_attr(feature = "serialize", derive(serde::Deserialize,
serde::Serialize))]
> | ^^^^^^^^^ could not find `Serialize` in `serde`
> |
> note: found an item that was configured out
> -->
/home/alice/.cargo/registry/src/index.crates.io-6f17d22bba15001f/serde-1.0.217/src/lib.rs:343:37
> |
> 343 | pub use serde_derive::{Deserialize, Serialize};
> | ^^^^^^^^^
> note: the item is gated behind the `serde_derive` feature
> -->
/home/alice/.cargo/registry/src/index.crates.io-6f17d22bba15001f/serde-1.0.217/src/lib.rs:341:7
> |
> 341 | #[cfg(feature = "serde_derive")]
> | ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
## Solution
Add the required feature flags and get bevy_ecs compiling standalone
corrctly.
## Testing
The command above now compiles succesfully. Note that several system
stepping tests are failing, and were not being tested in CI. That's a
different PR's problem though.
# Objective
Currently, `prepare_sprite_image_bind_group` spawns sprite batches onto
an individual representative entity of the batch. This poses significant
problems for multi-camera setups, since an entity may appear in multiple
phase instances.
## Solution
Instead, move batches into a resource that is keyed off the view and the
representative entity. Long term we should switch to mesh2d and use the
existing BinnedRenderPhase functionality rather than naively queueing
into transparent and doing our own ad-hoc batching logic.
Fixes#16867, #17351
## Testing
Tested repros in above issues.
# Objective
We have default query filters now, but there is no first-party marker
for entity disabling yet
Fixes#17458
## Solution
Add the marker, cool recursive features and/or potential hook changes
should be follow up work
## Testing
Added a unit test to check that the new marker is enabled by default
# Objective
Expose accessor functions to the `ObserverDescriptor`, so that users can
use the `Observer` component to inspect what the observer is watching.
This would be useful for me, I don't think there's any reason to hide
these.
# Objective
- Fix off by one error introduced in
https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/17540 causing:
```
Cursor image StrongHandle<Image>{ id: Index(AssetIndex { generation: 0, index: 3 }), path: Some(cursors/kenney_crosshairPack/Tilesheet/crosshairs_tilesheet_white.png) } is invalid: The specified hotspot (64, 64) is outside the image bounds (64x64).
```
- First PR commit and run shows the bug:
https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/actions/runs/13009405866/job/36283507530?pr=17571
- Second PR commit fixes it.
## Solution
- Hotspot coordinates are 0-indexed, so we need to subtract 1 from the
width and height.
## Testing
- Fix the tests which included the off-by-one error in their expected
values.
- Consolidate the tests into a single test for brevity.
- Test round trip transform to ensure we can "undo" to get back to the
original value.
- Add a specific bounds test.
- Ran the example again and observed there are no more error logs:
`cargo run --example custom_cursor_image --features=custom_cursor`.
# Objective
- Make working with `bevy_time` more ergonomic in `no_std` environments.
Currently `bevy_time` expects the getter in environments where time
can't be obtained automatically via the instruction set or the standard
library to be of type `*mut fn() -> Duration`.
[`fn()`](https://doc.rust-lang.org/beta/std/primitive.fn.html) is
already a function pointer, so `*mut fn()` is a _pointer to a function
pointer_. This is harder to use and error prone since creating a pointer
out of something like `&mut fn() -> Duration` when the lifetime of the
reference isn't static will lead to an undefined behavior once the
reference is freed
## Solution
- Accept a `fn() -> Duration` instead
## Testing
- I made a whole game on the Playdate that relies on `bevy_time`
heavily, see:
[bevydate_time](1b4f02adcd/src/lib.rs (L510-L546))
for usage of the Instant's getter.
---
## Showcase
<details>
<summary>Click to view showcase</summary>
https://github.com/user-attachments/assets/f687847f-6b62-4322-95f3-c908ada3db30
</details>
## Migration Guide
This is a breaking change but it's not for people coming from Bevy v0.15
### Small thank you note
Thanks to my friend https://github.com/repnop for helping me understand
how to deal with function pointers in `unsafe` environments
Co-authored-by: Wesley Norris <repnop@repnop.dev>
# Objective
Follow-up to #17615.
Bevy's entity collection types like `EntityHashSet` no longer implement
serde's `Serialize` and `Deserialize` after becoming newtypes instead of
type aliases in #16912. This broke some types that support serde for me
in Avian.
I also missed creating const constructors for `EntityIndexMap` and
`EntityIndexSet` in #17615. Oops!
## Solution
Implement `Serialize` and `Deserialize` for Bevy's entity collection
types, and add const constructors for `EntityIndexMap` and
`EntityIndexSet`.
I didn't implement `ReflectSerialize` or `ReflectDeserialize` here,
because I had some trouble fixing the resulting errors, and they were
not implemented previously either.
# Objective
- Linking to a specific AsBindGroup attribute is hard because it doesn't
use any headers and all the docs is in a giant block
## Solution
- Make each attribute it's own sub-header so they can be easily linked
---
## Showcase
Here's what the rustdoc output looks like with this change

## Notes
I kept the bullet point so the text is still indented like before. Not
sure if we should keep that or not
# Objective
- `ValArithmeticError` contains a typo, and one of it's variants is not
used
## Solution
- Rename `NonEvaluateable::NonEvaluateable ` variant to
`NonEvaluateable::NonEvaluable`.
- Remove variant `ValArithmeticError:: NonIdenticalVariants`.
## Testing
- `cargo run -p ci`
---
## Migration Guide
- `ValArithmeticError::NonEvaluateable` has been renamed to
`NonEvaluateable::NonEvaluable`
- `ValArithmeticError::NonIdenticalVariants ` has been removed
# Objective
- We kind of missed out on implementing the `Ease` trait for some
objects like `Isometry2D` and `Isometry3D` even though it makes sense
and isn't that hard
- Fixes#17539
## Testing
- wrote some minimal tests
- ~~noticed that quat easing isn't working as expected yet~~ I just
confused degrees and radians once again 🙈
# Objective
For most UI node entities there's a 1-to-1 mapping from the entity to
its associated Taffy node. Root UI nodes are an exception though, their
corresponding Taffy node in the Taffy tree is also given a parent that
represents the viewport. These viewport Taffy nodes are not removed when
a root UI node is despawned.
Parenting of an existing root UI node with an associated viewport Taffy
node also results in the leak of the viewport node.
These tests fail if added to the `layout` module's tests on the main
branch:
```rust
#[test]
fn no_viewport_node_leak_on_root_despawned() {
let (mut world, mut ui_schedule) = setup_ui_test_world();
let ui_root_entity = world.spawn(Node::default()).id();
// The UI schedule synchronizes Bevy UI's internal `TaffyTree` with the
// main world's tree of `Node` entities.
ui_schedule.run(&mut world);
// Two taffy nodes are added to the internal `TaffyTree` for each root UI entity.
// An implicit taffy node representing the viewport and a taffy node corresponding to the
// root UI entity which is parented to the viewport taffy node.
assert_eq!(
world.resource_mut::<UiSurface>().taffy.total_node_count(),
2
);
world.despawn(ui_root_entity);
// The UI schedule removes both the taffy node corresponding to `ui_root_entity` and its
// parent viewport node.
ui_schedule.run(&mut world);
// Both taffy nodes should now be removed from the internal `TaffyTree`
assert_eq!(
world.resource_mut::<UiSurface>().taffy.total_node_count(),
0
);
}
#[test]
fn no_viewport_node_leak_on_parented_root() {
let (mut world, mut ui_schedule) = setup_ui_test_world();
let ui_root_entity_1 = world.spawn(Node::default()).id();
let ui_root_entity_2 = world.spawn(Node::default()).id();
ui_schedule.run(&mut world);
// There are two UI root entities. Each root taffy node is given it's own viewport node parent,
// so a total of four taffy nodes are added to the `TaffyTree` by the UI schedule.
assert_eq!(
world.resource_mut::<UiSurface>().taffy.total_node_count(),
4
);
// Parent `ui_root_entity_2` onto `ui_root_entity_1` so now only `ui_root_entity_1` is a
// UI root entity.
world
.entity_mut(ui_root_entity_1)
.add_child(ui_root_entity_2);
// Now there is only one root node so the second viewport node is removed by
// the UI schedule.
ui_schedule.run(&mut world);
// There is only one viewport node now, so the `TaffyTree` contains 3 nodes in total.
assert_eq!(
world.resource_mut::<UiSurface>().taffy.total_node_count(),
3
);
}
```
Fixes#17594
## Solution
Change the `UiSurface::entity_to_taffy` to map to `LayoutNode`s. A
`LayoutNode` has a `viewport_id: Option<taffy::NodeId>` field which is
the id of the corresponding implicit "viewport" node if the node is a
root UI node, otherwise it is `None`. When removing or parenting nodes
this field is checked and the implicit viewport node is removed if
present.
## Testing
There are two new tests in `bevy_ui::layout::tests` included with this
PR:
* `no_viewport_node_leak_on_root_despawned`
* `no_viewport_node_leak_on_parented_root`
# Objective
Fix this comment in `queue_sprites`:
```
// batch_range and dynamic_offset will be calculated in prepare_sprites.
```
`Transparent2d` no longer has a `dynamic_offset` field and the
`batch_range` is calculated in `prepare_sprite_image_bind_groups` now.
# Objective
Fixes#17561
## Solution
The anti-aliasing function used by the UI fragment shader is this:
```wgsl
fn antialias(distance: f32) -> f32 {
return saturate(0.5 - distance); // saturate clamps between 0 and 1
}
```
The returned value is multiplied with the alpha channel value to get the
anti-aliasing effect.
The `distance` is a signed distance value. A positive `distance` means
we are outside the shape we're drawing and a negative `distance` means
we are on the inside.
So with `distance` at `0` (on the edge of the shape):
```
antialias(0) = saturate(0.5 - 0) = saturate(0.5) = 0.5
```
but we want it to be `1` at this point, so the entire interior of the
shape is given a solid colour, and then decrease as the signed distance
increases.
So in this PR we change it to:
```wgsl
fn antialias(distance: f32) -> f32 {
return saturate(1. - distance);
}
```
Then:
```
antialias(-0.5) = saturate(1 - (-1)) = saturate(2) = 1
antialias(1) = saturate(1 - 0) = 1
antialias(0.5) = saturate(1 - 0.5) = 0.5
antialias(1) = saturate(1 - 1) = 0
```
as desired.
## Testing
```cargo run --example button```
On main:
<img width="400" alt="bleg" src="https://github.com/user-attachments/assets/314994cb-4529-479d-b179-18e5c25f75bc" />
With this PR:
<img width="400" alt="bbwhite" src="https://github.com/user-attachments/assets/072f481d-8b67-4fae-9a5f-765090d1713f" />
Modified the `button` example to draw a white background to make the bleeding more obvious.
The code added in #14343 seems to be trying to ensure that a `Handle`
for each glTF node exists by topologically sorting the directed graph of
glTF nodes containing edges from parent to child and from skin to joint.
Unfortunately, such a graph can contain cycles, as there's no guarantee
that joints are descendants of nodes with the skin. In particular, glTF
exported from Maya using the popular babylon.js export plugin create
skins attached to nodes that animate their parent nodes. This was
causing the topological sort code to enter an infinite loop.
Assuming that the intent of the topological sort is indeed to ensure
that `Handle`s exist for each glTF node before populating them, there's
a better mechanism for this: `LoadContext::get_label_handle`. This is
the documented way to obtain a handle for a node before populating it,
obviating the need for a topological sort. This patch replaces the
topological sort with a pre-pass that uses
`LoadContext::get_label_handle` to get handles for each `Node` before
populating them. This fixes the problem with Maya rigs, in addition to
making the code simpler and faster.
I realized there wasn't a test for this yet and figured it would be
trivial to add. Why not? Unless there was a test for this, and I just
missed it?
I appreciate the unique error message it gives and wanted to make sure
it doesn't get broken at some point. Or worse, endlessly recurse.
---------
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
# Objective
- Improve CI when testing rendering by having smarter testbeds
## Solution
- CI testing no longer need a config file and will run with a default
config if not found
- It is now possible to give a name to a screenshot instead of just a
frame number
- 2d and 3d testbeds are now driven from code
- a new system in testbed will watch for state changed
- on state changed, trigger a screenshot 100 frames after (so that the
scene has time to render) with the name of the scene
- when the screenshot is taken (`Captured` component has been removed),
switch scene
- this means less setup to run a testbed (no need for a config file),
screenshots have better names, and it's faster as we don't wait 100
frames for the screenshot to be taken
## Testing
- `cargo run --example testbed_2d --features bevy_ci_testing`
# Objective
- Also support `f16` values when getting and setting colors.
## Solution
- Use the `half` crate to work with `f16` until it's in stable Rust.
# Objective
#16912 turned `EntityHashMap` and `EntityHashSet` into proper newtypes
instead of type aliases. However, this removed the ability to create
these collections in const contexts; previously, you could use
`EntityHashSet::with_hasher(EntityHash)`, but it doesn't exist anymore.
## Solution
Make `EntityHashMap::new` and `EntityHashSet::new` const methods.
# Objective
Pass the correct location to triggers when despawning entities.
`EntityWorldMut::despawn_with_caller()` currently passes
`Location::caller()` to some triggers instead of the `caller` parameter
it was passed. As `despawn_with_caller()` is not `#[track_caller]`, this
means the location will always be reported as `despawn_with_caller()`
itself.
## Solution
Pass `caller` instead of `Location::caller()`.
Adding these allows using `DetectChangesMut::set_if_neq` to only update
the values when needed. Currently you need to get the inner values first
(`String` and `Color`), to do any equality checks.
---------
Signed-off-by: Jean Mertz <git@jeanmertz.com>
# Objective
Fixes#17508
`bevy_color::Color` constructors don't have docs explaining the valid
range for the values passed.
## Solution
I've mostly copied the docs from the respective underlying type's docs,
because that seemed most consistent and accurate.
# Objective
The new `DeserializeWithRegistry` trait in 0.15 was designed to be used
with reflection, and so has a `trait DeserializeWithRegistry:
PartialReflect` bound. However, this bound is not actually necessary for
the trait to function properly. And this `PartialReflect` bound already
exists on:
```rs
impl<T: PartialReflect + for<'de> DeserializeWithRegistry<'de>> FromType<T>
for ReflectDeserializeWithRegistry
```
So there is no point in constraining the trait itself with this bound as
well.
This lets me use `DeserializeWithRegistry` with non-`Reflect` types,
which I want to do to avoid making a bunch of `FooDeserializer` structs
and `impl DeserializeSeed` on them.
## Solution
Removes this unnecessary bound.
## Testing
Trivial change, does not break compilation or `bevy_reflect` tests.
## Migration Guide
`DeserializeWithRegistry` types are no longer guaranteed to be
`PartialReflect` as well. If you were relying on this type bound, you
should add it to your own bounds manually.
```diff
- impl<T: DeserializeWithRegistry> Foo for T { .. }
+ impl<T: DeserializeWithRegistry + PartialReflect> Foo for T { .. }
```
This allows you to continue chaining method calls after calling
`EntityCommands::entry`:
```rust
commands
.entity(player.entity)
.entry::<Level>()
// Modify the component if it exists
.and_modify(|mut lvl| lvl.0 += 1)
// Otherwise insert a default value
.or_insert(Level(0))
// Return the EntityCommands for the entity
.entity()
// And continue chaining method calls
.insert(Name::new("Player"));
```
---------
Signed-off-by: Jean Mertz <git@jeanmertz.com>
# Objective
Two more optimisations for UI extraction:
* We only need to query for the camera's render entity when the target
camera changes. If the target camera is the same as for the previous UI
node we can use the previous render entity.
* The cheap checks for visibility and zero size should be performed
first before the camera queries.
## Solution
Add a new system param `UiCameraMap` that resolves the correct render
camera entity and only queries when necessary.
<img width="506" alt="tracee"
src="https://github.com/user-attachments/assets/f57d1e0d-f3a7-49ee-8287-4f01ffc8ba24"
/>
I don't like the `UiCameraMap` + `UiCameraMapper` implementation very
much, maybe someone else can suggest a better construction.
This is partly motivated by #16942 which adds further indirection and
these changes would ameliorate that performance regression.
# Objective
In #16547, we added `EntitySet`s/`EntitySetIterator`s. We can know
whenever an iterator only contains unique entities, however we do not
yet have the ability to collect and reuse these without either the
unsafe `UniqueEntityIter::from_iterator_unchecked`, or the expensive
`HashSet::from_iter`.
An important piece for being able to do this is a `Vec` that maintains
the uniqueness property, can be collected into, and is itself
`EntitySet`.
A lot of entity collections are already intended to be "unique", but
have no way of expressing that when stored, other than using an
aforementioned `HashSet`. Such a type helps by limiting or even removing
the need for unsafe on the user side when not using a validated `Set`
type, and makes it easier to interface with other infrastructure like
f.e. `RelationshipSourceCollection`s.
## Solution
We implement `UniqueEntityVec`.
This is a wrapper around `Vec`, that only ever contains unique elements.
It mirrors the API of `Vec`, however restricts any mutation as to not
violate the uniqueness guarantee. Meaning:
- Any inherent method which can introduce new elements or mutate
existing ones is now unsafe, f.e.: `insert`, `retain_mut`
- Methods that are impossible to use safely are omitted, f.e.: `fill`,
`extend_from_within`
A handful of the unsafe methods can do element-wise mutation
(`retain_mut`, `dedup_by`), which can be an unwind safety hazard were
the element-wise operation to panic. For those methods, we require that
each individual execution of the operation upholds uniqueness, not just
the entire method as a whole.
To be safe for mutable usage, slicing and the associated slice methods
require a matching `UniqueEntitySlice` type , which we leave for a
follow-up PR.
Because this type will deref into the `UniqueEntitySlice` type, we also
offer the immutable `Vec` methods on this type (which only amount to a
handful). "as inner" functionality is covered by additional
`as_vec`/`as_mut_vec` methods + `AsRef`/`Borrow` trait impls.
Like `UniqueEntityIter::from_iterator_unchecked`, this type has a
`from_vec_unchecked` method as well.
The canonical way to safely obtain this type however is via
`EntitySetIterator::collect_set` or
`UniqueEntityVec::from_entity_set_iter`. Like mentioned in #17513, these
are named suboptimally until supertrait item shadowing arrives, since a
normal `collect` will still run equality checks.
# Objective
This makes the `Image::get_color_at_3d` and `Image::set_color_at_3d`
methods work with 2D images with more than one layer.
## Solution
- The Z coordinate is interpreted as the layer number.
## Testing
- Added a test: `get_set_pixel_2d_with_layers`.
# Objective
- As discussed in
https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/17276#issuecomment-2611203714,
we should transform the cursor's hotspot if the user is asking for the
image to be flipped.
- This becomes more important when a `scale` transform option exists.
It's harder for users to transform the hotspot themselves when using
`scale` because they'd need to look up the image to get its dimensions.
Instead, we let Bevy handle the hotspot transforms and make the
`hotspot` field the "original/source" hotspot.
- Refs #17276.
## Solution
- When the image needs to be transformed, also transform the hotspot. If
the image does not need to be transformed (i.e. fast path), no hotspot
transformation is applied.
## Testing
- Ran the example: `cargo run --example custom_cursor_image
--features=custom_cursor`.
- Add unit tests for the hotspot transform function.
- I also ran the example I have in my `bevy_cursor_kit` crate, which I
think is a good illustration of the reason for this PR.
- In the following videos, there is an arrow pointing up. The button
hover event fires as I move the mouse over it.
- When I press `Y`, the cursor flips.
- In the first video, on `bevy@main` **before** this PR, notice how the
hotspot is wrong after flipping and no longer hovering the button. The
arrow head and hotspot are no longer synced.
- In the second video, on the branch of **this** PR, notice how the
hotspot gets flipped as soon as I press `Y` and the cursor arrow head is
in the correct position on the screen and still hovering the button.
Speaking back to the objective listed at the start: The user originally
defined the _source_ hotspot for the arrow. Later, they decide they want
to flip the cursor vertically: It's nice that Bevy can automatically
flip the _source_ hotspot for them at the same time it flips the
_source_ image.
First video (main):
https://github.com/user-attachments/assets/1955048c-2f85-4951-bfd6-f0e7cfef0cf8
Second video (this PR):
https://github.com/user-attachments/assets/73cb9095-ecb5-4bfd-af5b-9f772e92bd16
# Objective
Fixes#16628
## Solution
Matrices were being applied in the wrong order.
## Testing
Ran `skybox` example with rotations applied to the `Skybox` on the `x`,
`y`, and `z` axis (one at a time).
e.g.
```rust
Skybox {
image: skybox_handle.clone(),
brightness: 1000.0,
rotation: Quat::from_rotation_y(-45.0_f32.to_radians()),
}
```
## Showcase
[Screencast_20250121_151232.webm](https://github.com/user-attachments/assets/3df68714-f5f1-4d8c-8e08-cbab525a8bda)
# Objective
- Correct a mistake in the rustdoc for bevy_ecs::world::World.
## Solution
- The rustdoc wrongly stated that "Each component can have up to one
instance of each component type.". This sentence should presumably be
"Each *Entity* can have up to one instance of each component type.".
Applying this change makes the prior sentence "Each [`Entity`] has a set
of components." redundant.
---------
Co-authored-by: François Mockers <francois.mockers@vleue.com>
Minor improvement to the render_resource doc comments; specifically, the
gpu buffer types
- makes them consistently reference each other
- reorders them to be alphabetical
- removes duplicated entries
# Objective
The `ArgList::push` family of methods consume `self` and return a new
`ArgList` which means they can't be used with `&mut ArgList` references.
```rust
fn foo(args: &mut ArgList) {
args.push_owned(47_i32); // doesn't work :(
}
```
It's typical for `push` methods on other existing types to take `&mut
self`.
## Solution
Renamed the existing push methods to `with_arg`, `with_ref` etc and
added new `push` methods which take `&mut self`.
## Migration Guide
Uses of the `ArgList::push` methods should be replaced with the `with`
counterpart.
<details>
| old | new |
| --- | --- |
| push_arg | with_arg |
| push_ref | with_ref |
| push_mut | with_mut |
| push_owned | with_owned |
| push_boxed | with_boxed |
</details>
# Objective
The various `Query::sort()` methods have a lot of duplicated code
between them, including some unsafe code. Reduce the duplication to make
the code easier to read and maintain.
## Solution
Extract the duplicated code to a private method, and pass in the sorting
strategy as a closure.
## Testing
I used `cargo-show-asm` to verify that the closures were inlined, but I
didn't run anything through a profiler. The `sort()` method itself even
had identical assembly before and after this change, although the others
did not.
# Objective
I wrote a box shadow UI material naively thinking I could use the border
widths attribute to hold the border radius but it
doesn't work as the border widths are automatically set in the
extraction function. Need to send border radius to the shader seperately
for it to be viable.
## Solution
Add a `border_radius` vertex attribute to the ui material.
This PR also removes the normalization of border widths for custom UI
materials. The regular UI shader doesn't do this so it's a bit confusing
and means you can't use the logic from `ui.wgsl` in your custom UI
materials.
## Testing / Showcase
Made a change to the `ui_material` example to display border radius:
```cargo run --example ui_material```
<img width="569" alt="corners" src="https://github.com/user-attachments/assets/36412736-a9ee-4042-aadd-68b9cafb17cb" />
Unfortunately, Apple platforms don't have enough texture bindings to
properly support clustered decals. This should be fixed once `wgpu` has
first-class bindless texture support. In the meantime, we disable them.
Closes#17553.
---------
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
*Occlusion culling* allows the GPU to skip the vertex and fragment
shading overhead for objects that can be quickly proved to be invisible
because they're behind other geometry. A depth prepass already
eliminates most fragment shading overhead for occluded objects, but the
vertex shading overhead, as well as the cost of testing and rejecting
fragments against the Z-buffer, is presently unavoidable for standard
meshes. We currently perform occlusion culling only for meshlets. But
other meshes, such as skinned meshes, can benefit from occlusion culling
too in order to avoid the transform and skinning overhead for unseen
meshes.
This commit adapts the same [*two-phase occlusion culling*] technique
that meshlets use to Bevy's standard 3D mesh pipeline when the new
`OcclusionCulling` component, as well as the `DepthPrepass` component,
are present on the camera. It has these steps:
1. *Early depth prepass*: We use the hierarchical Z-buffer from the
previous frame to cull meshes for the initial depth prepass, effectively
rendering only the meshes that were visible in the last frame.
2. *Early depth downsample*: We downsample the depth buffer to create
another hierarchical Z-buffer, this time with the current view
transform.
3. *Late depth prepass*: We use the new hierarchical Z-buffer to test
all meshes that weren't rendered in the early depth prepass. Any meshes
that pass this check are rendered.
4. *Late depth downsample*: Again, we downsample the depth buffer to
create a hierarchical Z-buffer in preparation for the early depth
prepass of the next frame. This step is done after all the rendering, in
order to account for custom phase items that might write to the depth
buffer.
Note that this patch has no effect on the per-mesh CPU overhead for
occluded objects, which remains high for a GPU-driven renderer due to
the lack of `cold-specialization` and retained bins. If
`cold-specialization` and retained bins weren't on the horizon, then a
more traditional approach like potentially visible sets (PVS) or low-res
CPU rendering would probably be more efficient than the GPU-driven
approach that this patch implements for most scenes. However, at this
point the amount of effort required to implement a PVS baking tool or a
low-res CPU renderer would probably be greater than landing
`cold-specialization` and retained bins, and the GPU driven approach is
the more modern one anyway. It does mean that the performance
improvements from occlusion culling as implemented in this patch *today*
are likely to be limited, because of the high CPU overhead for occluded
meshes.
Note also that this patch currently doesn't implement occlusion culling
for 2D objects or shadow maps. Those can be addressed in a follow-up.
Additionally, note that the techniques in this patch require compute
shaders, which excludes support for WebGL 2.
This PR is marked experimental because of known precision issues with
the downsampling approach when applied to non-power-of-two framebuffer
sizes (i.e. most of them). These precision issues can, in rare cases,
cause objects to be judged occluded that in fact are not. (I've never
seen this in practice, but I know it's possible; it tends to be likelier
to happen with small meshes.) As a follow-up to this patch, we desire to
switch to the [SPD-based hi-Z buffer shader from the Granite engine],
which doesn't suffer from these problems, at which point we should be
able to graduate this feature from experimental status. I opted not to
include that rewrite in this patch for two reasons: (1) @JMS55 is
planning on doing the rewrite to coincide with the new availability of
image atomic operations in Naga; (2) to reduce the scope of this patch.
A new example, `occlusion_culling`, has been added. It demonstrates
objects becoming quickly occluded and disoccluded by dynamic geometry
and shows the number of objects that are actually being rendered. Also,
a new `--occlusion-culling` switch has been added to `scene_viewer`, in
order to make it easy to test this patch with large scenes like Bistro.
[*two-phase occlusion culling*]:
https://medium.com/@mil_kru/two-pass-occlusion-culling-4100edcad501
[Aaltonen SIGGRAPH 2015]:
https://www.advances.realtimerendering.com/s2015/aaltonenhaar_siggraph2015_combined_final_footer_220dpi.pdf
[Some literature]:
https://gist.github.com/reduz/c5769d0e705d8ab7ac187d63be0099b5?permalink_comment_id=5040452#gistcomment-5040452
[SPD-based hi-Z buffer shader from the Granite engine]:
https://github.com/Themaister/Granite/blob/master/assets/shaders/post/hiz.comp
## Migration guide
* When enqueuing a custom mesh pipeline, work item buffers are now
created with
`bevy::render::batching::gpu_preprocessing::get_or_create_work_item_buffer`,
not `PreprocessWorkItemBuffers::new`. See the
`specialized_mesh_pipeline` example.
## Showcase
Occlusion culling example:

Bistro zoomed out, before occlusion culling:

Bistro zoomed out, after occlusion culling:

In this scene, occlusion culling reduces the number of meshes Bevy has
to render from 1591 to 585.
Currently, our default maximum shadow cascade distance is 1000 m, which
is quite distant compared to that of Unity (150 m), Unreal Engine 5 (200
m), and Godot (100 m). I also adjusted the default first cascade far
bound to be 10 m, which matches that of Unity (10.05 m) and Godot (10
m). Together, these changes should improve the default sharpness of
shadows of directional lights for typical scenes.
## Migration Guide
* The default shadow cascade far distance has been changed from 1000 to
150, and the default first cascade far bound has been changed from 5 to
10, in order to be similar to the defaults of other engines.
# Objective
This allows for the usage of the MouseScrollUnit as a key to a HashSet
and HashMap. I have a need for this, but this basic functionality is
currently missing.
## Solution
Add the derive Hash attribute to the MouseScrollUnit type.
## Testing
- Did you test these changes? If so, how?
No, but I did perform a `cargo build`. My laptop is failing to run
`cargo test` without crashing.
- Are there any parts that need more testing?
If someone could run a `cargo test` for completeness, that would be
great but this is a trivial change.
- How can other people (reviewers) test your changes? Is there anything
specific they need to know?
They simply need to ensure that the common Hash derive macro works as
expected for the basic MouseScrollUnit type.
- If relevant, what platforms did you test these changes on, and are
there any important ones you can't test?
Ubuntu 22.04
# Objective
Implement `Eq` and `Hash` for the `BindGroup` and `BindGroupLayout`
wrappers.
## Solution
Implement based on the same assumption that the ID is unique, for
consistency with `PartialEq`.
## Testing
None; this should be straightforward. If there's an issue that would be
a design one.
This commit allows specular highlights to be tinted with a color and for
the reflectance and color tint values to vary across a model via a pair
of maps. The implementation follows the [`KHR_materials_specular`] glTF
extension. In order to reduce the number of samplers and textures in the
default `StandardMaterial` configuration, the maps are gated behind the
`pbr_specular_textures` Cargo feature.
Specular tinting is currently unsupported in the deferred renderer,
because I didn't want to bloat the deferred G-buffers. A possible fix
for this in the future would be to make the G-buffer layout more
configurable, so that specular tints could be supported on an opt-in
basis. As an alternative, Bevy could force meshes with specular tints to
render in forward mode. Both of these solutions require some more
design, so I consider them out of scope for now.
Note that the map is a *specular* map, not a *reflectance* map. In Bevy
and Filament terms, the reflectance values in the specular map range
from [0.0, 0.5], rather than [0.0, 1.0]. This is an unfortunate
[`KHR_materials_specular`] specification requirement that stems from the
fact that glTF is specified in terms of a specular strength model, not
the reflectance model that Filament and Bevy use. A workaround, which is
noted in the `StandardMaterial` documentation, is to set the
`reflectance` value to 2.0, which spreads the specular map range from
[0.0, 1.0] as normal.
The glTF loader has been updated to parse the [`KHR_materials_specular`]
extension. Note that, unless the non-default `pbr_specular_textures` is
supplied, the maps are ignored. The `specularFactor` value is applied as
usual. Note that, as with the specular map, the glTF `specularFactor` is
twice Bevy's `reflectance` value.
This PR adds a new example, `specular_tint`, which demonstrates the
specular tint and map features. Note that this example requires the
[`KHR_materials_specular`] Cargo feature.
[`KHR_materials_specular`]:
https://github.com/KhronosGroup/glTF/tree/main/extensions/2.0/Khronos/KHR_materials_specular
## Changelog
### Added
* Specular highlights can now be tinted with the `specular_tint` field
in `StandardMaterial`.
* Specular maps are now available in `StandardMaterial`, gated behind
the `pbr_specular_textures` Cargo feature.
* The `KHR_materials_specular` glTF extension is now supported, allowing
for customization of specular reflectance and specular maps. Note that
the latter are gated behind the `pbr_specular_textures` Cargo feature.
This commit adds support for *decal projectors* to Bevy, allowing for
textures to be projected on top of geometry. Decal projectors are
clusterable objects, just as punctual lights and light probes are. This
means that decals are only evaluated for objects within the conservative
bounds of the projector, and they don't require a second pass.
These clustered decals require support for bindless textures and as such
currently don't work on WebGL 2, WebGPU, macOS, or iOS. For an
alternative that doesn't require bindless, see PR #16600. I believe that
both contact projective decals in #16600 and clustered decals are
desirable to have in Bevy. Contact projective decals offer broader
hardware and driver support, while clustered decals don't require the
creation of bounding geometry.
A new example, `decal_projectors`, has been added, which demonstrates
multiple decals on a rotating object. The decal projectors can be scaled
and rotated with the mouse.
There are several limitations of this initial patch that can be
addressed in follow-ups:
1. There's no way to specify the Z-index of decals. That is, the order
in which multiple decals are blended on top of one another is arbitrary.
A follow-up could introduce some sort of Z-index field so that artists
can specify that some decals should be blended on top of others.
2. Decals don't take the normal of the surface they're projected onto
into account. Most decal implementations in other engines have a feature
whereby the angle between the decal projector and the normal of the
surface must be within some threshold for the decal to appear. Often,
artists can specify a fade-off range for a smooth transition between
oblique surfaces and aligned surfaces.
3. There's no distance-based fadeoff toward the end of the projector
range. Many decal implementations have this.
This addresses #2401.
## Showcase

# Objective
Bevy sprite image mode lacks proportional scaling for the underlying
texture. In many cases, it's required. For example, if it is desired to
support a wide variety of screens with a single texture, it's okay to
cut off some portion of the original texture.
## Solution
I added scaling of the texture during the preparation step. To fill the
sprite with the original texture, I scaled UV coordinates accordingly to
the sprite size aspect ratio and texture size aspect ratio. To fit
texture in a sprite the original `quad` is scaled and then the
additional translation is applied to place the scaled quad properly.
## Testing
For testing purposes could be used `2d/sprite_scale.rs`. Also, I am
thinking that it would be nice to have some tests for a
`crates/bevy_sprite/src/render/mod.rs:sprite_scale`.
---
## Showcase
<img width="1392" alt="image"
src="https://github.com/user-attachments/assets/c2c37b96-2493-4717-825f-7810d921b4bc"
/>
# Objective
We do not have `EntityIndexMap`/`EntityIndexSet`.
Usual `HashMap`s/`HashSet`s do not guarantee any order, which can be
awkward for some use cases.
The `indexmap` versions remember insertion order, which then also
becomes their iteration order.
They can be thought of as a `HashTable` + `Vec`, which means fast
iteration and removal, indexing by index (not just key), and slicing!
Performance should otherwise be comparable.
## Solution
Because `indexmap` is structured to mirror `hashbrown`, it suffers the
same issue of not having the `Hasher` generic on their iterators. #16912
solved this issue for `EntityHashMap`/`EntityHashSet` with a wrapper
around the hashbrown version, so this PR does the same.
Hopefully these wrappers can be removed again in the future by having
`hashbrown`/`indexmap` adopt that generic in their iterators themselves!
# Objective
Fixes#17487
- Adds a new field `refresh_interval` to `FpsOverlayConfig` to allow the
user setting a minimum time before each refresh of the FPS display
## Solution
- Add `refresh_interval` to `FpsOverlayConfig`
- When updating the on screen text, check a duration of
`refresh_interval` has passed, if not, don't update the FPS counter
## Testing
- Created a new bevy project
- Included the `FpsOverlayPlugin` with the default `refresh_interval`
(100 ms)
- Included the `FpsOverlayPlugin` with an obnoxious `refresh_interval`
(2 seconds)
---
---------
Co-authored-by: Benjamin Brienen <benjamin.brienen@outlook.com>
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
# Objective
- Trouble remembering the difference between `OnAdd` and `OnInsert` for
triggers. Would like a better doc for those triggers so it appears in my
editor tooltip.
## Solution
- Clarify docs for OnAdd, OnInsert, OnRemove, OnReplace. Based on
comments in the
[component_hook.rs](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/blob/main/examples/ecs/component_hooks.rs#L73)
example.
## Testing
- None, small doc fix.
# Objective
Some collections are more efficient to construct when we know that every
element is unique in advance.
We have `EntitySetIterator`s from #16547, but currently no API to safely
make use of them this way.
## Solution
Add `FromEntitySetIterator` as a subtrait to `FromIterator`, and
implement it for the `EntityHashSet`/`hashbrown::HashSet` types.
To match the normal `FromIterator`, we also add a
`EntitySetIterator::collect_set` method.
It'd be better if these methods could shadow `from_iter` and `collect`
completely, but https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/89151 is needed
for that.
While currently only `HashSet`s implement this trait, future
`UniqueEntityVec`/`UniqueEntitySlice` functionality comes with more
implementors.
Because `HashMap`s are collected from tuples instead of singular types,
implementing this same optimization for them is more complex, and has to
be done separately.
## Showcase
This is basically a free speedup for collecting `EntityHashSet`s!
```rust
pub fn collect_milk_dippers(dippers: Query<Entity, (With<Milk>, With<Cookies>)>) {
dippers.iter().collect_set::<EntityHashSet>();
// or
EntityHashSet::from_entity_set_iter(dippers);
}
---------
Co-authored-by: SpecificProtagonist <vincentjunge@posteo.net>
# Objective
- Make `CustomCursor::Image` easier to work with by splitting the enum
variants off into `CustomCursorImage` and `CustomCursorUrl` structs and
deriving `Default` on those structs.
- Refs #17276.
## Testing
- Ran two examples: `cargo run --example custom_cursor_image
--features=custom_cursor` and `cargo run --example window_settings
--features=custom_cursor`
- CI.
---
## Migration Guide
The `CustomCursor` enum's variants now hold instances of
`CustomCursorImage` or `CustomCursorUrl`. Update your uses of
`CustomCursor` accordingly.
# Objective
The `is_empty` checks that are meant to stop zero-sized uinodes from
being extracted are missing from `extract_uinode_background_colors`,
`extract_uinode_images` and `extract_ui_material_nodes`.
## Solution
Put them back.
Implement procedural atmospheric scattering from [Sebastien Hillaire's
2020 paper](https://sebh.github.io/publications/egsr2020.pdf). This
approach should scale well even down to mobile hardware, and is
physically accurate.
## Co-author: @mate-h
He helped massively with getting this over the finish line, ensuring
everything was physically correct, correcting several places where I had
misunderstood or misapplied the paper, and improving the performance in
several places as well. Thanks!
## Credits
@aevyrie: helped find numerous bugs and improve the example to best show
off this feature :)
Built off of @mtsr's original branch, which handled the transmittance
lut (arguably the most important part)
## Showcase:


## For followup
- Integrate with pcwalton's volumetrics code
- refactor/reorganize for better integration with other effects
- have atmosphere transmittance affect directional lights
- add support for generating skybox/environment map
---------
Co-authored-by: Emerson Coskey <56370779+EmersonCoskey@users.noreply.github.com>
Co-authored-by: atlv <email@atlasdostal.com>
Co-authored-by: JMS55 <47158642+JMS55@users.noreply.github.com>
Co-authored-by: Emerson Coskey <coskey@emerlabs.net>
Co-authored-by: Máté Homolya <mate.homolya@gmail.com>
# Objective
- Fix typo in `spin/portable-atomic` feature.
## Solution
- Replace with `spin/portable_atomic`
## Testing
- CI
---
## Notes
This is a very annoying design choice the `spin` developers made.
Because the _crate_ is called `portable-atomic` and is optional, Cargo
automatically registers the feature `portable-atomic`. But the
maintainers use `portable_atomic` for their _feature_ which enables the
support. Sneaks through CI because it's a valid feature and will only
cause breakage on atomically challenged platforms (which we currently
aren't testing in CI).
Should we test atomically challenged in CI? Right now I don't think so,
at least not until we've made "normal" `no_std` CI better with the main
`bevy` crate as the test-case rather than each individual crate.
# Objective
- Contributes to #16877
## Solution
- Moved `hashbrown`, `foldhash`, and related types out of `bevy_utils`
and into `bevy_platform_support`
- Refactored the above to match the layout of these types in `std`.
- Updated crates as required.
## Testing
- CI
---
## Migration Guide
- The following items were moved out of `bevy_utils` and into
`bevy_platform_support::hash`:
- `FixedState`
- `DefaultHasher`
- `RandomState`
- `FixedHasher`
- `Hashed`
- `PassHash`
- `PassHasher`
- `NoOpHash`
- The following items were moved out of `bevy_utils` and into
`bevy_platform_support::collections`:
- `HashMap`
- `HashSet`
- `bevy_utils::hashbrown` has been removed. Instead, import from
`bevy_platform_support::collections` _or_ take a dependency on
`hashbrown` directly.
- `bevy_utils::Entry` has been removed. Instead, import from
`bevy_platform_support::collections::hash_map` or
`bevy_platform_support::collections::hash_set` as appropriate.
- All of the above equally apply to `bevy::utils` and
`bevy::platform_support`.
## Notes
- I left `PreHashMap`, `PreHashMapExt`, and `TypeIdMap` in `bevy_utils`
as they might be candidates for micro-crating. They can always be moved
into `bevy_platform_support` at a later date if desired.
# Objective
- Contributes to #16877
## Solution
- Expanded `bevy_platform_support::sync` module to provide
API-compatible replacements for `std` items such as `RwLock`, `Mutex`,
and `OnceLock`.
- Removed `spin` from all crates except `bevy_platform_support`.
## Testing
- CI
---
## Notes
- The sync primitives, while verbose, entirely rely on `spin` for their
implementation requiring no `unsafe` and not changing the status-quo on
_how_ locks actually work within Bevy. This is just a refactoring to
consolidate the "hacks" and workarounds required to get a consistent
experience when either using `std::sync` or `spin`.
- I have opted to rely on `std::sync` for `std` compatible locks,
maintaining the status quo. However, now that we have these locks
factored out into the own module, it would be trivial to investigate
alternate locking backends, such as `parking_lot`.
- API for these locking types is entirely based on `std`. I have
implemented methods and types which aren't currently in use within Bevy
(e.g., `LazyLock` and `Once`) for the sake of completeness. As the
standard library is highly stable, I don't expect the Bevy and `std`
implementations to drift apart much if at all.
---------
Co-authored-by: BD103 <59022059+BD103@users.noreply.github.com>
Co-authored-by: Benjamin Brienen <benjamin.brienen@outlook.com>
# Objective
The UI can only target a single view and doesn't support `RenderLayers`,
so there doesn't seem to be any need for UI nodes to require
`ViewVisibility` and `VisibilityClass`.
Fixes#17400
## Solution
Remove the `ViewVisibility` and `VisibilityClass` component requires
from `Node` and change the visibility queries to only query for
`InheritedVisibility`.
## Testing
```cargo run --example many_buttons --release --features "trace_tracy"```
Yellow is this PR, red is main.
`bevy_render::view::visibility::reset_view_visibility`
<img width="531" alt="reset-view" src="https://github.com/user-attachments/assets/a44b215d-96bf-43ec-8669-31530ff98eae" />
`bevy_render::view::visibility::check_visibility`
<img width="445" alt="view_visibility" src="https://github.com/user-attachments/assets/fa111757-da91-434d-88e4-80bdfa29374f" />
Right now, we always include distance fog in the shader, which is
unfortunate as it's complex code and is rare. This commit changes it to
be a `#define` instead. I haven't confirmed that removing distance fog
meaningfully reduces VGPR usage, but it can't hurt.
# Objective
Dependabot tried up update this earlier, but it was noticed that this
broke wasm builds. A new release has happened since then which includes
a fix for that.
Here's the
[changelog](https://github.com/smol-rs/async-broadcast/blob/master/CHANGELOG.md).
Closes#11830
## Solution
Use `async-broadcast` `0.7.2`.
## Testing
I ran a few some examples involving assets on macos / wasm.
# Objective
Fixes#17457
## Solution
#[derive(FromWorld)] now works with enums by specifying which variant
should be used.
## Showcase
```rust
#[Derive(FromWorld)]
enum Game {
#[from_world]
Playing,
Stopped
}
```
---------
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Benjamin Brienen <benjamin.brienen@outlook.com>
# Objective
Make `Mesh::merge` more resilient to use.
Currently, it's difficult to make sure `Mesh::merge` will not panic
(we'd have to check if all attributes are compatible).
- I'd appreciate it for utility function to convert different mesh
representations such as:
https://github.com/dimforge/bevy_rapier/pull/628.
## Solution
- Make `Mesh::merge` return a `Result`.
## Testing
- It builds
## Migration Guide
- `Mesh::merge` now returns a `Result<(), MeshMergeError>`.
---------
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Greeble <166992735+greeble-dev@users.noreply.github.com>
Co-authored-by: Benjamin Brienen <benjamin.brienen@outlook.com>
# Objective
The doc comment for `Node::flex_basis` which refers to a`size` field
that was replaced by individual `width` and `height` fields sometime
ago.
## Solution
Refer to the individual fields instead.
# Objective
- Make the function signature for `ComponentHook` less verbose
## Solution
- Refactored `Entity`, `ComponentId`, and `Option<&Location>` into a new
`HookContext` struct.
## Testing
- CI
---
## Migration Guide
Update the function signatures for your component hooks to only take 2
arguments, `world` and `context`. Note that because `HookContext` is
plain data with all members public, you can use de-structuring to
simplify migration.
```rust
// Before
fn my_hook(
mut world: DeferredWorld,
entity: Entity,
component_id: ComponentId,
) { ... }
// After
fn my_hook(
mut world: DeferredWorld,
HookContext { entity, component_id, caller }: HookContext,
) { ... }
```
Likewise, if you were discarding certain parameters, you can use `..` in
the de-structuring:
```rust
// Before
fn my_hook(
mut world: DeferredWorld,
entity: Entity,
_: ComponentId,
) { ... }
// After
fn my_hook(
mut world: DeferredWorld,
HookContext { entity, .. }: HookContext,
) { ... }
```
# Objective
- Fix issue @mockersf identified with `example-showcase` where time was
not being received correctly from the render world.
## Solution
- Refactored to ensure `TimeReceiver` is always cleared even if it isn't
being used in the main world.
## Testing
- `cargo run -p example-showcase -- --page 1 --per-page 1 run
--screenshot-frame 200 --fixed-frame-time 0.0125 --stop-frame 450
--in-ci --show-logs`
# Objective
Alternative to #9660, which is outdated since "required components"
landed.
Fixes#9655
## Solution
This is a different approach than the linked PR, slotting the warning
into an existing check for zero or negative font sizes in the text
pipeline.
## Testing
Replaced a font size with `0.0` in `examples/ui/text.rs`.
```
2025-01-22T23:26:08.239688Z INFO bevy_winit::system: Creating new window App (0v1)
2025-01-22T23:26:08.617505Z WARN bevy_text::pipeline: Text span 10v1 has a font size <= 0.0. Nothing will be displayed.
```
# Objective
- Contributes to #15460
## Solution
- Switched `tracing` for `log` for the atomically challenged platforms
- Setup feature flags as required
- Added to `compile-check-no-std` CI task
- Made `crossbeam-channel` optional depending on `std`.
## Testing
- CI
---
## Notes
- `crossbeam-channel` provides a MPMC channel type which isn't readily
replicable in `no_std`, and is only used for a `bevy_render`
integration. As such, I've feature-gated the `TimeReceiver` and
`TimeSender` types.
---------
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
# Objective
Fixes#14708
Also fixes some commands not updating tracked location.
## Solution
`ObserverTrigger` has a new `caller` field with the
`track_change_detection` feature;
hooks take an additional caller parameter (which is `Some(…)` or `None`
depending on the feature).
## Testing
See the new tests in `src/observer/mod.rs`
---
## Showcase
Observers now know from where they were triggered (if
`track_change_detection` is enabled):
```rust
world.observe(move |trigger: Trigger<OnAdd, Foo>| {
println!("Added Foo from {}", trigger.caller());
});
```
## Migration
- hooks now take an additional `Option<&'static Location>` argument
---------
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
# Objective
- Contributes to #15460
## Solution
- Switched `tracing` for `log` for the atomically challenged platforms
- Setup feature flags as required
- Added to `compile-check-no-std` CI task
## Testing
- CI
---
## Notes
- _Very_ easy one this time. Most of the changes here are just feature
definitions and documentation within the `Cargo.toml`
# Objective
Add reflection support to more `glam` `Vec` types, specifically
* I8Vec2
* I8Vec3
* I8Vec4
* U8Vec2
* U8Vec3
* U8Vec4
* I16Vec2
* I16Vec3
* I16Vec4
* U16Vec2
* U16Vec3
* U16Vec4
I needed to do this because I'm using various of these in my Bevy types,
and due to the orphan rules, I can't make these impls locally.
## Solution
Used `impl_reflect!` like for the existing types.
## Testing
This should not require additional testing, though I have verified that
reflection now works for these types in my own project.
This commit makes Bevy use change detection to only update
`RenderMaterialInstances` and `RenderMeshMaterialIds` when meshes have
been added, changed, or removed. `extract_mesh_materials`, the system
that extracts these, now follows the pattern that
`extract_meshes_for_gpu_building` established.
This improves frame time of `many_cubes` from 3.9ms to approximately
3.1ms, which slightly surpasses the performance of Bevy 0.14.
(Resubmitted from #16878 to clean up history.)

---------
Co-authored-by: Charlotte McElwain <charlotte.c.mcelwain@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
## Objective
Most `try` methods on `World` return a `Result`, but `try_despawn` and
`try_insert_batch` don't. Since Bevy's error handling is advancing,
these should be brought in line.
## Solution
- Added `TryDespawnError` and `TryInsertBatchError`.
- `try_despawn`, `try_insert_batch`, and `try_insert_batch_if_new` now
return their respective errors.
- Fixed slightly incorrect behavior in `try_insert_batch_with_caller`.
- The method was always meant to continue with the rest of the batch if
an entity was missing, but that only worked after the first entity; if
the first entity was missing, the method would exit early. This has been
resolved.
## Migration Guide
- `World::try_despawn` now returns a `Result` rather than a `bool`.
- `World::try_insert_batch` and `World::try_insert_batch_if_new` now
return a `Result` where they previously returned nothing.
# Objective
`bevy_ecs`'s `system` module is something of a grab bag, and *very*
large. This is particularly true for the `system_param` module, which is
more than 2k lines long!
While it could be defensible to put `Res` and `ResMut` there (lol no
they're in change_detection.rs, obviously), it doesn't make any sense to
put the `Resource` trait there. This is confusing to navigate (and
painful to work on and review).
## Solution
- Create a root level `bevy_ecs/resource.rs` module to mirror
`bevy_ecs/component.rs`
- move the `Resource` trait to that module
- move the `Resource` derive macro to that module as well (Rust really
likes when you pun on the names of the derive macro and trait and put
them in the same path)
- fix all of the imports
## Notes to reviewers
- We could probably move more stuff into here, but I wanted to keep this
PR as small as possible given the absurd level of import changes.
- This PR is ground work for my upcoming attempts to store resource data
on components (resources-as-entities). Splitting this code out will make
the work and review a bit easier, and is the sort of overdue refactor
that's good to do as part of more meaningful work.
## Testing
cargo build works!
## Migration Guide
`bevy_ecs::system::Resource` has been moved to
`bevy_ecs::resource::Resource`.
# Objective
While being able to quickly add / remove components down a tree is
broadly useful (material changing!), it's particularly necessary when
combined with the newly added #13120.
## Solution
Write four methods: covering both adding and removal on both
`EntityWorldMut` and `EntityCommands`.
These methods are generic over the `RelationshipTarget`, thanks to the
freshly merged relations 🎉
## Testing
I've added a simple unit test for these methods.
---------
Co-authored-by: Zachary Harrold <zac@harrold.com.au>
# Objective
After #17398, Bevy now has relations! We don't teach users how to make /
work with these in the examples yet though, but we definitely should.
## Solution
- Add a simple abstract example that goes over defining, spawning,
traversing and removing a custom relations.
- ~~Add `Relationship` and `RelationshipTarget` to the prelude: the
trait methods are really helpful here.~~
- this causes subtle ambiguities with method names and weird compiler
errors. Not doing it here!
- Clean up related documentation that I referenced when writing this
example.
## Testing
`cargo run --example relationships`
## Notes to reviewers
1. Yes, I know that the cycle detection code could be more efficient. I
decided to reduce the caching to avoid distracting from the broader
point of "here's how you traverse relationships".
2. Instead of using an `App`, I've decide to use
`World::run_system_once` + system functions defined inside of `main` to
do something closer to literate programming.
---------
Co-authored-by: Joona Aalto <jondolf.dev@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: MinerSebas <66798382+MinerSebas@users.noreply.github.com>
Co-authored-by: Kristoffer Søholm <k.soeholm@gmail.com>
Fixes#17412
## Objective
`Parent` uses the "has a X" naming convention. There is increasing
sentiment that we should use the "is a X" naming convention for
relationships (following #17398). This leaves `Children` as-is because
there is prevailing sentiment that `Children` is clearer than `ParentOf`
in many cases (especially when treating it like a collection).
This renames `Parent` to `ChildOf`.
This is just the implementation PR. To discuss the path forward, do so
in #17412.
## Migration Guide
- The `Parent` component has been renamed to `ChildOf`.
# Objective
Fixes#17416
## Solution
I just included ReflectFromReflect in all macros and implementations. I
think this should be ok, at least it compiles properly and does fix the
errors in my test code.
## Testing
I generated a DynamicMap and tried to convert it into a concrete
`HashMap` as a `Box<dyn Reflect>`. Without my fix, it doesn't work,
because this line panics:
```rust
let rfr = ty.data::<ReflectFromReflect>().unwrap();
```
where `ty` is the `TypeRegistration` for the (matching) `HashMap`.
I don't know why `ReflectFromReflect` wasn't included everywhere, I
assume that it was an oversight and not an architecture decision I'm not
aware of.
# Migration Guide
The hasher in reflected `HashMap`s and `HashSet`s now have to implement
`Default`. This is the case for the ones provided by Bevy already, and
is generally a sensible thing to do.
# Objective
Some usecases in the ecosystems are blocked by the inability to stop
bevy internals and third party plugins from touching their entities.
However the specifics of a general purpose entity disabling system are
controversial and further complicated by hierarchies. We can partially
unblock these usecases with an opt-in approach: default query filters.
## Solution
- Introduce DefaultQueryFilters, these filters are automatically applied
to queries that don't otherwise mention the filtered component.
- End users and third party plugins can register default filters and are
responsible for handling entities they have hidden this way.
- Extra features can be left for after user feedback
- The default value could later include official ways to hide entities
---
## Changelog
- Add DefaultQueryFilters
# Objective
Diagnostics for labels don't suggest how to best implement them.
```
error[E0277]: the trait bound `Label: ScheduleLabel` is not satisfied
--> src/main.rs:15:35
|
15 | let mut sched = Schedule::new(Label);
| ------------- ^^^^^ the trait `ScheduleLabel` is not implemented for `Label`
| |
| required by a bound introduced by this call
|
= help: the trait `ScheduleLabel` is implemented for `Interned<(dyn ScheduleLabel + 'static)>`
note: required by a bound in `bevy_ecs::schedule::Schedule::new`
--> /home/vj/workspace/rust/bevy/crates/bevy_ecs/src/schedule/schedule.rs:297:28
|
297 | pub fn new(label: impl ScheduleLabel) -> Self {
| ^^^^^^^^^^^^^ required by this bound in `Schedule::new`
```
## Solution
`diagnostics::on_unimplemented` and `diagnostics::do_not_recommend`
## Showcase
New error message:
```
error[E0277]: the trait bound `Label: ScheduleLabel` is not satisfied
--> src/main.rs:15:35
|
15 | let mut sched = Schedule::new(Label);
| ------------- ^^^^^ the trait `ScheduleLabel` is not implemented for `Label`
| |
| required by a bound introduced by this call
|
= note: consider annotating `Label` with `#[derive(ScheduleLabel)]`
note: required by a bound in `bevy_ecs::schedule::Schedule::new`
--> /home/vj/workspace/rust/bevy/crates/bevy_ecs/src/schedule/schedule.rs:297:28
|
297 | pub fn new(label: impl ScheduleLabel) -> Self {
| ^^^^^^^^^^^^^ required by this bound in `Schedule::new`
```
docs: enhance documentation in `query.rs` to clarify borrowing rules.
Please, let me know if you don't agree with the wording.. There is
always room for improvement.
Tested locally and it looks like this:

---------
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
# Objective
Fixes#14970
## Solution
It seems the clamp call in `ui.wgsl` had the parameters order incorrect.
## Testing
Tested using examples/ui in native and my current project in wasm - both
in linux.
Could use some help with testing in other platforms.
---
# Objective
Noticed while doing #17449, I had left these `DerefMut` impls in.
Obtaining mutable references to those inner iterator types allows for
`mem::swap`, which can be used to swap an incorrectly behaving instance
into the wrappers.
## Solution
Remove them!
# Objective
The existing `RelationshipSourceCollection` uses `Vec` as the only
possible backing for our relationships. While a reasonable choice,
benchmarking use cases might reveal that a different data type is better
or faster.
For example:
- Not all relationships require a stable ordering between the
relationship sources (i.e. children). In cases where we a) have many
such relations and b) don't care about the ordering between them, a hash
set is likely a better datastructure than a `Vec`.
- The number of children-like entities may be small on average, and a
`smallvec` may be faster
## Solution
- Implement `RelationshipSourceCollection` for `EntityHashSet`, our
custom entity-optimized `HashSet`.
-~~Implement `DoubleEndedIterator` for `EntityHashSet` to make things
compile.~~
- This implementation was cursed and very surprising.
- Instead, by moving the iterator type on `RelationshipSourceCollection`
from an erased RPTIT to an explicit associated type we can add a trait
bound on the offending methods!
- Implement `RelationshipSourceCollection` for `SmallVec`
## Testing
I've added a pair of new tests to make sure this pattern compiles
successfully in practice!
## Migration Guide
`EntityHashSet` and `EntityHashMap` are no longer re-exported in
`bevy_ecs::entity` directly. If you were not using `bevy_ecs` / `bevy`'s
`prelude`, you can access them through their now-public modules,
`hash_set` and `hash_map` instead.
## Notes to reviewers
The `EntityHashSet::Iter` type needs to be public for this impl to be
allowed. I initially renamed it to something that wasn't ambiguous and
re-exported it, but as @Victoronz pointed out, that was somewhat
unidiomatic.
In
1a8564898f,
I instead made the `entity_hash_set` public (and its `entity_hash_set`)
sister public, and removed the re-export. I prefer this design (give me
module docs please), but it leads to a lot of churn in this PR.
Let me know which you'd prefer, and if you'd like me to split that
change out into its own micro PR.
# Objective
`Text2d` ignores `TextBounds` when calculating the offset for text
aligment.
On main a text entity positioned in the center of the window with center
justification and 600px horizontal text bounds isn't centered like it
should be but shifted off to the right:
<img width="305" alt="hellox"
src="https://github.com/user-attachments/assets/8896c6f0-1b9f-4633-9c12-1de6eff5f3e1"
/>
(second example in the testing section below)
Fixes#14266
I already had a PR in review for this (#14270) but it used post layout
adjustment (which we want to avoid) and ignored `TextBounds`.
## Solution
* If `TextBounds` are present for an axis, use them instead of the size
of the computed text layout size to calculate the offset.
* Adjust the vertical offset of text so it's top is aligned with the top
of the texts bounding rect (when present).
## Testing
```
use bevy::prelude::*;
use bevy::color::palettes;
use bevy::sprite::Anchor;
use bevy::text::TextBounds;
fn main() {
App::new()
.add_plugins(DefaultPlugins)
.add_systems(Startup, setup)
.run();
}
fn example(commands: &mut Commands, dest: Vec3, justify: JustifyText) {
commands.spawn((
Sprite {
color: palettes::css::YELLOW.into(),
custom_size: Some(10. * Vec2::ONE),
anchor: Anchor::Center,
..Default::default()
},
Transform::from_translation(dest),
));
for a in [
Anchor::TopLeft,
Anchor::TopRight,
Anchor::BottomRight,
Anchor::BottomLeft,
] {
commands.spawn((
Text2d(format!("L R\n{:?}\n{:?}", a, justify)),
TextFont {
font_size: 14.0,
..default()
},
TextLayout {
justify,
..Default::default()
},
TextBounds::new(300., 75.),
Transform::from_translation(dest + Vec3::Z),
a,
));
}
}
fn setup(mut commands: Commands) {
commands.spawn(Camera2d::default());
for (i, j) in [
JustifyText::Left,
JustifyText::Right,
JustifyText::Center,
JustifyText::Justified,
]
.into_iter()
.enumerate()
{
example(&mut commands, (300. - 150. * i as f32) * Vec3::Y, j);
}
commands.spawn(Sprite {
color: palettes::css::YELLOW.into(),
custom_size: Some(10. * Vec2::ONE),
anchor: Anchor::Center,
..Default::default()
});
}
```
<img width="566" alt="cap"
src="https://github.com/user-attachments/assets/e6a98fa5-80b2-4380-a9b7-155bb49635b8"
/>
This probably looks really confusing but it should make sense if you
imagine each block of text surrounded by a 300x75 rectangle that is
anchored to the center of the yellow square.
#
```
use bevy::prelude::*;
use bevy::sprite::Anchor;
use bevy::text::TextBounds;
fn main() {
App::new()
.add_plugins(DefaultPlugins)
.add_systems(Startup, setup)
.run();
}
fn setup(mut commands: Commands) {
commands.spawn(Camera2d::default());
commands.spawn((
Text2d::new("hello"),
TextFont {
font_size: 60.0,
..default()
},
TextLayout::new_with_justify(JustifyText::Center),
TextBounds::new(600., 200.),
Anchor::Center,
));
}
```
<img width="338" alt="hello"
src="https://github.com/user-attachments/assets/e5e89364-afda-4baa-aca8-df4cdacbb4ed"
/>
The text being above the center is intended. When `TextBounds` are
present, the text block's offset is calculated using its `TextBounds`
not the layout size returned by cosmic-text.
#
Probably we should add a vertical alignment setting for Text2d. Didn't
do it here as this is intended for a 0.15.2 release.
simple derive macro for `FromWorld`. Going to be needed for composable
pipeline specializers but probably a nice thing to have regardless
## Testing
simple manual testing, nothing seemed to blow up. I'm no proc macro pro
though, so there's a chance I've mishandled spans somewhere or
something.
# Objective
- Contributes to #16877
## Solution
- Initial creation of `bevy_platform_support` crate.
- Moved `bevy_utils::Instant` into new `bevy_platform_support` crate.
- Moved `portable-atomic`, `portable-atomic-util`, and
`critical-section` into new `bevy_platform_support` crate.
## Testing
- CI
---
## Showcase
Instead of needing code like this to import an `Arc`:
```rust
#[cfg(feature = "portable-atomic")]
use portable_atomic_util::Arc;
#[cfg(not(feature = "portable-atomic"))]
use alloc::sync::Arc;
```
We can now use:
```rust
use bevy_platform_support::sync::Arc;
```
This applies to many other types, but the goal is overall the same:
allowing crates to use `std`-like types without the boilerplate of
conditional compilation and platform-dependencies.
## Migration Guide
- Replace imports of `bevy_utils::Instant` with
`bevy_platform_support::time::Instant`
- Replace imports of `bevy::utils::Instant` with
`bevy::platform_support::time::Instant`
## Notes
- `bevy_platform_support` hasn't been reserved on `crates.io`
- ~~`bevy_platform_support` is not re-exported from `bevy` at this time.
It may be worthwhile exporting this crate, but I am unsure of a
reasonable name to export it under (`platform_support` may be a bit
wordy for user-facing).~~
- I've included an implementation of `Instant` which is suitable for
`no_std` platforms that are not Wasm for the sake of eliminating feature
gates around its use. It may be a controversial inclusion, so I'm happy
to remove it if required.
- There are many other items (`spin`, `bevy_utils::Sync(Unsafe)Cell`,
etc.) which should be added to this crate. I have kept the initial scope
small to demonstrate utility without making this too unwieldy.
---------
Co-authored-by: TimJentzsch <TimJentzsch@users.noreply.github.com>
Co-authored-by: Chris Russell <8494645+chescock@users.noreply.github.com>
Co-authored-by: François Mockers <francois.mockers@vleue.com>
Makes use of `std` explicit, simplifying a possible `no_std` port.
# Objective
- Contributes to #15460
- Simplify future `no_std` work on `bevy_asset`
## Solution
- Add `#![no_std]` to switch to `core::prelude` instead of
`std::prelude`
## Testing
- CI
---
## Notes
This is entirely a change around the names of imports and has no impact
on functionality. This just reduces the quantity of changes involved in
the (likely more controversial) `no_std`-ification of `bevy_asset`.
Fixes#17397.
Also renamed all variants into present-tense.
## Migration Guide
- `PointerAction::Pressed` has been seperated into two variants,
`PointerAction::Press` and `PointerAction::Release`.
- `PointerAction::Moved` has been renamed to `PointerAction::Move`.
- `PointerAction::Canceled` has been renamed to `PointerAction::Cancel`.
# Objective
It's not immediately obvious that `TargetCamera` only works with UI node
entities. It's natural to assume from looking at something like the
`multiple_windows` example that it will work with everything.
## Solution
Rename `TargetCamera` to `UiTargetCamera`.
## Migration Guide
`TargetCamera` has been renamed to `UiTargetCamera`.
# Objective
Segment2d and Segment3d are currently hard to work with because unlike
many other primary shapes, they are bound to the origin.
The objective of this PR is to allow these segments to exist anywhere in
cartesian space, making them much more useful in a variety of contexts.
## Solution
Reworking the existing segment type's internal fields and methods to
allow them to exist anywhere in cartesian space.
I have done both reworks for 2d and 3d segments but I was unsure if I
should just have it all here or not so feel free to tell me how I should
proceed, for now I have only pushed Segment2d changes.
As I am not a very seasoned contributor, this first implementation is
very likely sloppy and will need some additional work from my end, I am
open to all criticisms and willing to work to get this to bevy's
standards.
## Testing
I am not very familiar with the standards of testing. Of course my
changes had to pass the thorough existing tests for primitive shapes.
I also checked the gizmo 2d shapes intersection example and everything
looked fine.
I did add a few utility methods to the types that have no tests yet. I
am willing to implement some if it is deemed necessary
## Migration Guide
The segment type constructors changed so if someone previously created a
Segment2d with a direction and length they would now need to use the
`from_direction` constructor
---------
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Joona Aalto <jondolf.dev@gmail.com>
This adds support for one-to-many non-fragmenting relationships (with
planned paths for fragmenting and non-fragmenting many-to-many
relationships). "Non-fragmenting" means that entities with the same
relationship type, but different relationship targets, are not forced
into separate tables (which would cause "table fragmentation").
Functionally, this fills a similar niche as the current Parent/Children
system. The biggest differences are:
1. Relationships have simpler internals and significantly improved
performance and UX. Commands and specialized APIs are no longer
necessary to keep everything in sync. Just spawn entities with the
relationship components you want and everything "just works".
2. Relationships are generalized. Bevy can provide additional built in
relationships, and users can define their own.
**REQUEST TO REVIEWERS**: _please don't leave top level comments and
instead comment on specific lines of code. That way we can take
advantage of threaded discussions. Also dont leave comments simply
pointing out CI failures as I can read those just fine._
## Built on top of what we have
Relationships are implemented on top of the Bevy ECS features we already
have: components, immutability, and hooks. This makes them immediately
compatible with all of our existing (and future) APIs for querying,
spawning, removing, scenes, reflection, etc. The fewer specialized APIs
we need to build, maintain, and teach, the better.
## Why focus on one-to-many non-fragmenting first?
1. This allows us to improve Parent/Children relationships immediately,
in a way that is reasonably uncontroversial. Switching our hierarchy to
fragmenting relationships would have significant performance
implications. ~~Flecs is heavily considering a switch to non-fragmenting
relations after careful considerations of the performance tradeoffs.~~
_(Correction from @SanderMertens: Flecs is implementing non-fragmenting
storage specialized for asset hierarchies, where asset hierarchies are
many instances of small trees that have a well defined structure)_
2. Adding generalized one-to-many relationships is currently a priority
for the [Next Generation Scene / UI
effort](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/discussions/14437).
Specifically, we're interested in building reactions and observers on
top.
## The changes
This PR does the following:
1. Adds a generic one-to-many Relationship system
3. Ports the existing Parent/Children system to Relationships, which now
lives in `bevy_ecs::hierarchy`. The old `bevy_hierarchy` crate has been
removed.
4. Adds on_despawn component hooks
5. Relationships can opt-in to "despawn descendants" behavior, meaning
that the entire relationship hierarchy is despawned when
`entity.despawn()` is called. The built in Parent/Children hierarchies
enable this behavior, and `entity.despawn_recursive()` has been removed.
6. `world.spawn` now applies commands after spawning. This ensures that
relationship bookkeeping happens immediately and removes the need to
manually flush. This is in line with the equivalent behaviors recently
added to the other APIs (ex: insert).
7. Removes the ValidParentCheckPlugin (system-driven / poll based) in
favor of a `validate_parent_has_component` hook.
## Using Relationships
The `Relationship` trait looks like this:
```rust
pub trait Relationship: Component + Sized {
type RelationshipSources: RelationshipSources<Relationship = Self>;
fn get(&self) -> Entity;
fn from(entity: Entity) -> Self;
}
```
A relationship is a component that:
1. Is a simple wrapper over a "target" Entity.
2. Has a corresponding `RelationshipSources` component, which is a
simple wrapper over a collection of entities. Every "target entity"
targeted by a "source entity" with a `Relationship` has a
`RelationshipSources` component, which contains every "source entity"
that targets it.
For example, the `Parent` component (as it currently exists in Bevy) is
the `Relationship` component and the entity containing the Parent is the
"source entity". The entity _inside_ the `Parent(Entity)` component is
the "target entity". And that target entity has a `Children` component
(which implements `RelationshipSources`).
In practice, the Parent/Children relationship looks like this:
```rust
#[derive(Relationship)]
#[relationship(relationship_sources = Children)]
pub struct Parent(pub Entity);
#[derive(RelationshipSources)]
#[relationship_sources(relationship = Parent)]
pub struct Children(Vec<Entity>);
```
The Relationship and RelationshipSources derives automatically implement
Component with the relevant configuration (namely, the hooks necessary
to keep everything in sync).
The most direct way to add relationships is to spawn entities with
relationship components:
```rust
let a = world.spawn_empty().id();
let b = world.spawn(Parent(a)).id();
assert_eq!(world.entity(a).get::<Children>().unwrap(), &[b]);
```
There are also convenience APIs for spawning more than one entity with
the same relationship:
```rust
world.spawn_empty().with_related::<Children>(|s| {
s.spawn_empty();
s.spawn_empty();
})
```
The existing `with_children` API is now a simpler wrapper over
`with_related`. This makes this change largely non-breaking for existing
spawn patterns.
```rust
world.spawn_empty().with_children(|s| {
s.spawn_empty();
s.spawn_empty();
})
```
There are also other relationship APIs, such as `add_related` and
`despawn_related`.
## Automatic recursive despawn via the new on_despawn hook
`RelationshipSources` can opt-in to "despawn descendants" behavior,
which will despawn all related entities in the relationship hierarchy:
```rust
#[derive(RelationshipSources)]
#[relationship_sources(relationship = Parent, despawn_descendants)]
pub struct Children(Vec<Entity>);
```
This means that `entity.despawn_recursive()` is no longer required.
Instead, just use `entity.despawn()` and the relevant related entities
will also be despawned.
To despawn an entity _without_ despawning its parent/child descendants,
you should remove the `Children` component first, which will also remove
the related `Parent` components:
```rust
entity
.remove::<Children>()
.despawn()
```
This builds on the on_despawn hook introduced in this PR, which is fired
when an entity is despawned (before other hooks).
## Relationships are the source of truth
`Relationship` is the _single_ source of truth component.
`RelationshipSources` is merely a reflection of what all the
`Relationship` components say. By embracing this, we are able to
significantly improve the performance of the system as a whole. We can
rely on component lifecycles to protect us against duplicates, rather
than needing to scan at runtime to ensure entities don't already exist
(which results in quadratic runtime). A single source of truth gives us
constant-time inserts. This does mean that we cannot directly spawn
populated `Children` components (or directly add or remove entities from
those components). I personally think this is a worthwhile tradeoff,
both because it makes the performance much better _and_ because it means
theres exactly one way to do things (which is a philosophy we try to
employ for Bevy APIs).
As an aside: treating both sides of the relationship as "equivalent
source of truth relations" does enable building simple and flexible
many-to-many relationships. But this introduces an _inherent_ need to
scan (or hash) to protect against duplicates.
[`evergreen_relations`](https://github.com/EvergreenNest/evergreen_relations)
has a very nice implementation of the "symmetrical many-to-many"
approach. Unfortunately I think the performance issues inherent to that
approach make it a poor choice for Bevy's default relationship system.
## Followup Work
* Discuss renaming `Parent` to `ChildOf`. I refrained from doing that in
this PR to keep the diff reasonable, but I'm personally biased toward
this change (and using that naming pattern generally for relationships).
* [Improved spawning
ergonomics](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/discussions/16920)
* Consider adding relationship observers/triggers for "relationship
targets" whenever a source is added or removed. This would replace the
current "hierarchy events" system, which is unused upstream but may have
existing users downstream. I think triggers are the better fit for this
than a buffered event queue, and would prefer not to add that back.
* Fragmenting relations: My current idea hinges on the introduction of
"value components" (aka: components whose type _and_ value determines
their ComponentId, via something like Hashing / PartialEq). By labeling
a Relationship component such as `ChildOf(Entity)` as a "value
component", `ChildOf(e1)` and `ChildOf(e2)` would be considered
"different components". This makes the transition between fragmenting
and non-fragmenting a single flag, and everything else continues to work
as expected.
* Many-to-many support
* Non-fragmenting: We can expand Relationship to be a list of entities
instead of a single entity. I have largely already written the code for
this.
* Fragmenting: With the "value component" impl mentioned above, we get
many-to-many support "for free", as it would allow inserting multiple
copies of a Relationship component with different target entities.
Fixes#3742 (If this PR is merged, I think we should open more targeted
followup issues for the work above, with a fresh tracking issue free of
the large amount of less-directed historical context)
Fixes#17301Fixes#12235Fixes#15299Fixes#15308
## Migration Guide
* Replace `ChildBuilder` with `ChildSpawnerCommands`.
* Replace calls to `.set_parent(parent_id)` with
`.insert(Parent(parent_id))`.
* Replace calls to `.replace_children()` with `.remove::<Children>()`
followed by `.add_children()`. Note that you'll need to manually despawn
any children that are not carried over.
* Replace calls to `.despawn_recursive()` with `.despawn()`.
* Replace calls to `.despawn_descendants()` with
`.despawn_related::<Children>()`.
* If you have any calls to `.despawn()` which depend on the children
being preserved, you'll need to remove the `Children` component first.
---------
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
This allows this:
```rust
#[derive(Component)]
#[require(StateScoped<MyState>(StateScoped(MyState)))]
struct ComponentA;
```
To be shortened to this:
```rust
#[derive(Component)]
#[require(StateScoped<MyState>)]
struct ComponentA;
```
When `MyState` implements `Default`.
Signed-off-by: Jean Mertz <git@jeanmertz.com>
# Objective
Occasionally bevy users will want to store systems or observer systems
in a component or resource, but they first try to store `IntoSystem`
instead of `System`, which leads to some headaches having to deal with
the `M` marker type parameter. We should recommend they use the `X`
trait instead of the `IntoX` trait in that case, as well for returning
from a function.
## Solution
Add usage notes to the `IntoX` traits about using `X` instead.
# Objective
While working on more complex directional navigation work, I noticed a
few small things.
## Solution
Rather than stick them in a bigger PR, split them out now.
- Include more useful information when responding to
`DirectionalNavigationError`.
- Use the less controversial `Click` events (rather than `Pressed`) in
the example
- Implement add_looping_edges in terms of `add_edges`. Thanks @rparrett
for the idea.
## Testing
Ran the `directional_navigation` example and things still work.
# Objective
The safety documentation for `Ptr::assert_unique` is incomplete.
Currently it only mentions the existence of other `Ptr` instances, but
it should also mention that the underlying data must be mutable and that
there cannot be active references to it.
# Objective
While `add_looping_edges` is a helpful method for manually defining
directional navigation maps, we don't always want to loop around!
## Solution
Add a non-looping variant.
These commits are cherrypicked from the more complex #17247.
## Testing
I've updated the `directional_navigation` example to use these changes,
and verified that it works.
---------
Co-authored-by: Rob Parrett <robparrett@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Benjamin Brienen <benjamin.brienen@outlook.com>
# Objective
- Fix issue identified on the [Discord
server](https://discord.com/channels/691052431525675048/691052431974465548/1328922812530036839)
## Solution
- Implement `Clone` for `QueryIter` using the existing
`QueryIter::remaining` method
## Testing
- CI
---
## Showcase
Users can now explicitly clone a read-only `QueryIter`:
```rust
fn combinations(query: Query<&ComponentA>) {
let mut iter = query.iter();
while let Some(a) = iter.next() {
// Can now clone rather than use remaining
for b in iter.clone() {
// Check every combination (a, b)
}
}
}
```
## Notes
This doesn't add any new functionality outside the context of generic
code (e.g., `T: Iterator<...> + Clone`), it's mostly for
discoverability. Users are more likely to be familiar with
`Clone::clone` than they are with the methods on `QueryIter`.
# Objective
As raised in https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/17317, the `Event:
Component` trait bound is confusing to users.
In general, a type `E` (like `AppExit`) which implements `Event` should
not:
- be stored as a component on an entity
- be a valid option for `Query<&AppExit>`
- require the storage type and other component metadata to be specified
Events are not components (even if they one day use some of the same
internal mechanisms), and this trait bound is confusing to users.
We're also automatically generating `Component` impls with our derive
macro, which should be avoided when possible to improve explicitness and
avoid conflicts with user impls.
Closes#17317, closes#17333
## Solution
- We only care that each unique event type gets a unique `ComponentId`
- dynamic events need their own tools for getting identifiers anyways
- This avoids complicating the internals of `ComponentId` generation.
- Clearly document why this cludge-y solution exists.
In the medium term, I think that either a) properly generalizing
`ComponentId` (and moving it into `bevy_reflect?) or b) using a
new-typed `Entity` as the key for events is more correct. This change is
stupid simple though, and removes the offending trait bound in a way
that doesn't introduce complex tech debt and does not risk changes to
the internals.
This change does not:
- restrict our ability to implement dynamic buffered events (the main
improvement over #17317)
- there's still a fair bit of work to do, but this is a step in the
right direction
- limit our ability to store event metadata on entities in the future
- make it harder for users to work with types that are both events and
components (just add the derive / trait bound)
## Migration Guide
The `Event` trait no longer requires the `Component` trait. If you were
relying on this behavior, change your trait bounds from `Event` to
`Event + Component`. If you also want your `Event` type to implement
`Component`, add a derive.
---------
Co-authored-by: Chris Russell <8494645+chescock@users.noreply.github.com>
# Objective
UI node Outlines are clipped using their parent's clipping rect instead
of their own.
## Solution
Clip outlines using the UI node's own clipping rect.
I noticed that this component was not being returned correctly by the
`bevy_remote` api
```json
"errors": {
"bevy_picking::focus::PickingInteraction": {
"code": -23402,
"message": "Unknown component type: `bevy_picking::focus::PickingInteraction`"
}
}
```
# Objective
- Follow up work from
https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/17121#issuecomment-2576615700 to
keep the `cursor.rs` file more manageable.
## Solution
- Move `CustomCursor` and make it compile.
## Testing
- Ran the example: `cargo run --example custom_cursor_image
--features=custom_cursor`
- CI
# Objective
Fixes https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/17111
## Solution
Move `#![warn(clippy::allow_attributes,
clippy::allow_attributes_without_reason)]` to the workspace `Cargo.toml`
## Testing
Lots of CI testing, and local testing too.
---------
Co-authored-by: Benjamin Brienen <benjamin.brienen@outlook.com>
# Objective
- Bevy 0.15 added support for custom cursor images in
https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/14284.
- However, to do animated cursors using the initial support shipped in
0.15 means you'd have to animate the `Handle<Image>`: You can't use a
`TextureAtlas` like you can with sprites and UI images.
- For my use case, my cursors are spritesheets. To animate them, I'd
have to break them down into multiple `Image` assets, but that seems
less than ideal.
## Solution
- Allow users to specify a `TextureAtlas` field when creating a custom
cursor image.
- To create parity with Bevy's `TextureAtlas` support on `Sprite`s and
`ImageNode`s, this also allows users to specify `rect`, `flip_x` and
`flip_y`. In fact, for my own use case, I need to `flip_y`.
## Testing
- I added unit tests for `calculate_effective_rect` and
`extract_and_transform_rgba_pixels`.
- I added a brand new example for custom cursor images. It has controls
to toggle fields on and off. I opted to add a new example because the
existing cursor example (`window_settings`) would be far too messy for
showcasing these custom cursor features (I did start down that path but
decided to stop and make a brand new example).
- The new example uses a [Kenny cursor icon] sprite sheet. I included
the licence even though it's not required (and it's CC0).
- I decided to make the example just loop through all cursor icons for
its animation even though it's not a _realistic_ in-game animation
sequence.
- I ran the PNG through https://tinypng.com. Looks like it's about 35KB.
- I'm open to adjusting the example spritesheet if required, but if it's
fine as is, great.
[Kenny cursor icon]: https://kenney-assets.itch.io/crosshair-pack
---
## Showcase
https://github.com/user-attachments/assets/8f6be8d7-d1d4-42f9-b769-ef8532367749
## Migration Guide
The `CustomCursor::Image` enum variant has some new fields. Update your
code to set them.
Before:
```rust
CustomCursor::Image {
handle: asset_server.load("branding/icon.png"),
hotspot: (128, 128),
}
```
After:
```rust
CustomCursor::Image {
handle: asset_server.load("branding/icon.png"),
texture_atlas: None,
flip_x: false,
flip_y: false,
rect: None,
hotspot: (128, 128),
}
```
## References
- Feature request [originally raised in Discord].
[originally raised in Discord]:
https://discord.com/channels/691052431525675048/692572690833473578/1319836362219847681
# Objective
Support the parametrization of the WS_CLIPCHILDREN style on Windows.
Fixes#16544
## Solution
Added a window configuration in bevy_winit to control the usage of the
WS_CLIPCHILDREN style.
## Testing
- Did you test these changes? If so, how?
I did. I was able to create a Wry Webview with a transparent HTML
document and was also able to see my Bevy scene behind the webview
elements.
- Are there any parts that need more testing?
I don't believe so. I assume the option is extensively tested within
winit itself.
- How can other people (reviewers) test your changes? Is there anything
specific they need to know?
Test repositiory [here](https://github.com/nicholasc/bevy_wry_test).
Bevy's path will need to be updated in the Cargo.toml
- If relevant, what platforms did you test these changes on, and are
there any important ones you can't test?
This is a Windows specific issue. Should be tested accordingly.
---------
Co-authored-by: jf908 <jf908@users.noreply.github.com>
# Objective
- Currently, the `ObservedBy`-component is only public within the
`bevy_ecs` crate. Sometimes it is desirable to refer to this component
in the "game-code". Two examples that come in mind:
- Clearing all components in an entity, but intending to keep the
existing observers: Making `ObservedBy` public allows us to use
`commands.entity(entity).retain::<ObservedBy>();`, which clears all
other components, but keeps `ObservedBy`, which prevents the Observers
from despawning.
- The opposite of the above, clearing all of entities' Observers:
`commands.entity(entity).remove::<ObservedBy>` will despawn all
associated Observers. Admittedly, a cleaner solution would be something
like `commands.entity(entity).clear_observers()`, but this is
sufficient.
## Solution
- Removed `(crate)` "rule" and added `ObservedBy` to the prelude-module
## Testing
- Linked `bevy_ecs` locally with another project to see if `ObservedBy`
could be referenced.
# Objective
resolves#17326.
## Solution
Simply added the suggested run condition.
## Testing
A self-explanatory run condition. Fully verified by the operation of
`QueryFilter` in a system.
# Objective
- https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/17111
## Solution
Set the `clippy::allow_attributes` and
`clippy::allow_attributes_without_reason` lints to `warn`, and bring
`bevy_ecs` in line with the new restrictions.
## Testing
This PR is a WIP; testing will happen after it's finished.
# Objective
- https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/17111
## Solution
Set the `clippy::allow_attributes` and
`clippy::allow_attributes_without_reason` lints to `warn`, and bring
`bevy_macro_utils` in line with the new restrictions.
## Testing
`cargo clippy --tests --all-features --package bevy_macro_utils` was
run, and no warnings were encountered.
# Objective
- https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/17111
## Solution
Set the `clippy::allow_attributes` and
`clippy::allow_attributes_without_reason` lints to `warn`, and bring
`bevy_input_focus` in line with the new restrictions.
## Testing
`cargo clippy --tests --all-features --features
bevy_math/std,bevy_input/smol_str --package bevy_input_focus` was run,
and only an unrelated warning from `bevy_ecs` was encountered.
I could not test without the `bevy_math/std` feature due to compilation
errors with `glam`. Additionally, I had to use the `bevy_input/smol_str`
feature, as it appears some of `bevy_input_focus`' tests rely on that
feature. I will investigate these issues further, and make issues/PRs as
necessary.
# Objective
- https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/17111
## Solution
Set the `clippy::allow_attributes` and
`clippy::allow_attributes_without_reason` lints to `warn`, and bring
`bevy_dylib` in line with the new restrictions.
## Testing
`cargo clippy --tests --all-features --package bevy_dylib` was run, and
no warnings were encountered.
I would've skipped over this crate if there weren't the two lint
attributes in it - might as well handle it now, y'know?
# Objective
- https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/17111
## Solution
Set the `clippy::allow_attributes` and
`clippy::allow_attributes_without_reason` lints to `warn`, and bring
`bevy_core_pipeline` in line with the new restrictions.
## Testing
`cargo clippy` and `cargo test --package bevy_core_pipeline` were run,
and no warnings were encountered.
This commit allows Bevy to use `multi_draw_indirect_count` for drawing
meshes. The `multi_draw_indirect_count` feature works just like
`multi_draw_indirect`, but it takes the number of indirect parameters
from a GPU buffer rather than specifying it on the CPU.
Currently, the CPU constructs the list of indirect draw parameters with
the instance count for each batch set to zero, uploads the resulting
buffer to the GPU, and dispatches a compute shader that bumps the
instance count for each mesh that survives culling. Unfortunately, this
is inefficient when we support `multi_draw_indirect_count`. Draw
commands corresponding to meshes for which all instances were culled
will remain present in the list when calling
`multi_draw_indirect_count`, causing overhead. Proper use of
`multi_draw_indirect_count` requires eliminating these empty draw
commands.
To address this inefficiency, this PR makes Bevy fully construct the
indirect draw commands on the GPU instead of on the CPU. Instead of
writing instance counts to the draw command buffer, the mesh
preprocessing shader now writes them to a separate *indirect metadata
buffer*. A second compute dispatch known as the *build indirect
parameters* shader runs after mesh preprocessing and converts the
indirect draw metadata into actual indirect draw commands for the GPU.
The build indirect parameters shader operates on a batch at a time,
rather than an instance at a time, and as such each thread writes only 0
or 1 indirect draw parameters, simplifying the current logic in
`mesh_preprocessing`, which currently has to have special cases for the
first mesh in each batch. The build indirect parameters shader emits
draw commands in a tightly packed manner, enabling maximally efficient
use of `multi_draw_indirect_count`.
Along the way, this patch switches mesh preprocessing to dispatch one
compute invocation per render phase per view, instead of dispatching one
compute invocation per view. This is preparation for two-phase occlusion
culling, in which we will have two mesh preprocessing stages. In that
scenario, the first mesh preprocessing stage must only process opaque
and alpha tested objects, so the work items must be separated into those
that are opaque or alpha tested and those that aren't. Thus this PR
splits out the work items into a separate buffer for each phase. As this
patch rewrites so much of the mesh preprocessing infrastructure, it was
simpler to just fold the change into this patch instead of deferring it
to the forthcoming occlusion culling PR.
Finally, this patch changes mesh preprocessing so that it runs
separately for indexed and non-indexed meshes. This is because draw
commands for indexed and non-indexed meshes have different sizes and
layouts. *The existing code is actually broken for non-indexed meshes*,
as it attempts to overlay the indirect parameters for non-indexed meshes
on top of those for indexed meshes. Consequently, right now the
parameters will be read incorrectly when multiple non-indexed meshes are
multi-drawn together. *This is a bug fix* and, as with the change to
dispatch phases separately noted above, was easiest to include in this
patch as opposed to separately.
## Migration Guide
* Systems that add custom phase items now need to populate the indirect
drawing-related buffers. See the `specialized_mesh_pipeline` example for
an example of how this is done.
# Objective
- While all
[`MeshBuilder`](https://dev-docs.bevyengine.org/bevy/prelude/trait.MeshBuilder.html)s
can be created by first creating the primitive `bevy_math` type and
using
[`Meshable`](https://dev-docs.bevyengine.org/bevy/prelude/trait.Meshable.html),
most builders have their own `const` constructors that can be used
instead. Some builders are missing constructors, however, making them
unavailable in `const` contexts.
## Solution
- Add a `const` constructor for `RegularPolygonMeshBuilder`,
`RhombusMeshBuilder`, `Triangle2dMeshBuilder`, and
`RectangleMeshBuilder`.
- Add a note on the requirements of `ConvexPolygonMeshBuilder`, and
recommend using `ConvexPolygon::new().mesh()` instead.
- A constructor cannot easily be created for this type, since it
requires duplicating all of `ConvexPolygon::new()`'s verification code.
I may be able to work around this, but it requires touching a bit more
code surface. Opinions?
## Testing
Not much beyond CI! The changes are trivial enough that only a cursory
glance for typos and switched variables should be necessary.
## Note for Reviewers
Hi! I haven't directly used the types I modify in this PR beyond some
benchmarking work I did this morning. If you're familiar with these
types, please let me know if any of the constructors need additional
validation (or if the constructors shouldn't be there at all). Thanks!
---------
Co-authored-by: IQuick 143 <IQuick143cz@gmail.com>
# Objective
allow setting ambient light via component on cameras.
arguably fixes#7193
note i chose to use a component rather than an entity since it was not
clear to me how to manage multiple ambient sources for a single
renderlayer, and it makes for a very small changeset.
## Solution
- make ambient light a component as well as a resource
- extract it
- use the component if present on a camera, fallback to the resource
## Testing
i added
```rs
if index == 1 {
commands.entity(camera).insert(AmbientLight{
color: Color::linear_rgba(1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0),
brightness: 1000.0,
..Default::default()
});
}
```
at line 84 of the split_screen example
---------
Co-authored-by: François Mockers <mockersf@gmail.com>
# Objective
Add a method to mutate components with BRP.
Currently the only way to modify a component on an entity with BRP is to
insert a new one with the new values. This isn't ideal for several
reasons, one reason being that the client has to know what all the
fields are of the component and stay in sync with the server.
## Solution
Add a new BRP method called `bevy/mutate_component` to mutate a single
field in a component on an entity.
## Testing
Tested on a simple scene on all `Transform`, `Name`, and a custom
component.
---
## Showcase
Example JSON-RPC request to change the `Name` of an entity to "New
name!"
```json
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 0,
"method": "bevy/mutate_component",
"params": {
"entity": 4294967308,
"component": "bevy_ecs::name::Name",
"path": ".name",
"value": "New name!"
}
}
```
Or setting the X translation to 10.0 on a Transform:
```json
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 0,
"method": "bevy/mutate_component",
"params": {
"entity": 4294967308,
"component": "bevy_transform::components::transform::Transform",
"path": ".translation.x",
"value": 10.0
}
}
```
Clip of my Emacs BRP package using this method:
https://github.com/user-attachments/assets/a786b245-5c20-4189-859f-2261c5086a68
---------
Co-authored-by: François Mockers <mockersf@gmail.com>
# Objective
- Stop bevy from crashing when losing window focus
## Solution
- The InputFocus resource is optional but is accessed unconditionally in
bevy_winit. Make it optional.
## Testing
- Ran the window_settings example
## Note
It's possible this might not be a full fix for the issue, but this stop
bevy from crashing.
Closes#16961Closes#17227
# Objective
Diagnostics is reporting incorrect FPS and frame time.
## Solution
Looks like the smoothing value should be `2 / (history_length + 1)` not
`(history_length + 1) / 2`.
Co-authored-by: François Mockers <mockersf@gmail.com>
# Objective
Necessary conditions:
* Scale factor != 1
* Text is being displayed with Text2d
* The primary window is closed on a frame where the text or text's
bounds are modified.
Then when `update_text2d_layout` runs, it finds no primary window and
assumes a scale factor of 1.
The previous scale_factor was not equal to 1 and the text pipeline's old
font atlases were created for a non-1 scale factor, so it creates new
font atlases even though the app is closing.
The bug was first identified in #6666
## Minimal Example
```rust
use bevy::prelude::*;
fn main() {
App::new()
.add_plugins(DefaultPlugins.set(WindowPlugin {
primary_window: Some(Window {
present_mode: bevy:🪟:PresentMode::Immediate,
..Default::default()
}),
..default()
}))
.insert_resource(UiScale { scale: std::f64::consts::PI })
.add_startup_system(setup)
.add_system(update)
.run();
}
fn setup(mut commands: Commands, asset_server: Res<AssetServer>) {
commands.spawn(Camera2dBundle::default());
commands.spawn(Text2dBundle {
text: Text {
sections: (0..10).map(|i| TextSection {
value: i.to_string(),
style: TextStyle {
font: asset_server.load("fonts/FiraSans-Bold.ttf"),
font_size: (10 + i) as f32,
color: Color::WHITE,
}
}).collect(),
..Default::default()
},
..Default::default()
});
}
fn update(mut text: Query<&mut Text>) {
for mut text in text.iter_mut() {
text.set_changed();
}
}
```
## Output
On closing the window you'll see the warning (if you don't, increase the
number of text sections):
```
WARN bevy_text::glyph_brush: warning[B0005]: Number of font atlases has exceeded the maximum of 16. Performance and memory usage may suffer.
```
The app should only create font atlases on startup, but it doesn't
display this warning until after you close the window
## Solution
Skip `update_text_layout` when there is no primary window.
## Changelog
* If no primary window is found, skip `update_text2d_layout`.
* Added a `Local` flag `skipped` to `update_text2d_layout`. This should
ensure there are no edge cases where text might not get drawn at all.
---------
Co-authored-by: François Mockers <mockersf@gmail.com>
# Objective
- Use `Clone` on `SystemParam`, when applicable, in a generic context.
## Solution
- Add some derives
## Testing
- I ran `cargo test` once.
- I didn't even look at the output.
---------
Co-authored-by: François Mockers <mockersf@gmail.com>
# Objective
Fix the `bevy_time` unit tests occasionally failing on optimised Windows
builds.
# Background
I noticed that the `bevy_time` unit tests would fail ~50% of the time
after enabling `opt-level=1` in config.toml, or adding `--release` to
cargo test.
```
> cargo test -p bevy_time --release
thread 'real::test::test_update' panicked at crates\bevy_time\src\real.rs:164:9:
assertion `left != right` failed
left: Some(Instant { t: 9458.0756664s })
right: Some(Instant { t: 9458.0756664s })
```
Disabling optimisations would fix the issue, as would switching from Windows to Linux.
The failing path is roughly:
```rust
let mut time = Time::<Real>::new(Instant::now());
time.update();
time.update();
assert_ne!(time.last_update(), time.first_update());
```
Which kinda boils down to:
```rust
let left = Instant::now();
let right = Instant::now();
assert_ne!(left, right);
```
So the failure seems legit, since there's no guarantee that `Instant::now()` increases between calls.
I suspect it only triggers with a combination of Windows + fast CPU + optimisations (Windows has a lower resolution clock than Linux/MacOS). That would explain why it doesn't fail on the Bevy Github CI (optimisations disabled, and I'm guessing the runner CPUs are clocked lower).
# Solution
Make sure `Instant::now()` has increased before calling `time.update()`.
I also considered:
1. Change the unit tests to accept `Instant:now()` not increasing.
- In retrospect this is maybe the better change?
- There's other unit tests that cover time increasing.
- Could also add a deterministic test for zero delta updates.
- I can switch the PR to this if desired.
2. Avoid any paths that hit `Instant::now()` in unit tests.
- Arguably unit tests should always be deterministic.
- But that would mean a bunch of paths aren't tested.
## Testing
`cargo test -p bevy_time --release`
## System Info
`os: "Windows 10 Pro", kernel: "19045", cpu: "AMD Ryzen 9 7900 12-Core Processor", core_count: "12", memory: "63.2 GiB"`
Also tested on same computer with Linux pop-os 6.9.3.
Co-authored-by: François Mockers <mockersf@gmail.com>
We won't be able to retain render phases from frame to frame if the keys
are unstable. It's not as simple as simply keying off the main world
entity, however, because some main world entities extract to multiple
render world entities. For example, directional lights extract to
multiple shadow cascades, and point lights extract to one view per
cubemap face. Therefore, we key off a new type, `RetainedViewEntity`,
which contains the main entity plus a *subview ID*.
This is part of the preparation for retained bins.
---------
Co-authored-by: ickshonpe <david.curthoys@googlemail.com>
# Objective
I have an application where I'd like to measure average frame rate over
the entire life of the application, and it would be handy if I could
just configure this on the existing `FrameTimeDiagnosticsPlugin`.
Probably fixes#10948?
## Solution
Add `max_history_length` to `FrameTimeDiagnosticsPlugin`, and because
`smoothing_factor` seems to be based on history length, add that too.
## Discussion
I'm not totally sure that `DEFAULT_MAX_HISTORY_LENGTH` is a great
default for `FrameTimeDiagnosticsPlugin` (or any diagnostic?). That's
1/3 of a second at typical game frame rates. Moreover, the default print
interval for `LogDiagnosticsPlugin` is 1 second. So when the two are
combined, you are printing the average over the last third of the
duration between now and the previous print, which seems a bit wonky.
(related: #11429)
I'm pretty sure this default value discussed and the current value
wasn't totally arbitrary though.
Maybe it would be nice for `Diagnostic` to have a
`with_max_history_length_and_also_calculate_a_good_default_smoothing_factor`
method? And then make an explicit smoothing factor in
`FrameTimeDiagnosticsPlugin` optional?
Or add a `new(max_history_length: usize)` method to
`FrameTimeDiagnosticsPlugin` that sets a reasonable default
`smoothing_factor`? edit: This one seems like a no-brainer, doing it.
## Alternatives
It's really easy to roll your own `FrameTimeDiagnosticsPlugin`, but that
might not be super interoperable with, for example, third party FPS
overlays. Still, might be the right call.
## Testing
`cargo run --example many_sprites` (modified to use a custom
`max_history_length`)
## Migration Guide
`FrameTimeDiagnosticsPlugin` now contains two fields. Use
`FrameTimeDiagnosticsPlugin::default()` to match Bevy's previous
behavior or, for example, `FrameTimeDiagnosticsPlugin::new(60)` to
configure it.
# Objective
- Closes https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/14322.
## Solution
- Implement fast 4-sample bicubic filtering based on this shader toy
https://www.shadertoy.com/view/4df3Dn, with a small speedup from a ghost
of tushima presentation.
## Testing
- Did you test these changes? If so, how?
- Ran on lightmapped example. Practically no difference in that scene.
- Are there any parts that need more testing?
- Lightmapping a better scene.
## Changelog
- Lightmaps now have a higher quality bicubic sampling method (off by
default).
---------
Co-authored-by: Patrick Walton <pcwalton@mimiga.net>
- `Once` renamed to `Warn`.
- `param_warn_once()` renamed to `warn_param_missing()`.
- `never_param_warn()` renamed to `ignore_param_missing()`.
Also includes changes to the documentation of the above methods.
Fixes#17262.
## Migration Guide
- `ParamWarnPolicy::Once` has been renamed to `ParamWarnPolicy::Warn`.
- `ParamWarnPolicy::param_warn_once` has been renamed to
`ParamWarnPolicy::warn_param_missing`.
- `ParamWarnPolicy::never_param_warn` has been renamed to
`ParamWarnPolicy::ignore_param_missing`.
# Objective
With the `track_location` feature, the error message of trying to
acquire an entity that was despawned pointed to the wrong line if the
entity index has been reused.
## Showcase
```rust
use bevy_ecs::prelude::*;
fn main() {
let mut world = World::new();
let e = world.spawn_empty().id();
world.despawn(e);
world.flush();
let _ = world.spawn_empty();
world.entity(e);
}
```
Old message:
```
Entity 0v1 was despawned by src/main.rs:8:19
```
New message:
```
Entity 0v1 does not exist (its index has been reused)
```
# Objective
PR #17225 allowed for sprite picking to be opt-in. After some
discussion, it was agreed that `PickingBehavior` should be used to
opt-in to sprite picking behavior for entities. This leads to
`PickingBehavior` having two purposes: mark an entity for use in a
backend, and describe how it should be picked. Discussion led to the
name `Pickable`making more sense (also: this is what the component was
named before upstreaming).
A follow-up pass will be made after this PR to unify backends.
## Solution
Replace all instances of `PickingBehavior` and `picking_behavior` with
`Pickable` and `pickable`, respectively.
## Testing
CI
## Migration Guide
Change all instances of `PickingBehavior` to `Pickable`.
# Objective
The `camera_entity` field on the extracted uinode structs holds the
render world entity that has the extracted camera components
corresponding to the target camera world entity. It should be renamed so
that it's clear it isn't the target camera world entity itself.
## Solution
Rename the `camera_entity` field on each of the extracted UI item
structs to `extracted_camera_entity`.
# Objective
I realized that setting these to `deny` may have been a little
aggressive - especially since we upgrade warnings to denies in CI.
## Solution
Downgrades these lints to `warn`, so that compiles can work locally. CI
will still treat these as denies.
# Objective
- https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/17111
## Solution
Set the `clippy::allow_attributes` and
`clippy::allow_attributes_without_reason` lints to `deny`, and bring
`bevy_picking` in line with the new restrictions.
## Testing
`cargo clippy --tests --all-features --package bevy_picking` was run,
and no errors were encountered.
# Objective
- https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/17111
## Solution
Set the `clippy::allow_attributes` and
`clippy::allow_attributes_without_reason` lints to `deny`, and bring
`bevy_remote` in line with the new restrictions.
## Testing
`cargo clippy --tests --all-features --package bevy_remote` was run, and
no errors were encountered.
# Objective
- https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/17111
## Solution
Set the `clippy::allow_attributes` and
`clippy::allow_attributes_without_reason` lints to `deny`, and bring
`bevy_utils` in line with the new restrictions.
## Testing
`cargo clippy --tests --all-features --package bevy_utils` was run, and
no errors were encountered.
# Objective
- https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/17111
## Solution
Set the `clippy::allow_attributes` and
`clippy::allow_attributes_without_reason` lints to `deny`, and bring
`bevy_internal` in line with the new restrictions.
## Testing
`cargo clippy --tests --all-features --package bevy_internal` was run,
and no errors were encountered.
# Objective
Fixes#16783
## Solution
Works around a `cosmic-text` bug or limitation by triggering a re-layout
with the calculated width from the first layout run. See linked issue.
Credit to @ickshonpe for the clever solution.
## Performance
This has a significant performance impact only on unbounded text that
are not `JustifyText::Left`, which is still a bit of a bummer because
text2d performance in 0.15.1 is already not great. But this seems better
than alignment not working.
||many_text2d nfc re|many_text2d nfc re center|
|-|-|-|
|unbounded-layout-no-fix|3.06|3.10|
|unbounded-layout-fix|3.05 ⬜ -0.2%|2.71 🟥 -12.5%|
## Testing
I added a centered text to the `text2d` example.
`cargo run --example text2d`
We should look at other text examples and stress tests. I haven't tested
as thoroughly as I would like, so help testing that this doesn't break
something in UI would be appreciated.
# Objective
- https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/17111
## Solution
Set the `clippy::allow_attributes` and
`clippy::allow_attributes_without_reason` lints to `deny`, and bring
`bevy_image` in line with the new restrictions.
## Testing
`cargo clippy --tests --package bevy_image` was run, and no errors were
encountered.
I could not run the above command with `--all-features` due to some
compilation errors with `bevy_core_pipeline` and `bevy_math` - but
hopefully CI catches anything I missed.
---------
Co-authored-by: Benjamin Brienen <benjamin.brienen@outlook.com>
# Objective
- Fixes#17287
## Solution
- Added a dummy `LocalExecutor` (un)implementation to suppress
irrelevant errors.
- Added explicit `compiler_error!` when _not_ selecting either the
`async_executor` or `edge_executor` features
## Testing
- CI
# Objective
`bevy_image` appears to expect `bevy_math` to have reflection enabled.
If you attempt to build `bevy_image` without another dependency enabling
the `bevy_math/bevy_reflect` feature, then `bevy_image` will fail to
compile.
## Solution
Ideally, `bevy_image` would feature-gate all of its reflection behind a
new feature. However, for the sake of getting compilation fixed
immediately, I'm opting to specify the `bevy_math/bevy_reflect` feature
in `bevy_image`'s `Cargo.toml`.
Perhaps an upcoming PR can remove the forced `bevy_math/bevy_reflect`
feature, in favor of feature-gating `bevy_image`'s reflecton.
## Testing
`cargo clippy --package bevy_image` was ran, and no longer returns the
compilation errors that it did before.
# Objective
Stumbled upon a `from <-> form` transposition while reviewing a PR,
thought it was interesting, and went down a bit of a rabbit hole.
## Solution
Fix em
# Objective
`bevy_remote`'s reflection deserialization basically requires
`ReflectDeserialize` registrations in order to work correctly. In the
context of `bevy` (the library), this means that using `bevy_remote`
without using the `serialize` feature is a footgun, since
`#[reflect(Serialize)]` etc. are gated behind this feature.
The goal of this PR is to avoid this mistake by default.
## Solution
Make the `bevy_remote` feature enable the `serialize` feature, so that
it works as expected.
---
## Migration Guide
The `bevy_remote` feature of `bevy` now enables the `serialize` feature
automatically. If you wish to use `bevy_remote` without enabling the
`serialize` feature for Bevy subcrates, you must import `bevy_remote` on
its own.
# Objective
- https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/17111
## Solution
Set the `clippy::allow_attributes` and
`clippy::allow_attributes_without_reason` lints to `deny`, and bring
`bevy_state` in line with the new restrictions.
## Testing
Rust-analyzer did not return any errors once the deny was added.
# Objective
- https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/17111
## Solution
Set the `clippy::allow_attributes` and
`clippy::allow_attributes_without_reason` lints to `deny`, and bring
`bevy_scene` in line with the new restrictions.
## Testing
`cargo clippy --tests --all-features --package bevy_scene` was run, and
no errors were encountered.
# Objective
- https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/17111
## Solution
Set the `clippy::allow_attributes` and
`clippy::allow_attributes_without_reason` lints to `deny`, and bring
`bevy_pbr` in line with the new restrictions.
## Testing
`cargo clippy --tests --package bevy_pbr` was run, and no errors were
encountered.
# Objective
- https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/17111
## Solution
Set the `clippy::allow_attributes` and
`clippy::allow_attributes_without_reason` lints to `deny`, and bring
`bevy_gltf` in line with the new restrictions.
## Testing
`cargo clippy --tests --all-features --package bevy_gltf` was run, and
no errors were encountered.
# Objective
- https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/17111
## Solution
Set the `clippy::allow_attributes` and
`clippy::allow_attributes_without_reason` lints to `deny`, and bring
`bevy_text` in line with the new restrictions.
## Testing
`cargo clippy --tests --all-features --package bevy_text` was run, and
no errors were encountered.
# Objective
- https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/17111
## Solution
Set the `clippy::allow_attributes` and
`clippy::allow_attributes_without_reason` lints to `deny`, and bring
`bevy_transform` in line with the new restrictions.
## Testing
`cargo clippy --tests --all-features --package bevy_transform` was run,
and no errors were encountered.
# Objective
- https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/17111
## Solution
Set the `clippy::allow_attributes` and
`clippy::allow_attributes_without_reason` lints to `deny`, and bring
`bevy_hierarchy` in line with the new restrictions.
## Testing
Rust-analyzer did not discern any errors.
# Objective
- https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/17111
## Solution
Set the `clippy::allow_attributes` and
`clippy::allow_attributes_without_reason` lints to `deny`, and bring
`bevy_gizmos` in line with the new restrictions.
## Testing
`cargo clippy --tests --all-features --package bevy_gizmos` was run, and
no errors were encountered.
# Objective
Both `set_metrics` and `set_size` **can** trigger text re-layout and
re-shaping, if the values provided are different form what is already in
the `Buffer`.
## Solution
Combine the `set_metrics` and `set_size` calls.
This might be a small optimization in some situations, maybe when both
font size and text bounds change in the same frame, or when spawning new
text.
I did measure a ~500 microsecond improvement in `text_system` for
`many_buttons --respawn`, but that may have just been noise.
# Objective
Rework / build on #17043 to simplify the implementation. #17043 should
be merged first, and the diff from this PR will get much nicer after it
is merged (this PR is net negative LOC).
## Solution
1. Command and EntityCommand have been vastly simplified. No more marker
components. Just one function.
2. Command and EntityCommand are now generic on the return type. This
enables result-less commands to exist, and allows us to statically
distinguish between fallible and infallible commands, which allows us to
skip the "error handling overhead" for cases that don't need it.
3. There are now only two command queue variants: `queue` and
`queue_fallible`. `queue` accepts commands with no return type.
`queue_fallible` accepts commands that return a Result (specifically,
one that returns an error that can convert to
`bevy_ecs::result::Error`).
4. I've added the concept of the "default error handler", which is used
by `queue_fallible`. This is a simple direct call to the `panic()` error
handler by default. Users that want to override this can enable the
`configurable_error_handler` cargo feature, then initialize the
GLOBAL_ERROR_HANDLER value on startup. This is behind a flag because
there might be minor overhead with `OnceLock` and I'm guessing this will
be a niche feature. We can also do perf testing with OnceLock if someone
really wants it to be used unconditionally, but I don't personally feel
the need to do that.
5. I removed the "temporary error handler" on Commands (and all code
associated with it). It added more branching, made Commands bigger /
more expensive to initialize (note that we construct it at high
frequencies / treat it like a pointer type), made the code harder to
follow, and introduced a bunch of additional functions. We instead rely
on the new default error handler used in `queue_fallible` for most
things. In the event that a custom handler is required,
`handle_error_with` can be used.
6. EntityCommand now _only_ supports functions that take
`EntityWorldMut` (and all existing entity commands have been ported).
Removing the marker component from EntityCommand hinged on this change,
but I strongly believe this is for the best anyway, as this sets the
stage for more efficient batched entity commands.
7. I added `EntityWorldMut::resource` and the other variants for more
ergonomic resource access on `EntityWorldMut` (removes the need for
entity.world_scope, which also incurs entity-lookup overhead).
## Open Questions
1. I believe we could merge `queue` and `queue_fallible` into a single
`queue` which accepts both fallible and infallible commands (via the
introduction of a `QueueCommand` trait). Is this desirable?
# Objective
Gamepad / directional navigation needs an example, for both teaching and
testing purposes.
## Solution
- Add a simple grid-based example.
- Fix an intermittent panic caused by a race condition with bevy_a11y
- Clean up small issues noticed in bevy_input_focus

## To do: this PR
- [x] figure out why "enter" isn't doing anything
- [x] change button color on interaction rather than printing
- [x] add on-screen directions
- [x] move to an asymmetric grid to catch bugs
- [x] ~~fix colors not resetting on button press~~ lol this is mostly
just a problem with hacking `Interaction` for this
- [x] swap to using observers + bubbling, rather than `Interaction`
## To do: future work
- when I increase the button size, such that there is no line break, the
text on the buttons is no longer centered :( EDIT: this is
https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/16783
- add gamepad stick navigation
- add tools to find the nearest populated quadrant to make diagonal
inputs work
- add a `add_edges` method to `DirectionalNavigationMap`
- add a `add_grid` method to `DirectionalNavigationMap`
- make the example's layout more complex and realistic
- add tools to automatically generate this list
- add button shake on failed navigation rather than printing an error
- make Pressed events easier to mock: default fields, PointerId::Focus
## Testing
`cargo run --example directional_navigation`
---------
Co-authored-by: Rob Parrett <robparrett@gmail.com>
# Objective
Fixes#16903.
## Solution
- Make sprite picking opt-in by requiring a new `SpritePickingCamera`
component for cameras and usage of a new `Pickable` component for
entities.
- Update the `sprite_picking` example to reflect these changes.
- Some reflection cleanup (I hope that's ok).
## Testing
Ran the `sprite_picking` example
## Open Questions
<del>
<ul>
<li>Is the name `SpritePickable` appropriate?</li>
<li>Should `SpritePickable` be in `bevy_sprite::prelude?</li>
</ul>
</del>
## Migration Guide
The sprite picking backend is now strictly opt-in using the
`SpritePickingCamera` and `Pickable` components. You should add the
`Pickable` component any entities that you want sprite picking to be
enabled for, and mark their respective cameras with
`SpritePickingCamera`.
# Objective
- Shrink `bevy_utils` more.
- Refs #11478
## Solution
- Removes `assert_object_safe` from `bevy_utils` by using a compile time
check instead.
## Testing
- CI.
---
## Migration Guide
`assert_object_safe` is no longer exported by `bevy_utils`. Instead, you
can write a compile time check that your trait is "dyn compatible":
```rust
/// Assert MyTrait is dyn compatible
const _: Option<Box<dyn MyTrait>> = None;
```
---------
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
# Objective
Many instances of `clippy::too_many_arguments` linting happen to be on
systems - functions which we don't call manually, and thus there's not
much reason to worry about the argument count.
## Solution
Allow `clippy::too_many_arguments` globally, and remove all lint
attributes related to it.
# Objective
Fixed the issue where DragStart was triggered even when there was no
movement
https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/17230
## Solution
- When position delta is zero, don't trigger DragStart events, DragStart
is not triggered, so DragEnd is not triggered either. Everything is
fine.
## Testing
- tested with the code from the issue
---
## Migration Guide
> Fix the missing part of Drag
https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/16950
# Objective
- https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/17111
## Solution
Set the `clippy::allow_attributes` and
`clippy::allow_attributes_without_reason` lints to `deny`, and bring
`bevy_time` in line with the new restrictions.
No code changes have been made - except if a lint that was previously
`allow(...)`'d could be removed via small code changes. For example,
`unused_variables` can be handled by adding a `_` to the beginning of a
field's name.
## Testing
`cargo clippy`, `cargo clippy --package bevy_time` and `cargo test
--package bevy_time` were run, and no errors were encountered.
# Objective
- https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/17111
## Solution
Set the `clippy::allow_attributes` and
`clippy::allow_attributes_without_reason` lints to `deny`, and bring
`bevy_mesh` in line with the new restrictions.
## Testing
`cargo clippy --tests` and `cargo test --package bevy_mesh` were run,
and no errors were encountered.
# Objective
- https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/17111
## Solution
Set the `clippy::allow_attributes` and
`clippy::allow_attributes_without_reason` lints to `deny`, and bring
`bevy_winit` in line with the new restrictions.
## Testing
`cargo clippy --tests` was run, and no errors were encountered.
---------
Co-authored-by: Benjamin Brienen <benjamin.brienen@outlook.com>
# Objective
`extract_shadows` uses the render world entity corresponding to the
extracted camera when it queries the main world for the camera to get
the viewport size for the responsive viewport coords resolution and
fails. This means that viewport coords get resolved based on a viewport
size of zero.
## Solution
Use the main world camera entity.
This also includes suggestions and an example on how to limit the loop
speed.
Fixes#17147.
---------
Co-authored-by: François Mockers <francois.mockers@vleue.com>
# Objective
- https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/17111
## Solution
Set the `clippy::allow_attributes` and
`clippy::allow_attributes_without_reason` lints to `deny`, and bring
`bevy_log` in line with the new restrictions.
## Testing
`cargo clippy --tests --package bevy_log` was run, and no errors were
encountered.
# Objective
- https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/17111
## Solution
Set the `clippy::allow_attributes` and
`clippy::allow_attributes_without_reason` lints to `deny`, and bring
`bevy_gilrs` in line with the new restrictions.
## Testing
`cargo clippy --tests --package bevy_gilrs` was run, and no errors were
encountered.
# Objective
I never realized `clippy::type_complexity` was an allowed lint - I've
been assuming it'd generate a warning when performing my linting PRs.
## Solution
Removes any instances of `#[allow(clippy::type_complexity)]` and
`#[expect(clippy::type_complexity)]`
## Testing
`cargo clippy` ran without errors or warnings.
# Objective
In my crusade to give every lint attribute a reason, it appears I got
too complacent and copy-pasted this expect onto non-system functions.
## Solution
Fix up the reason on those non-system functions
## Testing
N/A
# Objective
- https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/17111
## Solution
Set the `clippy::allow_attributes` and
`clippy::allow_attributes_without_reason` lints to `deny`, and bring
`bevy_input` in line with the new restrictions.
## Testing
`cargo clippy --tests --package bevy_input` was run, and no errors were
encountered.